.
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1605637925.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/MANIFEST.in������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000777�0001750�0001750�00000000377�00000000000�016471� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������include README.md LICENSE CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
include requirements.txt requirements_docs.txt
include *.rst *.txt
recursive-include pept *.py *.pyx *.pxd *.c* *.h*
global-exclude .DS_Store
global-exclude __pycache__
global-exclude *.pyc
global-exclude *.so
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1619631590.0895839
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/PKG-INFO���������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000044500�00000000000�016015� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Metadata-Version: 2.1
Name: pept
Version: 0.3.2
Summary: A Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis and visualisation tools.
Home-page: https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept
Author: Andrei Leonard Nicusan
Author-email: a.l.nicusan@bham.ac.uk
License: GNU
Description:
[](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pept/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
[](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1G8XHP9zWMMDVu23PXzANLCOKNP_RjBEO)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/context:python)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/context:cpp)
[](https://dev.azure.com/conda-forge/feedstock-builds/_build/latest?definitionId=10178&branchName=master)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pept/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
[](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pept/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
# The `pept` Library
A Python library that integrates all the tools necessary to perform research using Positron Emission Particle Tracking (PEPT). It includes algorithms for the location, identification and tracking of particles, in addition to tools for visualisation and analysis, and utilities allowing the realistic simulation of PEPT data.
## Positron Emission Particle Tracking
PEPT is a technique developed at the University of Birmingham which allows the non-invasive, three-dimensional tracking of one or more 'tracer' particles through particulate, fluid or multiphase systems. The technique allows particle or fluid motion to be tracked with sub-millimetre accuracy and sub-millisecond temporal resolution and, due to its use of highly-penetrating 511keV gamma rays, can be used to probe the internal dynamics of even large, dense, optically opaque systems - making it ideal for industrial as well as scientific applications.
PEPT is performed by radioactively labelling a particle with a positron-emitting radioisotope such as fluorine-18 (18F) or gallium-66 (66Ga), and using the back-to-back gamma rays produced by electron-positron annihilation events in and around the tracer to triangulate its spatial position. Each detected gamma ray represents a line of response (LoR).

Transforming gamma rays, or lines of response (left) into individual tracer trajectories (right) using the `pept` library. Depicted is experimental data of two tracers rotating at 42 RPM, imaged using the University of Birmingham Positron Imaging Centre's parallel screens PEPT camera.
## Getting Started
These instructions will help you get started with PEPT data analysis.
### Prerequisites
This package supports Python 3.6 and above - it is built and tested for Python 3.6, 3.7 and 3.8 on Windows, Linux and macOS (thanks to [`conda-forge`](https://conda-forge.org/), which is awesome!).
You can install it using the batteries-included [Anaconda distribution](https://www.anaconda.com/products/individual) or the bare-bones [Python interpreter](https://www.python.org/downloads/). You can also check out our Python and `pept` tutorials [here](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/tutorials).
### Installation
The easiest and quickest installation, if you are using Anaconda:
```
conda install -c conda-forge pept
```
You can also install the latest release version of `pept` from PyPI:
```
pip install --upgrade pept
```
Or you can install the development version from the GitHub repository:
```
pip install --upgrade git+https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept
```
## Tutorials
Some PEPT analysis example scripts are available on [pept.readthedocs.io](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/). A minimal script can read PEPT from an online location (e.g. the experiment shown above - two radioactive tracers rotating at 42 RPM), transform the lines of response into accurate tracer locations and plot them in a browser-based interactive 3D graph (live version available [here](https://uob-positron-imaging-centre.github.io/live/sample_42rpm)):
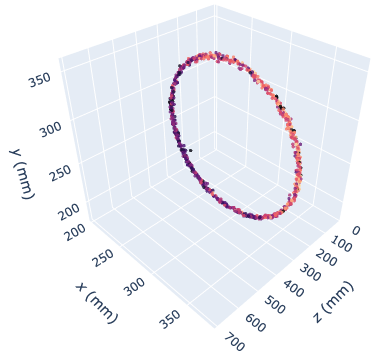
A more complete PEPT analysis script can track multiple tracers at the same time, produce "tight", separate trajectories and create multiple interactive Plotly subplots that are opened in a webpage (example live graph [here](https://uob-positron-imaging-centre.github.io/live/sample_full_42rpm)). The resulting trajectories can then be post-processed to extract system-specific data - e.g. residence time distributions.
You can download some PEPT data samples from the [UoB Positron Imaging Centre's Repository](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/example_data):
```
$> git clone https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/example_data
```
### Documentation
An absurd amount of time was spent making sure than *every* function and class in the `pept` library is well-documented (and most have examples) and all code is explained through comments - no dragons shall be dwelling in the `pept` source code. The library API / reference can be found [here](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html) - including a search function for quickly finding what you need.
A very fast-paced introduction to Python is available [here](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Uq8Ppiv8jR-XSVsKZMcCUNuXW-l6n_RI?usp=sharing); it is aimed at engineers whose background might be a few lines written MATLAB, as well as moderate C/C++ programmers.
A beginner-friendly tutorial for using the `pept` package is available [here](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1G8XHP9zWMMDVu23PXzANLCOKNP_RjBEO).
The links above point to Google Colaboratory, a Jupyter notebook-hosting website that lets you combine text with Python code, executing it on Google servers. Pretty neat, isn't it?
## Library Architecture
The main purpose of the `pept` library is to provide a common, consistent foundation for PEPT-related algorithms, including tracer tracking, visualisation and post-processing tools - such that they can be used interchangeably, mixed and matched for different systems. Virtually *any* PEPT processing routine follows these steps:
1. Convert raw gamma camera / scanner data into *3D lines* (i.e. the captured gamma rays, or lines of response - LoRs).
2. Take a *sample* of lines, locate tracer locations, then repeat for the next samples.
3. Separate out individual tracer trajectories.
4. Visualise and post-process trajectories.
For these algorithm-agnostic steps, `pept` provides five base data structures upon which the rest of the library is built:
1. [`pept.LineData`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#linedata): general 3D line samples, formatted as *[time, x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, extra...]*.
2. [`pept.PointData`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#pointdata): general 3D point samples, formatted as *[time, x, y, z, extra...]*.
3. [`pept.Pixels`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#pixels): single 2D pixellised space with physical dimensions, including fast line traversal.
4. [`pept.Voxels`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#voxels): single 3D voxellised space with physical dimensions, including fast line traversal.
5. [`pept.VoxelData`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#voxeldata): multiple samples of voxels, generated on demand, in parallel.
All the data structures above are built on top of NumPy and integrate natively with the rest of the Python / SciPy ecosystem. The rest of the `pept` library is organised into submodules:
- [`pept.scanners`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.scanners.html): converters between native scanner data and the base classes.
- [`pept.tracking`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.tracking.html): radioactive tracer tracking algorithms, e.g. the Birmingham method, PEPT-ML, FPI.
- [`pept.visualisation`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.visualisation.html): PEPT data visualisation subroutines.
- [`pept.utilities`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.utilities.html): general-purpose helpers, e.g. `read_csv`, `traverse3d`.
- [`pept.processing`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.processing.html): PEPT-oriented post-processing algorithms, e.g. `occupancy2d`.
## Performance
Significant effort has been put into making the algorithms in this package as fast as possible. The most computionally-intensive parts have been implemented in [`C`](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/search?l=c) / [`Cython`](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/search?l=Cython) and parallelised using `joblib` and `concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor`. For example, using the `peptml` subpackage, analysing 1,000,000 LoRs on the author's machine (mid 2012 MacBook Pro) takes about 26 s.
The tracking algorithms in `pept.tracking` successfully scaled up to hundreds of processors on BlueBEAR, the University of Birmingham's awesome [supercomputer](https://bear-apps.bham.ac.uk/applications/pept/0.2.2-foss-2019b-Python-3.7.4/).
## Help and Support
We recommend you check out [our tutorials](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1G8XHP9zWMMDVu23PXzANLCOKNP_RjBEO). If your issue is not suitably resolved there, please check the [issues](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/issues) page on our GitHub. Finally, if no solution is available there, feel free to [open an issue](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/issues/new); the authors will attempt to respond as soon as possible.
## Contributing
The `pept` library is not a one-man project; it is being built, improved and extended continuously (directly or indirectly) by an international team of researchers of diverse backgrounds - including programmers, mathematicians and chemical / mechanical / nuclear engineers. Want to contribute and become a PEPTspert yourself? Great, join the team!
There are multiple ways to help:
- [Open an issue](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/issues/new) mentioning any improvement you think `pept` could benefit from.
- Write a tutorial or share scripts you've developed that we can add to the [`pept` documentation](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) to help other people in the future.
- Share your PEPT-related algorithms - tracking, post-processing, visualisation, anything really! - so everybody can benefit from them.
Want to be a superhero and contribute code directly to the library itself? Grand - fork the project, add your code and submit a pull request (if that sounds like gibberish but you're an eager programmer, check [this article](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests)). We are more than happy to work with you on integrating your code into the library and, if helpful, we can schedule a screen-to-screen meeting for a more in-depth discussion about the `pept` package architecture.
Naturally, anything you contribute to the library will respect your authorship - protected by the strong GPL v3.0 open-source license (see the "Licensing" section below). If you include published work, please add a pointer to your publication in the code documentation.
## Citing
If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific publication, we ask you to cite the following paper:
> Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
As `pept` is a project bringing together the expertise of many people, it hosts multiple algorithms that were developed and published in other papers. Please check the documentation of the `pept` algorithms you are using in your research and cite the original papers mentioned accordingly.
## References
Papers presenting PEPT algorithms included in this library:
> [1] Parker DJ, Broadbent CJ, Fowles P, Hawkesworth MR, McNeil P. Positron emission particle tracking-a technique for studying flow within engineering equipment. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 1993 Mar 10;326(3):592-607.
> [2] Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
> [3] Wiggins C, Santos R, Ruggles A. A feature point identification method for positron emission particle tracking with multiple tracers. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2017 Jan 21;843:22-8.
## Licensing
The `pept` package is [GPL v3.0](https://choosealicense.com/licenses/gpl-3.0/) licensed. In non-lawyer terms, the key points of this license are:
- You can view, use, copy and modify this code **_freely_**.
- Your modifications must _also_ be licensed with GPL v3.0 or later.
- If you share your modifications with someone, you have to include the source code as well.
Essentially do whatever you want with the code, but don't try selling it saying it's yours :). This is a community-driven project building upon many other wonderful open-source projects (NumPy, Plotly, even Python itself!) without which `pept` simply would not have been possible. GPL v3.0 is indeed a very strong *copyleft* license; it was deliberately chosen to maintain the openness and transparency of great software and progress, and respect the researchers pushing PEPT forward. Frankly, open collaboration is way more efficient than closed, for-profit competition.
Copyright (C) 2021 the `pept` developers. Until now, this library was built directly or indirectly through the brain-time of:
- Andrei Leonard Nicusan (University of Birmingham)
- Dr. Kit Windows-Yule (University of Birmingham)
- Dr. Sam Manger (University of Birmingham)
- Matthew Herald (University of Birmingham)
- Chris Jones (University of Birmingham)
- Prof. David Parker (University of Birmingham)
- Dr. Antoine Renaud (University of Edinburgh)
- Dr. Cody Wiggins (Virginia Commonwealth University)
Keywords: pept positron emission particle tracking
Platform: UNKNOWN
Classifier: License :: OSI Approved :: GNU General Public License v3 or later (GPLv3+)
Classifier: Development Status :: 4 - Beta
Classifier: Intended Audience :: Science/Research
Classifier: Natural Language :: English
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3.6
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3.7
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: 3.9
Classifier: Programming Language :: Python :: Implementation :: CPython
Classifier: Programming Language :: Cython
Classifier: Programming Language :: C
Classifier: Programming Language :: C++
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Physics
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Information Analysis
Classifier: Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Visualization
Classifier: Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries :: Python Modules
Requires-Python: >=3.6.0
Description-Content-Type: text/markdown
Provides-Extra: docs
������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618748139.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/README.md��������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000777�0001750�0001750�00000036537�00000000000�016221� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������[](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pept/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
[](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1G8XHP9zWMMDVu23PXzANLCOKNP_RjBEO)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/context:python)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/context:cpp)
[](https://dev.azure.com/conda-forge/feedstock-builds/_build/latest?definitionId=10178&branchName=master)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pept/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
[](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pept/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/pept)
# The `pept` Library
A Python library that integrates all the tools necessary to perform research using Positron Emission Particle Tracking (PEPT). It includes algorithms for the location, identification and tracking of particles, in addition to tools for visualisation and analysis, and utilities allowing the realistic simulation of PEPT data.
## Positron Emission Particle Tracking
PEPT is a technique developed at the University of Birmingham which allows the non-invasive, three-dimensional tracking of one or more 'tracer' particles through particulate, fluid or multiphase systems. The technique allows particle or fluid motion to be tracked with sub-millimetre accuracy and sub-millisecond temporal resolution and, due to its use of highly-penetrating 511keV gamma rays, can be used to probe the internal dynamics of even large, dense, optically opaque systems - making it ideal for industrial as well as scientific applications.
PEPT is performed by radioactively labelling a particle with a positron-emitting radioisotope such as fluorine-18 (18F) or gallium-66 (66Ga), and using the back-to-back gamma rays produced by electron-positron annihilation events in and around the tracer to triangulate its spatial position. Each detected gamma ray represents a line of response (LoR).

Transforming gamma rays, or lines of response (left) into individual tracer trajectories (right) using the `pept` library. Depicted is experimental data of two tracers rotating at 42 RPM, imaged using the University of Birmingham Positron Imaging Centre's parallel screens PEPT camera.
## Getting Started
These instructions will help you get started with PEPT data analysis.
### Prerequisites
This package supports Python 3.6 and above - it is built and tested for Python 3.6, 3.7 and 3.8 on Windows, Linux and macOS (thanks to [`conda-forge`](https://conda-forge.org/), which is awesome!).
You can install it using the batteries-included [Anaconda distribution](https://www.anaconda.com/products/individual) or the bare-bones [Python interpreter](https://www.python.org/downloads/). You can also check out our Python and `pept` tutorials [here](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/tutorials).
### Installation
The easiest and quickest installation, if you are using Anaconda:
```
conda install -c conda-forge pept
```
You can also install the latest release version of `pept` from PyPI:
```
pip install --upgrade pept
```
Or you can install the development version from the GitHub repository:
```
pip install --upgrade git+https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept
```
## Tutorials
Some PEPT analysis example scripts are available on [pept.readthedocs.io](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/). A minimal script can read PEPT from an online location (e.g. the experiment shown above - two radioactive tracers rotating at 42 RPM), transform the lines of response into accurate tracer locations and plot them in a browser-based interactive 3D graph (live version available [here](https://uob-positron-imaging-centre.github.io/live/sample_42rpm)):

A more complete PEPT analysis script can track multiple tracers at the same time, produce "tight", separate trajectories and create multiple interactive Plotly subplots that are opened in a webpage (example live graph [here](https://uob-positron-imaging-centre.github.io/live/sample_full_42rpm)). The resulting trajectories can then be post-processed to extract system-specific data - e.g. residence time distributions.
You can download some PEPT data samples from the [UoB Positron Imaging Centre's Repository](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/example_data):
```
$> git clone https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/example_data
```
### Documentation
An absurd amount of time was spent making sure than *every* function and class in the `pept` library is well-documented (and most have examples) and all code is explained through comments - no dragons shall be dwelling in the `pept` source code. The library API / reference can be found [here](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html) - including a search function for quickly finding what you need.
A very fast-paced introduction to Python is available [here](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Uq8Ppiv8jR-XSVsKZMcCUNuXW-l6n_RI?usp=sharing); it is aimed at engineers whose background might be a few lines written MATLAB, as well as moderate C/C++ programmers.
A beginner-friendly tutorial for using the `pept` package is available [here](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1G8XHP9zWMMDVu23PXzANLCOKNP_RjBEO).
The links above point to Google Colaboratory, a Jupyter notebook-hosting website that lets you combine text with Python code, executing it on Google servers. Pretty neat, isn't it?
## Library Architecture
The main purpose of the `pept` library is to provide a common, consistent foundation for PEPT-related algorithms, including tracer tracking, visualisation and post-processing tools - such that they can be used interchangeably, mixed and matched for different systems. Virtually *any* PEPT processing routine follows these steps:
1. Convert raw gamma camera / scanner data into *3D lines* (i.e. the captured gamma rays, or lines of response - LoRs).
2. Take a *sample* of lines, locate tracer locations, then repeat for the next samples.
3. Separate out individual tracer trajectories.
4. Visualise and post-process trajectories.
For these algorithm-agnostic steps, `pept` provides five base data structures upon which the rest of the library is built:
1. [`pept.LineData`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#linedata): general 3D line samples, formatted as *[time, x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, extra...]*.
2. [`pept.PointData`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#pointdata): general 3D point samples, formatted as *[time, x, y, z, extra...]*.
3. [`pept.Pixels`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#pixels): single 2D pixellised space with physical dimensions, including fast line traversal.
4. [`pept.Voxels`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#voxels): single 3D voxellised space with physical dimensions, including fast line traversal.
5. [`pept.VoxelData`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pept_api.html#voxeldata): multiple samples of voxels, generated on demand, in parallel.
All the data structures above are built on top of NumPy and integrate natively with the rest of the Python / SciPy ecosystem. The rest of the `pept` library is organised into submodules:
- [`pept.scanners`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.scanners.html): converters between native scanner data and the base classes.
- [`pept.tracking`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.tracking.html): radioactive tracer tracking algorithms, e.g. the Birmingham method, PEPT-ML, FPI.
- [`pept.visualisation`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.visualisation.html): PEPT data visualisation subroutines.
- [`pept.utilities`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.utilities.html): general-purpose helpers, e.g. `read_csv`, `traverse3d`.
- [`pept.processing`](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api/pept.processing.html): PEPT-oriented post-processing algorithms, e.g. `occupancy2d`.
## Performance
Significant effort has been put into making the algorithms in this package as fast as possible. The most computionally-intensive parts have been implemented in [`C`](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/search?l=c) / [`Cython`](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/search?l=Cython) and parallelised using `joblib` and `concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor`. For example, using the `peptml` subpackage, analysing 1,000,000 LoRs on the author's machine (mid 2012 MacBook Pro) takes about 26 s.
The tracking algorithms in `pept.tracking` successfully scaled up to hundreds of processors on BlueBEAR, the University of Birmingham's awesome [supercomputer](https://bear-apps.bham.ac.uk/applications/pept/0.2.2-foss-2019b-Python-3.7.4/).
## Help and Support
We recommend you check out [our tutorials](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1G8XHP9zWMMDVu23PXzANLCOKNP_RjBEO). If your issue is not suitably resolved there, please check the [issues](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/issues) page on our GitHub. Finally, if no solution is available there, feel free to [open an issue](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/issues/new); the authors will attempt to respond as soon as possible.
## Contributing
The `pept` library is not a one-man project; it is being built, improved and extended continuously (directly or indirectly) by an international team of researchers of diverse backgrounds - including programmers, mathematicians and chemical / mechanical / nuclear engineers. Want to contribute and become a PEPTspert yourself? Great, join the team!
There are multiple ways to help:
- [Open an issue](https://github.com/uob-positron-imaging-centre/pept/issues/new) mentioning any improvement you think `pept` could benefit from.
- Write a tutorial or share scripts you've developed that we can add to the [`pept` documentation](https://pept.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) to help other people in the future.
- Share your PEPT-related algorithms - tracking, post-processing, visualisation, anything really! - so everybody can benefit from them.
Want to be a superhero and contribute code directly to the library itself? Grand - fork the project, add your code and submit a pull request (if that sounds like gibberish but you're an eager programmer, check [this article](https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests)). We are more than happy to work with you on integrating your code into the library and, if helpful, we can schedule a screen-to-screen meeting for a more in-depth discussion about the `pept` package architecture.
Naturally, anything you contribute to the library will respect your authorship - protected by the strong GPL v3.0 open-source license (see the "Licensing" section below). If you include published work, please add a pointer to your publication in the code documentation.
## Citing
If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific publication, we ask you to cite the following paper:
> Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
As `pept` is a project bringing together the expertise of many people, it hosts multiple algorithms that were developed and published in other papers. Please check the documentation of the `pept` algorithms you are using in your research and cite the original papers mentioned accordingly.
## References
Papers presenting PEPT algorithms included in this library:
> [1] Parker DJ, Broadbent CJ, Fowles P, Hawkesworth MR, McNeil P. Positron emission particle tracking-a technique for studying flow within engineering equipment. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 1993 Mar 10;326(3):592-607.
> [2] Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
> [3] Wiggins C, Santos R, Ruggles A. A feature point identification method for positron emission particle tracking with multiple tracers. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2017 Jan 21;843:22-8.
## Licensing
The `pept` package is [GPL v3.0](https://choosealicense.com/licenses/gpl-3.0/) licensed. In non-lawyer terms, the key points of this license are:
- You can view, use, copy and modify this code **_freely_**.
- Your modifications must _also_ be licensed with GPL v3.0 or later.
- If you share your modifications with someone, you have to include the source code as well.
Essentially do whatever you want with the code, but don't try selling it saying it's yours :). This is a community-driven project building upon many other wonderful open-source projects (NumPy, Plotly, even Python itself!) without which `pept` simply would not have been possible. GPL v3.0 is indeed a very strong *copyleft* license; it was deliberately chosen to maintain the openness and transparency of great software and progress, and respect the researchers pushing PEPT forward. Frankly, open collaboration is way more efficient than closed, for-profit competition.
Copyright (C) 2021 the `pept` developers. Until now, this library was built directly or indirectly through the brain-time of:
- Andrei Leonard Nicusan (University of Birmingham)
- Dr. Kit Windows-Yule (University of Birmingham)
- Dr. Sam Manger (University of Birmingham)
- Matthew Herald (University of Birmingham)
- Chris Jones (University of Birmingham)
- Prof. David Parker (University of Birmingham)
- Dr. Antoine Renaud (University of Edinburgh)
- Dr. Cody Wiggins (Virginia Commonwealth University)
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1619631590.0762506
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000755�0001750�0001750�00000000000�00000000000�015665� 5����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618748000.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/__init__.py�������������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000025127�00000000000�020005� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# File : __init__.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 19.08.2019
'''
PEPT
====
Summary
-------
A Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle Tracking (PEPT)
research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis and visualisation
tools.
Extended Summary
----------------
This Python library integrates all the tools necessary to perform research
using Positron Emission Particle Tracking (PEPT). The library includes
algorithms for the location, identification and tracking of particles, in
addition to tools for visualisation and analysis, and utilities allowing the
realistic simulation of PEPT data.
PEPT is a technique developed at the University of Birmingham [1]_ which allows
the non-invasive, three-dimensional tracking of one or more 'tracer' particles
through particulate, fluid or multiphase systems. The technique allows particle
or fluid motion to be tracked with sub-millimetre accuracy and sub-millisecond
temporal resolution and, due to its use of highly-penetrating 511keV gamma
rays, can be used to probe the internal dynamics of even large, dense,
optically opaque systems - making it ideal for industrial as well as
scientific applications.
PEPT is performed by radioactively labelling a particle with a positron-
emitting radioisotope such as fluorine-18 (18F) or gallium-66 (66Ga), and using
the back-to-back gamma rays produced by electron-positron annihilation events
in and around the tracer to triangulate its spatial position. Each detected
gamma ray represents a line of response (LoR) .
Subpackages Provided
--------------------
The `pept` package provides five base classes at its root - `PointData`,
`LineData`, `Pixels`, `Voxels` and `VoxelData` - acting as common data formats
that the rest of the package will use for its tracking, analysis and
visualisation algorithms. Thus any subroutine integrated in the `pept` package
can be used interchangeably with new PET / PEPT scanner geometries, data
formats or novel algorithms.
The rest of the package is grouped into subpackages and modules following the
hierarchy below:
::
pept
│
Base classes imported into the package root:
├── PointData : Base class encapsulating points.
├── LineData : Base class encapsulating lines (LoRs) w/ one timestamp.
├── Pixels : Base class managing pixels from a sample of lines.
├── Voxels : Base class managing voxels from a sample of lines.
├── VoxelData : Base class asynchronously managing multiple `Voxels`.
│
Subpackages:
├── base : Base classes (above).
├── cookbook : Pre-made PEPT analysis scripts, or recipes.
├── diagnostics : PET/PEPT scanner diagnostics.
├── processing : PEPT-oriented post-processing algorithms.
├── scanners : Transform other data formats into base classes.
├── simulation : Simulate radioactively-labeled tracers.
├── tests : Package unit tests.
├── tracking : Tracer identification and tracking algorithms.
│ ├── birmingham_method : The original Birmingham Method [1].
│ ├── fpi : The Feature Point Identification algorithm [3].
│ ├── peptml : The PEPT-ML algorithm [2].
│ └── trajectory_separation : Trajectory separation of tracked tracers.
├── utilities : Utility functions such as fast CSV-readers.
│ ├── cutpoints : Compute cutpoints from LoRs; Cython functions.
│ ├── misc : Miscellaneous, I/O, data aggregation.
│ ├── parallel : Call arbitrary functions using multithreading.
│ └── traverse : Traverse voxels for LoRs; Cython functions.
└── visualisation : Visualisation algorithms for LoRs, points, etc.
Each subpackage has its own documentation containing module, class and function
hierarchies such as the one above.
Performance
-----------
Significant effort has been put into making the algorithms in this package as
fast as possible. The most compute-intensive parts have been implemented in
`C` / `Cython` and parallelised, where possible, using `joblib` and
`concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor`. For example, using the `peptml`
subpackage [2]_, analysing 1,000,000 LoRs on the author's machine (mid 2012
MacBook Pro) takes ~26 seconds.
Citing
------
If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
publication, we ask you to cite the following paper:
Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking using
machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
Licensing
---------
The `pept` package is GNU v3.0 licensed.
Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers.
References
----------
Papers presenting PEPT algorithms included in this library: [1]_, [2]_, [3]_.
.. [1] Parker DJ, Broadbent CJ, Fowles P, Hawkesworth MR, McNeil P. Positron
emission particle tracking-a technique for studying flow within engineering
equipment. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A:
Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 1993
Mar 10;326(3):592-607.
.. [2] Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking using
machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments. 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
.. [3] Wiggins C, Santos R, Ruggles A. A feature point identification method
for positron emission particle tracking with multiple tracers. Nuclear
Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators,
Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment. 2017 Jan 21;843:22-8.
Examples
--------
You can download data samples from the UoB Positron Imaging Centre's
Repository (`link `_). A
small but complete analysis script using the PEPT-ML algorithm is given below.
First import the `pept` package and read in lines of response (LoRs) from our
online repository. We'll use a sample of real data from an experiment conducted
at Birmingham - two tracers rotating at 42RPM.
.. code-block:: python
import pept
lors_raw = pept.utilities.read_csv(
("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/uob-positron-imaging-centres/"
"example_data/master/sample_2p_42rpm.csv"), # Concatenate long string
skiprows = 16 # Skip file header
)
Our data is in a format typical of the parallel screens PEPT detector from
Birmingham. Convert it to our package's scanner-agnostic line format; we'll
iterate through them one sample at a time, tracking the tracer locations:
.. code-block:: python
lors = pept.scanners.ParallelScreens(
lors_raw, screen_separation = 712, sample_size = 200
)
Now it's time for some machine learning! Import the `peptml` package and
transform the LoRs into *cutpoints* that we'll use to find tracer locations.
.. code-block:: python
from pept.tracking import peptml
cutpoints = peptml.Cutpoints(lors, max_distance = 0.15)
Create a *clusterer* and use the cutpoints to find the centres of the tracers
as they move through our system:
.. code-block:: python
clusterer = peptml.HDBSCANClusterer()
centres = clusterer.fit(cutpoints)
This data looks alright (we'll plot everything in a minute), but we can do
better. We can iterate through the centres once more, clustering them again,
to get smooth, tight trajectories; for this, we'll set a small sample size and
large overlap:
.. code-block:: python
centres.sample_size = 60
centres.overlap = 59
centres_2pass = clusterer.fit(centres)
One more step! The locations of the two tracers tracked above are intertwined;
we need to separate them into individual trajectories. We have a module for
just that:
.. code-block:: python
import pept.tracking.trajectory_separation as tsp
points_window = 10
trajectory_cut_distance = 20
trajectories = tsp.segregate_trajectories(
centres_2pass, points_window, trajectory_cut_distance
)
Finally, let's plot some LoRs, the tracer centres after one pass of clustering
and after the second pass of clustering, and the separated trajectories. Let's
use Plotly to produce some beautiful, interactive, 3D graphs:
.. code-block:: python
from pept.visualisation import PlotlyGrapher
subplot_titles = ["Lines of Response (LoRs)", "HDBSCAN Clustering",
"2-pass Clustering", "Separated Trajectories"]
grapher = PlotlyGrapher(rows = 2, cols = 2, zlim = [0, 712],
subplot_titles = subplot_titles)
grapher.add_lines(lors.lines[:400]) # Only the first 400 LoRs
grapher.add_points(centres, col = 2)
grapher.add_points(centres_2pass, row = 2)
grapher.add_points(trajectories, row = 2, col = 2)
grapher.show()
A more in-depth tutorial is available on
`Google Colab `_.
'''
# Import base data structures
from .base.line_data import LineData
from .base.point_data import PointData
from .base.pixel_data import Pixels
from .base.voxel_data import Voxels
from .base.voxel_data import VoxelData
# Import subpackages
from . import cookbook
from . import diagnostics
from . import processing
from . import scanners
from . import simulation
from . import tracking
from . import utilities
from . import visualisation
# Import package version
from .__version__ import __version__
__all__ = [
'LineData',
'PointData',
'Pixels',
'Voxels',
'VoxelData',
'cookbook',
'diagnostics',
'processing',
'scanners',
'simulation',
'tracking',
'utilities',
'visualisation',
]
__author__ = ["The pept developers"]
__credits__ = [
"Andrei Leonard Nicusan (University of Birmingham)",
"Dr. Kit Windows-Yule (University of Birmingham)",
"Dr. Sam Manger (University of Birmingham)",
"Matthew Herald (University of Birmingham)",
"Chris Jones (University of Birmingham)",
"Prof. David Parker (University of Birmingham)",
"Dr. Antoine Renaud (University of Edinburgh)",
"Dr. Cody Wiggins (Virginia Commonwealth University",
]
__license__ = "GNU v3.0"
__maintainer__ = "Andrei Leonard Nicusan"
__email__ = "a.l.nicusan@bham.ac.uk"
__status__ = "Beta"
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1619631489.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/__version__.py����������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000000357�00000000000�020525� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# File : __version__.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 23.08.2019
VERSION = (0, 3, 2)
__version__ = '.'.join(map(str, VERSION))
���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1619631590.0762506
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/base/�������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000755�0001750�0001750�00000000000�00000000000�016577� 5����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1617302486.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/base/__init__.py��������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000002354�00000000000�020714� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# File : __init__.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 31.01.2020
'''PEPT base classes.
Subpackages Provided
--------------------
These classes are imported into the ``pept`` package root, so they are
available as ``pept.PointData``, ``pept.LineData``, etc., without going through
``base`` first.
::
pept.base
├── PointData : Encapsulate points for iteration and visualisation.
├── LineData : Encapsulate lines (LoRs) with a single timestamp.
├── Pixels : Encapsulate pixels for a single sample of lines.
├── Voxels : Encapsulate voxels for a single sample of lines.
└── VoxelData : Encapsulate voxels for line traversal and manipulation.
'''
from .line_data import LineData
from .point_data import PointData
from .voxel_data import VoxelData
from .voxel_data import Voxels
from .pixel_data import Pixels
__all__ = [
'LineData',
'PointData',
'Pixels',
'Voxels',
'VoxelData',
]
__license__ = "GNU v3.0"
__maintainer__ = "Andrei Leonard Nicusan"
__email__ = "a.l.nicusan@bham.ac.uk"
__status__ = "Beta"
������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1617302486.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/base/iterable_samples.py������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000024061�00000000000�022467� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you should cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# File : iterable_samples.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 09.04.2020
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class IterableSamples(ABC):
'''An abstract class for iterating through an array (or array-like) in
samples with potential overlap.
A class that inherits from ``IterableSamples`` must implement two
properties:
``data_samples``
The underlying data (e.g. a numpy array) that supports slicing.
``data_length``
The number of items in ``data_samples`` (e.g. for a 2D numpy array,
this is the number of rows).
Given an implementor's properties ``data_samples`` (e.g. a numpy array) and
``data_length``, this class can yield samples of the data of an adaptive
``sample_size`` and ``overlap``, without requiring additional storage.
The underlying data can be accessed using both indexing (``data[0]``) and
iteration (``for sample in data: ...``).
Particular cases:
1. If sample_size == 0, all data_samples is returned as one single
sample.
2. If overlap >= sample_size, an error is raised.
3. If overlap < 0, lines are skipped between samples.
Attributes
----------
data_samples : iterable that supports slicing
An iterable (e.g. numpy array) that supports slicing syntax (data[5:7])
storing the data that will be iterated over in samples. Must be
implemented by a subclass!
data_length : int
The number of elements in `data_samples`. For a numpy.ndarray, that
corresponds to len(`line_data`). Must be implemented by a subclass!
sample_size : int
An `int`` that defines the number of items that should be returned in
a single sample when iterating over `data_samples`. A `sample_size` of
0 yields all the data as one single sample.
overlap : int, optional
An `int` that defines the overlap between two consecutive samples that
are returned when iterating over `data_samples`. An overlap of 0
implies consecutive samples, while an overlap of (`sample_size` - 1)
means incrementing the samples by one. A negative overlap implies
skipping values between samples. An error is raised if `overlap` is
larger than or equal to `sample_size`.
number_of_samples : int
An `int` that corresponds to the number of samples that can be
accessed from the class. It takes `overlap` into consideration.
Methods
-------
sample(n)
Get sample number n (indexed from 0).
Raises
------
ValueError
If `overlap` >= `sample_size` unless `sample_size` is 0. Overlap
must be smaller than `sample_size`. Note that it can also be negative.
See Also
--------
pept.LineData : Encapsulate LoRs for ease of iteration and plotting.
pept.PointData : Encapsulate points for ease of iteration and plotting.
'''
def __init__(self, sample_size, overlap):
'''`IterableSamples` class constructor.
Parameters
----------
sample_size : int
An `int`` that defines the number of items that should be returned
in a single sample when iterating over `data_samples`. A
`sample_size` of 0 yields all the data as one single sample.
overlap : int, optional
An `int` that defines the overlap between two consecutive samples
that are returned when iterating over `data_samples`. An overlap of
0 implies consecutive samples, while an overlap of
(`sample_size` - 1) means incrementing the samples by one. A
negative overlap implies skipping values between samples. An error
is raised if `overlap` is larger than or equal to `sample_size`.
'''
sample_size = int(sample_size)
overlap = int(overlap)
if sample_size < 0:
raise ValueError((
f"\n[ERROR]: sample_size = {sample_size} must be positive "
"(>= 0).\n"
))
if sample_size != 0 and overlap >= sample_size:
raise ValueError((
f"\n[ERROR]: overlap = {overlap} must be smaller than "
f"sample_size = {sample_size}.\n"
))
self._index = 0
self._sample_size = sample_size
self._overlap = overlap
@property
@abstractmethod
def data_samples(self):
pass
@property
@abstractmethod
def data_length(self):
pass
@property
def sample_size(self):
return self._sample_size
@sample_size.setter
def sample_size(self, sample_size):
sample_size = int(sample_size)
if sample_size < 0:
raise ValueError((
f"\n[ERROR]: sample_size = {sample_size} must be positive "
"(>= 0). \n"
))
if sample_size != 0 and self._overlap >= sample_size:
raise ValueError((
f"\n[ERROR]: overlap = {self._overlap} must be smaller than "
f"sample_size = {sample_size}.\n"
))
self._index = 0
self._sample_size = sample_size
@property
def overlap(self):
return self._overlap
@overlap.setter
def overlap(self, overlap):
overlap = int(overlap)
if self._sample_size != 0 and overlap >= self._sample_size:
raise ValueError((
f"\n[ERROR]: overlap = {overlap} must be smaller than "
f"sample_size = {self._sample_size}.\n"
))
self._index = 0
self._overlap = overlap
@property
def number_of_samples(self):
# If self.sample_size == 0, all data is returned as a single sample.
if self._sample_size == 0:
return 1
# If self.sample_size != 0, check that there is at least one sample.
if self.data_length >= self._sample_size:
return (self.data_length - self._sample_size) // \
(self.sample_size - self.overlap) + 1
else:
return 0
def sample(self, n):
'''Get sample number n (indexed from 0, i.e. `n >= 0`)
Returns the items from `data_samples` included in sample number `n`.
Samples are numbered starting from 0.
Parameters
----------
n : int
The number of the sample required. Note that 1 <= n <=
number_of_samples.
Returns
-------
items from data_samples
The items returned from `point_data` using slicing, included in
sample `n`.
Raises
------
IndexError
If `sample_size == 0`, all data is returned as one single sample.
Raised if `n` is not 1.
IndexError
If `n > number_of_samples` or `n <= 0`.
'''
if self._sample_size == 0:
if n == 0:
return self.data_samples
else:
raise IndexError((
"\n[ERROR]: Tried to access a non-existent sample "
f"(samples indexed from 0): asked for sample {n}, when "
"there is only 1 sample (because `sample_size` == 0).\n"
))
elif (n >= self.number_of_samples) or n < 0:
raise IndexError((
"\n[ERROR]: Tried to access a non-existent sample (samples "
f"are indexed from 0): asked for sample {n}, when there are "
f"{self.number_of_samples} samples.\n"
))
start_index = n * (self._sample_size - self._overlap)
return self.data_samples[start_index:(start_index + self._sample_size)]
def __len__(self):
# Defined so that len(class_instance) returns the number of samples.
return self.number_of_samples
def __getitem__(self, key):
# Defined so that samples can be accessed as class_instance[0]
while key < 0:
key += self.number_of_samples
return self.sample(key)
def __iter__(self):
# Defined so the class can be iterated as
# `for sample in class_instance: ...`
return self
def __next__(self):
# sample_size = 0 => return all data
if self._sample_size == 0:
self._sample_size = -1
return self.data_samples
# Use -1 as a flag
if self._sample_size == -1:
self._sample_size = 0
raise StopIteration
# sample_size > 0 => return slices
if self._index != 0:
self._index = self._index + self._sample_size - self._overlap
else:
self._index = self._index + self._sample_size
if self._index > self.data_length:
self._index = 0
raise StopIteration
return self.data_samples[(self._index - self._sample_size):self._index]
�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618748000.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/base/line_data.py�������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000063423�00000000000�021101� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you must cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# File : line_data.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 19.08.2019
import time
import pickle
import numpy as np
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from .iterable_samples import IterableSamples
import pept
class LineData(IterableSamples):
'''A class for PEPT LoR data iteration, manipulation and visualisation.
Generally, PEPT Lines of Response (LoRs) are lines in 3D space, each
defined by two points, regardless of the geometry of the scanner used. This
class is used for the encapsulation of LoRs (or any lines!), efficiently
yielding samples of `lines` of an adaptive `sample_size` and `overlap`.
It is an abstraction over PET / PEPT scanner geometries and data formats,
as once the raw LoRs (be they stored as binary, ASCII, etc.) are
transformed into the common `LineData` format, any tracking, analysis or
visualisation algorithm in the `pept` package can be used interchangeably.
Moreover, it provides a stable, user-friendly interface for iterating over
LoRs in *samples* - this is useful for tracking algorithms, as they
generally take a few LoRs (a *sample*), produce a tracer position, then
move to the next sample of LoRs, repeating the procedure. Using overlapping
samples is also useful for improving the time resolution of the algorithms.
This is the base class for LoR data; the subroutines for transforming other
data formats into `LineData` can be found in `pept.scanners`. If you'd like
to integrate another scanner geometry or raw data format into this package,
you can check out the `pept.scanners.parallel_screens` module as an
example. This usually only involves writing a single function by hand; then
all attributes and methods from `LineData` will be available to your new
data format. If you'd like to use `LineData` as the base for other
algorithms, you can check out the `pept.tracking.peptml.cutpoints` module
as an example; the `Cutpoints` class iterates the samples of LoRs in any
`LineData` **in parallel**, using `concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor`.
Attributes
----------
lines : (N, M>=7) numpy.ndarray
An (N, M>=7) numpy array that stores the PEPT LoRs as time and
cartesian (3D) coordinates of two points defining a line, followed by
any additional data. The data columns are then
`[time, x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, etc.]`.
sample_size : int
An `int` that defines the number of lines that should be returned when
iterating over `lines`. The default is 0.
overlap : int
An `int` that defines the overlap between two consecutive samples that
are returned when iterating over `lines`. An overlap of 0 implies
consecutive samples, while an overlap of (`sample_size` - 1) implies
incrementing the samples by one. A negative overlap means skipping
values between samples. It is required to be smaller than
`sample_size`. The default is 0.
number_of_lines : int
An `int` that corresponds to len(`lines`), or the number of LoRs
stored by `lines`.
number_of_samples : int
An `int` that corresponds to the number of samples that can be accessed
from the class. It takes `overlap` into consideration.
Methods
-------
sample(n)
Get sample number n (indexed from 0).
to_csv(filepath)
Write `lines` to a CSV file.
save(filepath)
Save a `LineData` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
load(filepath)
Load a saved / pickled `LineData` object from `filepath`.
plot(sample_indices = ..., ax = None, alt_axes = False, colorbar_col = 0)
Plot lines from selected samples using matplotlib.
lines_trace(sample_indices = ..., width = 2, color = None, opacity = 0.6,\
colorbar = True, colorbar_col = 0, colorbar_title = None)
Get a Plotly trace for all the lines in selected samples.
copy()
Create a deep copy of an instance of this class, including a new inner
numpy array `lines`.
Raises
------
ValueError
If `overlap` >= `sample_size` unless `sample_size` is 0. Overlap
must be smaller than `sample_size`. Note that it can also be negative.
Notes
-----
The class saves `lines` as a **contiguous** numpy array for efficient
access in C / Cython functions. The inner data can be mutated, but do not
change the number of rows or columns after instantiating the class.
Examples
--------
Initialise a `LineData` instance containing 10 lines with a `sample_size`
of 3.
.. ipython::
In [3]: import pept
In [4]: import numpy as np
In [5]: lines_raw = np.arange(70).reshape(10, 7)
In [6]: print(lines_raw)
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6]
[ 7 8 9 10 11 12 13]
[14 15 16 17 18 19 20]
[21 22 23 24 25 26 27]
[28 29 30 31 32 33 34]
[35 36 37 38 39 40 41]
[42 43 44 45 46 47 48]
[49 50 51 52 53 54 55]
[56 57 58 59 60 61 62]
[63 64 65 66 67 68 69]]
In [7]: line_data = pept.LineData(lines_raw, sample_size = 3)
In [8]: print(line_data)
number_of_lines = 10
sample_size = 3
overlap = 0
number_of_samples = 3
lines =
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.]
[ 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13.]
[14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20.]
[21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27.]
[28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34.]
[35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41.]
[42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48.]
[49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55.]
[56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62.]
[63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69.]]
Access samples using subscript notation. Notice how the samples are
consecutive, as `overlap` is 0 by default.
.. ipython::
In [9]: line_data[0]
Out[9]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13.],
[14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20.]])
In [10]: line_data[1]
Out[10]:
array([[21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27.],
[28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.],
[35., 36., 37., 38., 39., 40., 41.]])
Now set an overlap of 2; notice how the number of samples changes:
.. ipython::
In [11]: len(line_data) # Number of samples
Out[11]: 3
In [12]: line_data.overlap = 2
In [13]: len(line_data)
Out[13]: 8
Notice how rows are repeated from one sample to the next when accessing
them, because `overlap` is now 2:
.. ipython::
In [14]: line_data[0]
Out[14]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13.],
[14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20.]])
In [15]: line_data[1]
Out[15]:
array([[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13.],
[14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20.],
[21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27.]])
Now change `sample_size` to 5 and notice again how the number of samples
changes:
.. ipython::
In [16]: len(line_data)
Out[16]: 8
In [17]: line_data.sample_size = 5
In [18]: len(line_data)
Out[18]: 2
In [19]: line_data[0]
Out[19]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13.],
[14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20.],
[21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27.],
[28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.]])
In [20]: line_data[1]
Out[20]:
array([[21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27.],
[28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.],
[35., 36., 37., 38., 39., 40., 41.],
[42., 43., 44., 45., 46., 47., 48.],
[49., 50., 51., 52., 53., 54., 55.]])
Notice how the samples do not cover the whole input `lines_raw` array, as
the last lines are omitted - think of the `sample_size` and `overlap`. They
are still inside the inner `lines` attribute of `line_data` though:
.. ipython::
In [21]: line_data.lines
Out[21]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6.],
[ 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13.],
[14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19., 20.],
[21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27.],
[28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.],
[35., 36., 37., 38., 39., 40., 41.],
[42., 43., 44., 45., 46., 47., 48.],
[49., 50., 51., 52., 53., 54., 55.],
[56., 57., 58., 59., 60., 61., 62.],
[63., 64., 65., 66., 67., 68., 69.]])
See Also
--------
pept.PointData : Encapsulate points for ease of iteration and plotting.
pept.utilities.read_csv : Fast CSV file reading into numpy arrays.
PlotlyGrapher : Easy, publication-ready plotting of PEPT-oriented data.
pept.tracking.peptml.Cutpoints : Compute cutpoints from `pept.LineData`.
'''
def __init__(
self,
lines,
sample_size = 0,
overlap = 0,
verbose = False
):
'''`LineData` class constructor.
Parameters
----------
lines : (N, M>=7) numpy.ndarray
An (N, M>=7) numpy array that stores the PEPT LoRs (or any generic
set of lines) as time and cartesian (3D) coordinates of two points
defining each line, followed by any additional data. The data
columns are then `[time, x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, etc.]`.
sample_size : int, default 0
An `int` that defines the number of lines that should be returned
when iterating over `lines`. A `sample_size` of 0 yields all the
data as one single sample.
overlap : int, default 0
An `int` that defines the overlap between two consecutive samples
that are returned when iterating over `lines`. An overlap of 0
means consecutive samples, while an overlap of (`sample_size` - 1)
means incrementing the samples by one. A negative overlap means
skipping values between samples. An error is raised if `overlap` is
larger than or equal to `sample_size`.
verbose : bool, default False
An option that enables printing the time taken for the
initialisation of an instance of the class. Useful when reading
large files (10gb files for PEPT data is not unheard of).
Raises
------
ValueError
If `lines` has fewer than 7 columns.
ValueError
If `overlap` >= `sample_size` unless `sample_size` is 0. Overlap
has to be smaller than `sample_size`. Note that it can also be
negative.
'''
if verbose:
start = time.time()
# If `lines` is not C-contiguous, create a C-contiguous copy
self._lines = np.asarray(lines, order = 'C', dtype = float)
# Check that lines has at least 7 columns.
if self._lines.ndim != 2 or self._lines.shape[1] < 7:
raise ValueError((
"\n[ERROR]: `lines` should have dimensions (M, N), where "
f"N >= 7. Received {self._lines.shape}.\n"
))
self._number_of_lines = len(self._lines)
# Call the IterableSamples constructor to make the class iterable in
# terms of samples with overlap.
IterableSamples.__init__(self, sample_size, overlap)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print(f"Initialised LineData class in {end - start} s.\n")
@property
def lines(self):
# The lines stored in the class.
return self._lines
@property
def data_samples(self):
# Implemented property for the IterableSamples parent class. See its
# documentation for more details.
return self._lines
@property
def data_length(self):
# Implemented property for the IterableSamples parent class. See its
# documentation for more details.
return self._number_of_lines
@property
def number_of_lines(self):
return self._number_of_lines
def to_csv(self, filepath, delimiter = " "):
'''Write `lines` to a CSV file.
Write all LoRs stored in the class to a CSV file.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
delimiter : str, default " "
The delimiter used to separate the values in the CSV file.
'''
np.savetxt(filepath, self._lines, delimiter = delimiter)
def save(self, filepath):
'''Save a `LineData` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
Saves the full object state, including the inner `.lines` NumPy array,
`sample_size`, etc. in a fast, portable binary format. Load back the
object using the `load` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Examples
--------
Save a `LineData` instance, then load it back:
>>> lines = pept.LineData([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]])
>>> lines.save("lines.pickle")
>>> lines_reloaded = pept.LineData.load("lines.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(self, f)
@staticmethod
def load(filepath):
'''Load a saved / pickled `LineData` object from `filepath`.
Most often the full object state was saved using the `.save` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Returns
-------
pept.LineData
The loaded `pept.LineData` instance.
Examples
--------
Save a `LineData` instance, then load it back:
>>> lines = pept.LineData([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]])
>>> lines.save("lines.pickle")
>>> lines_reloaded = pept.LineData.load("lines.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
obj = pickle.load(f)
return obj
def plot(
self,
sample_indices = ...,
ax = None,
alt_axes = False,
colorbar_col = 0,
):
'''Plot lines from selected samples using matplotlib.
Returns matplotlib figure and axes objects containing all lines
included in the samples selected by `sample_indices`.
`sample_indices` may be a single sample index (e.g. 0), an iterable
of indices (e.g. [1,5,6]), or an Ellipsis (`...`) for all samples.
Parameters
----------
sample_indices : int or iterable or Ellipsis, default Ellipsis
The index or indices of the samples of lines. An `int` signifies
the sample index, an iterable (list-like) signifies multiple sample
indices, while an Ellipsis (`...`) signifies all samples. The
default is `...` (all lines).
ax : mpl_toolkits.mplot3D.Axes3D object, optional
The 3D matplotlib-based axis for plotting. If undefined, new
Matplotlib figure and axis objects are created.
alt_axes : bool, default False
If `True`, plot using the alternative PEPT-style axes convention:
z is horizontal, y points upwards. Because Matplotlib cannot swap
axes, this is achieved by swapping the parameters in the plotting
call (i.e. `plt.plot(x, y, z)` -> `plt.plot(z, x, y)`).
colorbar_col : int, default -1
The column in the data samples that will be used to color the
lines. The default is -1 (the last column).
Returns
-------
fig, ax : matplotlib figure and axes objects
Notes
-----
Plotting all lines is very computationally-expensive for matplotlib. It
is recommended to only plot a couple of samples at a time, or use the
faster `pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher`.
Examples
--------
Plot the lines from sample 1 in a `LineData` instance:
>>> lors = pept.LineData(...)
>>> fig, ax = lors.plot(1)
>>> fig.show()
Plot the lines from samples 0, 1 and 2:
>>> fig, ax = lors.plot([0, 1, 2])
>>> fig.show()
'''
if ax is None:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection = '3d')
else:
fig = plt.gcf()
# Check if sample_indices is an iterable collection (list-like)
# otherwise just "iterate" over the single number or Ellipsis
if not hasattr(sample_indices, "__iter__"):
sample_indices = [sample_indices]
lines, color = [], []
# For each selected sample include all the lines' coordinates
for n in sample_indices:
# If an Ellipsis was received, then include all lines.
if n is Ellipsis:
sample = self.lines
else:
sample = self[n]
for line in sample:
lines.append(line[0:7])
color.append(line[colorbar_col])
color = np.array(color)
# Scatter x, y, z [color]
cmap = plt.cm.magma
color_array = cmap(color / color.max())
if alt_axes:
for i, line in enumerate(lines):
ax.plot(
[line[3], line[6]],
[line[1], line[4]],
[line[2], line[5]],
c = color_array[i],
alpha = 0.8
)
ax.set_xlabel("z (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("x (mm)")
ax.set_zlabel("y (mm)")
else:
for i, line in enumerate(lines):
ax.plot(
[line[1], line[4]],
[line[2], line[5]],
[line[3], line[6]],
c = color_array[i],
alpha = 0.8
)
ax.set_xlabel("x (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("y (mm)")
ax.set_zlabel("z (mm)")
return fig, ax
def lines_trace(
self,
sample_indices = ...,
width = 2.0,
color = None,
opacity = 0.6,
colorbar = True,
colorbar_col = 0,
colorscale = "Magma",
colorbar_title = None
):
'''Get a Plotly trace for all the lines in selected samples.
Creates a `plotly.graph_objects.Scatter3d` object for all the lines
included in the samples selected by `sample_indices`. `sample_indices`
may be a single sample index (e.g. 0), an iterable of indices (e.g.
[1,5,6]) or an Ellipsis (`...`) for all samples.
Can then be passed to the `plotly.graph_objects.figure.add_trace`
function or a `PlotlyGrapher` instance using the `add_trace` method.
Parameters
----------
sample_indices : int or iterable or Ellipsis, default Ellipsis
The index or indices of the samples of LoRs. An `int` signifies the
sample index, an iterable (list-like) signifies multiple sample
indices, while an Ellipsis (`...`) signifies all samples. The
default is `...` (all lines).
width : float, default 2.0
The width of the lines.
color : str or list-like, optional
Can be a single color (e.g. "black", "rgb(122, 15, 241)") or a
colorbar list. Overrides `colorbar` if set. For more information,
check the Plotly documentation. The default is None.
opacity : float, default 0.6
The opacity of the lines, where 0 is transparent and 1 is fully
opaque.
colorbar : bool, default True
If set to True, will color-code the data in the sample column
`colorbar_col`. Is overridden if `color` is set. The default is
True, so that every line has a different color.
colorbar_col : int, default 0
The column in the data samples that will be used to color the
points. Only has an effect if `colorbar` is set to True. The
default is 0 (the first column - time).
colorscale : str, default "Magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the `colorbar_col` column in the
input data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
colorbar_title : str, optional
If set, the colorbar will have this title above.
Returns
-------
plotly.graph_objs.Scatter3d
A Plotly trace of the LoRs.
Examples
--------
Use `PlotlyGrapher` (a user-friendly wrapper around the `plotly`
library for PEPT-oriented data) to plot the lines from sample 1 in a
`LineData` instance:
>>> lors = pept.LineData(...)
>>> grapher = pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher()
>>> trace = lors.lines_trace(1)
>>> grapher.add_trace(trace)
>>> grapher.show()
Use `plotly.graph_objs` to plot the lines from samples 0, 1 and 2:
>>> import plotly.graph_objs as go
>>> fig = go.Figure()
>>> fig.add_trace(lors.lines_trace([0, 1, 2]))
>>> fig.show()
'''
# Check if sample_indices is an iterable collection (list-like)
# otherwise just "iterate" over the single number or Ellipsis.
if not hasattr(sample_indices, "__iter__"):
sample_indices = [sample_indices]
marker = dict(
width = width,
color = color,
)
if colorbar:
if color is None:
marker['color'] = []
marker.update(colorscale = colorscale)
if colorbar_title is not None:
marker.update(colorbar = dict(title = colorbar_title))
coords_x = []
coords_y = []
coords_z = []
# For each selected sample include all the lines' coordinates
for n in sample_indices:
# If an Ellipsis was received, then include all lines.
if n is Ellipsis:
sample = self.lines
else:
sample = self[n]
for line in sample:
coords_x.extend([line[1], line[4], None])
coords_y.extend([line[2], line[5], None])
coords_z.extend([line[3], line[6], None])
if colorbar and color is None:
marker['color'].extend(3 * [line[colorbar_col]])
trace = go.Scatter3d(
x = coords_x,
y = coords_y,
z = coords_z,
mode = 'lines',
opacity = opacity,
line = marker
)
return trace
def copy(self):
'''Create a deep copy of an instance of this class, including a new
inner numpy array `lines`.
Returns
-------
pept.LineData
A new instance of the `pept.LineData` class with the same
attributes as this instance, deep-copied.
'''
return pept.LineData(
self._lines.copy(order = "C"),
sample_size = self._sample_size,
overlap = self._overlap,
verbose = False
)
def __str__(self):
# Shown when calling print(class)
docstr = (
f"number_of_lines = {self.number_of_lines}\n\n"
f"sample_size = {self._sample_size}\n"
f"overlap = {self._overlap}\n"
f"number_of_samples = {self.number_of_samples}\n\n"
f"lines = \n{self._lines}"
)
return docstr
def __repr__(self):
# Shown when writing the class on a REPR
docstr = (
"Class instance that inherits from `pept.LineData`.\n"
f"Type:\n{type(self)}\n\n"
"Attributes\n----------\n"
f"{self.__str__()}\n\n"
"Particular Cases\n----------------\n"
" > If sample_size == 0, all `lines` are returned as a "
"single sample.\n"
" > If overlap >= sample_size, an error is raised.\n"
" > If overlap < 0, lines are skipped between samples."
)
return docstr
���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618860716.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/base/pixel_data.py������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000073347�00000000000�021301� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you must cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# File : pixel_data.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 07.01.2020
import pickle
import time
import textwrap
import numpy as np
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pept.utilities.traverse import traverse2d
class Pixels(np.ndarray):
'''A class that manages a 2D pixel space, including tools for pixel
traversal of lines, manipulation and visualisation.
This class can be instantiated in a couple of ways:
1. The constructor receives a pre-defined pixel space (i.e. a 2D numpy
array), along with the space boundaries `xlim` and `ylim`.
2. The `from_lines` method receives a sample of 2D lines (i.e. a 2D numpy
array), each defined by two points, creating a pixel space and
traversing / pixellising the lines.
3. The `empty` method creates a pixel space filled with zeros.
This subclasses the `numpy.ndarray` class, so any `Pixels` object acts
exactly like a 2D numpy array. All numpy methods and operations are valid
on `Pixels` (e.g. add 1 to all pixels with `pixels += 1`).
It is possible to add multiple samples of lines to the same pixel space
using the `add_lines` method.
Attributes
----------
pixels: (M, N) numpy.ndarray
The 2D numpy array containing the number of lines that pass through
each pixel. They are stored as `float`s. This class assumes a uniform
grid of pixels - that is, the pixel size in each dimension is constant,
but can vary from one dimension to another. The number of pixels in
each dimension is defined by `number_of_pixels`.
number_of_pixels: 2-tuple
A 2-tuple corresponding to the shape of `pixels`.
pixel_size: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lengths of a pixel in the x- and y-dimensions, respectively.
xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max].
ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max].
pixel_grids: list[numpy.ndarray]
A list containing the pixel gridlines in the x- and y-dimensions.
Each dimension's gridlines are stored as a numpy of the pixel
delimitations, such that it has length (M + 1), where M is the number
of pixels in a given dimension.
Methods
-------
save(filepath)
Save a `Pixels` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
load(filepath)
Load a saved / pickled `Pixels` object from `filepath`.
from_lines(lines, number_of_pixels, xlim = None, ylim = None, \
verbose = True)
Create a pixel space and traverse / pixellise a given sample of
`lines`.
empty(number_of_pixels, xlim, ylim, verbose = False)
Create an empty pixel space for the 2D rectangle bounded by `xlim` and
`ylim`.
get_cutoff(p1, p2)
Return a numpy array containing the minimum and maximum value found
across the two input arrays.
add_lines(lines, verbose = False)
Pixellise a sample of lines, adding 1 to each pixel traversed, for
each line in the sample.
cube_trace(index, color = None, opacity = 0.4, colorbar = True,\
colorscale = "magma")
Get the Plotly `Mesh3d` trace for a single pixel at `index`.
cubes_traces(condition = lambda pixels: pixels > 0, color = None,\
opacity = 0.4, colorbar = True, colorscale = "magma")
Get a list of Plotly `Mesh3d` traces for all pixel selected by the
`condition` filtering function.
pixels_trace(condition = lambda pixels: pixels > 0, size = 4,\
color = None, opacity = 0.4, colorbar = True,\
colorscale = "Magma", colorbar_title = None)
Create and return a trace for all the pixels in this class, with
possible filtering.
heatmap_trace(ix = None, iy = None, iz = None, width = 0,\
colorscale = "Magma", transpose = True)
Create and return a Plotly `Heatmap` trace of a 2D slice through the
voxels.
Notes
-----
The traversed lines do not need to be fully bounded by the pixel space.
Their intersection is automatically computed.
The class saves `pixels` as a **contiguous** numpy array for efficient
access in C / Cython functions. The inner data can be mutated, but do not
change the shape of the array after instantiating the class.
Examples
--------
This class is most often instantiated from a sample of lines to pixellise:
>>> import pept
>>> import numpy as np
>>> lines = np.arange(70).reshape(10, 7)
>>> number_of_pixels = [3, 4]
>>> pixels = pept.Pixels.from_lines(lines, number_of_pixels)
>>> Initialised Pixels class in 0.0006861686706542969 s.
>>> print(pixels)
>>> pixels:
>>> [[[2. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 2. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
>>> [[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 1. 1. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 1. 1. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
>>> [[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 2. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 1. 2.]]]
>>> number_of_pixels = (3, 4, 5)
>>> pixel_size = [22. 16.5 13.2]
>>> xlim = [ 1. 67.]
>>> ylim = [ 2. 68.]
>>> zlim = [ 3. 69.]
>>> pixel_grids:
>>> [array([ 1., 23., 45., 67.]),
>>> array([ 2. , 18.5, 35. , 51.5, 68. ]),
>>> array([ 3. , 16.2, 29.4, 42.6, 55.8, 69. ])]
Note that it is important to define the `number_of_pixels`.
See Also
--------
pept.LineData : Encapsulate lines for ease of iteration and plotting.
pept.PointData : Encapsulate points for ease of iteration and plotting.
pept.utilities.read_csv : Fast CSV file reading into numpy arrays.
PlotlyGrapher : Easy, publication-ready plotting of PEPT-oriented data.
'''
def __new__(
cls,
pixels_array,
xlim,
ylim,
):
'''`Pixels` class constructor.
Parameters
----------
pixels_array: 3D numpy.ndarray
A 3D numpy array, corresponding to a pre-defined pixel space.
xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max].
ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max].
Raises
------
ValueError
If `pixels_array` does not have exactly 3 dimensions or if
`xlim` or `ylim` do not have exactly 2 values each.
'''
# Type-checking inputs
pixels_array = np.asarray(
pixels_array,
order = "C",
dtype = float
)
if pixels_array.ndim != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `pixels_array` must contain an array-like with "
"exactly three dimensions (i.e. pre-made pixels array). "
f"Received an array with {pixels_array.ndim} dimensions. "
"Note: if you would like to create pixels from a sample of"
"lines, use the `Pixels.from_lines` method. "
)))
xlim = np.asarray(xlim, dtype = float)
if xlim.ndim != 1 or len(xlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `xlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the x-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {xlim.shape}."
)))
ylim = np.asarray(ylim, dtype = float)
if ylim.ndim != 1 or len(ylim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `ylim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
# Setting class attributes
pixels = pixels_array.view(cls)
pixels._number_of_pixels = pixels.shape
pixels._xlim = xlim
pixels._ylim = ylim
pixels._pixel_size = np.array([
(pixels._xlim[1] - pixels._xlim[0]) / pixels._number_of_pixels[0],
(pixels._ylim[1] - pixels._ylim[0]) / pixels._number_of_pixels[1],
])
pixels._pixel_grids = tuple([
np.linspace(lim[0], lim[1], pixels._number_of_pixels[i] + 1)
for i, lim in enumerate((pixels._xlim, pixels._ylim))
])
return pixels
def __array_finalize__(self, pixels):
# Required method for numpy subclassing
if pixels is None:
return
self._number_of_pixels = getattr(pixels, "_number_of_pixels", None)
self._pixel_size = getattr(pixels, "_pixel_size", None)
self._xlim = getattr(pixels, "_xlim", None)
self._ylim = getattr(pixels, "_ylim", None)
self._zlim = getattr(pixels, "_zlim", None)
self._pixel_grids = getattr(pixels, "_pixel_grids", None)
def __reduce__(self):
# __reduce__ and __setstate__ ensure correct pickling behaviour. See
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26598109/preserve-custom-
# attributes-when-pickling-subclass-of-numpy-array
# Get the parent's __reduce__ tuple
pickled_state = super(Pixels, self).__reduce__()
# Create our own tuple to pass to __setstate__
new_state = pickled_state[2] + (
self._number_of_pixels,
self._xlim,
self._ylim,
self._pixel_size,
self._pixel_grids,
)
# Return a tuple that replaces the parent's __setstate__ tuple with
# our own
return (pickled_state[0], pickled_state[1], new_state)
def __setstate__(self, state):
# __reduce__ and __setstate__ ensure correct pickling behaviour
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26598109/preserve-custom-
# attributes-when-pickling-subclass-of-numpy-array
# Set the class attributes
self._pixel_grids = state[-1]
self._pixel_size = state[-2]
self._ylim = state[-3]
self._xlim = state[-4]
self._number_of_pixels = state[-5]
# Call the parent's __setstate__ with the other tuple elements.
super(Pixels, self).__setstate__(state[0:-5])
@property
def pixels(self):
return self.__array__()
@property
def number_of_pixels(self):
return self._number_of_pixels
@property
def xlim(self):
return self._xlim
@property
def ylim(self):
return self._ylim
@property
def pixel_size(self):
return self._pixel_size
@property
def pixel_grids(self):
return self._pixel_grids
@staticmethod
def from_lines(
lines,
number_of_pixels,
xlim = None,
ylim = None,
verbose = True,
):
'''Create a pixel space and traverse / pixellise a given sample of
`lines`.
The `number_of_pixels` in each dimension must be defined. If the
pixel space boundaries `xlim` or `ylim` are not defined, they
are inferred as the boundaries of the `lines`.
Parameters
----------
lines : (M, N>=5) numpy.ndarray
The lines that will be pixellised, each defined by a timestamp and
two 2D points, so that the data columns are [time, x1, y1, x2, y2].
Note that extra columns are ignored.
number_of_pixels : (2,) list[int]
The number of pixels in the x- and y-dimensions, respectively.
xlim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of `lines`.
ylim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of `lines`.
Returns
-------
pept.Pixels
A new `Pixels` object with the pixels through which the lines were
traversed.
Raises
------
ValueError
If the input `lines` does not have the shape (M, N>=5). If the
`number_of_pixels` is not a 1D list with exactly 2 elements, or
any dimension has fewer than 2 pixels.
'''
if verbose:
start = time.time()
# Type-checking inputs
lines = np.asarray(lines, order = "C", dtype = float)
if lines.ndim != 2 or lines.shape[1] < 5:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `lines` must be a 2D numpy array containing lines "
"defined by a timestamp and two 2D points, with every row "
"formatted as [t, x1, y1, x2, y2]. The `lines` must then have "
f"shape (M, 5). Received array with shape {lines.shape}."
)))
number_of_pixels = np.asarray(
number_of_pixels,
order = "C",
dtype = int
)
if number_of_pixels.ndim != 1 or len(number_of_pixels) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must be a list-like "
"with exactly two values, corresponding to the "
"number of pixels in the x- and y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {number_of_pixels.shape}."
)))
if (number_of_pixels < 2).any():
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must set at least two "
"pixels in each dimension (i.e. all elements in "
"`number_of_elements` must be larger or equal to two). "
f"Received `{number_of_pixels}`."
)))
if xlim is None:
xlim = Pixels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 1], lines[:, 3])
else:
xlim = np.asarray(xlim, dtype = float)
if xlim.ndim != 1 or len(xlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `xlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the x-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {xlim.shape}."
)))
if ylim is None:
ylim = Pixels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 1], lines[:, 3])
else:
ylim = np.asarray(ylim, dtype = float)
if ylim.ndim != 1 or len(ylim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `ylim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
pixels_array = np.zeros(tuple(number_of_pixels))
pixels = Pixels(
pixels_array,
xlim = xlim,
ylim = ylim,
)
pixels.add_lines(lines, verbose = False)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print((
f"Initialised Pixels class in {end - start} s."
))
return pixels
@staticmethod
def empty(number_of_pixels, xlim, ylim):
'''Create an empty pixel space for the 3D cube bounded by `xlim` and
`ylim`.
Parameters
----------
number_of_pixels: (2,) numpy.ndarray
A list-like containing the number of pixels to be created in the
x- and y-dimension, respectively.
xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max].
ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the pixellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max].
Time the pixellisation step and print it to the terminal.
Raises
------
ValueError
If `number_of_pixels` does not have exactly 2 values, or it has
values smaller than 2. If `xlim` or `ylim` do not have exactly 2
values each.
'''
number_of_pixels = np.asarray(
number_of_pixels,
order = "C",
dtype = int
)
if number_of_pixels.ndim != 1 or len(number_of_pixels) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must be a list-like "
"with exactly three values, corresponding to the "
"number of pixels in the x- and y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {number_of_pixels.shape}."
)))
if (number_of_pixels < 2).any():
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must set at least two "
"pixels in each dimension (i.e. all elements in "
"`number_of_elements` must be larger or equal to two). "
f"Received `{number_of_pixels}`."
)))
number_of_pixels = tuple(number_of_pixels)
empty_pixels = np.zeros(number_of_pixels)
return Pixels(
empty_pixels,
xlim = xlim,
ylim = ylim,
)
@staticmethod
def get_cutoff(p1, p2):
'''Return a numpy array containing the minimum and maximum value found
across the two input arrays.
Parameters
----------
p1 : (N,) numpy.ndarray
The first 1D numpy array.
p2 : (N,) numpy.ndarray
The second 1D numpy array.
Returns
-------
(2,) numpy.ndarray
The minimum and maximum value found across `p1` and `p2`.
Notes
-----
The input parameters *must* be numpy arrays, otherwise an error will
be raised.
'''
return np.array([
min(p1.min(), p2.min()),
max(p1.max(), p2.max()),
])
def save(self, filepath):
'''Save a `Pixels` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
Saves the full object state, including the inner `.pixels` NumPy array,
`xlim`, etc. in a fast, portable binary format. Load back the object
using the `load` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Examples
--------
Save a `Pixels` instance, then load it back:
>>> pixels = pept.Pixels.empty((640, 480), [0, 20], [0, 10])
>>> pixels.save("pixels.pickle")
>>> pixels_reloaded = pept.Pixels.load("pixels.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(self, f)
@staticmethod
def load(filepath):
'''Load a saved / pickled `Pixels` object from `filepath`.
Most often the full object state was saved using the `.save` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Returns
-------
pept.Pixels
The loaded `pept.Pixels` instance.
Examples
--------
Save a `Pixels` instance, then load it back:
>>> pixels = pept.Pixels.empty((640, 480), [0, 20], [0, 10])
>>> pixels.save("pixels.pickle")
>>> pixels_reloaded = pept.Pixels.load("pixels.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
obj = pickle.load(f)
return obj
def add_lines(self, lines, verbose = False):
'''Pixellise a sample of lines, adding 1 to each pixel traversed, for
each line in the sample.
Parameters
----------
lines : (M, N >= 5) numpy.ndarray
The sample of 2D lines to pixellise. Each line is defined as a
timestamp followed by two 2D points, such that the data columns are
`[time, x1, y1, x2, y2, ...]`. Note that there can be extra data
columns which will be ignored.
verbose : bool, default False
Time the pixel traversal and print it to the terminal.
Raises
------
ValueError
If `lines` has fewer than 5 columns.
'''
lines = np.asarray(lines, order = "C", dtype = float)
if lines.ndim != 2 or lines.shape[1] < 5:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `lines` must be a 2D array of lines, where each "
"line (i.e. row) is defined by a timestamp and two 2D points, "
"so the data columns are [time, x1, y1, x2, y2]. "
f"Received array of shape {lines.shape}."
)))
if verbose:
start = time.time()
traverse2d(
self.pixels,
lines,
self._pixel_grids[0],
self._pixel_grids[1],
)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print(f"Traversing {len(lines)} lines took {end - start} s.")
def pixels_trace(
self,
condition = lambda pixels: pixels > 0,
opacity = 0.9,
colorscale = "Magma",
):
'''Create and return a trace with all the pixels in this class, with
possible filtering.
Creates a `plotly.graph_objects.Surface` object for the centres of
all pixels encapsulated in a `pept.Pixels` instance, colour-coding the
pixel value.
The `condition` parameter is a filtering function that should return
a boolean mask (i.e. it is the result of a condition evaluation). For
example `lambda x: x > 0` selects all pixels that have a value larger
than 0.
Parameters
----------
condition : function, default `lambda pixels: pixels > 0`
The filtering function applied to the pixel data before plotting
it. It should return a boolean mask (a numpy array of the same
shape, filled with True and False), selecting all pixels that
should be plotted. The default, `lambda x: x > 0` selects all
pixels which have a value larger than 0.
opacity : float, default 0.4
The opacity of the surface, where 0 is transparent and 1 is fully
opaque.
colorscale : str, default "Magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the voxel values in the input
data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
Examples
--------
Pixellise an array of lines and add them to a `PlotlyGrapher` instance:
>>> grapher = PlotlyGrapher()
>>> lines = np.array(...) # shape (N, M >= 7)
>>> lines2d = lines[:, [0, 1, 2, 4, 5]] # select x, y of lines
>>> number_of_pixels = [10, 10]
>>> pixels = pept.Pixels.from_lines(lines2d, number_of_pixels)
>>> grapher.add_lines(lines)
>>> grapher.add_trace(pixels.pixels_trace())
>>> grapher.show()
'''
filtered = self.copy()
filtered[~condition(self)] = 0.
# Compute the pixel centres
x = self.pixel_grids[0]
x = (x[1:] + x[:-1]) / 2
y = self.pixel_grids[1]
y = (y[1:] + y[:-1]) / 2
trace = go.Surface(
x = x,
y = y,
z = filtered,
opacity = opacity,
colorscale = colorscale,
)
return trace
def heatmap_trace(
self,
colorscale = "Magma",
transpose = True,
xgap = 0.,
ygap = 0.,
):
'''Create and return a Plotly `Heatmap` trace of the pixels.
Parameters
----------
colorscale : str, default "Magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the pixel values in the input
data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
transpose : bool, default True
Transpose the heatmap (i.e. flip it across its diagonal).
Examples
--------
Pixellise an array of lines and add them to a `PlotlyGrapher2D`
instance:
>>> lines = np.array(...) # shape (N, M >= 7)
>>> lines2d = lines[:, [0, 1, 2, 4, 5]] # select x, y of lines
>>> number_of_pixels = [10, 10]
>>> pixels = pept.Pixels.from_lines(lines2d, number_of_pixels)
>>> grapher = pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher2D()
>>> grapher.add_pixels(pixels)
>>> grapher.show()
Or add them directly to a raw `plotly.graph_objs` figure:
>>> import plotly.graph_objs as go
>>> fig = go.Figure()
>>> fig.add_trace(pixels.heatmap_trace())
>>> fig.show()
'''
# Compute the pixel centres
x = self.pixel_grids[0]
x = (x[1:] + x[:-1]) / 2
y = self.pixel_grids[1]
y = (y[1:] + y[:-1]) / 2
heatmap = dict(
x = x,
y = y,
z = self,
colorscale = colorscale,
transpose = transpose,
xgap = xgap,
ygap = ygap,
)
return go.Heatmap(heatmap)
def plot(self, ax = None):
'''Plot pixels as a heatmap using Matplotlib.
Returns matplotlib figure and axes objects containing the pixel values
colour-coded in a Matplotlib image (i.e. heatmap).
Parameters
----------
ax : mpl_toolkits.mplot3D.Axes3D object, optional
The 3D matplotlib-based axis for plotting. If undefined, new
Matplotlib figure and axis objects are created.
Returns
-------
fig, ax : matplotlib figure and axes objects
Examples
--------
Pixellise an array of lines and plot them with Matplotlib:
>>> lines = np.array(...) # shape (N, M >= 7)
>>> lines2d = lines[:, [0, 1, 2, 4, 5]] # select x, y of lines
>>> number_of_pixels = [10, 10]
>>> pixels = pept.Pixels.from_lines(lines2d, number_of_pixels)
>>> fig, ax = pixels.plot()
>>> fig.show()
'''
if ax is None:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
else:
fig = plt.gcf()
# Plot the values in pixels (this class is a numpy array subclass)
ax.imshow(self)
# Compute the pixel centres and set them in the Matplotlib image
x = self.pixel_grids[0]
x = (x[1:] + x[:-1]) / 2
y = self.pixel_grids[1]
y = (y[1:] + y[:-1]) / 2
# Matplotlib shows numbers in a long format ("102.000032411"), so round
# them to two decimals before plotting
ax.set_xticklabels(np.round(x, 2))
ax.set_yticklabels(np.round(y, 2))
ax.set_xlabel("x (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("y (mm)")
return fig, ax
def __str__(self):
# Shown when calling print(class)
docstr = (
f"{self.__array__()}\n\n"
f"number_of_pixels = {self._number_of_pixels}\n"
f"pixel_size = {self._pixel_size}\n\n"
f"xlim = {self._xlim}\n"
f"ylim = {self._ylim}\n"
f"pixel_grids:\n"
f"([{self._pixel_grids[0][0]} ... {self._pixel_grids[0][-1]}],\n"
f" [{self._pixel_grids[1][0]} ... {self._pixel_grids[1][-1]}])"
)
return docstr
def __repr__(self):
# Shown when writing the class on a REPR
docstr = (
"Class instance that inherits from `pept.Pixels`.\n"
f"Type:\n{type(self)}\n\n"
"Attributes\n----------\n"
f"{self.__str__()}"
)
return docstr
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618748000.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/base/point_data.py������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000061162�00000000000�021301� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you must cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# File : point_data.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 19.08.2019
import pickle
import time
import numpy as np
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from .iterable_samples import IterableSamples
import pept
class PointData(IterableSamples):
'''A class for general PEPT point-like data iteration, manipulation and
visualisation.
In the context of positron-based particle tracking, points are defined by a
timestamp, 3D coordinates and any other extra information (such as
trajectory label or some tracer signature). This class is used for the
encapsulation of 3D points - be they tracer locations, cutpoints, etc. -,
efficiently yielding samples of `points` of an adaptive `sample_size` and
`overlap`.
Much like a complement to `LineData`, `PointData` is an abstraction over
point-like data that may be encountered in the context of PEPT (e.g.
pre-tracked tracer locations), as once the raw points are transformed into
the common `PointData` format, any tracking, analysis or visualisation
algorithm in the `pept` package can be used interchangeably. Moreover, it
provides a stable, user-friendly interface for iterating over points in
*samples* - this can be useful for tracking algorithms, as some take a few
points (a *sample*), produce an accurate tracer location, then move to the
next sample of points, repeating the procedure. Using overlapping samples
is also useful for improving the time resolution of the algorithms.
This is the base class for point-like data; subroutines that accept and/or
return `PointData` instances (or subclasses thereof) can be found
throughout the `pept` package. If you'd like to create new algorithms based
on them, you can check out the `pept.tracking.peptml.cutpoints` module as
an example; the `Cutpoints` class receives a `LineData` instance,
transforms the samples of LoRs into cutpoints, then initialises itself as a
`PointData` subclass - thereby inheriting all its methods and attributes.
Attributes
----------
points : (N, M) numpy.ndarray
An (N, M >= 4) numpy array that stores the points as time, followed by
cartesian (3D) coordinates of the point, followed by any extra
information. The data columns are then `[time, x, y, z, etc]`.
sample_size : int
An `int` that defines the number of lines that should be returned when
iterating over `points`. The default is 0.
overlap : int
An `int` that defines the overlap between two consecutive samples that
are returned when iterating over `points`. An overlap of 0 means
consecutive samples, while an overlap of (`sample_size` - 1) means
incrementing the samples by one. A negative overlap means skipping
values between samples. It is required to be smaller than
`sample_size`. The default is 0.
number_of_points : int
An `int` that corresponds to len(`points`), or the number of points
stored by `points`.
number_of_samples : int
An `int` that corresponds to the number of samples that can be accessed
from the class, taking the `overlap` into consideration.
Methods
-------
sample(n)
Get sample number n (indexed from 0).
to_csv(filepath)
Write `points` to a CSV file.
save(filepath)
Save a `PointData` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
load(filepath)
Load a saved / pickled `PointData` object from `filepath`.
plot(sample_indices = ..., ax = None, alt_axes = False, colorbar_col = -1)
Plot points from selected samples using matplotlib.
points_trace(sample_indices = ..., size = 2, color = None, opacity = 0.8,\
colorbar = True, colorbar_col = -1, colorscale = "Magma",\
colorbar_title = None)
Get a Plotly trace for all points in selected samples, with possible
color-coding.
copy()
Create a deep copy of an instance of this class, including a new inner
numpy array `points`.
Raises
------
ValueError
If `overlap` >= `sample_size`. Overlap is required to be smaller than
`sample_size`, unless `sample_size` is 0. Note that it can also be
negative.
Notes
-----
This class saves `points` as a **contiguous** numpy array for efficient
access in C / Cython functions. The inner data can be mutated, but do not
change the number of rows or columns after instantiating the class.
Examples
--------
Initialise a `PointData` instance containing 10 points with a `sample_size`
of 3.
.. ipython::
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: import pept
In [3]: points_raw = np.arange(40).reshape(10, 4)
In [4]: print(points_raw)
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]
[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]
[24 25 26 27]
[28 29 30 31]
[32 33 34 35]
[36 37 38 39]]
In [5]: point_data = pept.PointData(points_raw, sample_size = 3)
In [6]: print(point_data)
number_of_points = 10
sample_size = 3
overlap = 0
number_of_samples = 3
points =
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3.]
[ 4. 5. 6. 7.]
[ 8. 9. 10. 11.]
[12. 13. 14. 15.]
[16. 17. 18. 19.]
[20. 21. 22. 23.]
[24. 25. 26. 27.]
[28. 29. 30. 31.]
[32. 33. 34. 35.]
[36. 37. 38. 39.]]
Access samples using subscript notation. Notice how the samples are
consecutive, as `overlap` is 0 by default.
.. ipython::
In [7]: point_data[0]
Out[7]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],
[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.]])
In [8]: point_data[1]
Out[8]:
array([[12., 13., 14., 15.],
[16., 17., 18., 19.],
[20., 21., 22., 23.]])
Now set an overlap of 2; notice how the number of samples changes:
.. ipython::
In [9]: len(point_data) # Number of samples
Out[9]: 3
In [10]: point_data.overlap = 2
In [11]: len(point_data)
Out[11]: 8
Notice how rows are repeated from one sample to the next when accessing
them, because `overlap` is now 2:
.. ipython::
In [12]: point_data[0]
Out[12]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],
[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.]])
In [13]: point_data[1]
Out[13]:
array([[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14., 15.]])
Now change `sample_size` to 5 and notice again how the number of samples
changes:
.. ipython::
In [14]: len(point_data)
Out[14]: 8
In [15]: point_data.sample_size = 5
In [16]: len(point_data)
Out[16]: 2
In [17]: point_data[0]
Out[17]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],
[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14., 15.],
[16., 17., 18., 19.]])
In [18]: point_data[1]
Out[18]:
array([[12., 13., 14., 15.],
[16., 17., 18., 19.],
[20., 21., 22., 23.],
[24., 25., 26., 27.],
[28., 29., 30., 31.]])
Notice how the samples do not cover the whole input `points_raw` array, as
the last lines are omitted - think of the `sample_size` and `overlap`. They
are still inside the inner `points` attribute of `point_data` though:
.. ipython::
In [19]: point_data.points
Out[19]:
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],
[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14., 15.],
[16., 17., 18., 19.],
[20., 21., 22., 23.],
[24., 25., 26., 27.],
[28., 29., 30., 31.],
[32., 33., 34., 35.],
[36., 37., 38., 39.]])
See Also
--------
pept.LineData : Encapsulate LoRs for ease of iteration and plotting.
pept.utilities.read_csv : Fast CSV file reading into numpy arrays.
PlotlyGrapher : Easy, publication-ready plotting of PEPT-oriented data.
pept.tracking.peptml.Cutpoints : Compute cutpoints from `pept.LineData`.
'''
def __init__(
self,
points,
sample_size = 0,
overlap = 0,
verbose = False
):
'''`PointData` class constructor.
Parameters
----------
points : (N, M) numpy.ndarray
An (N, M >= 4) numpy array that stores points (or any generic 2D
set of data). It expects that the first column is time, followed by
cartesian (3D) coordinates of points, followed by any extra
information the user needs. The data columns are then
`[time, x, y, z, etc]`.
sample_size : int, default 0
An `int`` that defines the number of points that should be returned
when iterating over `points`. A `sample_size` of 0 yields all the
data as one single sample.
overlap : int, default 0
An `int` that defines the overlap between two consecutive samples
that are returned when iterating over `points`. An overlap of 0
means consecutive samples, while an overlap of (`sample_size` - 1)
implies incrementing the samples by one. A negative overlap means
skipping values between samples. An error is raised if `overlap` is
larger than or equal to `sample_size`.
verbose : bool, default False
An option that enables printing the time taken for the
initialisation of an instance of the class. Useful when reading
large files (10gb files for PEPT data is not unheard of).
Raises
------
ValueError
If `line_data` does not have (N, M) shape, where M >= 4.
'''
if verbose:
start = time.time()
# If `points` is not C-contiguous, create a C-contiguous copy.
self._points = np.asarray(points, order = 'C', dtype = float)
# Check that points has at least 4 columns.
if self._points.ndim != 2 or self._points.shape[1] < 4:
raise ValueError((
"\n[ERROR]: `points` should have dimensions (M, N), where "
f"N >= 4. Received {self._points.shape}.\n"
))
self._number_of_points = len(self._points)
# Call the IterableSamples constructor to make the class iterable in
# samples with overlap.
IterableSamples.__init__(self, sample_size, overlap)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print(f"Initialised PointData class in {end - start} s.")
@property
def points(self):
return self._points
@property
def data_samples(self):
# Implemented property for the `IterableSamples` parent class. See its
# documentation for more details.
return self._points
@property
def data_length(self):
# Implemented property for the IterableSamples parent class. See its
# documentation for more details.
return self._number_of_points
@property
def number_of_points(self):
return self._number_of_points
def to_csv(self, filepath):
'''Write `points` to a CSV file.
Write all points (and any extra data) stored in the class to a CSV
file.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
'''
np.savetxt(filepath, self._points)
def save(self, filepath):
'''Save a `PointData` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
Saves the full object state, including the inner `.points` NumPy array,
`sample_size`, etc. in a fast, portable binary format. Load back the
object using the `load` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Examples
--------
Save a `PointData` instance, then load it back:
>>> points = pept.PointData([[1, 2, 3, 4]])
>>> points.save("points.pickle")
>>> points_reloaded = pept.PointData.load("points.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(self, f)
@staticmethod
def load(filepath):
'''Load a saved / pickled `PointData` object from `filepath`.
Most often the full object state was saved using the `.save` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Returns
-------
pept.PointData
The loaded `pept.PointData` instance.
Examples
--------
Save a `PointData` instance, then load it back:
>>> points = pept.PointData([[1, 2, 3, 4]])
>>> points.save("points.pickle")
>>> points_reloaded = pept.PointData.load("points.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
obj = pickle.load(f)
return obj
def plot(
self,
sample_indices = ...,
ax = None,
alt_axes = False,
colorbar_col = -1,
):
'''Plot points from selected samples using matplotlib.
Returns matplotlib figure and axes objects containing all points
included in the samples selected by `sample_indices`.
`sample_indices` may be a single sample index (e.g. 0), an iterable
of indices (e.g. [1,5,6]), or an Ellipsis (`...`) for all samples.
Parameters
----------
sample_indices : int or iterable or Ellipsis, default Ellipsis
The index or indices of the samples of points. An `int` signifies
the sample index, an iterable (list-like) signifies multiple sample
indices, while an Ellipsis (`...`) signifies all samples. The
default is `...` (all points).
ax : mpl_toolkits.mplot3D.Axes3D object, optional
The 3D matplotlib-based axis for plotting. If undefined, new
Matplotlib figure and axis objects are created.
alt_axes : bool, default False
If `True`, plot using the alternative PEPT-style axes convention:
z is horizontal, y points upwards. Because Matplotlib cannot swap
axes, this is achieved by swapping the parameters in the plotting
call (i.e. `plt.plot(x, y, z)` -> `plt.plot(z, x, y)`).
colorbar_col : int, default -1
The column in the data samples that will be used to color the
points. The default is -1 (the last column).
Returns
-------
fig, ax : matplotlib figure and axes objects
Notes
-----
Plotting all points is very computationally-expensive for matplotlib.
It is recommended to only plot a couple of samples at a time, or use
the faster `pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher`.
Examples
--------
Plot the points from sample 1 in a `PointData` instance:
>>> point_data = pept.PointData(...)
>>> fig, ax = point_data.plot(1)
>>> fig.show()
Plot the points from samples 0, 1 and 2:
>>> fig, ax = point_data.plot([0, 1, 2])
>>> fig.show()
'''
if ax is None:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection = '3d')
else:
fig = plt.gcf()
# Check if sample_indices is an iterable collection (list-like)
# otherwise just "iterate" over the single number or Ellipsis
if not hasattr(sample_indices, "__iter__"):
sample_indices = [sample_indices]
if sample_indices[0] == Ellipsis:
x = self._points[:, 1],
y = self._points[:, 2],
z = self._points[:, 3],
color = self._points[:, colorbar_col]
else:
x, y, z, color = [], [], [], []
for n in sample_indices:
sample = self[n]
x.extend(sample[:, 1])
y.extend(sample[:, 2])
z.extend(sample[:, 3])
color.extend(sample[:, colorbar_col])
color = np.array(color)
# Scatter x, y, z, [color]
cmap = plt.cm.magma
color_array = cmap(color / color.max())
if alt_axes:
ax.scatter(z, x, y, c = color_array)
ax.set_xlabel("z (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("x (mm)")
ax.set_zlabel("y (mm)")
else:
ax.scatter(x, y, z, c = color_array)
ax.set_xlabel("x (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("y (mm)")
ax.set_zlabel("z (mm)")
return fig, ax
def points_trace(
self,
sample_indices = ...,
size = 2,
color = None,
opacity = 0.8,
colorbar = True,
colorbar_col = -1,
colorscale = "Magma",
colorbar_title = None
):
'''Get a Plotly trace for all points in selected samples, with possible
color-coding.
Returns a `plotly.graph_objects.Scatter3d` trace containing all points
included in in the samples selected by `sample_indices`.
`sample_indices` may be a single sample index (e.g. 0), an iterable
of indices (e.g. [1,5,6]), or an Ellipsis (`...`) for all samples.
Can then be passed to the `plotly.graph_objects.figure.add_trace`
function or a `PlotlyGrapher` instance using the `add_trace` method.
Parameters
----------
sample_indices : int or iterable or Ellipsis, default Ellipsis
The index or indices of the samples of points. An `int` signifies
the sample index, an iterable (list-like) signifies multiple sample
indices, while an Ellipsis (`...`) signifies all samples. The
default is `...` (all points).
size : float, default 2
The marker size of the points.
color : str or list-like, optional
Can be a single color (e.g. "black", "rgb(122, 15, 241)") or a
colorbar list. Overrides `colorbar` if set. For more information,
check the Plotly documentation.
opacity : float, default 0.8
The opacity of the lines, where 0 is transparent and 1 is fully
opaque.
colorbar : bool, default True
If set to True, will color-code the data in the sample column
`colorbar_col`. Is overridden if `color` is set.
colorbar_col : int, default -1
The column in the data samples that will be used to color the
points. Only has an effect if `colorbar` is set to True. The
default is -1 (the last column).
colorscale : str, default "Magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the `colorbar_col` column in the
input data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
colorbar_title : str, optional
If set, the colorbar will have this title above.
Returns
-------
plotly.graph_objs.Scatter3d
A Plotly trace of the points.
Examples
--------
Use `PlotlyGrapher` (a user-friendly wrapper around the `plotly`
library for PEPT-oriented data) to plot the points from sample 1 in a
`PointData` instance:
>>> point_data = pept.PointData(...)
>>> grapher = pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher()
>>> trace = point_data.points_trace(1)
>>> grapher.add_trace(trace)
>>> grapher.show()
Use `plotly.graph_objs` to plot the lines from samples 0, 1 and 2:
>>> import plotly.graph_objs as go
>>> fig = go.Figure()
>>> fig.add_trace(point_data.points_trace([0, 1, 2]))
>>> fig.show()
'''
# Check if sample_indices is an iterable collection (list-like)
# otherwise just "iterate" over the single number or Ellipsis
if not hasattr(sample_indices, "__iter__"):
sample_indices = [sample_indices]
coords_x = []
coords_y = []
coords_z = []
marker = dict(
size = size,
color = color,
opacity = opacity
)
if colorbar:
if color is None:
marker['color'] = []
marker.update(colorscale = colorscale)
if colorbar_title is not None:
marker.update(colorbar = dict(title = colorbar_title))
# If an Ellipsis was received, include all points
if sample_indices[0] is Ellipsis:
coords_x = self.points[:, 1]
coords_y = self.points[:, 2]
coords_z = self.points[:, 3]
if colorbar and color is None:
marker['color'] = self.points[:, colorbar_col]
else:
# For each selected sample include all the needed coordinates
for n in sample_indices:
sample = self[n]
coords_x.extend(sample[:, 1])
coords_y.extend(sample[:, 2])
coords_z.extend(sample[:, 3])
if colorbar and color is None:
marker['color'].extend(sample[:, colorbar_col])
trace = go.Scatter3d(
x = coords_x,
y = coords_y,
z = coords_z,
mode = "markers",
marker = marker
)
return trace
def copy(self):
'''Create a deep copy of an instance of this class, including a new
inner numpy array `points`.
Returns
-------
pept.PointData
A new instance of the `pept.PointData` class with the same
attributes as this instance, deep-copied.
'''
return pept.PointData(
self._points.copy(order = "C"),
sample_size = self._sample_size,
overlap = self._overlap,
verbose = False
)
def __str__(self):
# Shown when calling print(class)
docstr = (
f"number_of_points = {self.number_of_points}\n\n"
f"sample_size = {self._sample_size}\n"
f"overlap = {self._overlap}\n"
f"number_of_samples = {self.number_of_samples}\n\n"
f"points = \n{self._points}"
)
return docstr
def __repr__(self):
# Shown when writing the class on a REPL
docstr = (
"Class instance that inherits from `pept.PointData`.\n"
f"Type:\n{type(self)}\n\n"
"Attributes\n----------\n"
f"{self.__str__()}\n\n"
"Particular Cases\n----------------\n"
" > If sample_size == 0, all `points` are returned as a "
"single sample.\n"
" > If overlap >= sample_size, an error is raised.\n"
" > If overlap < 0, points are skipped between samples."
)
return docstr
��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1619077468.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/base/voxel_data.py������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000204607�00000000000�021310� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you must cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# File : voxel_data.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 07.01.2020
import pickle
import time
import textwrap
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import numpy as np
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import tqdm
import pept
from pept.utilities.traverse import traverse3d
class Voxels(np.ndarray):
'''A class that manages a single 3D voxel space, including tools for voxel
traversal of lines, manipulation and visualisation.
This class can be instantiated in a couple of ways:
1. The constructor receives a pre-defined voxel space (i.e. a 3D numpy
array), along with the space boundaries `xlim`, `ylim` and `zlim`.
2. The `from_lines` method receives a sample of 3D lines (i.e. a 2D numpy
array), each defined by two points, creating a voxel space and
traversing / voxellising the lines.
3. The `empty` method creates a voxel space filled with zeros.
This subclasses the `numpy.ndarray` class, so any `Voxels` object acts
exactly like a 3D numpy array. All numpy methods and operations are valid
on `Voxels` (e.g. add 1 to all voxels with `voxels += 1`).
It is possible to add multiple samples of lines to the same voxel space
using the `add_lines` method.
If you want to voxellise multiple samples of lines, see the `VoxelData`
class.
Attributes
----------
voxels: (M, N, P) numpy.ndarray
The 3D numpy array containing the number of lines that pass through
each voxel. They are stored as `float`s. This class assumes a uniform
grid of voxels - that is, the voxel size in each dimension is constant,
but can vary from one dimension to another. The number of voxels in
each dimension is defined by `number_of_voxels`.
number_of_voxels: 3-tuple
A 3-tuple corresponding to the shape of `voxels`.
voxel_size: (3,) numpy.ndarray
The lengths of a voxel in the x-, y- and z-dimensions, respectively.
xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max].
ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max].
zlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
z-dimension, formatted as [z_min, z_max].
voxel_grids: list[numpy.ndarray]
A list containing the voxel gridlines in the x-, y-, and z-dimensions.
Each dimension's gridlines are stored as a numpy of the voxel
delimitations, such that it has length (M + 1), where M is the number
of voxels in given dimension.
Methods
-------
save(filepath)
Save a `Voxels` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
load(filepath)
Load a saved / pickled `Voxels` object from `filepath`.
from_lines(lines, number_of_voxels, xlim = None, ylim = None, zlim = None,\
verbose = True)
Create a voxel space and traverse / voxellise a given sample of
`lines`.
empty(number_of_voxels, xlim, ylim, zlim, verbose = False)
Create an empty voxel space for the 3D cube bounded by `xlim`,
`ylim` and `zlim`.
get_cutoff(p1, p2)
Return a numpy array containing the minimum and maximum value found
across the two input arrays.
add_lines(lines, verbose = False)
Voxellise a sample of lines, adding 1 to each voxel traversed, for
each line in the sample.
cube_trace(index, color = None, opacity = 0.4, colorbar = True,\
colorscale = "magma")
Get the Plotly `Mesh3d` trace for a single voxel at `index`.
cubes_traces(condition = lambda voxels: voxels > 0, color = None,\
opacity = 0.4, colorbar = True, colorscale = "magma")
Get a list of Plotly `Mesh3d` traces for all voxels selected by the
`condition` filtering function.
voxels_trace(condition = lambda voxel_data: voxel_data > 0, size = 4,\
color = None, opacity = 0.4, colorbar = True,\
colorscale = "Magma", colorbar_title = None)
Create and return a trace for all the voxels in this class, with
possible filtering.
heatmap_trace(ix = None, iy = None, iz = None, width = 0,\
colorscale = "Magma", transpose = True)
Create and return a Plotly `Heatmap` trace of a 2D slice through the
voxels.
Notes
-----
The traversed lines do not need to be fully bounded by the voxel space.
Their intersection is automatically computed.
The class saves `voxels` as a **contiguous** numpy array for efficient
access in C / Cython functions. The inner data can be mutated, but do not
change the shape of the array after instantiating the class.
Examples
--------
This class is most often instantiated from a sample of lines to voxellise:
>>> import pept
>>> import numpy as np
>>> lines = np.arange(70).reshape(10, 7)
>>> number_of_voxels = [3, 4, 5]
>>> voxels = pept.Voxels.from_lines(lines, number_of_voxels)
>>> Initialised Voxels class in 0.0006861686706542969 s.
>>> print(voxels)
>>> voxels:
>>> [[[2. 1. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 2. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
>>> [[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 1. 1. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 1. 1. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]]
>>> [[0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 2. 0.]
>>> [0. 0. 0. 1. 2.]]]
>>> number_of_voxels = (3, 4, 5)
>>> voxel_size = [22. 16.5 13.2]
>>> xlim = [ 1. 67.]
>>> ylim = [ 2. 68.]
>>> zlim = [ 3. 69.]
>>> voxel_grids:
>>> [array([ 1., 23., 45., 67.]),
>>> array([ 2. , 18.5, 35. , 51.5, 68. ]),
>>> array([ 3. , 16.2, 29.4, 42.6, 55.8, 69. ])]
Note that it is important to define the `number_of_voxels`.
See Also
--------
pept.VoxelData : Asynchronously manage multiple voxel spaces.
pept.LineData : Encapsulate lines for ease of iteration and plotting.
pept.PointData : Encapsulate points for ease of iteration and plotting.
PlotlyGrapher : Easy, publication-ready plotting of PEPT-oriented data.
'''
def __new__(
cls,
voxels_array,
xlim,
ylim,
zlim,
):
'''`Voxels` class constructor.
Parameters
----------
voxels_array: 3D numpy.ndarray
A 3D numpy array, corresponding to a pre-defined voxel space.
xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max].
ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max].
zlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
z-dimension, formatted as [z_min, z_max].
Raises
------
ValueError
If `voxels_array` does not have exactly 3 dimensions or if
`xlim`, `ylim` or `zlim` do not have exactly 2 values each.
'''
# Type-checking inputs
voxels_array = np.asarray(
voxels_array,
order = "C",
dtype = float
)
if voxels_array.ndim != 3:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `voxels_array` must contain an array-like with "
"exactly three dimensions (i.e. pre-made voxels array). "
f"Received an array with {voxels_array.ndim} dimensions. "
"Note: if you would like to create voxels from a sample of"
"lines, use the `Voxels.from_lines` method. "
)))
xlim = np.asarray(xlim, dtype = float)
if xlim.ndim != 1 or len(xlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `xlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the x-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {xlim.shape}."
)))
ylim = np.asarray(ylim, dtype = float)
if ylim.ndim != 1 or len(ylim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `ylim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
zlim = np.asarray(zlim, dtype = float)
if zlim.ndim != 1 or len(zlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `zlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the z-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {zlim.shape}."
)))
# Setting class attributes
voxels = voxels_array.view(cls)
voxels._number_of_voxels = voxels.shape
voxels._xlim = xlim
voxels._ylim = ylim
voxels._zlim = zlim
voxels._voxel_size = np.array([
(voxels._xlim[1] - voxels._xlim[0]) / voxels._number_of_voxels[0],
(voxels._ylim[1] - voxels._ylim[0]) / voxels._number_of_voxels[1],
(voxels._zlim[1] - voxels._zlim[0]) / voxels._number_of_voxels[2],
])
voxels._voxel_grids = tuple([
np.linspace(lim[0], lim[1], voxels._number_of_voxels[i] + 1)
for i, lim in enumerate((voxels._xlim, voxels._ylim, voxels._zlim))
])
return voxels
def __array_finalize__(self, voxels):
if voxels is None:
return
self._number_of_voxels = getattr(voxels, "_number_of_voxels", None)
self._voxel_size = getattr(voxels, "_voxel_size", None)
self._xlim = getattr(voxels, "_xlim", None)
self._ylim = getattr(voxels, "_ylim", None)
self._zlim = getattr(voxels, "_zlim", None)
self._voxel_grids = getattr(voxels, "_voxel_grids", None)
def __reduce__(self):
# __reduce__ and __setstate__ ensure correct pickling behaviour. See
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26598109/preserve-custom-
# attributes-when-pickling-subclass-of-numpy-array
# Get the parent's __reduce__ tuple
pickled_state = super(Voxels, self).__reduce__()
# Create our own tuple to pass to __setstate__
new_state = pickled_state[2] + (
self._number_of_voxels,
self._voxel_size,
self._xlim,
self._ylim,
self._zlim,
self._voxel_grids,
)
# Return a tuple that replaces the parent's __setstate__ tuple with
# our own
return (pickled_state[0], pickled_state[1], new_state)
def __setstate__(self, state):
# __reduce__ and __setstate__ ensure correct pickling behaviour
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26598109/preserve-custom-
# attributes-when-pickling-subclass-of-numpy-array
# Set the class attributes
self._voxel_grids = state[-1]
self._zlim = state[-2]
self._ylim = state[-3]
self._xlim = state[-4]
self._voxel_size = state[-5]
self._number_of_voxels = state[-6]
# Call the parent's __setstate__ with the other tuple elements.
super(Voxels, self).__setstate__(state[0:-6])
@property
def voxels(self):
return self.__array__()
@property
def number_of_voxels(self):
return self._number_of_voxels
@property
def xlim(self):
return self._xlim
@property
def ylim(self):
return self._ylim
@property
def zlim(self):
return self._zlim
@property
def voxel_size(self):
return self._voxel_size
@property
def voxel_grids(self):
return self._voxel_grids
@staticmethod
def from_lines(
lines,
number_of_voxels,
xlim = None,
ylim = None,
zlim = None,
verbose = True,
):
'''Create a voxel space and traverse / voxellise a given sample of
`lines`.
The `number_of_voxels` in each dimension must be defined. If the
voxel space boundaries `xlim`, `ylim` or `zlim` are not defined, they
are inferred as the boundaries of the `lines`.
Parameters
----------
lines : (M, N>=7) numpy.ndarray or pept.LineData
The lines that will be voxellised, each defined by a timestamp and
two 3D points, so that the data columns are [time, x1, y1, z1,
x2, y2, z2, ...]. Note that extra columns are ignored.
number_of_voxels : (3,) list[int]
The number of voxels in the x-, y-, and z-dimensions, respectively.
xlim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of `lines`.
ylim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of `lines`.
zlim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
z-dimension, formatted as [z_min, z_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of `lines`.
Returns
-------
pept.Voxels
A new `Voxels` object with the voxels through which the lines were
traversed.
Raises
------
ValueError
If the input `lines` does not have the shape (M, N>=7). If the
`number_of_voxels` is not a 1D list with exactly 3 elements, or
any dimension has fewer than 2 voxels.
'''
if verbose:
start = time.time()
# Type-checking inputs
if isinstance(lines, pept.LineData):
lines = lines.lines
lines = np.asarray(lines, order = "C", dtype = float)
if lines.ndim != 2 or lines.shape[1] < 7:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `lines` must be a 2D numpy array containing lines "
"defined by two points, with every row is formatted as "
"[time, x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, ...]. The `lines` must then "
"have shape (M, N >= 7). Received array with shape "
f"{lines.shape}."
)))
number_of_voxels = np.asarray(
number_of_voxels,
order = "C",
dtype = int
)
if number_of_voxels.ndim != 1 or len(number_of_voxels) != 3:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_voxels` must be a list-like "
"with exactly three values, corresponding to the "
"number of voxels in the x-, y-, and z-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {number_of_voxels.shape}."
)))
if (number_of_voxels < 2).any():
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_voxels` must set at least two "
"voxels in each dimension (i.e. all elements in "
"`number_of_elements` must be larger or equal to two). "
f"Received `{number_of_voxels}`."
)))
if xlim is None:
xlim = Voxels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 1], lines[:, 4])
else:
xlim = np.asarray(xlim, dtype = float)
if xlim.ndim != 1 or len(xlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `xlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the x-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {xlim.shape}."
)))
if ylim is None:
ylim = Voxels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 2], lines[:, 5])
else:
ylim = np.asarray(ylim, dtype = float)
if ylim.ndim != 1 or len(ylim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `ylim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
if zlim is None:
zlim = Voxels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 3], lines[:, 6])
else:
zlim = np.asarray(zlim, dtype = float)
if zlim.ndim != 1 or len(zlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `zlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the z-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
voxels_array = np.zeros(tuple(number_of_voxels))
voxels = Voxels(
voxels_array,
xlim = xlim,
ylim = ylim,
zlim = zlim,
)
voxels.add_lines(lines, verbose = False)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print((
f"Initialised Voxels class in {end - start} s."
))
return voxels
@staticmethod
def empty(number_of_voxels, xlim, ylim, zlim):
'''Create an empty voxel space for the 3D cube bounded by `xlim`,
`ylim` and `zlim`.
Parameters
----------
number_of_voxels: (3,) numpy.ndarray
A list-like containing the number of voxels to be created in the
x-, y- and z-dimension, respectively.
xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max].
ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max].
zlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
z-dimension, formatted as [z_min, z_max].
Raises
------
ValueError
If `number_of_voxels` does not have exactly 3 values, or it has
values smaller than 2. If `xlim`, `ylim` or `zlim` do not have
exactly 2 values each.
'''
number_of_voxels = np.asarray(
number_of_voxels,
order = "C",
dtype = int
)
if number_of_voxels.ndim != 1 or len(number_of_voxels) != 3:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_voxels` must be a list-like "
"with exactly three values, corresponding to the "
"number of voxels in the x-, y-, and z-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {number_of_voxels.shape}."
)))
if (number_of_voxels < 2).any():
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_voxels` must set at least two "
"voxels in each dimension (i.e. all elements in "
"`number_of_elements` must be larger or equal to two). "
f"Received `{number_of_voxels}`."
)))
number_of_voxels = tuple(number_of_voxels)
empty_voxels = np.zeros(number_of_voxels)
return Voxels(
empty_voxels,
xlim = xlim,
ylim = ylim,
zlim = zlim,
)
@staticmethod
def get_cutoff(p1, p2):
'''Return a numpy array containing the minimum and maximum value found
across the two input arrays.
Parameters
----------
p1 : (N,) numpy.ndarray
The first 1D numpy array.
p2 : (N,) numpy.ndarray
The second 1D numpy array.
Returns
-------
(2,) numpy.ndarray
The minimum and maximum value found across `p1` and `p2`.
Notes
-----
The input parameters *must* be numpy arrays, otherwise an error will
be raised.
'''
return np.array([
min(p1.min(), p2.min()),
max(p1.max(), p2.max()),
])
def save(self, filepath):
'''Save a `Voxels` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
Saves the full object state, including the inner `.voxels` NumPy array,
`xlim`, etc. in a fast, portable binary format. Load back the object
using the `load` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Examples
--------
Save a `Voxels` instance, then load it back:
>>> voxels = pept.Voxels.empty((64, 48, 32), [0, 20], [0, 10], [0, 5])
>>> voxels.save("voxels.pickle")
>>> voxels_reloaded = pept.Voxels.load("voxels.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(self, f)
@staticmethod
def load(filepath):
'''Load a saved / pickled `Voxels` object from `filepath`.
Most often the full object state was saved using the `.save` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Returns
-------
pept.Voxels
The loaded `pept.Voxels` instance.
Examples
--------
Save a `Voxels` instance, then load it back:
>>> voxels = pept.Voxels.empty((64, 48, 32), [0, 20], [0, 10], [0, 5])
>>> voxels.save("voxels.pickle")
>>> voxels_reloaded = pept.Voxels.load("voxels.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
obj = pickle.load(f)
return obj
def add_lines(self, lines, verbose = False):
'''Voxellise a sample of lines, adding 1 to each voxel traversed, for
each line in the sample.
Parameters
----------
lines : (M, N >= 7) numpy.ndarray
The sample of 3D lines to voxellise. Each line is defined as a
timestamp followed by two 3D points, such that the data columns are
`[time, x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, ...]`. Note that there can be extra
data columns which will be ignored.
verbose : bool, default False
Time the voxel traversal and print it to the terminal.
Raises
------
ValueError
If `lines` has fewer than 7 columns.
'''
lines = np.asarray(lines, order = "C", dtype = float)
if lines.ndim != 2 or lines.shape[1] < 7:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `lines` must be a 2D array of lines, where each "
"line (i.e. row) is defined by a timestamp and two 3D points, "
"so the data columns are [time, x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2]. "
f"Received array of shape {lines.shape}."
)))
if verbose:
start = time.time()
traverse3d(
self.voxels,
lines,
self._voxel_grids[0],
self._voxel_grids[1],
self._voxel_grids[2]
)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print(f"Traversing {len(lines)} lines took {end - start} s.")
def plot(
self,
condition = lambda voxel_data: voxel_data > 0,
ax = None,
alt_axes = False,
):
'''Plot the voxels in this class using Matplotlib.
This plots the centres of all voxels encapsulated in a `pept.Voxels`
instance, colour-coding the voxel value.
The `condition` parameter is a filtering function that should return
a boolean mask (i.e. it is the result of a condition evaluation). For
example `lambda x: x > 0` selects all voxels that have a value larger
than 0.
Parameters
----------
condition : function, default `lambda voxel_data: voxel_data > 0`
The filtering function applied to the voxel data before plotting
it. It should return a boolean mask (a numpy array of the same
shape, filled with True and False), selecting all voxels that
should be plotted. The default, `lambda x: x > 0` selects all
voxels which have a value larger than 0.
ax : mpl_toolkits.mplot3D.Axes3D object, optional
The 3D matplotlib-based axis for plotting. If undefined, new
Matplotlib figure and axis objects are created.
alt_axes : bool, default False
If `True`, plot using the alternative PEPT-style axes convention:
z is horizontal, y points upwards. Because Matplotlib cannot swap
axes, this is achieved by swapping the parameters in the plotting
call (i.e. `plt.plot(x, y, z)` -> `plt.plot(z, x, y)`).
Returns
-------
fig, ax : matplotlib figure and axes objects
Notes
-----
Plotting all points is very computationally-expensive for matplotlib.
It is recommended to only plot a couple of samples at a time, or use
the faster `pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher`.
Examples
--------
Voxellise an array of lines and add them to a `PlotlyGrapher` instance:
>>> lines = np.array(...) # shape (N, M >= 7)
>>> number_of_voxels = [10, 10, 10]
>>> voxels = pept.Voxels(lines, number_of_voxels)
>>> fig, ax = voxels.plot()
>>> fig.show()
'''
if ax is None:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection = '3d')
else:
fig = plt.gcf()
filtered_indices = np.argwhere(condition(self))
positions = self._voxel_size * (0.5 + filtered_indices) + \
[self._xlim[0], self._ylim[0], self._zlim[0]]
x = positions[:, 0]
y = positions[:, 1]
z = positions[:, 2]
voxel_vals = np.array([self[tuple(fi)] for fi in filtered_indices])
cmap = plt.cm.magma
color_array = cmap(voxel_vals / voxel_vals.max())
if alt_axes:
ax.scatter(z, x, y, c = color_array, marker = "s")
ax.set_xlabel("z (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("x (mm)")
ax.set_zlabel("y (mm)")
else:
ax.scatter(x, y, z, c = color_array, marker = "s")
ax.set_xlabel("x (mm)")
ax.set_ylabel("y (mm)")
ax.set_zlabel("z (mm)")
return fig, ax
def cube_trace(
self,
index,
color = None,
opacity = 0.4,
colorbar = True,
colorscale = "magma",
):
'''Get the Plotly `Mesh3d` trace for a single voxel at `index`.
This renders the voxel as a cube. While visually accurate, this method
is *very* computationally intensive - only use it for fewer than 100
cubes. For more voxels, use the `voxels_trace` method.
Parameters
----------
index: (3,) tuple
The voxel indices, given as a 3-tuple.
color : str or list-like, optional
Can be a single color (e.g. "black", "rgb(122, 15, 241)") or a
colorbar list. Overrides `colorbar` if set. For more information,
check the Plotly documentation. The default is None.
opacity : float, default 0.4
The opacity of the lines, where 0 is transparent and 1 is fully
opaque.
colorbar : bool, default True
If set to True, will color-code the voxel values. Is overridden if
`color` is set.
colorscale : str, default "Magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the voxel values in the input
data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
Raises
------
ValueError
If `index` does not contain exactly three values.
Notes
-----
If you want to render a small number of voxels as cubes using Plotly,
use the `cubes_traces` method, which creates a list of individual cubes
for all voxels, using this function.
'''
index = np.asarray(index, dtype = int)
if index.ndim != 1 or len(index) != 3:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `index` must contain exactly three values, "
"corresponding to the x, y, z indices of the voxel to plot. "
f"Received {index}."
)))
xyz = self._voxel_size * index + \
[self._xlim[0], self._ylim[0], self._zlim[0]]
x = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1]) * self._voxel_size[0]
y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0]) * self._voxel_size[1]
z = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]) * self._voxel_size[2]
i = np.array([7, 0, 0, 0, 4, 4, 6, 6, 4, 0, 3, 2])
j = np.array([3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 6, 5, 2, 0, 1, 6, 3])
k = np.array([0, 7, 2, 3, 6, 7, 1, 1, 5, 5, 7, 6])
cube = dict(
x = x + xyz[0],
y = y + xyz[1],
z = z + xyz[2],
i = i,
j = j,
k = k,
opacity = opacity,
color = color
)
if colorbar and color is None:
cmap = matplotlib.cm.get_cmap(colorscale)
c = cmap(self[tuple(index)] / (self.max() or 1))
cube.update(
color = "rgb({},{},{})".format(c[0], c[1], c[2])
)
return go.Mesh3d(cube)
def cubes_traces(
self,
condition = lambda voxels: voxels > 0,
color = None,
opacity = 0.4,
colorbar = True,
colorscale = "magma",
):
'''Get a list of Plotly `Mesh3d` traces for all voxels selected by the
`condition` filtering function.
The `condition` parameter is a filtering function that should return
a boolean mask (i.e. it is the result of a condition evaluation). For
example `lambda x: x > 0` selects all voxels that have a value larger
than 0.
This renders each voxel as individual cubes. While visually accurate,
this method is *very* computationally intensive - only use it for fewer
than 100 cubes. For more voxels, use the `voxels_trace` method.
Parameters
----------
condition : function, default `lambda voxels: voxels > 0`
The filtering function applied to the voxel data before plotting
it. It should return a boolean mask (a numpy array of the same
shape, filled with True and False), selecting all voxels that
should be plotted. The default, `lambda x: x > 0` selects all
voxels which have a value larger than 0.
color : str or list-like, optional
Can be a single color (e.g. "black", "rgb(122, 15, 241)") or a
colorbar list. Overrides `colorbar` if set. For more information,
check the Plotly documentation. The default is None.
opacity : float, default 0.4
The opacity of the lines, where 0 is transparent and 1 is fully
opaque.
colorbar : bool, default True
If set to True, will color-code the voxel values. Is overridden if
`color` is set.
colorscale : str, default "magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the voxel values in the input
data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
Examples
--------
Voxellise an array of lines and add them to a `PlotlyGrapher` instance:
>>> grapher = PlotlyGrapher()
>>> lines = np.array(...) # shape (N, M >= 7)
>>> number_of_voxels = [10, 10, 10]
>>> voxels = pept.Voxels(lines, number_of_voxels)
>>> grapher.add_lines(lines)
>>> grapher.add_traces(voxels.cubes_traces()) # small number of voxels
>>> grapher.show()
'''
indices = np.argwhere(condition(self))
traces = [
self.cube_trace(
i,
color = color,
opacity = opacity,
colorbar = colorbar,
colorscale = colorscale,
) for i in indices
]
return traces
def voxels_trace(
self,
condition = lambda voxel_data: voxel_data > 0,
size = 4,
color = None,
opacity = 0.4,
colorbar = True,
colorscale = "Magma",
colorbar_title = None,
):
'''Create and return a trace for all the voxels in this class, with
possible filtering.
Creates a `plotly.graph_objects.Scatter3d` object for the centres of
all voxels encapsulated in a `pept.Voxels` instance, colour-coding the
voxel value.
The `condition` parameter is a filtering function that should return
a boolean mask (i.e. it is the result of a condition evaluation). For
example `lambda x: x > 0` selects all voxels that have a value larger
than 0.
Parameters
----------
condition : function, default `lambda voxel_data: voxel_data > 0`
The filtering function applied to the voxel data before plotting
it. It should return a boolean mask (a numpy array of the same
shape, filled with True and False), selecting all voxels that
should be plotted. The default, `lambda x: x > 0` selects all
voxels which have a value larger than 0.
size : float, default 4
The size of the plotted voxel points. Note that due to the large
number of voxels in typical applications, the *voxel centres* are
plotted as square points, which provides an easy to understand
image that is also fast and responsive.
color : str or list-like, optional
Can be a single color (e.g. "black", "rgb(122, 15, 241)") or a
colorbar list. Overrides `colorbar` if set. For more information,
check the Plotly documentation. The default is None.
opacity : float, default 0.4
The opacity of the lines, where 0 is transparent and 1 is fully
opaque.
colorbar : bool, default True
If set to True, will color-code the voxel values. Is overridden if
`color` is set.
colorscale : str, default "Magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the voxel values in the input
data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
colorbar_title : str, optional
If set, the colorbar will have this title above it.
Examples
--------
Voxellise an array of lines and add them to a `PlotlyGrapher` instance:
>>> grapher = PlotlyGrapher()
>>> lines = np.array(...) # shape (N, M >= 7)
>>> number_of_voxels = [10, 10, 10]
>>> voxels = pept.Voxels.from_lines(lines, number_of_voxels)
>>> grapher.add_lines(lines)
>>> grapher.add_trace(voxels.voxels_trace())
>>> grapher.show()
'''
filtered_indices = np.argwhere(condition(self))
positions = self._voxel_size * (0.5 + filtered_indices) + \
[self._xlim[0], self._ylim[0], self._zlim[0]]
marker = dict(
size = size,
color = color,
symbol = "square",
)
if colorbar and color is None:
voxel_vals = [self[tuple(fi)] for fi in filtered_indices]
marker.update(colorscale = "Magma", color = voxel_vals)
if colorbar_title is not None:
marker.update(colorbar = dict(title = colorbar_title))
voxels = dict(
x = positions[:, 0],
y = positions[:, 1],
z = positions[:, 2],
opacity = opacity,
mode = "markers",
marker = marker,
)
return go.Scatter3d(voxels)
def heatmap_trace(
self,
ix = None,
iy = None,
iz = None,
width = 0,
colorscale = "Magma",
transpose = True
):
'''Create and return a Plotly `Heatmap` trace of a 2D slice through the
voxels.
The orientation of the slice is defined by the input `ix` (for the YZ
plane), `iy` (XZ), `iz` (XY) parameters - which correspond to the
voxel index in the x-, y-, and z-dimension. Importantly, at least one
of them must be defined.
Parameters
----------
ix : int, optional
The index along the x-axis of the voxels at which a YZ slice is to
be taken. One of `ix`, `iy` or `iz` must be defined.
iy: int, optional
The index along the y-axis of the voxels at which a XZ slice is to
be taken. One of `ix`, `iy` or `iz` must be defined.
iz : int, optional
The index along the z-axis of the voxels at which a XY slice is to
be taken. One of `ix`, `iy` or `iz` must be defined.
width : int, default 0
The number of voxel layers around the given slice index to collapse
(i.e. accumulate) onto the heatmap.
colorscale : str, default "Magma"
The Plotly scheme for color-coding the voxel values in the input
data. Typical ones include "Cividis", "Viridis" and "Magma".
A full list is given at `plotly.com/python/builtin-colorscales/`.
Only has an effect if `colorbar = True` and `color` is not set.
transpose : bool, default True
Transpose the heatmap (i.e. flip it across its diagonal).
Raises
------
ValueError
If neither of `ix`, `iy` or `iz` was defined.
Examples
--------
Voxellise an array of lines and add them to a `PlotlyGrapher` instance:
>>> lines = np.array(...) # shape (N, M >= 7)
>>> number_of_voxels = [10, 10, 10]
>>> voxels = pept.Voxels(lines, number_of_voxels)
>>> import plotly.graph_objs as go
>>> fig = go.Figure()
>>> fig.add_trace(voxels.heatmap_trace())
>>> fig.show()
'''
if ix is not None:
x = self._voxel_grids[1]
y = self._voxel_grids[2]
z = self[ix, :, :]
for i in range(1, width + 1):
z = z + self[ix + i, :, :]
z = z + self[ix - i, :, :]
elif iy is not None:
x = self._voxel_grids[0]
y = self._voxel_grids[2]
z = self[:, iy, :]
for i in range(1, width + 1):
z = z + self[:, iy + i, :]
z = z + self[:, iy - i, :]
elif iz is not None:
x = self._voxel_grids[0]
y = self._voxel_grids[1]
z = self[:, :, iz]
for i in range(1, width + 1):
z = z + self[:, :, iz + i]
z = z + self[:, :, iz - i]
else:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"[ERROR]: One of the `ix`, `iy`, `iz` slice indices must be "
"provided."
)))
heatmap = dict(
x = x,
y = y,
z = z,
colorscale = colorscale,
transpose = transpose,
)
return go.Heatmap(heatmap)
def __str__(self):
# Shown when calling print(class)
docstr = (
f"{self.__array__()}\n\n"
f"number_of_voxels = {self._number_of_voxels}\n"
f"voxel_size = {self._voxel_size}\n\n"
f"xlim = {self._xlim}\n"
f"ylim = {self._ylim}\n"
f"zlim = {self._zlim}\n\n"
f"voxel_grids:\n"
f"([{self._voxel_grids[0][0]} ... {self._voxel_grids[0][-1]}],\n"
f" [{self._voxel_grids[1][0]} ... {self._voxel_grids[1][-1]}],\n"
f" [{self._voxel_grids[2][0]} ... {self._voxel_grids[2][-1]}])"
)
return docstr
def __repr__(self):
# Shown when writing the class on a REPR
docstr = (
"Class instance that inherits from `pept.Voxels`.\n"
f"Type:\n{type(self)}\n\n"
"Attributes\n----------\n"
f"{self.__str__()}"
)
return docstr
class VoxelData:
'''A class that can voxellise multiple samples of lines (from a `LineData`)
lazily / on demand.
Voxellisation is a computationally-intensive step - in terms of both time
and memory - especially for many thousands of lines or samples; although
optimised, the `Voxels` class only manages a single voxel space. The simple
solution for multiple samples:
.. code-block:: python
lines = pept.LineData(...)
voxels = []
for sample in lines:
voxels.append( pept.Voxels(sample, (100, 100, 100)) )
Is very inefficient, as it uses a single thread and stores all voxel
spaces in memory (voxels use up a lot of memory!). This class solves these
problems by:
1. Voxellising the samples of lines in parallel, on any number of threads.
2. Creating the voxel spaces on demand. Optionally, it can save / cache
the expensive voxellisation steps (`save_cache = True`).
The individual voxellisation steps are still done using `Voxels`, which are
then accessible in a list (`voxels.voxels` or `voxels[0]`).
Attributes
----------
line_data : pept.LineData
The samples of lines encapsulated in a `pept.LineData` that will be
used to create the corresponding voxellised spaces.
voxels : list[pept.Voxels | None]
The list of cached voxellised spaces. Initially, it is a list of
`None`s of the same length as the number of samples in `line_data`. If
`save_cache` is True, the voxellised samples of lines will be cached
here.
number_of_voxels : 3-tuple
A 3-tuple corresponding to the shape of `voxels`.
xlim : (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max].
ylim : (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max].
zlim : (2,) numpy.ndarray
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
z-dimension, formatted as [z_min, z_max].
max_workers : int
The number of threads that will be used to voxellise the lines in
parallel.
save_cache : bool
Whether to cache the voxellised spaces *when their computation is
requested* (e.g. when calling `traverse()`). The `voxels` attribute is
only populated if this is `True`.
Methods
-------
save(filepath)
Save a `VoxelData` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
load(filepath)
Load a saved / pickled `VoxelData` object from `filepath`.
traverse(sample_indices = ..., verbose = True)
Voxellise the samples in `line_data` at indices `samples_indices`.
accumulate(sample_indices = ..., verbose = True):
Superimpose the voxellised samples in `line_data` at indices
`samples_indices` into the same voxel space.
Notes
-----
Upon instantiating the class with an instance of `LineData`, a copy is
made. It is a logic error to change the `sample_size` and `overlap` after
instantiation; these should remain constant for the `voxels` list to
remain correct.
Examples
--------
Create a short list of 3D lines and encapsulate them in a `LineData` class
to simulate multiple samples of lines.
>>> import pept
>>> import numpy as np
>>> lines_raw = np.arange(70).reshape(10, 7)
>>> lines = pept.LineData(lines_raw, sample_size = 2)
The `VoxelData` does not voxellise the samples of lines immediately upon
instantiation by default:
>>> number_of_voxels = [3, 4, 5]
>>> voxel_data = pept.VoxelData(lines, number_of_voxels)
>>> voxel_data.voxels
>>> [None, None, None, None, None]
You can iterate through the `VoxelData` and it will voxellise the samples
on demand:
>>> for vox in voxel_data:
>>> print(vox) # not cached by default
This is the most efficient way to use `VoxelData`, as the voxellised
samples are NOT cached by default; they are deleted after each loop above
(voxels consume a lot of memory!):
>>> voxel_data.voxels
>>> [None, None, None, None, None]
If you have enough memory to store all the voxel spaces at once, set
`save_cache` to True when instantiating the class, or afterwards:
>>> number_of_voxels = [3, 4, 5]
>>> voxel_data = pept.VoxelData(lines, number_of_voxels, save_cache = True)
>>> voxel_data.voxels
>>> [None, None, None, None, None]
>>> voxel_data.traverse() # Actually voxellises each sample
>>> voxel_data.voxels
>>> [..Voxels.. , ..Voxels.., ...]
If you voxellised the samples once and `save_cache = True`, the results are
cached, so new iterations use the pre-computed voxel spaces:
>>> voxel_data.accumulate() # Almost instantaneous, uses cache
See Also
--------
pept.Voxels : Manage a single voxellised sample of lines.
pept.LineData : Encapsulate lines for ease of iteration and plotting.
pept.PointData : Encapsulate points for ease of iteration and plotting.
PlotlyGrapher : Easy, publication-ready plotting of PEPT-oriented data.
'''
def __init__(
self,
line_data,
number_of_voxels,
xlim = None,
ylim = None,
zlim = None,
max_workers = None,
save_cache = False,
traverse = False,
verbose = True,
):
'''`VoxelData` class constructor.
Parameters
----------
line_data : pept.LineData
The samples of lines encapsulated in a `pept.LineData` that will be
used to create the corresponding voxellised spaces.
number_of_voxels : (3,) list[int]
The number of voxels in the x-, y-, and z-dimensions, respectively.
xlim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
x-dimension, formatted as [x_min, x_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of the lines in `line_data`.
ylim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
y-dimension, formatted as [y_min, y_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of the lines in `line_data`.
zlim : (2,) list[float], optional
The lower and upper boundaries of the voxellised volume in the
z-dimension, formatted as [z_min, z_max]. If undefined, it is
inferred from the boundaries of the lines in `line_data`.
max_workers : int, optional
The number of threads that will be used to voxellise the lines in
parallel. If undefined, the value returned by `os.cpu_count()` is
used.
save_cache : bool, default False
Whether to cache the voxellised spaces *when their computation is
requested* (e.g. when calling `traverse()`). The `voxels` attribute
is only populated if this is `True`.
traverse : bool, default False
Whether to immediately voxellise all the samples of lines in
`line_data`. If `True`, `save_cache` is also set to `True` and the
`traverse()` method is called.
verbose : bool, default True
Show extra information as the voxellisation runs.
Raises
------
TypeError
If `line_data` is not an instance (or subclass) of `pept.LineData`.
ValueError
If `number_of_voxels` does not have exactly 3 values, or it has
values smaller than 2. If `xlim`, `ylim` or `zlim` do not have
exactly 2 values each.
'''
# Type-checking inputs
if not isinstance(line_data, pept.LineData):
raise TypeError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `line_data` must be an instance (or subclass "
f"thereof!) of `pept.LineData`. Received {type(line_data)}."
)))
number_of_voxels = np.asarray(
number_of_voxels,
order = "C",
dtype = int
)
if number_of_voxels.ndim != 1 or len(number_of_voxels) != 3:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_voxels` must be a list-like "
"with exactly three values, corresponding to the "
"number of voxels in the x-, y-, and z-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {number_of_voxels.shape}."
)))
if (number_of_voxels < 2).any():
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_voxels` must set at least two "
"voxels in each dimension (i.e. all elements in "
"`number_of_elements` must be larger or equal to two). "
f"Received `{number_of_voxels}`."
)))
# Alias for the whole array of lines in `line_data`
lines = line_data.lines
if xlim is None:
xlim = Voxels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 1], lines[:, 4])
else:
xlim = np.asarray(xlim, dtype = float)
if xlim.ndim != 1 or len(xlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `xlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the x-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {xlim.shape}."
)))
if ylim is None:
ylim = Voxels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 2], lines[:, 5])
else:
ylim = np.asarray(ylim, dtype = float)
if ylim.ndim != 1 or len(ylim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `ylim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
if zlim is None:
zlim = Voxels.get_cutoff(lines[:, 3], lines[:, 6])
else:
zlim = np.asarray(zlim, dtype = float)
if zlim.ndim != 1 or len(zlim) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `zlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the voxel space in the z-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
save_cache = bool(save_cache)
traverse = bool(traverse)
# Setting class attributes
self._line_data = line_data.copy()
self._number_of_voxels = tuple(number_of_voxels)
self._xlim = xlim
self._ylim = ylim
self._zlim = zlim
self._max_workers = max_workers
self._save_cache = save_cache
self._voxels_index = 0
self._voxels = [None for _ in range(len(self._line_data))]
if traverse:
self._save_cache = True
self.traverse(verbose = verbose)
@property
def line_data(self):
return self._line_data
@property
def voxels(self):
return self._voxels
@property
def number_of_voxels(self):
return self._number_of_voxels
@property
def xlim(self):
return self._xlim
@property
def ylim(self):
return self._ylim
@property
def zlim(self):
return self._zlim
@property
def max_workers(self):
return self._max_workers
@property
def save_cache(self):
return self._save_cache
@save_cache.setter
def save_cache(self, new_save_cache):
self._save_cache = bool(new_save_cache)
def save(self, filepath):
'''Save a `VoxelData` instance as a binary `pickle` object.
Saves the full object state, including the inner `.voxels` NumPy array,
`xlim`, etc. in a fast, portable binary format. Load back the object
using the `load` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Examples
--------
Save a `VoxelData` instance (created from lines), then load it back:
>>> lines = pept.LineData([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]])
>>> voxel_data = pept.VoxelData(lines, (64, 48, 32))
>>> voxel_data.save("voxel_data.pickle")
>>> voxel_data_reloaded = pept.VoxelData.load("voxel_data.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(self, f)
@staticmethod
def load(filepath):
'''Load a saved / pickled `VoxelData` object from `filepath`.
Most often the full object state was saved using the `.save` method.
Parameters
----------
filepath : filename or file handle
If filepath is a path (rather than file handle), it is relative
to where python is called.
Returns
-------
pept.VoxelData
The loaded `pept.VoxelData` instance.
Examples
--------
Save a `VoxelData` instance (created from lines), then load it back:
>>> lines = pept.LineData([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]])
>>> voxel_data = pept.VoxelData(lines, (64, 48, 32))
>>> voxel_data.save("voxel_data.pickle")
>>> voxel_data_reloaded = pept.VoxelData.load("voxel_data.pickle")
'''
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
obj = pickle.load(f)
return obj
def traverse(
self,
sample_indices = ...,
verbose = True,
):
'''Voxellise the samples in `line_data` at indices `samples_indices`.
If `save_cache` is `True`, the voxellised spaces are also cached in the
`voxels` attribute. Otherwise, they are only returned as a list.
Parameters
----------
sample_indices : int or iterable or Ellipsis, default Ellipsis
The index or indices of the samples of lines. An `int` signifies
the sample index, an iterable (list-like) signifies multiple sample
indices, while an Ellipsis (`...`) signifies all samples. The
default is `...` (all samples).
verbose : bool, default True
Show extra information as the voxellisation runs.
Returns
-------
list[Voxels]
A list of the voxellised samples of lines (each as a `Voxels`
class) selected by `sample_indices`.
Examples
--------
This method is automatically called if the instantiation of the class
sets `traverse = True`:
>>> import pept
>>> import numpy as np
>>> lines_raw = np.arange(70).reshape(10, 7)
>>> lines = pept.LineData(lines_raw, sample_size = 2)
>>> number_of_voxels = [3, 4, 5]
>>> voxel_data = pept.VoxelData(
>>> lines, number_of_voxels, traverse = True
>>> )
>>> voxel_data.voxels
>>> [..Voxels.. , ..Voxels.., ...]
You can also call the method after the instantiation. If the results
were cached (i.e. `save_cache = True`), they are returned without
re-computing them:
>>> voxel_list = voxel_data.traverse()
Alternatively, you can only voxellise a few samples at once (still in
parallel):
>>> voxel_list = voxel_data.traverse([1, 5, 2])
Of course, the list of `Voxels` will have the same ordering as the
list of indices given to the function.
'''
# Check if sample_indices is an iterable collection (list-like)
# otherwise just "iterate" over the single number or Ellipsis.
if sample_indices is Ellipsis:
sample_indices = np.arange(len(self._line_data))
elif not hasattr(sample_indices, "__iter__"):
sample_indices = [sample_indices]
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers = self._max_workers) as executor:
# Use pre-computed voxels and voxellise the other samples
selected_voxels = [None for _ in range(len(sample_indices))]
selected_futures = [None for _ in range(len(sample_indices))]
# Voxellise each selected sample
for i, n in enumerate(sample_indices):
# Optimisation: if this sample was already voxellised, reuse it
if self._voxels[n] is not None:
selected_voxels[i] = self._voxels[n].copy()
continue
# Otherwise, voxellise the sample asynchronously
selected_futures[i] = executor.submit(
pept.Voxels.from_lines,
self._line_data[n],
self._number_of_voxels,
xlim = self._xlim,
ylim = self._ylim,
zlim = self._zlim,
verbose = False,
)
if verbose:
sample_indices = tqdm(sample_indices)
# Iterate through all the futures; if not None (i.e. we voxellised
# the sample now), get the result. Otherwise it was pre-computed
for i, n in enumerate(sample_indices):
if selected_futures[i] is not None:
selected_voxels[i] = selected_futures[i].result()
# If we voxellised this sample and we use "save_cache",
# cache the result in self.voxels
if self._save_cache:
self._voxels[n] = selected_voxels[i]
return selected_voxels
def accumulate(self, sample_indices = ..., verbose = True):
'''Superimpose the voxellised samples in `line_data` at indices
`samples_indices` into the same voxel space.
This method can be used to voxellise multiple samples of lines into the
same `Voxels` class. The computation is done in parallel and uses the
least amount of memory possible.
Parameters
----------
sample_indices : int or iterable or Ellipsis, default Ellipsis
The index or indices of the samples of lines. An `int` signifies
the sample index, an iterable (list-like) signifies multiple sample
indices, while an Ellipsis (`...`) signifies all samples. The
default is `...` (all samples).
verbose : bool, default True
Show extra information as the voxellisation runs.
Returns
-------
Voxels
The single voxellised space that contains the superimposed
voxellised representations of the samples of lines selected by
`sample_indices`.
Examples
--------
This method is helpful for splitting the voxellisation that would be
done by a single `Voxels` class across multiple threads:
>>> import pept
>>> import numpy as np
>>> lines_raw = np.arange(70).reshape(10, 7)
>>> lines = pept.LineData(lines_raw, sample_size = 2)
>>> number_of_voxels = [3, 4, 5]
>>> voxel_data = pept.VoxelData(lines, number_of_voxels)
>>> vox = voxel_data.accumulate()
'''
# Check if sample_indices is an iterable collection (list-like)
# otherwise just "iterate" over the single number or Ellipsis.
if sample_indices is Ellipsis:
sample_indices = np.arange(len(self._line_data))
elif not hasattr(sample_indices, "__iter__"):
sample_indices = [sample_indices]
vox = Voxels.empty(
self._number_of_voxels,
self._xlim,
self._ylim,
self._zlim,
)
# Voxellise each selected sample
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers = self._max_workers) as executor:
# Use pre-computed voxels and voxellise the other samples
selected_futures = [None for _ in range(len(sample_indices))]
for i, n in enumerate(sample_indices):
# Optimisation: if this sample was already voxellised, reuse it
if self._voxels[n] is not None:
continue
# Otherwise, voxellise the sample asynchronously
selected_futures[i] = executor.submit(
pept.Voxels.from_lines,
self._line_data[n],
self._number_of_voxels,
xlim = self._xlim,
ylim = self._ylim,
zlim = self._zlim,
verbose = False,
)
if verbose:
sample_indices = tqdm(sample_indices)
# Iterate through all the futures; if not None (i.e. we voxellised
# the sample now), get the result. Otherwise it was pre-computed
for i, n in enumerate(sample_indices):
if selected_futures[i] is not None:
vox += selected_futures[i].result()
else:
vox += self._voxels[n]
return vox
def __getitem__(self, key):
# For accessing voxels using subscript notation
key = int(key)
# Allow negative indices
while key < 0:
key += len(self._voxels)
if key >= len(self._voxels):
raise IndexError(textwrap.fill((
f"The index `{key}` was out of range. There are "
f"{len(self._voxels)} samples of lines to be voxellised, "
"indexed from 0."
)))
if self._voxels[key] is not None:
return self._voxels[key]
vox = pept.Voxels.from_lines(
self._line_data[key],
self._number_of_voxels,
xlim = self._xlim,
ylim = self._ylim,
zlim = self._zlim,
verbose = False,
)
if self._save_cache:
self._voxels[key] = vox
return vox
def __iter__(self):
return self
def __next__(self):
# Finish iteration
if self._voxels_index >= len(self._line_data):
self._voxels_index = 0
raise StopIteration
# If we already traversed and saved this sample, return it directly
if self._voxels[self._voxels_index] is not None:
self._voxels_index += 1
return self._voxels[self._voxels_index - 1]
vox = pept.Voxels.from_lines(
self._line_data[self._voxels_index],
self._number_of_voxels,
xlim = self._xlim,
ylim = self._ylim,
zlim = self._zlim,
verbose = False,
)
if self._save_cache:
self._voxels[self._voxels_index] = vox
self._voxels_index += 1
return vox
def __len__(self):
return len(self._voxels)
def __str__(self):
# Shown when calling print(class)
traversed = sum((v is not None for v in self._voxels))
total = len(self._voxels)
# Indent LineData docstring with an extra tab
line_data_str = " ".join(self._line_data.__str__().splitlines(True))
docstr = (
f"voxels: {traversed} / {total} traversed & cached\n"
f"number_of_voxels = {self._number_of_voxels}\n"
f"xlim = {self._xlim}\n"
f"ylim = {self._ylim}\n"
f"zlim = {self._zlim}\n\n"
f"line_data:\n {line_data_str}\n\n"
f"save_cache = {self._save_cache}\n"
f"max_workers = {self._max_workers}\n"
)
return docstr
def __repr__(self):
# Shown when writing the class on a REPR
docstr = (
"Class instance that inherits from `pept.VoxelData`.\n"
f"Type:\n{type(self)}\n\n"
"Attributes\n----------\n"
f"{self.__str__()}"
)
return docstr
�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1619631590.0762506
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/cookbook/���������������������������������������������������������������������������0000755�0001750�0001750�00000000000�00000000000�017473� 5����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1617302486.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/cookbook/__init__.py����������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000003516�00000000000�021611� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# File : __init__.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 22.06.2020
'''The PEPT cookbook, containing example analysis scripts (or recipes) that are
easy to hack into.
Summary
-------
Following the cookbook metaphor, this package contains a collection of scripts
combining different parts of the `pept` library (i.e. ingredients) to
accomplish a certain task -> recipes! Much like when cooking, it is more than
recommended to take the recipes (i.e. code) and make them yours; they are
well-commented and user-friendly.
Extended Summary
----------------
The recipes are implemented *as classes*, such that once they've been run (i.e.
instantiated), all the relevant objects (such as clusterers, graphers, etc.)
can be accessed as class attributes.
Modules Provided
----------------
::
pept.cookbook
│
Classes imported into the subpackage root:
├── PEPTMLUser : Use PEPT-ML to turn LoRs into trajectories.
└── PEPTMLFindParameters : Visual aid for PEPT-ML clustering parameters.
Notes
-----
At the moment, the subpackages in `pept` are biased towards PEPT-ML, as there
aren't many algorithms integrated into package *yet*. New algorithms and/or
recommendations for the package are more than welcome! `pept` aims to be a
community effort, be it academic, industrial, medical, or just from PEPT
enthusiasts - so it is open to help with documentation, algorithms, utilities
or analysis scripts, tutorials, and pull requests in general!
'''
from .peptml import PEPTMLUser
from .peptml import PEPTMLFindParameters
__all__ = [
"PEPTMLUser",
"PEPTMLFindParameters"
]
__license__ = "GNU v3.0"
__maintainer__ = "Andrei Leonard Nicusan"
__email__ = "a.l.nicusan@bham.ac.uk"
__status__ = "Beta"
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1617302486.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/cookbook/peptml.py������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000157157�00000000000�021366� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you should cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# File : peptml.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 22.06.2020
import textwrap
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
import pept
from pept.tracking import peptml
import pept.tracking.trajectory_separation as tsp
from pept.visualisation import PlotlyGrapher
# Colours for printing to the terminal, taken from blender build scripts.
class bcolors:
HEADER = '\033[95m'
OKBLUE = '\033[94m'
OKGREEN = '\033[92m'
WARNING = '\033[93m'
FAIL = '\033[91m'
ENDC = '\033[0m' # Return to normal colour
BOLD = '\033[1m'
UNDERLINE = '\033[4m'
class PEPTMLUser:
'''This is an example script analysing PEPT data using the PEPT-ML
algorithm from the `pept` library.
The script is encapsulated in a class such that, after running it (i.e.
instantiating the class), all the relevant analysis objects can be accessed
as class attributes (e.g. LoRs, clusterers, tracer locations).
The class has three methods:
1. __init__ : the class constructor that is run when instantiating it; it
contains the actual PEPT-ML algorithm.
2. typecheck_and_create_attributes : typecheck input parameters and create
class attributes.
3. minimal : the minimal PEPT-ML code, without pretty-printing to the
terminal.
It is more than recommended to look through the code, copy and hack into
it! The class constructor (`__init__`) contains the PEPT-ML algorithm with
printing functionality to the terminal; if you'd like the code without such
additions, use the equivalent code in the `minimal` method.
The main steps of the PEPT-ML-User algorithm are:
-- Done beforehand, by the user --
1. Initialise LoRs in a `pept.LineData` instance (if they are stored in a
file, you can use `pept.utilities.read_csv`). **You must do this before
using this script**.
-- Done by this script --
2. Compute the cutpoints from the LoRs using the `peptml.Cutpoints` class.
3. Cluster them once using `peptml.HDBSCANClusterer` to find the tracer
locations (i.e. cluster *centres*) - this is *1-pass clustering*.
4. Cluster the tracer locations from the previous step again, using another
`peptml.HDBSCANClusterer` - this is *2-pass clustering*.
5. Segregate the intertwined points from the tracer trajectories using
`trajectory_separation.segregate_trajectories`.
6. Reconnect the trajectories of tracers with gaps in their tracks (such as
when they collide) based on their cluster size using
`trajectory_separation.connect_trajectories`.
For more details check out the PEPT-ML paper (doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251)
and the documentation of the functions used.
The parameters below are, of course, easy to change. Their default values
represent some (heuristically) good starting parameters that should work in
the majority of cases. Perhaps the most important ones to change would be
`k1` (a larger value represents harsher clustering; lower it for very
noisy data), `trajectory_cut_distance` (for segregating pre-tracked points)
and `max_signature_difference` (for reconnecting trajectories with gaps).
Attributes
----------
lors : pept.LineData instance
The input lines of response (LoRs). As they can be stored in various
sources (CSV files, binary data, different scanner geometries), it is
expected that users initialise them as `pept.LineData` (or a subclass
thereof) *before* using this script.
max_tracers : int
The maximum number of tracers that may be present in the field of view
at any time. Note that the PEPT-ML algorithm does not *need* this
number (and can work well even when tracers leave the FoV); however, it
is useful when setting the sample sizes, overlaps and clustering
parameters.
sample_size : int, optional
The `lors.sample_size`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints. By
default, it is set to 200 * `max_tracers`.
overlap : int, optional
The `lors.overlap`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints. By
default, it is set to 150 * `max_tracers`.
sample_size2 : int, optional
The `centres.sample_size`, used for the second pass of clustering (i.e.
re-clustering the tracer locations found from the cutpoints). By
default, it is set to 30 * `max_tracers`; this small value is fine as
the data is already very clean after the first pass of clustering.
overlap2 : int, optional
The `centres.overlap`, used for the second pass of clustering (i.e.
re-clustering the tracer locations found from the cutpoints). By
default, it is set to `sample_size2` - 1, such that the loss of time
resolution is minimised.
max_distance : float, default 0.15
The maximum allowed distance between two LoRs for their cutpoint to be
considered; used by `peptml.Cutpoints`.
k1 : float, default 0.15
The fitting parameter for setting the `min_cluster_size` of the
`clusterer` used for the first pass of clustering. As the number of
cutpoints around a tracer scales with the sample_size and (inversely)
`max_tracers`, the following formula is used -
`min_cluster_size` = int(k1 * cutpoints.sample_size / max_tracers)`.
A larger value represents "harsher" clustering. Lower it for very noisy
data.
k2 : float, default 0.6
The fitting parameter for setting the `min_cluster_size` of the
`clusterer2` used for the second pass of clustering. As the number of
points around a tracer scales with the sample_size and (inversely)
`max_tracers`, the following formula is used -
`min_cluster_size2` = int(k2 * centres.sample_size / max_tracers)`.
A larger value represents "harsher" clustering.
points_window : int, optional
The number of points included in the sliding window used when
segregating the intertwined points from multiple trajectories using
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.segregate_trajectories`. By
default, it is set to 10 * `max_tracers`.
trajectory_cut_distance : float, default 10.0
Cut trajectories that are further apart than this value and consider
the remaining ones distinct trajectories. This depends on how close the
points in the data set are. Used by
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.segregate_trajectories`.
max_time_difference : float, default 150
Only try to re-connect trajectories with gaps if their ends are closer
time-wise than `max_time_difference`. Used by
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.connect_trajectories`. Check the
consistency of the units used for time.
max_signature_difference : float, default 100
Re-connect trajectories with gaps if the difference in cluster size
(i.e. tracer signature) of the closest points is smaller than this
value. An average of the 50 closest points is used. Used by
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.connect_trajectories`.
cutpoints : pept.tracking.peptml.Cutpoints instance
The cutpoints computed from `lors`. It is a subclass of
`pept.PointData`, such that all its methods and attributes can be used.
min_cluster_size : int
The minimum cluster size parameter used by the clusterer for the first
pass of clustering.
clusterer : pept.tracking.peptml.HDBSCANClusterer instance
The clusterer used for the first pass of clustering. It also appends
the "cluster size" (i.e. the number of points in the cluster
surrounding a tracer) to `centres`.
centres : pept.PointData instance
The tracer locations (i.e. cluster *centres*) found after the first
pass of clustering. The last column represents the cluster size; that
is, the number of points in the cluster surrounding the tracer. This
can act as a tracer signature for when their identity is temporarily
lost, like when they collide.
labelled_cutpoints : pept.PointData instance
The cutpoints that were clustered, including their cluster labels as
the last column.
min_cluster_size2 : int
The minimum cluster size parameter used by the clusterer for the second
pass of clustering.
clusterer2 : pept.tracking.peptml.HDBSCANClusterer instance
The clusterer used for the second pass of clustering.
centres2 : pept.PointData instance
The tracer locations (i.e. cluster *centres*) found after the second
pass of clustering.
labelled_cetres : pept.PointData instance
The centres that were clustered, including their cluster labels as the
last column.
segregated_trajectories : pept.PointData instance
The segregated trajectories found from the intertwined tracer locations
in `centres2`. It contains the same data as `centres2`, but with an
added column representing the trajectory label (or index); they are
indexed from 0, with -1 signifying noise. Returned by
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.segregate_trajectories`.
trajectories : pept.PointData instance
The final separated trajectories, after reconnecting the
`segregated_trajectories` based on their cluster size using
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.connect_trajectories`. It contains
the same data as `segregated_trajectories`, but the last column (i.e.
trajectory label) is changed to reflect the final trajectories.
trajectory_list : list of numpy.ndarray
The trajectories from `trajectories` are separated into a list of
individual trajectories, based on their last column (i.e. trajectory
label).
grapher : pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher instance
The grapher organising the 3D subplots.
Methods
-------
typecheck_and_create_attributes(\
lors,\
max_tracers,\
sample_size = None,\
overlap = None,\
sample_size2 = None,\
overlap2 = None,\
max_distance = 0.15,\
k1 = 0.15,\
k2 = 0.6,\
points_window = None,\
trajectory_cut_distance = 10.0,\
max_time_difference = 150.0,\
max_signature_difference = 100.0\
)
Typecheck input parameters and create class attributes. Used by the
class constructor for checks that are not relevant to the actual
PEPT-ML aglorithm.
minimal(\
lors,\
max_tracers,\
sample_size = None,\
overlap = None,\
sample_size2 = None,\
overlap2 = None,\
max_distance = 0.15,\
k1 = 0.15,\
k2 = 0.6,\
points_window = None,\
trajectory_cut_distance = 10.0,\
max_time_difference = 150,\
max_signature_difference = 100\
)
The minimal code for using the PEPT-ML algorithm, without
pretty-printing to the terminal. Useful for copy-pasting the code and
hacking into it.
Raises
------
TypeError
If `lors` is not an instance of `pept.LineData` (or subclass thereof!).
AssertionError
If `max_tracers` is smaller than 1.
Notes
-----
The `pept` package is modular, meaning it can be used in many ways, to suit
(m)any circumstances. This is just an example, which you can modify as you
see fit.
If you're not sure what a class or method does, you can always consult the
documentation online, at "uob-positron-imaging-centre.github.io", or by
adding a questions mark in front of a package / module / class / function
name in the Python shell or using the `help` command. For example:
>>> import pept
>>> ?pept.LineData # Short documentation
>>> ??pept.LineData # Long documentation
>>> help(pept.LineData) # Even more info
Examples
--------
An example call would be:
>>> lors_raw = pept.utilities.read_csv("csv_file.csv") # two tracers CSV
>>> lors = pept.LineData(lors_raw)
>>> user = pept.cookbook.PEPTMLUser(lors, 2) # max_tracers = 2
'''
def __init__(
self,
lors, # Essential, pept.LineData
max_tracers, # Essential, int
sample_size = None, # Default 200 * max_tracers
overlap = None, # Default 150 * max_tracers
sample_size2 = None, # Default 30 * max_tracers
overlap2 = None, # Default sample_size2 - 1
max_distance = 0.15, # mm
k1 = 0.15, # non-dimensional, important
k2 = 0.6, # non-dimensional
points_window = None, # Default 10 * max_tracers
trajectory_cut_distance = 10.0, # mm, important
max_time_difference = 150, # ms
max_signature_difference = 100 # cluster size difference
):
'''PEPTMLUser class constructor. This is the PEPT-ML algorithm with
pretty-printing of the relevant objects to the terminal.
Parameters
----------
lors : pept.LineData instance
The input lines of response (LoRs). As they can be stored in
various sources (CSV files, binary data, different scanner
geometries), it is expected that users initialise them as
`pept.LineData` (or a subclass thereof) *before* using this script.
max_tracers : int
The maximum number of tracers that may be present in the field of
view at any time. Note that the PEPT-ML algorithm does not *need*
this number (and can work well even when tracers leave the FoV);
however, it is useful to know when setting the sample sizes,
overlaps and clustering parameters.
sample_size : int, optional
The `lors.sample_size`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints.
By default, it is set to 200 * `max_tracers`.
overlap : int, optional
The `lors.overlap`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints. By
default, it is set to 150 * `max_tracers`.
sample_size2 : int, optional
The `centres.sample_size`, used for the second pass of clustering
(i.e. re-clustering the tracer locations found from the cutpoints).
By default, it is set to 30 * `max_tracers`; this small value is
fine as the data is already very clean after the first pass of
clustering.
overlap2 : int, optional
The `centres.overlap`, used for the second pass of clustering (i.e.
re-clustering the tracer locations found from the cutpoints). By
default, it is set to `sample_size2` - 1, such that the loss of
time resolution is minimised.
max_distance : float, default 0.15
The maximum allowed distance between two LoRs for their cutpoint to
be considered; used by `peptml.Cutpoints`.
k1 : float, default 0.15
The fitting parameter for setting the `min_cluster_size` of the
`clusterer` used for the first pass of clustering. As the number of
cutpoints around a tracer scales with the sample_size and
(inversely) `max_tracers`, the following formula is used -
`min_cluster_size` = int(k1 * cutpoints.sample_size / max_tracers)`
A larger value represents "harsher" clustering. Lower it for very
noisy data.
k2 : float, default 0.6
The fitting parameter for setting the `min_cluster_size` of the
`clusterer2` used for the second pass of clustering. As the number
of points around a tracer scales with the sample_size and
(inversely) `max_tracers`, the following formula is used -
`min_cluster_size2` = int(k2 * centres.sample_size / max_tracers)`.
A larger value represents "harsher" clustering.
points_window : int, optional
The number of points included in the sliding window used when
segregating the intertwined points from multiple trajectories using
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.segregate_trajectories`. By
default, it is set to 10 * `max_tracers`.
trajectory_cut_distance : float, default 10.0
Cut trajectories that are further apart than this value and
consider the remaining ones as distinct trajectories. This depends
on how close the points in the data set are. Used by
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.segregate_trajectories`.
max_time_difference : float, default 150
Only try to re-connect trajectories with gaps if their ends are
closer time-wise than `max_time_difference`. Used by
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.connect_trajectories`. Check
the consistency of the units used for time.
max_signature_difference : float, default 100
Re-connect trajectories with gaps if the difference in cluster size
(i.e. tracer signature) of the closest points is smaller than this
value. An average of the 50 closest points is used. Used by
`pept.tracking.trajectory_separation.connect_trajectories`.
Raises
------
TypeError
If `lors` is not an instance of `pept.LineData` (or subclass
thereof!).
AssertionError
If `max_tracers` is smaller than 1.
'''
# Initial type-checking of input parameters + properties
# initialisation.
self.typecheck_and_create_attributes(
lors, max_tracers, sample_size, overlap, sample_size2, overlap2,
max_distance, k1, k2, points_window, trajectory_cut_distance,
max_time_difference, max_signature_difference
)
# Start the PEPT-ML algorithm; you can copy-paste the code below and
# hack into it! It's recommended actually!
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "=" * 70 + # Use colours when printing
"\nPEPT-ML User Start\n" +
"=" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC # End colour
)
# Print input LoRs and max_tracers. For `lors`, print its printable
# representation (i.e. long representation) using repr().
self.lors.sample_size = self.sample_size
self.lors.overlap = self.overlap
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"LoRs:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.lors)}\n"
))
print((
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"max_tracers = {self.max_tracers}"
f"{bcolors.ENDC}\n\n"
))
# Transform the LoRs into cutpoints using the `Cutpoints` class. It is
# a `pept.PointData` subclass, so we inherit all its attributes and
# methods!
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nTransforming LoRs into Cutpoints\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"max_distance = {self.max_distance}"
f"{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
))
self.cutpoints = peptml.Cutpoints(lors, max_distance)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"Finding cutpoints completed.\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Cutpoints:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.cutpoints)}\n\n"
))
# Find the tracer locations using peptml.HDBSCANClusterer. This is
# 1-pass clustering.
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nClustering Cutpoints using HDBSCANClusterer " +
"(1-pass clustering)\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
# The cluster size (i.e. number of cutpoints around each tracer
# location) scales with the maximum number of tracers that might be
# present in the field of view at any time.
self.min_cluster_size = int(self.k1 * self.cutpoints.sample_size /
self.max_tracers)
self.clusterer = peptml.HDBSCANClusterer(self.min_cluster_size)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Clusterer for 1-pass clustering:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.clusterer)}\n"
))
self.centres, self.labelled_cutpoints = self.clusterer.fit(
self.cutpoints, get_labels = True
)
# Set the sample size and overlap of the tracer locations from the
# first pass of clustering. The data is already very clean from the
# previous steps, so we'll set a small sample size and large overlap to
# minimise smoothing, or the temporal resolution lost.
self.centres.sample_size = self.sample_size2
self.centres.overlap = self.overlap2
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"1-pass clustering completed.\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Cluster centres (i.e. tracer locations):{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.centres)}\n\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Labelled cutpoints:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.labelled_cutpoints)}\n\n"
))
# Create smoother, tighter tracer locations using
# peptml.HDBSCANClusterer. This is 2-pass clustering.
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nClustering Centres using HDBSCANClusterer " +
"(2-pass clustering)\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
self.min_cluster_size2 = int(self.k2 * self.centres.sample_size /
self.max_tracers)
self.clusterer2 = peptml.HDBSCANClusterer(self.min_cluster_size2)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Clusterer for 2-pass clustering:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.clusterer2)}\n"
))
self.centres2, self.labelled_centres = self.clusterer2.fit(
self.centres, get_labels = True
)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"2-pass clustering completed.\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Tracer locations after 2-pass clustering:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.centres2)}\n\n"
))
# Segregate the intertwined points of the previous step.
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nSegregate the intertwined points from the 2-pass clustering\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
self.segregated_trajectories = tsp.segregate_trajectories(
self.centres2, self.points_window, self.trajectory_cut_distance
)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"Trajectory segregation completed.\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Segregated trajectories:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.segregated_trajectories)}\n"
))
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
"Number of trajectories found after segregation: "
f"{self.segregated_trajectories.points[:, -1].max() + 1}\n\n"
))
# Connect the segregated trajectories based on their cluster size.
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nConnect the segregated trajectories based on their cluster " +
"size\n" + "-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
self.trajectories = tsp.connect_trajectories(
self.segregated_trajectories,
self.max_time_difference,
self.max_signature_difference
)
self.trajectory_list = pept.utilities.group_by_column(
self.trajectories.points, -1
)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"Trajectory connecting completed.\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Trajectories:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.trajectories)}\n"
))
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
"Number of trajectories found: "
f"{self.trajectories.points[:, -1].max() + 1}\n\n"
))
# Plotting time!
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nPlotting Results using PlotlyGrapher\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
# Instantiate a PlotlyGrapher instance with 2x3 subplots:
self.grapher = PlotlyGrapher(rows = 2, cols = 3, subplot_titles = [
"LoRs, first two samples",
"Labelled cutpoints, first 10 samples, 1-pass",
"Tracer locations, 1-pass (coloured cluster size)",
"Tracer locations, 2-pass (coloured cluster size)",
"Segregated tracer locations",
"Individual trajectories"
])
# Add traces to the grapher figure. row = 1, col = 1 by default.
# If there are less than 2 samples of LoRs, plot all LoRs.
if len(self.lors) >= 2:
self.grapher.add_trace(self.lors.lines_trace([0, 1]))
else:
self.grapher.add_lines(self.lors)
# If there are less than 10 samples of cutpoints, plot all of them
if len(self.labelled_cutpoints) >= 10:
self.grapher.add_trace(self.labelled_cutpoints.points_trace(
range(0, 10)
), row = 1, col = 2)
else:
self.grapher.add_trace(self.labelled_cutpoints.points_trace(),
col = 2)
self.grapher.add_points(self.centres, row = 1, col = 3)
self.grapher.add_points(self.centres2, colorbar_col = 4,
row = 2, col = 1)
self.grapher.add_points(self.segregated_trajectories, row = 2, col = 2)
self.grapher.add_points(self.trajectories, row = 2, col = 3)
self.grapher.show()
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"Plotting completed."
f"{bcolors.ENDC}\n\n"
))
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "=" * 70 + # Use colorrs when printing
"\nPEPT-ML User End\n" +
"=" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC # End colour
)
@staticmethod
def minimal(
lors, # Essential, pept.LineData
max_tracers, # Essential, int
sample_size = None, # Default 200 * max_tracers
overlap = None, # Default 150 * max_tracers
sample_size2 = None, # Default 30 * max_tracers
overlap2 = None, # Default sample_size2 - 1
max_distance = 0.15, # mm
k1 = 0.15, # non-dimensional, important
k2 = 0.6, # non-dimensional
points_window = None, # Default 10 * max_tracers
trajectory_cut_distance = 10.0, # mm, important
max_time_difference = 150, # ms
max_signature_difference = 100 # cluster size difference
):
# Check `lors` is an instance of `pept.LineData`; this includes any
# subclass! (e.g. `pept.scanners.ParallelScreens`). If it's not, raise
# an error.
if not isinstance(lors, pept.LineData):
raise TypeError(
textwrap.fill((
"\n[ERROR]: `lors` should be an instance of `pept."
f"LineData` (or subclass thereof). Received {type(lors)}."
"Note: you can read in LoR data from a CSV file using "
"`pept.utilities.read_csv`; initialise them in a `pept."
"LineData` before calling this function. Check this "
"script's documentation for more.\n"
), replace_whitespace = False)
)
# If any of sample_size, overlap, sample_size2, overlap2 were left
# to the default `None`, set them to the default values.
if sample_size is None:
sample_size = 200 * max_tracers
if overlap is None:
overlap = 150 * max_tracers
if sample_size2 is None:
sample_size2 = 30 * max_tracers
if overlap2 is None:
overlap2 = sample_size2 - 1
# Set points_window to a default value.
if points_window is None:
points_window = max_tracers * 10
# Beginning of the PEPT-ML User algorithm:
# Compute cutpoints from LoRs
lors.sample_size = sample_size
lors.overlap = overlap
cutpoints = peptml.Cutpoints(lors, max_distance)
# 1-pass clustering
min_cluster_size = int(k1 * cutpoints.sample_size / max_tracers)
clusterer = peptml.HDBSCANClusterer(min_cluster_size)
centres, labelled_cutpoints = clusterer.fit(cutpoints,
get_labels = True)
# 2-pass clustering
centres.sample_size = sample_size2
centres.overlap = overlap2
min_cluster_size2 = int(k2 * centres.sample_size / max_tracers)
clusterer2 = peptml.HDBSCANClusterer(min_cluster_size2)
centres2, labelled_centres = clusterer2.fit(centres,
get_labels = True)
# Segregate the intertwined points
segregated_trajectories = tsp.segregate_trajectories(
centres2, points_window, trajectory_cut_distance
)
# Connect segregated points based on cluster size
trajectories = tsp.connect_trajectories(
segregated_trajectories,
max_time_difference,
max_signature_difference
)
# Create a list of individual trajectories
# trajectory_list = pept.utilities.group_by_column(
# trajectories.points, -1
# )
# Plot everything using PlotlyGrapher
grapher = PlotlyGrapher(rows = 2, cols = 3, subplot_titles = [
"LoRs, first two samples",
"Labelled cutpoints, first 10 samples, 1-pass",
"Tracer locations, 1-pass (coloured cluster size)",
"Tracer locations, 2-pass (coloured cluster size)",
"Segregated tracer locations",
"Individual trajectories"
])
grapher.add_trace(lors.lines_trace([0, 1]))
grapher.add_trace(labelled_cutpoints.points_trace(range(0, 10)),
col = 2)
grapher.add_points(centres, col = 3)
grapher.add_points(centres2, colorbar_col = 4, row = 2, col = 1)
grapher.add_points(segregated_trajectories, row = 2, col = 2)
grapher.add_points(trajectories, row = 2, col = 3)
grapher.show()
def typecheck_and_create_attributes(
self,
lors,
max_tracers,
sample_size = None,
overlap = None,
sample_size2 = None,
overlap2 = None,
max_distance = 0.15,
k1 = 0.15,
k2 = 0.6,
points_window = None,
trajectory_cut_distance = 10.0,
max_time_difference = 150.0,
max_signature_difference = 100.0
):
# Check `lors` is an instance of `pept.LineData`; this includes any
# subclass! (e.g. `pept.scanners.ParallelScreens`). If it's not, raise
# an error.
if not isinstance(lors, pept.LineData):
raise TypeError(
textwrap.fill((
"\n[ERROR]: `lors` should be an instance of `pept."
f"LineData` (or subclass thereof). Received {type(lors)}. "
"Note: you can read in LoR data from a CSV file using "
"`pept.utilities.read_csv`; initialise them in a `pept."
"LineData` before calling this function. Check this "
"script's documentation for more information.\n"
), replace_whitespace = False)
)
# Attach lors to our class instance so we can access it as a class
# property. Attach the next variables used too.
self.lors = lors
# Make sure max_tracers is an `int` that's larger or equal to 1
max_tracers = int(max_tracers)
assert max_tracers >= 1, textwrap.fill(
"[ERROR]: `max_tracers` should be an `int` >= 1."
)
self.max_tracers = max_tracers
# If any of sample_size, overlap, sample_size2, overlap2 were left
# to the default `None`, set them to the default values. Otherwise
# type-check them; also set lors.sample_size and lors.overlap.
if sample_size is None:
sample_size = 200 * max_tracers
else:
sample_size = int(sample_size)
self.sample_size = sample_size
if overlap is None:
overlap = 150 * max_tracers
else:
overlap = int(overlap)
self.overlap = overlap
if sample_size2 is None:
sample_size2 = 30 * max_tracers
else:
sample_size2 = int(sample_size2)
self.sample_size2 = sample_size2
if overlap2 is None:
overlap2 = sample_size2 - 1
else:
int(overlap2)
self.overlap2 = overlap2
# Type-check max_distance (for cutpoints), k1 (for 1-pass clusterer)
# and k2 (for the 2-pass clusterer)
max_distance = float(max_distance)
self.max_distance = max_distance
k1 = float(k1)
self.k1 = k1
k2 = float(k2)
self.k2 = k2
# Type-check parameters for segregate_trajectories
if points_window is None:
self.points_window = self.max_tracers * 10
else:
self.points_window = int(points_window)
self.trajectory_cut_distance = float(trajectory_cut_distance)
# Type-check parameters for connect_trajectories
self.max_time_difference = float(max_time_difference)
self.max_signature_difference = float(max_signature_difference)
class PEPTMLFindParameters:
'''This is an example script that visually helps find the best clustering
parameters for the PEPT-ML algorithm from the `pept` library.
The script is encapsulated in a class such that, after running it (i.e.
instantiating the class), all the relevant analysis objects can be accessed
as class attributes (e.g. LoRs, clusterers, tracer locations).
The class has three methods:
1. __init__ : the class constructor that is run when instantiating it;
it contains the actual PEPT-ML algorithm.
2. typecheck_and_create_attributes : typecheck input parameters and
create class attributes.
3. minimal : the minimal PEPT-ML code, without pretty-printing to the
terminal.
It is more than recommended to look through the code, copy and hack into
it! The class constructor (`__init__`) contains the PEPT-ML algorithm with
printing functionality to the terminal; if you'd like the code without such
additions, use the equivalent code in the `minimal` method.
The main steps of the PEPT-ML-User algorithm are:
-- Done beforehand, by the user --
1. Initialise LoRs in a `pept.LineData` instance (if they are stored in
a file, you can use `pept.utilities.read_csv`). **You must do this
before using this script**.
-- Done by this script --
2. Compute the cutpoints from the LoRs using the `peptml.Cutpoints`
class.
3. For every value in `np.linspace(k1[0], k1[1], iterations)`, cluster
the cutpoints using `peptml.HDBSCANClusterer` to find the tracer
locations (i.e. cluster *centres*) - this is *1-pass clustering*.
The function then plots the clustered cutpoints with colour-coded cluster
labels and tracer locations for each value of k1 that was chosen. The user
can then visually select the value of k1 that works best for clustering the
given dataset.
For more details check out the PEPT-ML paper (doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251)
and the documentation of the functions used.
Attributes
----------
lors : pept.LineData instance
The input lines of response (LoRs). As they can be stored in various
sources (CSV files, binary data, different scanner geometries), it is
expected that users initialise them as `pept.LineData` (or a subclass
thereof) *before* using this script.
max_tracers : int
The maximum number of tracers that may be present in the field of view
at any time. Note that the PEPT-ML algorithm does not *need* this
number (and can work well even when tracers leave the FoV); however, it
is useful when setting the sample sizes, overlaps and clustering
parameters.
sample_size : int, optional
The `lors.sample_size`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints. By
default, it is set to 200 * `max_tracers`.
overlap : int, optional
The `lors.overlap`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints. By
default, it is set to 150 * `max_tracers`.
max_distance : float, default 0.15
The maximum allowed distance between two LoRs for their cutpoint to be
considered; used by `peptml.Cutpoints`.
k1 : list[float], default [0.05, 0.8]
The range to explor of the fitting parameter for setting the
`min_cluster_size` of the `clusterer` used for the first pass of
clustering. As the number of cutpoints around a tracer scales with the
sample_size and (inversely) `max_tracers`, the following formula is
used -
`min_cluster_size` = int(k1 * cutpoints.sample_size / max_tracers)`.
A larger value represents "harsher" clustering. This class will iterate
through `iterations` equally-spaced values between k1[0] and k1[1] for
one-pass clustering.
iterations : int, default 5
The number of values of k1 that will be taken between k1[0] and k1[1]
for the different clusterers.
cutpoints : pept.tracking.peptml.Cutpoints instance
The cutpoints computed from `lors`. It is a subclass of
`pept.PointData`, such that all its methods and attributes can be used.
ks : np.ndarray
The values of k1 that will be used for the clusterers. It is equivalent
to a call to `np.linspace(k1[0], k1[1], iterations, dtype = float)`.
clusterers : list[pept.tracking.peptml.HDBSCANClusterer]
The list of clusterers with different `min_cluster_size` values from
`ks` that will be used for one-pass clustering.
centres : list[pept.PointData]
A list of the tracer locations (i.e. cluster *centres*) found after the
first pass of clustering, for every value of k1 in `ks`. The last
column in each `pept.PointData` represents the cluster size; that is,
the number of points in the cluster surrounding the tracer. This can
act as a tracer signature for when their identity is temporarily lost,
like when they collide.
labelled_cutpoints : list[pept.PointData]
A list of the cutpoints that were clustered for every value of k1 in
`ks`, including their cluster labels as the last column.
grapher : pept.visualisation.PlotlyGrapher instance
The grapher organising the 3D subplots.
Methods
-------
typecheck_and_create_attributes(\
lors,\
max_tracers,\
sample_size = None,\
overlap = None,\
max_distance = 0.15,\
k1 = [0.05, 0.8],\
iterations = 5\
)
Typecheck input parameters and create class attributes. Used by the
class constructor for checks that are not relevant to the actual
PEPT-ML aglorithm.
minimal(\
lors,\
max_tracers,\
sample_size = None,\
overlap = None,\
max_distance = 0.15,\
k1 = [0.05, 0.8],\
iterations = 5\
)
The minimal code for using the algorithm in this class, without
pretty-printing to the terminal. Useful for copy-pasting the code and
hacking into it.
Raises
------
TypeError
If `lors` is not an instance of `pept.LineData` (or subclass thereof!).
AssertionError
If `max_tracers` is smaller than 1.
Notes
-----
The `pept` package is modular, meaning it can be used in many ways, to suit
(m)any circumstances. This is just an example, which you can modify as you
see fit.
If you're not sure what a class or method does, you can always consult the
documentation online, at "uob-positron-imaging-centre.github.io", or by
adding a questions mark in front of a package / module / class / function
name in the Python shell or using the `help` command. For example:
>>> import pept
>>> ?pept.LineData # Short documentation
>>> ??pept.LineData # Long documentation
>>> help(pept.LineData) # Even more info
Examples
--------
An example call would be:
>>> lors_raw = pept.utilities.read_csv("csv_file.csv") # two tracers CSV
>>> lors = pept.LineData(lors_raw)
>>> user = pept.cookbook.PEPTMLFindParameters(lors, 2) # max_tracers = 2
'''
def __init__(
self,
lors, # Essential, pept.LineData
max_tracers, # Essential, int
sample_size = None, # Default 200 * max_tracers
overlap = None, # Default 150 * max_tracers
max_distance = 0.15, # mm
k1 = [0.05, 0.8], # non-dimensional, important
iterations = 5 # number of points between k1[0] and k1[1]
):
'''The PEPTMLFindParameters class constructor.
Parameters
----------
lors : pept.LineData instance
The input lines of response (LoRs). As they can be stored in
various sources (CSV files, binary data, different scanner
geometries), it is expected that users initialise them as
`pept.LineData` (or a subclass thereof) *before* using this script.
max_tracers : int
The maximum number of tracers that may be present in the field of
view at any time. Note that the PEPT-ML algorithm does not *need*
this number (and can work well even when tracers leave the FoV);
however, it is useful when setting the sample sizes, overlaps and
clustering parameters.
sample_size : int, optional
The `lors.sample_size`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints.
By default, it is set to 200 * `max_tracers`.
overlap : int, optional
The `lors.overlap`, used when transforming LoRs into cutpoints. By
default, it is set to 150 * `max_tracers`.
max_distance : float, default 0.15
The maximum allowed distance between two LoRs for their cutpoint to
be considered; used by `peptml.Cutpoints`.
k1 : list[float], default [0.05, 0.8]
The range to explor of the fitting parameter for setting the
`min_cluster_size` of the `clusterer` used for the first pass of
clustering. As the number of cutpoints around a tracer scales with
the sample_size and (inversely) `max_tracers`, the following
formula is used -
`min_cluster_size` = int(k1 * cutpoints.sample_size / max_tracers)`
A larger value represents "harsher" clustering. This class will
iterate through `iterations` equally-spaced values between k1[0]
and k1[1] for one-pass clustering.
iterations : int, default 5
The number of values of k1 that will be taken between k1[0] and
k1[1] for the different clusterers.
Raises
------
TypeError
If `lors` is not an instance of `pept.LineData` (or subclass
thereof!).
AssertionError
If `max_tracers` is smaller than 1.
'''
# Initial type-checking of input parameters + properties
# initialisation.
self.typecheck_and_create_attributes(
lors, max_tracers, sample_size, overlap, max_distance, k1,
iterations
)
# Start the PEPT-ML algorithm; you can copy-paste the code below and
# hack into it! It's recommended actually!
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "=" * 70 + # Use colours when printing
"\nPEPT-ML Find Parameters Start\n" +
"=" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC # End colour
)
# Print input LoRs and max_tracers. For `lors`, print its printable
# representation (i.e. long representation) using repr().
self.lors.sample_size = self.sample_size
self.lors.overlap = self.overlap
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"LoRs:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.lors)}\n"
))
print((
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"max_tracers = {self.max_tracers}"
f"{bcolors.ENDC}\n\n"
))
# Transform the LoRs into cutpoints using the `Cutpoints` class. It is
# a `pept.PointData` subclass, so we inherit all its attributes and
# methods!
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nTransforming LoRs into Cutpoints\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"max_distance = {self.max_distance}"
f"{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
))
self.cutpoints = peptml.Cutpoints(lors, max_distance)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"Finding cutpoints completed.\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}"
f"Cutpoints:{bcolors.ENDC}\n"
f"{repr(self.cutpoints)}\n\n"
))
# Cluster our cutpoints using peptml.HDBSCANClusterer for every value
# of k1 between k1[0] and k1[1], at `iterations` points.
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nClustering Cutpoints using HDBSCANClusterer " +
"(1-pass clustering)\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
self.ks = np.linspace(k1[0], k1[1], iterations, dtype = float)
print((
"\nFormula for setting the clusterer min_cluster_size:\n"
" min_cluster_size = int(k1 * cutpoints.sample_size / "
"max_tracers)\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}For values of k1 from:\n"
f" {self.ks}{bcolors.ENDC}\n\n"
))
# Create a list of clusterers.
self.clusterers = [peptml.HDBSCANClusterer(
int(k * self.cutpoints.sample_size / self.max_tracers)
) for k in self.ks]
# For each clusterer, fit the cutpoints and append the results to a
# list. Use `tqdm` to show a progress bar.
self.centres = []
self.labelled_cutpoints = []
for clusterer in tqdm(self.clusterers):
centres1, labelled_cutpoints1 = clusterer.fit(
self.cutpoints,
get_labels = True,
verbose = False
)
self.centres.append(centres1)
self.labelled_cutpoints.append(labelled_cutpoints1)
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"Clustering cutpoints for every value of k1 completed.\n\n"
f"{bcolors.OKBLUE}" +
textwrap.fill(
"Tracer locations (i.e. cluster centres) for every value of "
"k1 were saved as a list in the `centres` attribute of this "
"class. Similarily, the labelled cutpoints (i.e. the "
"cutpoints with an extra column of cluster labels) were saved "
"as a list in the `labelled_cutpoints` attribute of this "
"class."
) +
f"{bcolors.ENDC}\n\n"
))
# Plotting time!
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "-" * 70 +
"\nPlotting Results using PlotlyGrapher\n" +
"-" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC
)
# Instantiate a PlotlyGrapher instance with 2 rows and `iterations`
# columns:
self.grapher = PlotlyGrapher(
rows = 2,
cols = self.iterations,
subplot_titles = [
f"k1 = {k}, labelled cutpoints" for k in self.ks
] + [
f"k1 = {k}, cluster centres" for k in self.ks
]
)
# For every value of k1 we used, on the first row plot the labelled
# cutpoints, and on the second row plot the tracer locations (i.e.
# cluster centres).
for i in range(self.iterations):
self.grapher.add_trace(
self.labelled_cutpoints[i].points_trace(), row = 1, col = i + 1
)
self.grapher.add_trace(
self.centres[i].points_trace(), row = 2, col = i + 1
)
self.grapher.show()
print((
f"\n{bcolors.OKGREEN}"
f"Plotting completed."
f"{bcolors.ENDC}\n\n"
))
print(
bcolors.HEADER + "=" * 70 + # Use colorrs when printing
"\nPEPT-ML Find Parameters End\n" +
"=" * 70 + bcolors.ENDC # End colour
)
@staticmethod
def minimal(
lors, # Essential, pept.LineData
max_tracers, # Essential, int
sample_size = None, # Default 200 * max_tracers
overlap = None, # Default 150 * max_tracers
sample_size2 = None, # Default 30 * max_tracers
overlap2 = None, # Default sample_size2 - 1
max_distance = 0.15, # mm
k1 = [0.05, 0.8], # non-dimensional, important
iterations = 5 # number of points between k1[0] and k1[1]
):
# Check `lors` is an instance of `pept.LineData`; this includes any
# subclass! (e.g. `pept.scanners.ParallelScreens`). If it's not, raise
# an error.
if not isinstance(lors, pept.LineData):
raise TypeError(
textwrap.fill((
"\n[ERROR]: `lors` should be an instance of `pept."
f"LineData` (or subclass thereof). Received {type(lors)}."
"Note: you can read in LoR data from a CSV file using "
"`pept.utilities.read_csv`; initialise them in a `pept."
"LineData` before calling this function. Check this "
"script's documentation for more.\n"
), replace_whitespace = False)
)
# If any of sample_size, overlap, sample_size2, overlap2 were left
# to the default `None`, set them to the default values.
if sample_size is None:
sample_size = 200 * max_tracers
if overlap is None:
overlap = 150 * max_tracers
if sample_size2 is None:
sample_size2 = 30 * max_tracers
if overlap2 is None:
overlap2 = sample_size2 - 1
lors.sample_size = sample_size
lors.overlap = overlap
cutpoints = peptml.Cutpoints(lors, max_distance)
ks = np.linspace(k1[0], k1[1], iterations, dtype = float)
clusterers = [peptml.HDBSCANClusterer(
int(k * cutpoints.sample_size / max_tracers)
) for k in ks]
centres = []
labelled_cutpoints = []
for clusterer in tqdm(clusterers):
centres1, labelled_cutpoints1 = clusterer.fit(
cutpoints,
get_labels = True,
verbose = False
)
centres.append(centres1)
labelled_cutpoints.append(labelled_cutpoints1)
grapher = PlotlyGrapher(
rows = 2,
cols = iterations,
subplot_titles = [
f"k1 = {k}, labelled cutpoints" for k in ks
] + [
f"k1 = {k}, cluster centres" for k in ks
]
)
for i in range(iterations):
grapher.add_trace(
labelled_cutpoints[i].points_trace(), row = 1, col = i + 1
)
grapher.add_trace(
centres[i].points_trace(), row = 2, col = i + 1
)
grapher.show()
def typecheck_and_create_attributes(
self,
lors, # Essential, pept.LineData
max_tracers, # Essential, int
sample_size = None, # Default 200 * max_tracers
overlap = None, # Default 150 * max_tracers
max_distance = 0.15, # mm
k1 = [0.05, 0.8], # non-dimensional, important
iterations = 5 # number of points between k1[0] and k1[1]
):
# Check `lors` is an instance of `pept.LineData`; this includes any
# subclass! (e.g. `pept.scanners.ParallelScreens`). If it's not, raise
# an error.
if not isinstance(lors, pept.LineData):
raise TypeError(
textwrap.fill((
"\n[ERROR]: `lors` should be an instance of `pept."
f"LineData` (or subclass thereof). Received {type(lors)}."
"Note: you can read in LoR data from a CSV file using "
"`pept.utilities.read_csv`; initialise them in a `pept."
"LineData` before calling this function. Check this "
"script's documentation for more.\n"
), replace_whitespace = False)
)
# Attach lors to our class instance so we can access it as a class
# property. Attach the next variables used too.
self.lors = lors
# Make sure max_tracers is an `int` that's larger or equal to 1
max_tracers = int(max_tracers)
assert max_tracers >= 1, textwrap.fill(
"[ERROR]: `max_tracers` should be an `int` >= 1."
)
self.max_tracers = max_tracers
# If any of sample_size, overlap, sample_size2, overlap2 were left
# to the default `None`, set them to the default values. Otherwise
# type-check them; also set lors.sample_size and lors.overlap.
if sample_size is None:
sample_size = 200 * max_tracers
self.sample_size = sample_size
if overlap is None:
overlap = 150 * max_tracers
self.overlap = overlap
# Type-check max_distance (for cutpoints), k1 (for 1-pass clusterer)
# and k2 (for the 2-pass clusterer)
self.max_distance = float(max_distance)
# We will use `iterations` points between k1[0] and k1[1]. Make sure
# k1 is list-like with length 2.
k1 = list(k1)
assert len(k1) == 2, textwrap.fill(
"[ERROR]: k1 should be list-like with exactly two elements."
)
self.k1 = k1
self.iterations = int(iterations)
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1619631590.0762506
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/diagnostics/������������������������������������������������������������������������0000755�0001750�0001750�00000000000�00000000000�020174� 5����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1605637926.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/diagnostics/__init__.py�������������������������������������������������������������0000777�0001750�0001750�00000000267�00000000000�022321� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# File : __init__.py
# License: License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 27.08.2019
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1619631590.079584
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/processing/�������������������������������������������������������������������������0000755�0001750�0001750�00000000000�00000000000�020041� 5����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1607280412.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/processing/._occupancy_ext.html�����������������������������������������������������0000777�0001750�0001750�00000010000�00000000000�024006� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Mac OS X ����� ���2��������������������������������������������������ATTR�������������������������������������������com.apple.lastuseddate#PS�����ۻ_������{4������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������This resource fork intentionally left blank ��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618748000.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/processing/__init__.py��������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000002374�00000000000�022160� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# File : __init__.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 22.06.2020
'''The PEPT-oriented post-processing suite, including occupancy grid,
vector velocity fields, etc.
Summary
-------
This module contains fast, robust functions that operate on PEPT-like data
and integrate with the `pept` library's base classes.
Modules Provided
----------------
::
pept.processing
│
Functions imported into the subpackage root:
├── circles2d : Pixellise circles onto occupancy grid.
├── occupancy2d : Pixellise trajectories onto occupancy grid.
├── circles2d_ext : Circle pixellisation low-level Cython routine.
└── occupancy2d_ext : Trajectory pixellisation low-level C routine.
'''
from .occupancy import circles2d
from .occupancy import occupancy2d
from .circles_ext import circles2d_ext
from .occupancy_ext import occupancy2d_ext
__all__ = [
"circles2d",
"occupancy2d",
"circles2d_ext",
"occupancy2d_ext",
]
__license__ = "GNU v3.0"
__maintainer__ = "Andrei Leonard Nicusan"
__email__ = "a.l.nicusan@bham.ac.uk"
__status__ = "Beta"
��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1619626438.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/processing/circles_ext.c������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00003226747�00000000000�022536� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������/* Generated by Cython 0.29.23 */
/* BEGIN: Cython Metadata
{
"distutils": {
"depends": [],
"extra_compile_args": [
"-Ofast",
"-flto",
"-Werror=vla",
"/O2",
"/fp:fast",
"/GL"
],
"extra_link_args": [
"-flto",
"/LTCG"
],
"include_dirs": [
"/tmp/pip-build-env-_m6gckns/overlay/lib/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/core/include"
],
"name": "pept.processing.circles_ext",
"sources": [
"pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx"
]
},
"module_name": "pept.processing.circles_ext"
}
END: Cython Metadata */
#ifndef PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN
#define PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN
#endif /* PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN */
#include "Python.h"
#ifndef Py_PYTHON_H
#error Python headers needed to compile C extensions, please install development version of Python.
#elif PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02060000 || (0x03000000 <= PY_VERSION_HEX && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03030000)
#error Cython requires Python 2.6+ or Python 3.3+.
#else
#define CYTHON_ABI "0_29_23"
#define CYTHON_HEX_VERSION 0x001D17F0
#define CYTHON_FUTURE_DIVISION 1
#include
#ifndef offsetof
#define offsetof(type, member) ( (size_t) & ((type*)0) -> member )
#endif
#if !defined(WIN32) && !defined(MS_WINDOWS)
#ifndef __stdcall
#define __stdcall
#endif
#ifndef __cdecl
#define __cdecl
#endif
#ifndef __fastcall
#define __fastcall
#endif
#endif
#ifndef DL_IMPORT
#define DL_IMPORT(t) t
#endif
#ifndef DL_EXPORT
#define DL_EXPORT(t) t
#endif
#define __PYX_COMMA ,
#ifndef HAVE_LONG_LONG
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x02070000
#define HAVE_LONG_LONG
#endif
#endif
#ifndef PY_LONG_LONG
#define PY_LONG_LONG LONG_LONG
#endif
#ifndef Py_HUGE_VAL
#define Py_HUGE_VAL HUGE_VAL
#endif
#ifdef PYPY_VERSION
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY 1
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 0
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03050000
#undef CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS)
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 0
#undef CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
#define CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS 1
#undef CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS 0
#undef CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS
#define CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS 0
#undef CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE 0
#undef CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL 0
#undef CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
#define CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
#define CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
#define CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK 0
#elif defined(PYSTON_VERSION)
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON 1
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON 0
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS 0
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 0
#ifndef CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
#define CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS 0
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS
#define CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE 0
#undef CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL 0
#undef CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
#define CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
#define CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
#define CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK 0
#else
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON 1
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS 1
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070000
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP)
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 1
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
#undef CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS)
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 1
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070000
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS)
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030300F0
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER)
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
#define CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS 0
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS
#define CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
#define CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03050000)
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
#define CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030400a1)
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030600B1)
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
#define CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030700A3)
#endif
#endif
#if !defined(CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL)
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL (CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL && PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030600B1)
#endif
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#include "longintrepr.h"
#undef SHIFT
#undef BASE
#undef MASK
#ifdef SIZEOF_VOID_P
enum { __pyx_check_sizeof_voidp = 1 / (int)(SIZEOF_VOID_P == sizeof(void*)) };
#endif
#endif
#ifndef __has_attribute
#define __has_attribute(x) 0
#endif
#ifndef __has_cpp_attribute
#define __has_cpp_attribute(x) 0
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_RESTRICT
#if defined(__GNUC__)
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT __restrict__
#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER >= 1400
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT __restrict
#elif defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT restrict
#else
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT
#endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_UNUSED
# if defined(__GNUC__)
# if !(defined(__cplusplus)) || (__GNUC__ > 3 || (__GNUC__ == 3 && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= 4))
# define CYTHON_UNUSED __attribute__ ((__unused__))
# else
# define CYTHON_UNUSED
# endif
# elif defined(__ICC) || (defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && !defined(_MSC_VER))
# define CYTHON_UNUSED __attribute__ ((__unused__))
# else
# define CYTHON_UNUSED
# endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_MAYBE_UNUSED_VAR
# if defined(__cplusplus)
template void CYTHON_MAYBE_UNUSED_VAR( const T& ) { }
# else
# define CYTHON_MAYBE_UNUSED_VAR(x) (void)(x)
# endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED
# if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
# define CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED
# else
# define CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED CYTHON_UNUSED
# endif
#endif
#define __Pyx_void_to_None(void_result) ((void)(void_result), Py_INCREF(Py_None), Py_None)
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#ifndef _MSC_STDINT_H_
#if _MSC_VER < 1300
typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
#else
typedef unsigned __int8 uint8_t;
typedef unsigned __int32 uint32_t;
#endif
#endif
#else
#include
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#if defined(__cplusplus) && __cplusplus >= 201103L
#if __has_cpp_attribute(fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH [[fallthrough]]
#elif __has_cpp_attribute(clang::fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH [[clang::fallthrough]]
#elif __has_cpp_attribute(gnu::fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH [[gnu::fallthrough]]
#endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#if __has_attribute(fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH __attribute__((fallthrough))
#else
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#endif
#endif
#if defined(__clang__ ) && defined(__apple_build_version__)
#if __apple_build_version__ < 7000000
#undef CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#endif
#endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_INLINE
#if defined(__clang__)
#define CYTHON_INLINE __inline__ __attribute__ ((__unused__))
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
#define CYTHON_INLINE __inline__
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
#define CYTHON_INLINE __inline
#elif defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L
#define CYTHON_INLINE inline
#else
#define CYTHON_INLINE
#endif
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070600 && !defined(Py_OptimizeFlag)
#define Py_OptimizeFlag 0
#endif
#define __PYX_BUILD_PY_SSIZE_T "n"
#define CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "z"
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
#define __Pyx_BUILTIN_MODULE_NAME "__builtin__"
#define __Pyx_PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)\
PyCode_New(a+k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)
#define __Pyx_DefaultClassType PyClass_Type
#else
#define __Pyx_BUILTIN_MODULE_NAME "builtins"
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800A4 && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800B2
#define __Pyx_PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)\
PyCode_New(a, 0, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)\
PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)
#endif
#define __Pyx_DefaultClassType PyType_Type
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES
#define Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES 0
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_INDEX
#define Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_INDEX 0
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER
#define Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER 0
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE
#define Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE 0
#endif
#ifndef METH_STACKLESS
#define METH_STACKLESS 0
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX <= 0x030700A3 || !defined(METH_FASTCALL)
#ifndef METH_FASTCALL
#define METH_FASTCALL 0x80
#endif
typedef PyObject *(*__Pyx_PyCFunctionFast) (PyObject *self, PyObject *const *args, Py_ssize_t nargs);
typedef PyObject *(*__Pyx_PyCFunctionFastWithKeywords) (PyObject *self, PyObject *const *args,
Py_ssize_t nargs, PyObject *kwnames);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCFunctionFast _PyCFunctionFast
#define __Pyx_PyCFunctionFastWithKeywords _PyCFunctionFastWithKeywords
#endif
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
#define __Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(func)\
((PyCFunction_Check(func) && (METH_FASTCALL == (PyCFunction_GET_FLAGS(func) & ~(METH_CLASS | METH_STATIC | METH_COEXIST | METH_KEYWORDS | METH_STACKLESS)))))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(func) 0
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyObject_Malloc)
#define PyObject_Malloc(s) PyMem_Malloc(s)
#define PyObject_Free(p) PyMem_Free(p)
#define PyObject_Realloc(p) PyMem_Realloc(p)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030400A1
#define PyMem_RawMalloc(n) PyMem_Malloc(n)
#define PyMem_RawRealloc(p, n) PyMem_Realloc(p, n)
#define PyMem_RawFree(p) PyMem_Free(p)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON
#define __Pyx_PyCode_HasFreeVars(co) PyCode_HasFreeVars(co)
#define __Pyx_PyFrame_SetLineNumber(frame, lineno) PyFrame_SetLineNumber(frame, lineno)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCode_HasFreeVars(co) (PyCode_GetNumFree(co) > 0)
#define __Pyx_PyFrame_SetLineNumber(frame, lineno) (frame)->f_lineno = (lineno)
#endif
#if !CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE || PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070000
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current PyThreadState_GET()
#elif PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03060000
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current _PyThreadState_UncheckedGet()
#elif PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03000000
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current PyThreadState_GET()
#else
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current _PyThreadState_Current
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030700A2 && !defined(PyThread_tss_create) && !defined(Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT)
#include "pythread.h"
#define Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT 0
typedef int Py_tss_t;
static CYTHON_INLINE int PyThread_tss_create(Py_tss_t *key) {
*key = PyThread_create_key();
return 0;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE Py_tss_t * PyThread_tss_alloc(void) {
Py_tss_t *key = (Py_tss_t *)PyObject_Malloc(sizeof(Py_tss_t));
*key = Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT;
return key;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void PyThread_tss_free(Py_tss_t *key) {
PyObject_Free(key);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int PyThread_tss_is_created(Py_tss_t *key) {
return *key != Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void PyThread_tss_delete(Py_tss_t *key) {
PyThread_delete_key(*key);
*key = Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int PyThread_tss_set(Py_tss_t *key, void *value) {
return PyThread_set_key_value(*key, value);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void * PyThread_tss_get(Py_tss_t *key) {
return PyThread_get_key_value(*key);
}
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON || defined(_PyDict_NewPresized)
#define __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(n) ((n <= 8) ? PyDict_New() : _PyDict_NewPresized(n))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(n) PyDict_New()
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 || CYTHON_FUTURE_DIVISION
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Divide(x,y) PyNumber_TrueDivide(x,y)
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_InPlaceDivide(x,y) PyNumber_InPlaceTrueDivide(x,y)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Divide(x,y) PyNumber_Divide(x,y)
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_InPlaceDivide(x,y) PyNumber_InPlaceDivide(x,y)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON && PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030500A1 && CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(dict, name) _PyDict_GetItem_KnownHash(dict, name, ((PyASCIIObject *) name)->hash)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(dict, name) PyDict_GetItem(dict, name)
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX > 0x03030000 && defined(PyUnicode_KIND)
#define CYTHON_PEP393_ENABLED 1
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READY(op) (likely(PyUnicode_IS_READY(op)) ?\
0 : _PyUnicode_Ready((PyObject *)(op)))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u) PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ_CHAR(u, i) PyUnicode_READ_CHAR(u, i)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_MAX_CHAR_VALUE(u) PyUnicode_MAX_CHAR_VALUE(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_KIND(u) PyUnicode_KIND(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_DATA(u) PyUnicode_DATA(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ(k, d, i) PyUnicode_READ(k, d, i)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_WRITE(k, d, i, ch) PyUnicode_WRITE(k, d, i, ch)
#if defined(PyUnicode_IS_READY) && defined(PyUnicode_GET_SIZE)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_IS_TRUE(u) (0 != (likely(PyUnicode_IS_READY(u)) ? PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u) : PyUnicode_GET_SIZE(u)))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_IS_TRUE(u) (0 != PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u))
#endif
#else
#define CYTHON_PEP393_ENABLED 0
#define PyUnicode_1BYTE_KIND 1
#define PyUnicode_2BYTE_KIND 2
#define PyUnicode_4BYTE_KIND 4
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READY(op) (0)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u) PyUnicode_GET_SIZE(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ_CHAR(u, i) ((Py_UCS4)(PyUnicode_AS_UNICODE(u)[i]))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_MAX_CHAR_VALUE(u) ((sizeof(Py_UNICODE) == 2) ? 65535 : 1114111)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_KIND(u) (sizeof(Py_UNICODE))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_DATA(u) ((void*)PyUnicode_AS_UNICODE(u))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ(k, d, i) ((void)(k), (Py_UCS4)(((Py_UNICODE*)d)[i]))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_WRITE(k, d, i, ch) (((void)(k)), ((Py_UNICODE*)d)[i] = ch)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_IS_TRUE(u) (0 != PyUnicode_GET_SIZE(u))
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_Concat(a, b) PyNumber_Add(a, b)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_ConcatSafe(a, b) PyNumber_Add(a, b)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_Concat(a, b) PyUnicode_Concat(a, b)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_ConcatSafe(a, b) ((unlikely((a) == Py_None) || unlikely((b) == Py_None)) ?\
PyNumber_Add(a, b) : __Pyx_PyUnicode_Concat(a, b))
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyUnicode_Contains)
#define PyUnicode_Contains(u, s) PySequence_Contains(u, s)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyByteArray_Check)
#define PyByteArray_Check(obj) PyObject_TypeCheck(obj, &PyByteArray_Type)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyObject_Format)
#define PyObject_Format(obj, fmt) PyObject_CallMethod(obj, "__format__", "O", fmt)
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyString_FormatSafe(a, b) ((unlikely((a) == Py_None || (PyString_Check(b) && !PyString_CheckExact(b)))) ? PyNumber_Remainder(a, b) : __Pyx_PyString_Format(a, b))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FormatSafe(a, b) ((unlikely((a) == Py_None || (PyUnicode_Check(b) && !PyUnicode_CheckExact(b)))) ? PyNumber_Remainder(a, b) : PyUnicode_Format(a, b))
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyString_Format(a, b) PyUnicode_Format(a, b)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyString_Format(a, b) PyString_Format(a, b)
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 && !defined(PyObject_ASCII)
#define PyObject_ASCII(o) PyObject_Repr(o)
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define PyBaseString_Type PyUnicode_Type
#define PyStringObject PyUnicodeObject
#define PyString_Type PyUnicode_Type
#define PyString_Check PyUnicode_Check
#define PyString_CheckExact PyUnicode_CheckExact
#ifndef PyObject_Unicode
#define PyObject_Unicode PyObject_Str
#endif
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_Check(obj) PyUnicode_Check(obj)
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_CheckExact(obj) PyUnicode_CheckExact(obj)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_Check(obj) (PyString_Check(obj) || PyUnicode_Check(obj))
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_CheckExact(obj) (PyString_CheckExact(obj) || PyUnicode_CheckExact(obj))
#endif
#ifndef PySet_CheckExact
#define PySet_CheckExact(obj) (Py_TYPE(obj) == &PySet_Type)
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030900A4
#define __Pyx_SET_REFCNT(obj, refcnt) Py_SET_REFCNT(obj, refcnt)
#define __Pyx_SET_SIZE(obj, size) Py_SET_SIZE(obj, size)
#else
#define __Pyx_SET_REFCNT(obj, refcnt) Py_REFCNT(obj) = (refcnt)
#define __Pyx_SET_SIZE(obj, size) Py_SIZE(obj) = (size)
#endif
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define __Pyx_PySequence_SIZE(seq) Py_SIZE(seq)
#else
#define __Pyx_PySequence_SIZE(seq) PySequence_Size(seq)
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define PyIntObject PyLongObject
#define PyInt_Type PyLong_Type
#define PyInt_Check(op) PyLong_Check(op)
#define PyInt_CheckExact(op) PyLong_CheckExact(op)
#define PyInt_FromString PyLong_FromString
#define PyInt_FromUnicode PyLong_FromUnicode
#define PyInt_FromLong PyLong_FromLong
#define PyInt_FromSize_t PyLong_FromSize_t
#define PyInt_FromSsize_t PyLong_FromSsize_t
#define PyInt_AsLong PyLong_AsLong
#define PyInt_AS_LONG PyLong_AS_LONG
#define PyInt_AsSsize_t PyLong_AsSsize_t
#define PyInt_AsUnsignedLongMask PyLong_AsUnsignedLongMask
#define PyInt_AsUnsignedLongLongMask PyLong_AsUnsignedLongLongMask
#define PyNumber_Int PyNumber_Long
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define PyBoolObject PyLongObject
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 && CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
#ifndef PyUnicode_InternFromString
#define PyUnicode_InternFromString(s) PyUnicode_FromString(s)
#endif
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030200A4
typedef long Py_hash_t;
#define __Pyx_PyInt_FromHash_t PyInt_FromLong
#define __Pyx_PyInt_AsHash_t PyInt_AsLong
#else
#define __Pyx_PyInt_FromHash_t PyInt_FromSsize_t
#define __Pyx_PyInt_AsHash_t PyInt_AsSsize_t
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyMethod_New(func, self, klass) ((self) ? ((void)(klass), PyMethod_New(func, self)) : __Pyx_NewRef(func))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyMethod_New(func, self, klass) PyMethod_New(func, self, klass)
#endif
#if CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030500B1
#define __Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct PyAsyncMethods
#define __Pyx_PyType_AsAsync(obj) (Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_as_async)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyType_AsAsync(obj) ((__Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct*) (Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_reserved))
#endif
#else
#define __Pyx_PyType_AsAsync(obj) NULL
#endif
#ifndef __Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct
typedef struct {
unaryfunc am_await;
unaryfunc am_aiter;
unaryfunc am_anext;
} __Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct;
#endif
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(MS_WINDOWS)
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#endif
#include
#ifdef NAN
#define __PYX_NAN() ((float) NAN)
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE float __PYX_NAN() {
float value;
memset(&value, 0xFF, sizeof(value));
return value;
}
#endif
#if defined(__CYGWIN__) && defined(_LDBL_EQ_DBL)
#define __Pyx_truncl trunc
#else
#define __Pyx_truncl truncl
#endif
#define __PYX_MARK_ERR_POS(f_index, lineno) \
{ __pyx_filename = __pyx_f[f_index]; (void)__pyx_filename; __pyx_lineno = lineno; (void)__pyx_lineno; __pyx_clineno = __LINE__; (void)__pyx_clineno; }
#define __PYX_ERR(f_index, lineno, Ln_error) \
{ __PYX_MARK_ERR_POS(f_index, lineno) goto Ln_error; }
#ifndef __PYX_EXTERN_C
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define __PYX_EXTERN_C extern "C"
#else
#define __PYX_EXTERN_C extern
#endif
#endif
#define __PYX_HAVE__pept__processing__circles_ext
#define __PYX_HAVE_API__pept__processing__circles_ext
/* Early includes */
#include
#include
#include "pythread.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include "pystate.h"
#ifdef _OPENMP
#include
#endif /* _OPENMP */
#if defined(PYREX_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS) && !defined(CYTHON_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS)
#define CYTHON_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS
#endif
typedef struct {PyObject **p; const char *s; const Py_ssize_t n; const char* encoding;
const char is_unicode; const char is_str; const char intern; } __Pyx_StringTabEntry;
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII 0
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_UTF8 0
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT (PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 && __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_UTF8)
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING ""
#define __Pyx_PyObject_FromString __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyObject_FromStringAndSize __Pyx_PyBytes_FromStringAndSize
#define __Pyx_uchar_cast(c) ((unsigned char)c)
#define __Pyx_long_cast(x) ((long)x)
#define __Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(v, type, is_signed) (\
(sizeof(type) < sizeof(Py_ssize_t)) ||\
(sizeof(type) > sizeof(Py_ssize_t) &&\
likely(v < (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ||\
v == (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX) &&\
(!is_signed || likely(v > (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MIN ||\
v == (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MIN))) ||\
(sizeof(type) == sizeof(Py_ssize_t) &&\
(is_signed || likely(v < (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ||\
v == (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX))) )
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_is_valid_index(Py_ssize_t i, Py_ssize_t limit) {
return (size_t) i < (size_t) limit;
}
#if defined (__cplusplus) && __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) std::abs(value)
#elif SIZEOF_INT >= SIZEOF_SIZE_T
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) abs(value)
#elif SIZEOF_LONG >= SIZEOF_SIZE_T
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) labs(value)
#elif defined (_MSC_VER)
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) ((Py_ssize_t)_abs64(value))
#elif defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) llabs(value)
#elif defined (__GNUC__)
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) __builtin_llabs(value)
#else
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) ((value<0) ? -value : value)
#endif
static CYTHON_INLINE const char* __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE const char* __Pyx_PyObject_AsStringAndSize(PyObject*, Py_ssize_t* length);
#define __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromString(s) PyByteArray_FromStringAndSize((const char*)s, strlen((const char*)s))
#define __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromStringAndSize(s, l) PyByteArray_FromStringAndSize((const char*)s, l)
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString PyBytes_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_FromStringAndSize PyBytes_FromStringAndSize
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromString(const char*);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromString __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromStringAndSize __Pyx_PyBytes_FromStringAndSize
#else
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromString __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromStringAndSize __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsWritableString(s) ((char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsWritableSString(s) ((signed char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsWritableUString(s) ((unsigned char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsString(s) ((const char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsSString(s) ((const signed char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsUString(s) ((const unsigned char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsWritableString(s) ((char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsWritableSString(s) ((signed char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsWritableUString(s) ((unsigned char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsSString(s) ((const signed char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsUString(s) ((const unsigned char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyObject_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyStr_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromString((const char*)s)
static CYTHON_INLINE size_t __Pyx_Py_UNICODE_strlen(const Py_UNICODE *u) {
const Py_UNICODE *u_end = u;
while (*u_end++) ;
return (size_t)(u_end - u - 1);
}
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromUnicode(u) PyUnicode_FromUnicode(u, __Pyx_Py_UNICODE_strlen(u))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromUnicodeAndLength PyUnicode_FromUnicode
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_AsUnicode PyUnicode_AsUnicode
#define __Pyx_NewRef(obj) (Py_INCREF(obj), obj)
#define __Pyx_Owned_Py_None(b) __Pyx_NewRef(Py_None)
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject * __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(long b);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrueAndDecref(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(PyObject* x);
#define __Pyx_PySequence_Tuple(obj)\
(likely(PyTuple_CheckExact(obj)) ? __Pyx_NewRef(obj) : PySequence_Tuple(obj))
static CYTHON_INLINE Py_ssize_t __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject * __Pyx_PyInt_FromSize_t(size_t);
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define __pyx_PyFloat_AsDouble(x) (PyFloat_CheckExact(x) ? PyFloat_AS_DOUBLE(x) : PyFloat_AsDouble(x))
#else
#define __pyx_PyFloat_AsDouble(x) PyFloat_AsDouble(x)
#endif
#define __pyx_PyFloat_AsFloat(x) ((float) __pyx_PyFloat_AsDouble(x))
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Int(x) (PyLong_CheckExact(x) ? __Pyx_NewRef(x) : PyNumber_Long(x))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Int(x) (PyInt_CheckExact(x) ? __Pyx_NewRef(x) : PyNumber_Int(x))
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Float(x) (PyFloat_CheckExact(x) ? __Pyx_NewRef(x) : PyNumber_Float(x))
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 && __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII
static int __Pyx_sys_getdefaultencoding_not_ascii;
static int __Pyx_init_sys_getdefaultencoding_params(void) {
PyObject* sys;
PyObject* default_encoding = NULL;
PyObject* ascii_chars_u = NULL;
PyObject* ascii_chars_b = NULL;
const char* default_encoding_c;
sys = PyImport_ImportModule("sys");
if (!sys) goto bad;
default_encoding = PyObject_CallMethod(sys, (char*) "getdefaultencoding", NULL);
Py_DECREF(sys);
if (!default_encoding) goto bad;
default_encoding_c = PyBytes_AsString(default_encoding);
if (!default_encoding_c) goto bad;
if (strcmp(default_encoding_c, "ascii") == 0) {
__Pyx_sys_getdefaultencoding_not_ascii = 0;
} else {
char ascii_chars[128];
int c;
for (c = 0; c < 128; c++) {
ascii_chars[c] = c;
}
__Pyx_sys_getdefaultencoding_not_ascii = 1;
ascii_chars_u = PyUnicode_DecodeASCII(ascii_chars, 128, NULL);
if (!ascii_chars_u) goto bad;
ascii_chars_b = PyUnicode_AsEncodedString(ascii_chars_u, default_encoding_c, NULL);
if (!ascii_chars_b || !PyBytes_Check(ascii_chars_b) || memcmp(ascii_chars, PyBytes_AS_STRING(ascii_chars_b), 128) != 0) {
PyErr_Format(
PyExc_ValueError,
"This module compiled with c_string_encoding=ascii, but default encoding '%.200s' is not a superset of ascii.",
default_encoding_c);
goto bad;
}
Py_DECREF(ascii_chars_u);
Py_DECREF(ascii_chars_b);
}
Py_DECREF(default_encoding);
return 0;
bad:
Py_XDECREF(default_encoding);
Py_XDECREF(ascii_chars_u);
Py_XDECREF(ascii_chars_b);
return -1;
}
#endif
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT && PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(c_str, size) PyUnicode_DecodeUTF8(c_str, size, NULL)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(c_str, size) PyUnicode_Decode(c_str, size, __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING, NULL)
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT
static char* __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING;
static int __Pyx_init_sys_getdefaultencoding_params(void) {
PyObject* sys;
PyObject* default_encoding = NULL;
char* default_encoding_c;
sys = PyImport_ImportModule("sys");
if (!sys) goto bad;
default_encoding = PyObject_CallMethod(sys, (char*) (const char*) "getdefaultencoding", NULL);
Py_DECREF(sys);
if (!default_encoding) goto bad;
default_encoding_c = PyBytes_AsString(default_encoding);
if (!default_encoding_c) goto bad;
__PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING = (char*) malloc(strlen(default_encoding_c) + 1);
if (!__PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING) goto bad;
strcpy(__PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING, default_encoding_c);
Py_DECREF(default_encoding);
return 0;
bad:
Py_XDECREF(default_encoding);
return -1;
}
#endif
#endif
/* Test for GCC > 2.95 */
#if defined(__GNUC__) && (__GNUC__ > 2 || (__GNUC__ == 2 && (__GNUC_MINOR__ > 95)))
#define likely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 1)
#define unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 0)
#else /* !__GNUC__ or GCC < 2.95 */
#define likely(x) (x)
#define unlikely(x) (x)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_pretend_to_initialize(void* ptr) { (void)ptr; }
static PyObject *__pyx_m = NULL;
static PyObject *__pyx_d;
static PyObject *__pyx_b;
static PyObject *__pyx_cython_runtime = NULL;
static PyObject *__pyx_empty_tuple;
static PyObject *__pyx_empty_bytes;
static PyObject *__pyx_empty_unicode;
static int __pyx_lineno;
static int __pyx_clineno = 0;
static const char * __pyx_cfilenm= __FILE__;
static const char *__pyx_filename;
static const char *__pyx_f[] = {
"pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx",
"stringsource",
};
/* MemviewSliceStruct.proto */
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj;
typedef struct {
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview;
char *data;
Py_ssize_t shape[8];
Py_ssize_t strides[8];
Py_ssize_t suboffsets[8];
} __Pyx_memviewslice;
#define __Pyx_MemoryView_Len(m) (m.shape[0])
/* Atomics.proto */
#include
#ifndef CYTHON_ATOMICS
#define CYTHON_ATOMICS 1
#endif
#define __pyx_atomic_int_type int
#if CYTHON_ATOMICS && __GNUC__ >= 4 && (__GNUC_MINOR__ > 1 ||\
(__GNUC_MINOR__ == 1 && __GNUC_PATCHLEVEL >= 2)) &&\
!defined(__i386__)
#define __pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(value, lock) __sync_fetch_and_add(value, 1)
#define __pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(value, lock) __sync_fetch_and_sub(value, 1)
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#warning "Using GNU atomics"
#endif
#elif CYTHON_ATOMICS && defined(_MSC_VER) && 0
#include
#undef __pyx_atomic_int_type
#define __pyx_atomic_int_type LONG
#define __pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(value, lock) InterlockedIncrement(value)
#define __pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(value, lock) InterlockedDecrement(value)
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#pragma message ("Using MSVC atomics")
#endif
#elif CYTHON_ATOMICS && (defined(__ICC) || defined(__INTEL_COMPILER)) && 0
#define __pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(value, lock) _InterlockedIncrement(value)
#define __pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(value, lock) _InterlockedDecrement(value)
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#warning "Using Intel atomics"
#endif
#else
#undef CYTHON_ATOMICS
#define CYTHON_ATOMICS 0
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#warning "Not using atomics"
#endif
#endif
typedef volatile __pyx_atomic_int_type __pyx_atomic_int;
#if CYTHON_ATOMICS
#define __pyx_add_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#define __pyx_sub_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#else
#define __pyx_add_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_add_acquisition_count_locked(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#define __pyx_sub_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_sub_acquisition_count_locked(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#endif
/* ForceInitThreads.proto */
#ifndef __PYX_FORCE_INIT_THREADS
#define __PYX_FORCE_INIT_THREADS 0
#endif
/* NoFastGil.proto */
#define __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure PyGILState_Ensure
#define __Pyx_PyGILState_Release PyGILState_Release
#define __Pyx_FastGIL_Remember()
#define __Pyx_FastGIL_Forget()
#define __Pyx_FastGilFuncInit()
/* BufferFormatStructs.proto */
#define IS_UNSIGNED(type) (((type) -1) > 0)
struct __Pyx_StructField_;
#define __PYX_BUF_FLAGS_PACKED_STRUCT (1 << 0)
typedef struct {
const char* name;
struct __Pyx_StructField_* fields;
size_t size;
size_t arraysize[8];
int ndim;
char typegroup;
char is_unsigned;
int flags;
} __Pyx_TypeInfo;
typedef struct __Pyx_StructField_ {
__Pyx_TypeInfo* type;
const char* name;
size_t offset;
} __Pyx_StructField;
typedef struct {
__Pyx_StructField* field;
size_t parent_offset;
} __Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem;
typedef struct {
__Pyx_StructField root;
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem* head;
size_t fmt_offset;
size_t new_count, enc_count;
size_t struct_alignment;
int is_complex;
char enc_type;
char new_packmode;
char enc_packmode;
char is_valid_array;
} __Pyx_BufFmt_Context;
/*--- Type declarations ---*/
struct __pyx_array_obj;
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj;
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj;
/* "View.MemoryView":105
*
* @cname("__pyx_array")
* cdef class array: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef:
*/
struct __pyx_array_obj {
PyObject_HEAD
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array *__pyx_vtab;
char *data;
Py_ssize_t len;
char *format;
int ndim;
Py_ssize_t *_shape;
Py_ssize_t *_strides;
Py_ssize_t itemsize;
PyObject *mode;
PyObject *_format;
void (*callback_free_data)(void *);
int free_data;
int dtype_is_object;
};
/* "View.MemoryView":279
*
* @cname('__pyx_MemviewEnum')
* cdef class Enum(object): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef object name
* def __init__(self, name):
*/
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj {
PyObject_HEAD
PyObject *name;
};
/* "View.MemoryView":330
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview')
* cdef class memoryview(object): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef object obj
*/
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj {
PyObject_HEAD
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *__pyx_vtab;
PyObject *obj;
PyObject *_size;
PyObject *_array_interface;
PyThread_type_lock lock;
__pyx_atomic_int acquisition_count[2];
__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count_aligned_p;
Py_buffer view;
int flags;
int dtype_is_object;
__Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo;
};
/* "View.MemoryView":965
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryviewslice')
* cdef class _memoryviewslice(memoryview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Internal class for passing memoryview slices to Python"
*
*/
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj {
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj __pyx_base;
__Pyx_memviewslice from_slice;
PyObject *from_object;
PyObject *(*to_object_func)(char *);
int (*to_dtype_func)(char *, PyObject *);
};
/* "View.MemoryView":105
*
* @cname("__pyx_array")
* cdef class array: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef:
*/
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array {
PyObject *(*get_memview)(struct __pyx_array_obj *);
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array *__pyx_vtabptr_array;
/* "View.MemoryView":330
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview')
* cdef class memoryview(object): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef object obj
*/
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview {
char *(*get_item_pointer)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*is_slice)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*setitem_slice_assignment)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*setitem_slice_assign_scalar)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*setitem_indexed)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*convert_item_to_object)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *);
PyObject *(*assign_item_from_object)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *, PyObject *);
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *__pyx_vtabptr_memoryview;
/* "View.MemoryView":965
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryviewslice')
* cdef class _memoryviewslice(memoryview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Internal class for passing memoryview slices to Python"
*
*/
struct __pyx_vtabstruct__memoryviewslice {
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview __pyx_base;
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct__memoryviewslice *__pyx_vtabptr__memoryviewslice;
/* --- Runtime support code (head) --- */
/* Refnanny.proto */
#ifndef CYTHON_REFNANNY
#define CYTHON_REFNANNY 0
#endif
#if CYTHON_REFNANNY
typedef struct {
void (*INCREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void (*DECREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void (*GOTREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void (*GIVEREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void* (*SetupContext)(const char*, int, const char*);
void (*FinishContext)(void**);
} __Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct;
static __Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct *__Pyx_RefNanny = NULL;
static __Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct *__Pyx_RefNannyImportAPI(const char *modname);
#define __Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations void *__pyx_refnanny = NULL;
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
#define __Pyx_RefNannySetupContext(name, acquire_gil)\
if (acquire_gil) {\
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = PyGILState_Ensure();\
__pyx_refnanny = __Pyx_RefNanny->SetupContext((name), __LINE__, __FILE__);\
PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);\
} else {\
__pyx_refnanny = __Pyx_RefNanny->SetupContext((name), __LINE__, __FILE__);\
}
#else
#define __Pyx_RefNannySetupContext(name, acquire_gil)\
__pyx_refnanny = __Pyx_RefNanny->SetupContext((name), __LINE__, __FILE__)
#endif
#define __Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext()\
__Pyx_RefNanny->FinishContext(&__pyx_refnanny)
#define __Pyx_INCREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->INCREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_DECREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->DECREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_GOTREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->GOTREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_GIVEREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->GIVEREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_XINCREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_INCREF(r); }} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XDECREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_DECREF(r); }} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XGOTREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_GOTREF(r); }} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XGIVEREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_GIVEREF(r);}} while(0)
#else
#define __Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
#define __Pyx_RefNannySetupContext(name, acquire_gil)
#define __Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext()
#define __Pyx_INCREF(r) Py_INCREF(r)
#define __Pyx_DECREF(r) Py_DECREF(r)
#define __Pyx_GOTREF(r)
#define __Pyx_GIVEREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XINCREF(r) Py_XINCREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XDECREF(r) Py_XDECREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XGOTREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XGIVEREF(r)
#endif
#define __Pyx_XDECREF_SET(r, v) do {\
PyObject *tmp = (PyObject *) r;\
r = v; __Pyx_XDECREF(tmp);\
} while (0)
#define __Pyx_DECREF_SET(r, v) do {\
PyObject *tmp = (PyObject *) r;\
r = v; __Pyx_DECREF(tmp);\
} while (0)
#define __Pyx_CLEAR(r) do { PyObject* tmp = ((PyObject*)(r)); r = NULL; __Pyx_DECREF(tmp);} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XCLEAR(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {PyObject* tmp = ((PyObject*)(r)); r = NULL; __Pyx_DECREF(tmp);}} while(0)
/* PyObjectGetAttrStr.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(o,n) PyObject_GetAttr(o,n)
#endif
/* GetBuiltinName.proto */
static PyObject *__Pyx_GetBuiltinName(PyObject *name);
/* RaiseArgTupleInvalid.proto */
static void __Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid(const char* func_name, int exact,
Py_ssize_t num_min, Py_ssize_t num_max, Py_ssize_t num_found);
/* RaiseDoubleKeywords.proto */
static void __Pyx_RaiseDoubleKeywordsError(const char* func_name, PyObject* kw_name);
/* ParseKeywords.proto */
static int __Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(PyObject *kwds, PyObject **argnames[],\
PyObject *kwds2, PyObject *values[], Py_ssize_t num_pos_args,\
const char* function_name);
/* MemviewSliceInit.proto */
#define __Pyx_BUF_MAX_NDIMS %(BUF_MAX_NDIMS)d
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_DIRECT 1
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_PTR 2
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_FULL 4
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_CONTIG 8
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_STRIDED 16
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_FOLLOW 32
#define __Pyx_IS_C_CONTIG 1
#define __Pyx_IS_F_CONTIG 2
static int __Pyx_init_memviewslice(
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview,
int ndim,
__Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice,
int memview_is_new_reference);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __pyx_add_acquisition_count_locked(
__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count, PyThread_type_lock lock);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __pyx_sub_acquisition_count_locked(
__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count, PyThread_type_lock lock);
#define __pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview) (memview->acquisition_count_aligned_p)
#define __pyx_get_slice_count(memview) (*__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview))
#define __PYX_INC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil) __Pyx_INC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil, __LINE__)
#define __PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil) __Pyx_XDEC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil, __LINE__)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_INC_MEMVIEW(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int);
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_XDEC_MEMVIEW(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int);
/* ArgTypeTest.proto */
#define __Pyx_ArgTypeTest(obj, type, none_allowed, name, exact)\
((likely((Py_TYPE(obj) == type) | (none_allowed && (obj == Py_None)))) ? 1 :\
__Pyx__ArgTypeTest(obj, type, name, exact))
static int __Pyx__ArgTypeTest(PyObject *obj, PyTypeObject *type, const char *name, int exact);
/* PyObjectCall.proto */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_Call(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg, PyObject *kw);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_Call(func, arg, kw) PyObject_Call(func, arg, kw)
#endif
/* PyThreadStateGet.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_declare PyThreadState *__pyx_tstate;
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_assign __pyx_tstate = __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current;
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Occurred() __pyx_tstate->curexc_type
#else
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Occurred() PyErr_Occurred()
#endif
/* PyErrFetchRestore.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Clear() __Pyx_ErrRestore(NULL, NULL, NULL)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestoreWithState(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(PyThreadState_GET(), type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetchWithState(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(PyThreadState_GET(), type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestore(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetch(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb);
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
#define __Pyx_PyErr_SetNone(exc) (Py_INCREF(exc), __Pyx_ErrRestore((exc), NULL, NULL))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyErr_SetNone(exc) PyErr_SetNone(exc)
#endif
#else
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Clear() PyErr_Clear()
#define __Pyx_PyErr_SetNone(exc) PyErr_SetNone(exc)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestoreWithState(type, value, tb) PyErr_Restore(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetchWithState(type, value, tb) PyErr_Fetch(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(tstate, type, value, tb) PyErr_Restore(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(tstate, type, value, tb) PyErr_Fetch(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestore(type, value, tb) PyErr_Restore(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetch(type, value, tb) PyErr_Fetch(type, value, tb)
#endif
/* RaiseException.proto */
static void __Pyx_Raise(PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb, PyObject *cause);
/* PyCFunctionFastCall.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(PyObject *func, PyObject **args, Py_ssize_t nargs);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(func, args, nargs) (assert(0), NULL)
#endif
/* PyFunctionFastCall.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCall(func, args, nargs)\
__Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallDict((func), (args), (nargs), NULL)
#if 1 || PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030600B1
static PyObject *__Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallDict(PyObject *func, PyObject **args, Py_ssize_t nargs, PyObject *kwargs);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallDict(func, args, nargs, kwargs) _PyFunction_FastCallDict(func, args, nargs, kwargs)
#endif
#define __Pyx_BUILD_ASSERT_EXPR(cond)\
(sizeof(char [1 - 2*!(cond)]) - 1)
#ifndef Py_MEMBER_SIZE
#define Py_MEMBER_SIZE(type, member) sizeof(((type *)0)->member)
#endif
static size_t __pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset = 0;
#include "frameobject.h"
#define __Pxy_PyFrame_Initialize_Offsets()\
((void)__Pyx_BUILD_ASSERT_EXPR(sizeof(PyFrameObject) == offsetof(PyFrameObject, f_localsplus) + Py_MEMBER_SIZE(PyFrameObject, f_localsplus)),\
(void)(__pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset = ((size_t)PyFrame_Type.tp_basicsize) - Py_MEMBER_SIZE(PyFrameObject, f_localsplus)))
#define __Pyx_PyFrame_GetLocalsplus(frame)\
(assert(__pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset), (PyObject **)(((char *)(frame)) + __pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset))
#endif
/* PyObjectCall2Args.proto */
static CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(PyObject* function, PyObject* arg1, PyObject* arg2);
/* PyObjectCallMethO.proto */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_CallMethO(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg);
#endif
/* PyObjectCallOneArg.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg);
/* IncludeStringH.proto */
#include
/* BytesEquals.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyBytes_Equals(PyObject* s1, PyObject* s2, int equals);
/* UnicodeEquals.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyUnicode_Equals(PyObject* s1, PyObject* s2, int equals);
/* StrEquals.proto */
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyString_Equals __Pyx_PyUnicode_Equals
#else
#define __Pyx_PyString_Equals __Pyx_PyBytes_Equals
#endif
/* UnaryNegOverflows.proto */
#define UNARY_NEG_WOULD_OVERFLOW(x)\
(((x) < 0) & ((unsigned long)(x) == 0-(unsigned long)(x)))
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_array_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_array_get_memview(struct __pyx_array_obj *); /*proto*/
/* GetAttr.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetAttr(PyObject *, PyObject *);
/* GetItemInt.proto */
#define __Pyx_GetItemInt(o, i, type, is_signed, to_py_func, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck)\
(__Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(i, type, is_signed) ?\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_Fast(o, (Py_ssize_t)i, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck) :\
(is_list ? (PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "list index out of range"), (PyObject*)NULL) :\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(o, to_py_func(i))))
#define __Pyx_GetItemInt_List(o, i, type, is_signed, to_py_func, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck)\
(__Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(i, type, is_signed) ?\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_List_Fast(o, (Py_ssize_t)i, wraparound, boundscheck) :\
(PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "list index out of range"), (PyObject*)NULL))
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_List_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
int wraparound, int boundscheck);
#define __Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple(o, i, type, is_signed, to_py_func, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck)\
(__Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(i, type, is_signed) ?\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple_Fast(o, (Py_ssize_t)i, wraparound, boundscheck) :\
(PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "tuple index out of range"), (PyObject*)NULL))
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
int wraparound, int boundscheck);
static PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(PyObject *o, PyObject* j);
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
int is_list, int wraparound, int boundscheck);
/* ObjectGetItem.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(PyObject *obj, PyObject* key);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(obj, key) PyObject_GetItem(obj, key)
#endif
/* decode_c_string_utf16.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors) {
int byteorder = 0;
return PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(s, size, errors, &byteorder);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16LE(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors) {
int byteorder = -1;
return PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(s, size, errors, &byteorder);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16BE(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors) {
int byteorder = 1;
return PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(s, size, errors, &byteorder);
}
/* decode_c_string.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_decode_c_string(
const char* cstring, Py_ssize_t start, Py_ssize_t stop,
const char* encoding, const char* errors,
PyObject* (*decode_func)(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors));
/* PyErrExceptionMatches.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatches(err) __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatchesInState(__pyx_tstate, err)
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatchesInState(PyThreadState* tstate, PyObject* err);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatches(err) PyErr_ExceptionMatches(err)
#endif
/* GetAttr3.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetAttr3(PyObject *, PyObject *, PyObject *);
/* PyDictVersioning.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS && CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define __PYX_DICT_VERSION_INIT ((PY_UINT64_T) -1)
#define __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict) (((PyDictObject*)(dict))->ma_version_tag)
#define __PYX_UPDATE_DICT_CACHE(dict, value, cache_var, version_var)\
(version_var) = __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict);\
(cache_var) = (value);
#define __PYX_PY_DICT_LOOKUP_IF_MODIFIED(VAR, DICT, LOOKUP) {\
static PY_UINT64_T __pyx_dict_version = 0;\
static PyObject *__pyx_dict_cached_value = NULL;\
if (likely(__PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(DICT) == __pyx_dict_version)) {\
(VAR) = __pyx_dict_cached_value;\
} else {\
(VAR) = __pyx_dict_cached_value = (LOOKUP);\
__pyx_dict_version = __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(DICT);\
}\
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PY_UINT64_T __Pyx_get_tp_dict_version(PyObject *obj);
static CYTHON_INLINE PY_UINT64_T __Pyx_get_object_dict_version(PyObject *obj);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_object_dict_version_matches(PyObject* obj, PY_UINT64_T tp_dict_version, PY_UINT64_T obj_dict_version);
#else
#define __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict) (0)
#define __PYX_UPDATE_DICT_CACHE(dict, value, cache_var, version_var)
#define __PYX_PY_DICT_LOOKUP_IF_MODIFIED(VAR, DICT, LOOKUP) (VAR) = (LOOKUP);
#endif
/* GetModuleGlobalName.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(var, name) {\
static PY_UINT64_T __pyx_dict_version = 0;\
static PyObject *__pyx_dict_cached_value = NULL;\
(var) = (likely(__pyx_dict_version == __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(__pyx_d))) ?\
(likely(__pyx_dict_cached_value) ? __Pyx_NewRef(__pyx_dict_cached_value) : __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(name)) :\
__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name, &__pyx_dict_version, &__pyx_dict_cached_value);\
}
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalNameUncached(var, name) {\
PY_UINT64_T __pyx_dict_version;\
PyObject *__pyx_dict_cached_value;\
(var) = __Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name, &__pyx_dict_version, &__pyx_dict_cached_value);\
}
static PyObject *__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(PyObject *name, PY_UINT64_T *dict_version, PyObject **dict_cached_value);
#else
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(var, name) (var) = __Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name)
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalNameUncached(var, name) (var) = __Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name)
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(PyObject *name);
#endif
/* RaiseTooManyValuesToUnpack.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseTooManyValuesError(Py_ssize_t expected);
/* RaiseNeedMoreValuesToUnpack.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseNeedMoreValuesError(Py_ssize_t index);
/* RaiseNoneIterError.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseNoneNotIterableError(void);
/* ExtTypeTest.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_TypeTest(PyObject *obj, PyTypeObject *type);
/* GetTopmostException.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
static _PyErr_StackItem * __Pyx_PyErr_GetTopmostException(PyThreadState *tstate);
#endif
/* SaveResetException.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_ExceptionSave(type, value, tb) __Pyx__ExceptionSave(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionSave(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#define __Pyx_ExceptionReset(type, value, tb) __Pyx__ExceptionReset(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionReset(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb);
#else
#define __Pyx_ExceptionSave(type, value, tb) PyErr_GetExcInfo(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ExceptionReset(type, value, tb) PyErr_SetExcInfo(type, value, tb)
#endif
/* GetException.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_GetException(type, value, tb) __Pyx__GetException(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static int __Pyx__GetException(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#else
static int __Pyx_GetException(PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#endif
/* SwapException.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_ExceptionSwap(type, value, tb) __Pyx__ExceptionSwap(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionSwap(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ExceptionSwap(PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#endif
/* Import.proto */
static PyObject *__Pyx_Import(PyObject *name, PyObject *from_list, int level);
/* FastTypeChecks.proto */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
#define __Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, type) __Pyx_IsSubtype(Py_TYPE(obj), (PyTypeObject *)type)
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_IsSubtype(PyTypeObject *a, PyTypeObject *b);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(PyObject *err, PyObject *type);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches2(PyObject *err, PyObject *type1, PyObject *type2);
#else
#define __Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, type) PyObject_TypeCheck(obj, (PyTypeObject *)type)
#define __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type) PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type)
#define __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches2(err, type1, type2) (PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type1) || PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type2))
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyException_Check(obj) __Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, PyExc_Exception)
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_memoryview_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /*proto*/
/* ListCompAppend.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS && CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_ListComp_Append(PyObject* list, PyObject* x) {
PyListObject* L = (PyListObject*) list;
Py_ssize_t len = Py_SIZE(list);
if (likely(L->allocated > len)) {
Py_INCREF(x);
PyList_SET_ITEM(list, len, x);
__Pyx_SET_SIZE(list, len + 1);
return 0;
}
return PyList_Append(list, x);
}
#else
#define __Pyx_ListComp_Append(L,x) PyList_Append(L,x)
#endif
/* PyIntBinop.proto */
#if !CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
static PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_AddObjC(PyObject *op1, PyObject *op2, long intval, int inplace, int zerodivision_check);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyInt_AddObjC(op1, op2, intval, inplace, zerodivision_check)\
(inplace ? PyNumber_InPlaceAdd(op1, op2) : PyNumber_Add(op1, op2))
#endif
/* ListExtend.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyList_Extend(PyObject* L, PyObject* v) {
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
PyObject* none = _PyList_Extend((PyListObject*)L, v);
if (unlikely(!none))
return -1;
Py_DECREF(none);
return 0;
#else
return PyList_SetSlice(L, PY_SSIZE_T_MAX, PY_SSIZE_T_MAX, v);
#endif
}
/* ListAppend.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS && CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyList_Append(PyObject* list, PyObject* x) {
PyListObject* L = (PyListObject*) list;
Py_ssize_t len = Py_SIZE(list);
if (likely(L->allocated > len) & likely(len > (L->allocated >> 1))) {
Py_INCREF(x);
PyList_SET_ITEM(list, len, x);
__Pyx_SET_SIZE(list, len + 1);
return 0;
}
return PyList_Append(list, x);
}
#else
#define __Pyx_PyList_Append(L,x) PyList_Append(L,x)
#endif
/* None.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseUnboundLocalError(const char *varname);
/* ImportFrom.proto */
static PyObject* __Pyx_ImportFrom(PyObject* module, PyObject* name);
/* HasAttr.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_HasAttr(PyObject *, PyObject *);
/* PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03070000
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict PyObject_GenericGetAttr
#endif
/* PyObject_GenericGetAttr.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03070000
static PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr PyObject_GenericGetAttr
#endif
/* SetVTable.proto */
static int __Pyx_SetVtable(PyObject *dict, void *vtable);
/* PyObjectGetAttrStrNoError.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStrNoError(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
/* SetupReduce.proto */
static int __Pyx_setup_reduce(PyObject* type_obj);
/* CLineInTraceback.proto */
#ifdef CYTHON_CLINE_IN_TRACEBACK
#define __Pyx_CLineForTraceback(tstate, c_line) (((CYTHON_CLINE_IN_TRACEBACK)) ? c_line : 0)
#else
static int __Pyx_CLineForTraceback(PyThreadState *tstate, int c_line);
#endif
/* CodeObjectCache.proto */
typedef struct {
PyCodeObject* code_object;
int code_line;
} __Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry;
struct __Pyx_CodeObjectCache {
int count;
int max_count;
__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry* entries;
};
static struct __Pyx_CodeObjectCache __pyx_code_cache = {0,0,NULL};
static int __pyx_bisect_code_objects(__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry* entries, int count, int code_line);
static PyCodeObject *__pyx_find_code_object(int code_line);
static void __pyx_insert_code_object(int code_line, PyCodeObject* code_object);
/* AddTraceback.proto */
static void __Pyx_AddTraceback(const char *funcname, int c_line,
int py_line, const char *filename);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
static int __Pyx_GetBuffer(PyObject *obj, Py_buffer *view, int flags);
static void __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(Py_buffer *view);
#else
#define __Pyx_GetBuffer PyObject_GetBuffer
#define __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer PyBuffer_Release
#endif
/* BufferStructDeclare.proto */
typedef struct {
Py_ssize_t shape, strides, suboffsets;
} __Pyx_Buf_DimInfo;
typedef struct {
size_t refcount;
Py_buffer pybuffer;
} __Pyx_Buffer;
typedef struct {
__Pyx_Buffer *rcbuffer;
char *data;
__Pyx_Buf_DimInfo diminfo[8];
} __Pyx_LocalBuf_ND;
/* MemviewSliceIsContig.proto */
static int __pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(const __Pyx_memviewslice mvs, char order, int ndim);
/* OverlappingSlices.proto */
static int __pyx_slices_overlap(__Pyx_memviewslice *slice1,
__Pyx_memviewslice *slice2,
int ndim, size_t itemsize);
/* Capsule.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__pyx_capsule_create(void *p, const char *sig);
/* IsLittleEndian.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_Is_Little_Endian(void);
/* BufferFormatCheck.proto */
static const char* __Pyx_BufFmt_CheckString(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx, const char* ts);
static void __Pyx_BufFmt_Init(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx,
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem* stack,
__Pyx_TypeInfo* type);
/* TypeInfoCompare.proto */
static int __pyx_typeinfo_cmp(__Pyx_TypeInfo *a, __Pyx_TypeInfo *b);
/* MemviewSliceValidateAndInit.proto */
static int __Pyx_ValidateAndInit_memviewslice(
int *axes_specs,
int c_or_f_flag,
int buf_flags,
int ndim,
__Pyx_TypeInfo *dtype,
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem stack[],
__Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice,
PyObject *original_obj);
/* ObjectToMemviewSlice.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE __Pyx_memviewslice __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_dsds_double(PyObject *, int writable_flag);
/* ObjectToMemviewSlice.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE __Pyx_memviewslice __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_ds_double(PyObject *, int writable_flag);
/* MemviewSliceCopyTemplate.proto */
static __Pyx_memviewslice
__pyx_memoryview_copy_new_contig(const __Pyx_memviewslice *from_mvs,
const char *mode, int ndim,
size_t sizeof_dtype, int contig_flag,
int dtype_is_object);
/* GCCDiagnostics.proto */
#if defined(__GNUC__) && (__GNUC__ > 4 || (__GNUC__ == 4 && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= 6))
#define __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#endif
/* CIntFromPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyInt_As_int(PyObject *);
/* CIntFromPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE long __Pyx_PyInt_As_long(PyObject *);
/* CIntToPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(int value);
/* CIntToPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_From_long(long value);
/* CIntFromPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE char __Pyx_PyInt_As_char(PyObject *);
/* CheckBinaryVersion.proto */
static int __Pyx_check_binary_version(void);
/* InitStrings.proto */
static int __Pyx_InitStrings(__Pyx_StringTabEntry *t);
static PyObject *__pyx_array_get_memview(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto*/
static char *__pyx_memoryview_get_item_pointer(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_is_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_obj); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assignment(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_dst, PyObject *__pyx_v_src); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assign_scalar(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_dst, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_indexed(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_convert_item_to_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_assign_item_from_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_convert_item_to_object(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_assign_item_from_object(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
/* Module declarations from 'libc.math' */
/* Module declarations from 'libc.float' */
/* Module declarations from 'pept.processing.circles_ext' */
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_array_type = 0;
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_MemviewEnum_type = 0;
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_memoryview_type = 0;
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_type = 0;
static PyObject *generic = 0;
static PyObject *strided = 0;
static PyObject *indirect = 0;
static PyObject *contiguous = 0;
static PyObject *indirect_contiguous = 0;
static int __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used;
static PyThread_type_lock __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[8];
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_fabs(double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist(double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist2(double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_triangle(double, double, double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist_pl(double, double, double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circular_segment(double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_zero_corner(Py_ssize_t *, double, double, double, double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_one_corner(Py_ssize_t *, double, double, double, double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_two_corner(Py_ssize_t *, double, double, double, double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_three_corner(Py_ssize_t *, double, double, double, double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_four_corner(Py_ssize_t *, double, double, double, double, double, double, double); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext(__Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, int __pyx_skip_dispatch); /*proto*/
static struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_array_new(PyObject *, Py_ssize_t, char *, char *, char *); /*proto*/
static void *__pyx_align_pointer(void *, size_t); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_new(PyObject *, int, int, __Pyx_TypeInfo *); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE int __pyx_memoryview_check(PyObject *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *_unellipsify(PyObject *, int); /*proto*/
static PyObject *assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *, int); /*proto*/
static struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_memview_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_slice_memviewslice(__Pyx_memviewslice *, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, int, int, int *, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, int, int, int, int); /*proto*/
static char *__pyx_pybuffer_index(Py_buffer *, char *, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memslice_transpose(__Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_fromslice(__Pyx_memviewslice, int, PyObject *(*)(char *), int (*)(char *, PyObject *), int); /*proto*/
static __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, __Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, __Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, __Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t); /*proto*/
static char __pyx_get_best_slice_order(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int); /*proto*/
static void _copy_strided_to_strided(char *, Py_ssize_t *, char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, size_t); /*proto*/
static void copy_strided_to_strided(__Pyx_memviewslice *, __Pyx_memviewslice *, int, size_t); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_memoryview_slice_get_size(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_fill_contig_strides_array(Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t, int, char); /*proto*/
static void *__pyx_memoryview_copy_data_to_temp(__Pyx_memviewslice *, __Pyx_memviewslice *, char, int); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err_extents(int, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err_dim(PyObject *, char *, int); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err(PyObject *, char *); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_copy_contents(__Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, int, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice(char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_slice_assign_scalar(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, size_t, void *, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview__slice_assign_scalar(char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, size_t, void *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *, PyObject *); /*proto*/
static __Pyx_TypeInfo __Pyx_TypeInfo_double = { "double", NULL, sizeof(double), { 0 }, 0, 'R', 0, 0 };
#define __Pyx_MODULE_NAME "pept.processing.circles_ext"
extern int __pyx_module_is_main_pept__processing__circles_ext;
int __pyx_module_is_main_pept__processing__circles_ext = 0;
/* Implementation of 'pept.processing.circles_ext' */
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_range;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_ValueError;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_MemoryError;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_enumerate;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_TypeError;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_Ellipsis;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_id;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_IndexError;
static const char __pyx_k_O[] = "O";
static const char __pyx_k_c[] = "c";
static const char __pyx_k_id[] = "id";
static const char __pyx_k_new[] = "__new__";
static const char __pyx_k_obj[] = "obj";
static const char __pyx_k_base[] = "base";
static const char __pyx_k_dict[] = "__dict__";
static const char __pyx_k_main[] = "__main__";
static const char __pyx_k_mode[] = "mode";
static const char __pyx_k_name[] = "name";
static const char __pyx_k_ndim[] = "ndim";
static const char __pyx_k_pack[] = "pack";
static const char __pyx_k_size[] = "size";
static const char __pyx_k_step[] = "step";
static const char __pyx_k_stop[] = "stop";
static const char __pyx_k_test[] = "__test__";
static const char __pyx_k_xlim[] = "xlim";
static const char __pyx_k_ylim[] = "ylim";
static const char __pyx_k_ASCII[] = "ASCII";
static const char __pyx_k_class[] = "__class__";
static const char __pyx_k_error[] = "error";
static const char __pyx_k_flags[] = "flags";
static const char __pyx_k_radii[] = "radii";
static const char __pyx_k_range[] = "range";
static const char __pyx_k_shape[] = "shape";
static const char __pyx_k_start[] = "start";
static const char __pyx_k_encode[] = "encode";
static const char __pyx_k_format[] = "format";
static const char __pyx_k_import[] = "__import__";
static const char __pyx_k_name_2[] = "__name__";
static const char __pyx_k_pickle[] = "pickle";
static const char __pyx_k_pixels[] = "pixels";
static const char __pyx_k_reduce[] = "__reduce__";
static const char __pyx_k_struct[] = "struct";
static const char __pyx_k_unpack[] = "unpack";
static const char __pyx_k_update[] = "update";
static const char __pyx_k_fortran[] = "fortran";
static const char __pyx_k_memview[] = "memview";
static const char __pyx_k_Ellipsis[] = "Ellipsis";
static const char __pyx_k_getstate[] = "__getstate__";
static const char __pyx_k_itemsize[] = "itemsize";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_type[] = "__pyx_type";
static const char __pyx_k_setstate[] = "__setstate__";
static const char __pyx_k_TypeError[] = "TypeError";
static const char __pyx_k_enumerate[] = "enumerate";
static const char __pyx_k_positions[] = "positions";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_state[] = "__pyx_state";
static const char __pyx_k_reduce_ex[] = "__reduce_ex__";
static const char __pyx_k_IndexError[] = "IndexError";
static const char __pyx_k_ValueError[] = "ValueError";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_result[] = "__pyx_result";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_vtable[] = "__pyx_vtable__";
static const char __pyx_k_MemoryError[] = "MemoryError";
static const char __pyx_k_PickleError[] = "PickleError";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_checksum[] = "__pyx_checksum";
static const char __pyx_k_stringsource[] = "stringsource";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_getbuffer[] = "__pyx_getbuffer";
static const char __pyx_k_reduce_cython[] = "__reduce_cython__";
static const char __pyx_k_View_MemoryView[] = "View.MemoryView";
static const char __pyx_k_allocate_buffer[] = "allocate_buffer";
static const char __pyx_k_dtype_is_object[] = "dtype_is_object";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_PickleError[] = "__pyx_PickleError";
static const char __pyx_k_setstate_cython[] = "__setstate_cython__";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_unpickle_Enum[] = "__pyx_unpickle_Enum";
static const char __pyx_k_cline_in_traceback[] = "cline_in_traceback";
static const char __pyx_k_strided_and_direct[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_strided_and_indirect[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_contiguous_and_direct[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_MemoryView_of_r_object[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_MemoryView_of_r_at_0x_x[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_contiguous_and_indirect[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_Cannot_index_with_type_s[] = "Cannot index with type '%s'";
static const char __pyx_k_Invalid_shape_in_axis_d_d[] = "Invalid shape in axis %d: %d.";
static const char __pyx_k_itemsize_0_for_cython_array[] = "itemsize <= 0 for cython.array";
static const char __pyx_k_unable_to_allocate_array_data[] = "unable to allocate array data.";
static const char __pyx_k_strided_and_direct_or_indirect[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_Buffer_view_does_not_expose_stri[] = "Buffer view does not expose strides";
static const char __pyx_k_Can_only_create_a_buffer_that_is[] = "Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.";
static const char __pyx_k_Cannot_assign_to_read_only_memor[] = "Cannot assign to read-only memoryview";
static const char __pyx_k_Cannot_create_writable_memory_vi[] = "Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview";
static const char __pyx_k_Empty_shape_tuple_for_cython_arr[] = "Empty shape tuple for cython.array";
static const char __pyx_k_Incompatible_checksums_s_vs_0xb0[] = "Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))";
static const char __pyx_k_Indirect_dimensions_not_supporte[] = "Indirect dimensions not supported";
static const char __pyx_k_Invalid_mode_expected_c_or_fortr[] = "Invalid mode, expected 'c' or 'fortran', got %s";
static const char __pyx_k_Out_of_bounds_on_buffer_access_a[] = "Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)";
static const char __pyx_k_Unable_to_convert_item_to_object[] = "Unable to convert item to object";
static const char __pyx_k_got_differing_extents_in_dimensi[] = "got differing extents in dimension %d (got %d and %d)";
static const char __pyx_k_no_default___reduce___due_to_non[] = "no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__";
static const char __pyx_k_unable_to_allocate_shape_and_str[] = "unable to allocate shape and strides.";
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_ASCII;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Buffer_view_does_not_expose_stri;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Can_only_create_a_buffer_that_is;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Cannot_assign_to_read_only_memor;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Cannot_create_writable_memory_vi;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Cannot_index_with_type_s;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_Ellipsis;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Empty_shape_tuple_for_cython_arr;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Incompatible_checksums_s_vs_0xb0;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_IndexError;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Indirect_dimensions_not_supporte;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Invalid_mode_expected_c_or_fortr;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Invalid_shape_in_axis_d_d;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_MemoryError;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_MemoryView_of_r_at_0x_x;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_MemoryView_of_r_object;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_b_O;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Out_of_bounds_on_buffer_access_a;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_PickleError;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_TypeError;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_Unable_to_convert_item_to_object;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_ValueError;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_View_MemoryView;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_allocate_buffer;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_base;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_c;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_u_c;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_class;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_cline_in_traceback;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_contiguous_and_direct;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_contiguous_and_indirect;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_dict;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_dtype_is_object;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_encode;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_enumerate;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_error;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_flags;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_format;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_fortran;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_u_fortran;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_getstate;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_got_differing_extents_in_dimensi;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_id;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_import;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_itemsize;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_itemsize_0_for_cython_array;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_main;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_memview;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_mode;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_name;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_name_2;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_ndim;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_new;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_obj;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pack;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pickle;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pixels;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_positions;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_PickleError;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_checksum;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_getbuffer;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_result;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_state;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_type;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_unpickle_Enum;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_pyx_vtable;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_radii;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_range;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_reduce;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_reduce_cython;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_reduce_ex;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_setstate;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_setstate_cython;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_shape;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_size;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_start;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_step;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_stop;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_strided_and_direct;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_strided_and_direct_or_indirect;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_strided_and_indirect;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_stringsource;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_struct;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_test;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_unable_to_allocate_array_data;
static PyObject *__pyx_kp_s_unable_to_allocate_shape_and_str;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_unpack;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_update;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_xlim;
static PyObject *__pyx_n_s_ylim;
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext(CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_self, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_pixels, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_positions, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_radii, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_xlim, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_ylim); /* proto */
static int __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array___cinit__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_itemsize, PyObject *__pyx_v_format, PyObject *__pyx_v_mode, int __pyx_v_allocate_buffer); /* proto */
static int __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_2__getbuffer__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /* proto */
static void __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_4__dealloc__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_7memview___get__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_6__len__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_8__getattr__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_attr); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_10__getitem__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item); /* proto */
static int __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_12__setitem__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_array___reduce_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_array_2__setstate_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /* proto */
static int __pyx_MemviewEnum___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_4Enum___init__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_name); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_MemviewEnum___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_4Enum_2__repr__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_MemviewEnum___reduce_cython__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_MemviewEnum_2__setstate_cython__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /* proto */
static int __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview___cinit__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_obj, int __pyx_v_flags, int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object); /* proto */
static void __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_2__dealloc__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4__getitem__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index); /* proto */
static int __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6__setitem__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto */
static int __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8__getbuffer__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_1T___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4base___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_5shape___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_7strides___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10suboffsets___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4ndim___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8itemsize___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6nbytes___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4size___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10__len__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_12__repr__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_14__str__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_16is_c_contig(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_18is_f_contig(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_20copy(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_22copy_fortran(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryview___reduce_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryview_2__setstate_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /* proto */
static void __pyx_memoryviewslice___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice___dealloc__(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice_4base___get__(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryviewslice___reduce_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryviewslice_2__setstate_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView___pyx_unpickle_Enum(CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_type, long __pyx_v___pyx_checksum, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /* proto */
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new_array(PyTypeObject *t, PyObject *a, PyObject *k); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new_Enum(PyTypeObject *t, PyObject *a, PyObject *k); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new_memoryview(PyTypeObject *t, PyObject *a, PyObject *k); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new__memoryviewslice(PyTypeObject *t, PyObject *a, PyObject *k); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_int_0;
static PyObject *__pyx_int_1;
static PyObject *__pyx_int_184977713;
static PyObject *__pyx_int_neg_1;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple_;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__2;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__3;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__4;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__5;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__6;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__7;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__8;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__9;
static PyObject *__pyx_slice__15;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__10;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__11;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__12;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__13;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__14;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__16;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__17;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__18;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__19;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__20;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__21;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__22;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__23;
static PyObject *__pyx_tuple__24;
static PyObject *__pyx_codeobj__25;
/* Late includes */
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":55
*
*
* cdef inline double fabs(double x) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return (x if x >= 0 else -x)
*
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_fabs(double __pyx_v_x) {
double __pyx_r;
double __pyx_t_1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":56
*
* cdef inline double fabs(double x) nogil:
* return (x if x >= 0 else -x) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
if (((__pyx_v_x >= 0.0) != 0)) {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_x;
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = (-__pyx_v_x);
}
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":55
*
*
* cdef inline double fabs(double x) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return (x if x >= 0 else -x)
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":59
*
*
* cdef inline double dist(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Distance between two 2D points
* return sqrt((x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2)
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist(double __pyx_v_x1, double __pyx_v_y1, double __pyx_v_x2, double __pyx_v_y2) {
double __pyx_r;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":61
* cdef inline double dist(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil:
* # Distance between two 2D points
* return sqrt((x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = sqrt((pow((__pyx_v_x1 - __pyx_v_x2), 2.0) + pow((__pyx_v_y1 - __pyx_v_y2), 2.0)));
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":59
*
*
* cdef inline double dist(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Distance between two 2D points
* return sqrt((x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2)
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":64
*
*
* cdef inline double dist2(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Squared distance between two 2D points
* return (x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist2(double __pyx_v_x1, double __pyx_v_y1, double __pyx_v_x2, double __pyx_v_y2) {
double __pyx_r;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":66
* cdef inline double dist2(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil:
* # Squared distance between two 2D points
* return (x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = (pow((__pyx_v_x1 - __pyx_v_x2), 2.0) + pow((__pyx_v_y1 - __pyx_v_y2), 2.0));
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":64
*
*
* cdef inline double dist2(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Squared distance between two 2D points
* return (x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":69
*
*
* cdef inline double term(double r, double _c, double _p) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Term in calculation of `one_corner`
* # Same for xc / xp and yc / yp
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(double __pyx_v_r, double __pyx_v__c, double __pyx_v__p) {
double __pyx_r;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":72
* # Term in calculation of `one_corner`
* # Same for xc / xp and yc / yp
* return sqrt(r ** 2 - (_c - _p) ** 2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = sqrt((pow(__pyx_v_r, 2.0) - pow((__pyx_v__c - __pyx_v__p), 2.0)));
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":69
*
*
* cdef inline double term(double r, double _c, double _p) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Term in calculation of `one_corner`
* # Same for xc / xp and yc / yp
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":75
*
*
* cdef inline double triangle( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3
* ) nogil:
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_triangle(double __pyx_v_x1, double __pyx_v_y1, double __pyx_v_x2, double __pyx_v_y2, double __pyx_v_x3, double __pyx_v_y3) {
double __pyx_r;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":78
* double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3
* ) nogil:
* return 0.5 * fabs(x1 * (y2 - y3) + x2 * (y3 - y1) + x3 * (y1 - y2)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = (0.5 * __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_fabs((((__pyx_v_x1 * (__pyx_v_y2 - __pyx_v_y3)) + (__pyx_v_x2 * (__pyx_v_y3 - __pyx_v_y1))) + (__pyx_v_x3 * (__pyx_v_y1 - __pyx_v_y2)))));
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":75
*
*
* cdef inline double triangle( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3
* ) nogil:
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":81
*
*
* cdef inline double dist_pl( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* double x0,
* double y0,
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist_pl(double __pyx_v_x0, double __pyx_v_y0, double __pyx_v_x1, double __pyx_v_y1, double __pyx_v_x2, double __pyx_v_y2) {
double __pyx_v_denom;
double __pyx_v_nom;
double __pyx_r;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":91
* # Distance from a point (x0, y0) to a line defined by two points
* # (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)
* denom = dist(x1, y1, x2, y2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* nom = fabs((y2 - y1) * x0 - (x2 - x1) * y0 + x2 * y1 - y2 * x1)
*
*/
__pyx_v_denom = __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist(__pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1, __pyx_v_x2, __pyx_v_y2);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":92
* # (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)
* denom = dist(x1, y1, x2, y2)
* nom = fabs((y2 - y1) * x0 - (x2 - x1) * y0 + x2 * y1 - y2 * x1) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return nom / denom
*/
__pyx_v_nom = __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_fabs((((((__pyx_v_y2 - __pyx_v_y1) * __pyx_v_x0) - ((__pyx_v_x2 - __pyx_v_x1) * __pyx_v_y0)) + (__pyx_v_x2 * __pyx_v_y1)) - (__pyx_v_y2 * __pyx_v_x1)));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":94
* nom = fabs((y2 - y1) * x0 - (x2 - x1) * y0 + x2 * y1 - y2 * x1)
*
* return nom / denom # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = (__pyx_v_nom / __pyx_v_denom);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":81
*
*
* cdef inline double dist_pl( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* double x0,
* double y0,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":97
*
*
* cdef inline double circular_segment(double r, double h) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Area of a circular segment from a circle of radius r and a line
* # If the distance from the circle centre to the line is d, then
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circular_segment(double __pyx_v_r, double __pyx_v_h) {
double __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":101
* # If the distance from the circle centre to the line is d, then
* # h = r - d
* if h < 0.0: # Happens for very small distances (d = r * 1e-13) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return 0.0
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_h < 0.0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":102
* # h = r - d
* if h < 0.0: # Happens for very small distances (d = r * 1e-13)
* return 0.0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return r ** 2 * acos((r - h) / r) - (r - h) * sqrt(2 * r * h - h ** 2)
*/
__pyx_r = 0.0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":101
* # If the distance from the circle centre to the line is d, then
* # h = r - d
* if h < 0.0: # Happens for very small distances (d = r * 1e-13) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return 0.0
*
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":104
* return 0.0
*
* return r ** 2 * acos((r - h) / r) - (r - h) * sqrt(2 * r * h - h ** 2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = ((pow(__pyx_v_r, 2.0) * acos(((__pyx_v_r - __pyx_v_h) / __pyx_v_r))) - ((__pyx_v_r - __pyx_v_h) * sqrt((((2.0 * __pyx_v_r) * __pyx_v_h) - pow(__pyx_v_h, 2.0)))));
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":97
*
*
* cdef inline double circular_segment(double r, double h) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Area of a circular segment from a circle of radius r and a line
* # If the distance from the circle centre to the line is d, then
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":107
*
*
* cdef inline double zero_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_zero_corner(CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_corners, double __pyx_v_px, double __pyx_v_py, double __pyx_v_xsize, double __pyx_v_ysize, double __pyx_v_x0, double __pyx_v_y0, double __pyx_v_r) {
double __pyx_v_h;
double __pyx_v_area;
double __pyx_v_xmin;
double __pyx_v_xmax;
double __pyx_v_ymin;
double __pyx_v_ymax;
double __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":146
* # intersections above and h = (r - d)
* cdef double h
* cdef double area = 0. # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_area = 0.;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":147
* cdef double h
* cdef double area = 0.
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmin = (__pyx_v_px - (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":148
* cdef double area = 0.
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmax = (__pyx_v_px + (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":149
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*
*/
__pyx_v_ymin = (__pyx_v_py - (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":150
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Corner case - if zero corners are inside, there might be no intersection
*/
__pyx_v_ymax = (__pyx_v_py + (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":154
* # Corner case - if zero corners are inside, there might be no intersection
* # This happens when the centre of the particle is in one of the corners
* if ((x0 <= xmin and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom left # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom right
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_x0 <= __pyx_v_xmin) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_2) {
goto __pyx_L5_next_or;
} else {
}
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_y0 <= __pyx_v_ymin) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_L5_next_or:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":155
* # This happens when the centre of the particle is in one of the corners
* if ((x0 <= xmin and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom left
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom right # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right
* (x0 <= xmin and y0 >= ymax)): # Top left
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_x0 >= __pyx_v_xmax) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_2) {
goto __pyx_L7_next_or;
} else {
}
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_y0 <= __pyx_v_ymin) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_L7_next_or:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":156
* if ((x0 <= xmin and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom left
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom right
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (x0 <= xmin and y0 >= ymax)): # Top left
* return 0.
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_x0 >= __pyx_v_xmax) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_2) {
goto __pyx_L9_next_or;
} else {
}
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_y0 >= __pyx_v_ymax) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_L9_next_or:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":157
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom right
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right
* (x0 <= xmin and y0 >= ymax)): # Top left # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return 0.
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_x0 <= __pyx_v_xmin) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_y0 >= __pyx_v_ymax) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L4_bool_binop_done:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":154
* # Corner case - if zero corners are inside, there might be no intersection
* # This happens when the centre of the particle is in one of the corners
* if ((x0 <= xmin and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom left # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom right
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right
*/
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":158
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right
* (x0 <= xmin and y0 >= ymax)): # Top left
* return 0. # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Particle is fully encapsulated
*/
__pyx_r = 0.;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":154
* # Corner case - if zero corners are inside, there might be no intersection
* # This happens when the centre of the particle is in one of the corners
* if ((x0 <= xmin and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom left # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom right
* (x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":161
*
* # Particle is fully encapsulated
* if xmin < x0 < xmax and ymin < y0 < ymax: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return M_PI * r * r
* # Below
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_xmin < __pyx_v_x0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_x0 < __pyx_v_xmax);
}
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_3) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_3;
goto __pyx_L13_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_ymin < __pyx_v_y0);
if (__pyx_t_3) {
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_y0 < __pyx_v_ymax);
}
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_3 != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L13_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":162
* # Particle is fully encapsulated
* if xmin < x0 < xmax and ymin < y0 < ymax:
* return M_PI * r * r # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Below
* elif xmin < x0 < xmax:
*/
__pyx_r = ((M_PI * __pyx_v_r) * __pyx_v_r);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":161
*
* # Particle is fully encapsulated
* if xmin < x0 < xmax and ymin < y0 < ymax: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return M_PI * r * r
* # Below
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":164
* return M_PI * r * r
* # Below
* elif xmin < x0 < xmax: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* h = ysize / 2 + r - fabs(py - y0)
* # Above
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_xmin < __pyx_v_x0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_x0 < __pyx_v_xmax);
}
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":165
* # Below
* elif xmin < x0 < xmax:
* h = ysize / 2 + r - fabs(py - y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Above
* else:
*/
__pyx_v_h = (((__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0) + __pyx_v_r) - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_fabs((__pyx_v_py - __pyx_v_y0)));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":164
* return M_PI * r * r
* # Below
* elif xmin < x0 < xmax: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* h = ysize / 2 + r - fabs(py - y0)
* # Above
*/
goto __pyx_L12;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":168
* # Above
* else:
* h = xsize / 2 + r - fabs(px - x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of the circular segment
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_h = (((__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0) + __pyx_v_r) - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_fabs((__pyx_v_px - __pyx_v_x0)));
}
__pyx_L12:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":171
*
* # Area of the circular segment
* area += circular_segment(r, h) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return area
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circular_segment(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_h));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":173
* area += circular_segment(r, h)
*
* return area # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_area;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":107
*
*
* cdef inline double zero_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":176
*
*
* cdef inline double one_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_one_corner(Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_corners, double __pyx_v_px, double __pyx_v_py, double __pyx_v_xsize, double __pyx_v_ysize, double __pyx_v_x0, double __pyx_v_y0, double __pyx_v_r) {
double __pyx_v_xc;
double __pyx_v_yc;
double __pyx_v_x1;
double __pyx_v_y1;
double __pyx_v_x2;
double __pyx_v_y2;
double __pyx_v_d;
double __pyx_v_h;
double __pyx_v_area;
double __pyx_v_xmin;
double __pyx_v_xmax;
double __pyx_v_ymin;
double __pyx_v_ymax;
double __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":213
*
* # The bounded corner coordinates
* cdef double xc = 0, yc = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
*/
__pyx_v_xc = 0.0;
__pyx_v_yc = 0.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":216
*
* # The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
* cdef double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Distance from circle centre x0, y0 to line defined by the two
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_y1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_x2 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_y2 = 0.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":222
* cdef double d, h
*
* cdef double area = 0. # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Pixel boundaries
*/
__pyx_v_area = 0.;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":225
*
* # Pixel boundaries
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmin = (__pyx_v_px - (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":226
* # Pixel boundaries
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmax = (__pyx_v_px + (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":227
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*
*/
__pyx_v_ymin = (__pyx_v_py - (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":228
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Lower left corner
*/
__pyx_v_ymax = (__pyx_v_py + (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":231
*
* # Lower left corner
* if corners[0] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmin
* yc = ymin
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (((__pyx_v_corners[0]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":232
* # Lower left corner
* if corners[0] == 1:
* xc = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":233
* if corners[0] == 1:
* xc = xmin
* yc = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_yc = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":235
* yc = ymin
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = yc
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = (__pyx_v_x0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":236
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0)
* y1 = yc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = xc
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = __pyx_v_yc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":238
* y1 = yc
*
* x2 = xc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = y0 + term(r, xc, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = __pyx_v_xc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":239
*
* x2 = xc
* y2 = y0 + term(r, xc, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Lower right corner
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = (__pyx_v_y0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":231
*
* # Lower left corner
* if corners[0] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmin
* yc = ymin
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":242
*
* # Lower right corner
* elif corners[1] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmax
* yc = ymin
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (((__pyx_v_corners[1]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":243
* # Lower right corner
* elif corners[1] == 1:
* xc = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":244
* elif corners[1] == 1:
* xc = xmax
* yc = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = xc
*/
__pyx_v_yc = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":246
* yc = ymin
*
* x1 = xc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = __pyx_v_xc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":247
*
* x1 = xc
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = (__pyx_v_y0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":249
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc, x0)
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = yc
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = (__pyx_v_x0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":250
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0)
* y2 = yc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Upper right corner
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = __pyx_v_yc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":242
*
* # Lower right corner
* elif corners[1] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmax
* yc = ymin
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":253
*
* # Upper right corner
* elif corners[2] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmax
* yc = ymax
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (((__pyx_v_corners[2]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":254
* # Upper right corner
* elif corners[2] == 1:
* xc = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":255
* elif corners[2] == 1:
* xc = xmax
* yc = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_yc = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":257
* yc = ymax
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = yc
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = (__pyx_v_x0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":258
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0)
* y1 = yc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = xc
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = __pyx_v_yc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":260
* y1 = yc
*
* x2 = xc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = y0 - term(r, xc, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = __pyx_v_xc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":261
*
* x2 = xc
* y2 = y0 - term(r, xc, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Upper left corner
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = (__pyx_v_y0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":253
*
* # Upper right corner
* elif corners[2] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmax
* yc = ymax
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":264
*
* # Upper left corner
* elif corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmin
* yc = ymax
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (((__pyx_v_corners[3]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":265
* # Upper left corner
* elif corners[3] == 1:
* xc = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":266
* elif corners[3] == 1:
* xc = xmin
* yc = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_yc = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":268
* yc = ymax
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = yc
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = (__pyx_v_x0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":269
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0)
* y1 = yc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = xc
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = __pyx_v_yc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":271
* y1 = yc
*
* x2 = xc # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = y0 - term(r, xc, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = __pyx_v_xc;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":272
*
* x2 = xc
* y2 = y0 - term(r, xc, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = (__pyx_v_y0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":264
*
* # Upper left corner
* elif corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc = xmin
* yc = ymax
*/
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":274
* y2 = y0 - term(r, xc, x0)
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* h = r - d
*
*/
__pyx_v_d = __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist_pl(__pyx_v_x0, __pyx_v_y0, __pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1, __pyx_v_x2, __pyx_v_y2);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":275
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
* h = r - d # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of the circular segment
*/
__pyx_v_h = (__pyx_v_r - __pyx_v_d);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":278
*
* # Area of the circular segment
* area += circular_segment(r, h) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of the triangle
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circular_segment(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_h));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":281
*
* # Area of the triangle
* area += dist(xc, yc, x1, y1) * dist(xc, yc, x2, y2) / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return area
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + ((__pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist(__pyx_v_xc, __pyx_v_yc, __pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1) * __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist(__pyx_v_xc, __pyx_v_yc, __pyx_v_x2, __pyx_v_y2)) / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":283
* area += dist(xc, yc, x1, y1) * dist(xc, yc, x2, y2) / 2
*
* return area # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_area;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":176
*
*
* cdef inline double one_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":286
*
*
* cdef inline double two_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_two_corner(Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_corners, double __pyx_v_px, double __pyx_v_py, double __pyx_v_xsize, double __pyx_v_ysize, double __pyx_v_x0, double __pyx_v_y0, double __pyx_v_r) {
double __pyx_v_xc1;
double __pyx_v_yc1;
double __pyx_v_xc2;
double __pyx_v_yc2;
double __pyx_v_x1;
double __pyx_v_y1;
double __pyx_v_x2;
double __pyx_v_y2;
double __pyx_v_d;
double __pyx_v_h;
double __pyx_v_area;
double __pyx_v_xmin;
double __pyx_v_xmax;
double __pyx_v_ymin;
double __pyx_v_ymax;
double __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":323
*
* # The bounded corner coordinates
* cdef double xc1 = 0, yc1 = 0, xc2 = 0, yc2 = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_yc1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_xc2 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_yc2 = 0.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":326
*
* # The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
* cdef double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Distance from circle centre x0, y0 to line defined by the two
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_y1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_x2 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_y2 = 0.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":332
* cdef double d, h
*
* cdef double area = 0. # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Pixel boundaries
*/
__pyx_v_area = 0.;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":335
*
* # Pixel boundaries
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmin = (__pyx_v_px - (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":336
* # Pixel boundaries
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmax = (__pyx_v_px + (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":337
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*
*/
__pyx_v_ymin = (__pyx_v_py - (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":338
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Bottom corners
*/
__pyx_v_ymax = (__pyx_v_py + (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":341
*
* # Bottom corners
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[0]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[1]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L4_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":342
* # Bottom corners
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":343
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmax
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":345
* yc1 = ymin
*
* xc2 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":346
*
* xc2 = xmax
* yc2 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = xc1
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":348
* yc2 = ymin
*
* x1 = xc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc1, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = __pyx_v_xc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":349
*
* x1 = xc1
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc1, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = xc2
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = (__pyx_v_y0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc1, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":351
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc1, x0)
*
* x2 = xc2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = y0 + term(r, xc2, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = __pyx_v_xc2;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":352
*
* x2 = xc2
* y2 = y0 + term(r, xc2, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Top corners
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = (__pyx_v_y0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc2, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":341
*
* # Bottom corners
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":355
*
* # Top corners
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymax
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[2]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L6_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[3]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L6_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":356
* # Top corners
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":357
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmax
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":359
* yc1 = ymax
*
* xc2 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":360
*
* xc2 = xmax
* yc2 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = xc1
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":362
* yc2 = ymax
*
* x1 = xc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = __pyx_v_xc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":363
*
* x1 = xc1
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = xc2
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = (__pyx_v_y0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc1, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":365
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0)
*
* x2 = xc2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = y0 - term(r, xc2, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = __pyx_v_xc2;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":366
*
* x2 = xc2
* y2 = y0 - term(r, xc2, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Right corners
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = (__pyx_v_y0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc2, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":355
*
* # Top corners
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymax
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":369
*
* # Right corners
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymin
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[1]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L8_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[2]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L8_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":370
* # Right corners
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1:
* xc1 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":371
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1:
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmax
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":373
* yc1 = ymin
*
* xc2 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":374
*
* xc2 = xmax
* yc2 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":376
* yc2 = ymax
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = yc1
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = (__pyx_v_x0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc1, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":377
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0)
* y1 = yc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc2, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = __pyx_v_yc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":379
* y1 = yc1
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc2, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = yc2
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = (__pyx_v_x0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc2, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":380
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc2, y0)
* y2 = yc2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Left corners
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = __pyx_v_yc2;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":369
*
* # Right corners
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymin
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":383
*
* # Left corners
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[0]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L10_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[3]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L10_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":384
* # Left corners
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":385
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmin
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":387
* yc1 = ymin
*
* xc2 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":388
*
* xc2 = xmin
* yc2 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":390
* yc2 = ymax
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = yc1
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = (__pyx_v_x0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc1, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":391
*
* x1 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0)
* y1 = yc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc2, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = __pyx_v_yc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":393
* y1 = yc1
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc2, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = yc2
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = (__pyx_v_x0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc2, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":394
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc2, y0)
* y2 = yc2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = __pyx_v_yc2;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":383
*
* # Left corners
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin
*/
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":396
* y2 = yc2
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* h = r - d
*
*/
__pyx_v_d = __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist_pl(__pyx_v_x0, __pyx_v_y0, __pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1, __pyx_v_x2, __pyx_v_y2);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":397
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
* h = r - d # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of the circular segment
*/
__pyx_v_h = (__pyx_v_r - __pyx_v_d);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":400
*
* # Area of the circular segment
* area += circular_segment(r, h) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of triangle1 and triangle2
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circular_segment(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_h));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":403
*
* # Area of triangle1 and triangle2
* area += triangle(x1, y1, xc2, yc2, xc1, yc1) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* area += triangle(x1, y1, xc2, yc2, x2, y2)
*
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_triangle(__pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1, __pyx_v_xc2, __pyx_v_yc2, __pyx_v_xc1, __pyx_v_yc1));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":404
* # Area of triangle1 and triangle2
* area += triangle(x1, y1, xc2, yc2, xc1, yc1)
* area += triangle(x1, y1, xc2, yc2, x2, y2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return area
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_triangle(__pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1, __pyx_v_xc2, __pyx_v_yc2, __pyx_v_x2, __pyx_v_y2));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":406
* area += triangle(x1, y1, xc2, yc2, x2, y2)
*
* return area # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_area;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":286
*
*
* cdef inline double two_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":409
*
*
* cdef inline double three_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_three_corner(Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_corners, double __pyx_v_px, double __pyx_v_py, double __pyx_v_xsize, double __pyx_v_ysize, double __pyx_v_x0, double __pyx_v_y0, double __pyx_v_r) {
double __pyx_v_xc1;
double __pyx_v_yc1;
CYTHON_UNUSED double __pyx_v_xc2;
CYTHON_UNUSED double __pyx_v_yc2;
double __pyx_v_xc3;
double __pyx_v_yc3;
double __pyx_v_xc4;
double __pyx_v_yc4;
double __pyx_v_x1;
double __pyx_v_y1;
double __pyx_v_x2;
double __pyx_v_y2;
double __pyx_v_d;
double __pyx_v_h;
double __pyx_v_area;
double __pyx_v_xmin;
double __pyx_v_xmax;
double __pyx_v_ymin;
double __pyx_v_ymax;
double __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":446
*
* # The bounded corner coordinates
* cdef double xc1 = 0, yc1 = 0, xc2 = 0, yc2 = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double xc3 = 0, yc3 = 0, xc4 = 0, yc4 = 0
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_yc1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_xc2 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_yc2 = 0.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":447
* # The bounded corner coordinates
* cdef double xc1 = 0, yc1 = 0, xc2 = 0, yc2 = 0
* cdef double xc3 = 0, yc3 = 0, xc4 = 0, yc4 = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
*/
__pyx_v_xc3 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_yc3 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_xc4 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_yc4 = 0.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":450
*
* # The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
* cdef double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Distance from circle centre x0, y0 to line defined by the two
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_y1 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_x2 = 0.0;
__pyx_v_y2 = 0.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":456
* cdef double d, h
*
* cdef double area = 0. # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Pixel boundaries
*/
__pyx_v_area = 0.;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":459
*
* # Pixel boundaries
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmin = (__pyx_v_px - (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":460
* # Pixel boundaries
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*/
__pyx_v_xmax = (__pyx_v_px + (__pyx_v_xsize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":461
* cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
*
*/
__pyx_v_ymin = (__pyx_v_py - (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":462
* cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
* cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
* cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Bottom right three corners
*/
__pyx_v_ymax = (__pyx_v_py + (__pyx_v_ysize / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":465
*
* # Bottom right three corners
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[0]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[1]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[2]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L4_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":466
* # Bottom right three corners
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":467
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmax
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":469
* yc1 = ymin
*
* xc2 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":470
*
* xc2 = xmax
* yc2 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc3 = xmax
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":472
* yc2 = ymin
*
* xc3 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc3 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc3 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":473
*
* xc3 = xmax
* yc3 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc4 = xmin # Corner outside
*/
__pyx_v_yc3 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":475
* yc3 = ymax
*
* xc4 = xmin # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc4 = ymax # Corner outside
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc4 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":476
*
* xc4 = xmin # Corner outside
* yc4 = ymax # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc3, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_yc4 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":478
* yc4 = ymax # Corner outside
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc3, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = yc3
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = (__pyx_v_x0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc3, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":479
*
* x1 = x0 - term(r, yc3, y0)
* y1 = yc3 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = xc1
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = __pyx_v_yc3;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":481
* y1 = yc3
*
* x2 = xc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = y0 + term(r, xc1, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = __pyx_v_xc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":482
*
* x2 = xc1
* y2 = y0 + term(r, xc1, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Top right three corners
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = (__pyx_v_y0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc1, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":465
*
* # Bottom right three corners
* if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymin
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":485
*
* # Top right three corners
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymin
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[1]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L7_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[2]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L7_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[3]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L7_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":486
* # Top right three corners
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":487
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmax
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":489
* yc1 = ymin
*
* xc2 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":490
*
* xc2 = xmax
* yc2 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc3 = xmin
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":492
* yc2 = ymax
*
* xc3 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc3 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc3 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":493
*
* xc3 = xmin
* yc3 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc4 = xmin # Corner outside
*/
__pyx_v_yc3 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":495
* yc3 = ymax
*
* xc4 = xmin # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc4 = ymin # Corner outside
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc4 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":496
*
* xc4 = xmin # Corner outside
* yc4 = ymin # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = xc3
*/
__pyx_v_yc4 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":498
* yc4 = ymin # Corner outside
*
* x1 = xc3 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc3, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = __pyx_v_xc3;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":499
*
* x1 = xc3
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc3, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = (__pyx_v_y0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc3, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":501
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc3, x0)
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = yc1
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = (__pyx_v_x0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc1, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":502
*
* x2 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0)
* y2 = yc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Top left three corners
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = __pyx_v_yc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":485
*
* # Top right three corners
* elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymin
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":505
*
* # Top left three corners
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1 and corners[0] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymax
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[2]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L10_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[3]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L10_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[0]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L10_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":506
* # Top left three corners
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1 and corners[0] == 1:
* xc1 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":507
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1 and corners[0] == 1:
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmin
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":509
* yc1 = ymax
*
* xc2 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":510
*
* xc2 = xmin
* yc2 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc3 = xmin
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":512
* yc2 = ymax
*
* xc3 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc3 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc3 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":513
*
* xc3 = xmin
* yc3 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc4 = xmax # Corner outside
*/
__pyx_v_yc3 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":515
* yc3 = ymin
*
* xc4 = xmax # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc4 = ymin # Corner outside
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc4 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":516
*
* xc4 = xmax # Corner outside
* yc4 = ymin # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = xc1
*/
__pyx_v_yc4 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":518
* yc4 = ymin # Corner outside
*
* x1 = xc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = __pyx_v_xc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":519
*
* x1 = xc1
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc3, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = (__pyx_v_y0 - __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc1, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":521
* y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0)
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc3, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = yc3
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = (__pyx_v_x0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc3, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":522
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc3, y0)
* y2 = yc3 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Bottom left three corners
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = __pyx_v_yc3;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":505
*
* # Top left three corners
* elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1 and corners[0] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmax
* yc1 = ymax
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":525
*
* # Bottom left three corners
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymax
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[0]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L13_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[1]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L13_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_corners[3]) == 1) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L13_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":526
* # Bottom left three corners
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc1 = ymax
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc1 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":527
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc2 = xmin
*/
__pyx_v_yc1 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":529
* yc1 = ymax
*
* xc2 = xmin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc2 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc2 = __pyx_v_xmin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":530
*
* xc2 = xmin
* yc2 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc3 = xmax
*/
__pyx_v_yc2 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":532
* yc2 = ymin
*
* xc3 = xmax # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc3 = ymin
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc3 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":533
*
* xc3 = xmax
* yc3 = ymin # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* xc4 = xmax # Corner outside
*/
__pyx_v_yc3 = __pyx_v_ymin;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":535
* yc3 = ymin
*
* xc4 = xmax # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* yc4 = ymax # Corner outside
*
*/
__pyx_v_xc4 = __pyx_v_xmax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":536
*
* xc4 = xmax # Corner outside
* yc4 = ymax # Corner outside # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x1 = xc3
*/
__pyx_v_yc4 = __pyx_v_ymax;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":538
* yc4 = ymax # Corner outside
*
* x1 = xc3 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc3, x0)
*
*/
__pyx_v_x1 = __pyx_v_xc3;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":539
*
* x1 = xc3
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc3, x0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0)
*/
__pyx_v_y1 = (__pyx_v_y0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_xc3, __pyx_v_x0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":541
* y1 = y0 + term(r, xc3, x0)
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y2 = yc1
*
*/
__pyx_v_x2 = (__pyx_v_x0 + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_term(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_yc1, __pyx_v_y0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":542
*
* x2 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0)
* y2 = yc1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
*/
__pyx_v_y2 = __pyx_v_yc1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":525
*
* # Bottom left three corners
* elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[3] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* xc1 = xmin
* yc1 = ymax
*/
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":544
* y2 = yc1
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* h = r - d
*
*/
__pyx_v_d = __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist_pl(__pyx_v_x0, __pyx_v_y0, __pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1, __pyx_v_x2, __pyx_v_y2);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":545
*
* d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
* h = r - d # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of the circular segment
*/
__pyx_v_h = (__pyx_v_r - __pyx_v_d);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":548
*
* # Area of the circular segment
* area += circular_segment(r, h) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of the rectangle
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circular_segment(__pyx_v_r, __pyx_v_h));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":551
*
* # Area of the rectangle
* area += xsize * ysize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Area of triangle
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area + (__pyx_v_xsize * __pyx_v_ysize));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":554
*
* # Area of triangle
* area -= dist(x1, y1, xc4, yc4) * dist(x2, y2, xc4, yc4) / 2 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return area
*/
__pyx_v_area = (__pyx_v_area - ((__pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist(__pyx_v_x1, __pyx_v_y1, __pyx_v_xc4, __pyx_v_yc4) * __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist(__pyx_v_x2, __pyx_v_y2, __pyx_v_xc4, __pyx_v_yc4)) / 2.0));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":556
* area -= dist(x1, y1, xc4, yc4) * dist(x2, y2, xc4, yc4) / 2
*
* return area # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_area;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":409
*
*
* cdef inline double three_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":559
*
*
* cdef inline double four_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE double __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_four_corner(CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_corners, CYTHON_UNUSED double __pyx_v_px, CYTHON_UNUSED double __pyx_v_py, double __pyx_v_xsize, double __pyx_v_ysize, CYTHON_UNUSED double __pyx_v_x0, CYTHON_UNUSED double __pyx_v_y0, CYTHON_UNUSED double __pyx_v_r) {
double __pyx_r;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":595
* '''
*
* return xsize * ysize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = (__pyx_v_xsize * __pyx_v_ysize);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":559
*
*
* cdef inline double four_corner( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
* double px,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":599
*
*
* cpdef void circles2d_ext( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* double[:, :] pixels,
* double[:, :] positions,
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_1circles2d_ext(PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext(__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_pixels, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_positions, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_radii, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_xlim, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_ylim, CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_skip_dispatch) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_nrows;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_nx;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_ny;
double __pyx_v_xsize;
double __pyx_v_ysize;
double __pyx_v_x;
double __pyx_v_y;
double __pyx_v_r;
double __pyx_v_px;
double __pyx_v_py;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_min_nx;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_max_nx;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_min_ny;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_max_ny;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_num_corners;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_corners[4];
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_i;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_j;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_k;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_l;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_5;
int __pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_t_7;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_8;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_9;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_10;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_11;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_12;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_13;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_14;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":651
*
* '''
* cdef Py_ssize_t nrows = positions.shape[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t nx = pixels.shape[0]
*/
__pyx_v_nrows = (__pyx_v_positions.shape[0]);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":653
* cdef Py_ssize_t nrows = positions.shape[0]
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t nx = pixels.shape[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t ny = pixels.shape[1]
*
*/
__pyx_v_nx = (__pyx_v_pixels.shape[0]);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":654
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t nx = pixels.shape[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t ny = pixels.shape[1] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef double xsize = (xlim[1] - xlim[0]) / nx
*/
__pyx_v_ny = (__pyx_v_pixels.shape[1]);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":656
* cdef Py_ssize_t ny = pixels.shape[1]
*
* cdef double xsize = (xlim[1] - xlim[0]) / nx # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef double ysize = (ylim[1] - ylim[0]) / ny
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = 1;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_xsize = (((*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_xlim.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_xlim.strides[0]) ))) - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_xlim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_xlim.strides[0]) )))) / ((double)__pyx_v_nx));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":657
*
* cdef double xsize = (xlim[1] - xlim[0]) / nx
* cdef double ysize = (ylim[1] - ylim[0]) / ny # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # print((
*/
__pyx_t_2 = 1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_v_ysize = (((*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_ylim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_ylim.strides[0]) ))) - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_ylim.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_ylim.strides[0]) )))) / ((double)__pyx_v_ny));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":678
* cdef Py_ssize_t i, j, k, l
*
* for i in range(nrows): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Aliases
* x = positions[i, 0]
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_nrows;
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_t_3;
for (__pyx_t_5 = 0; __pyx_t_5 < __pyx_t_4; __pyx_t_5+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_5;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":680
* for i in range(nrows):
* # Aliases
* x = positions[i, 0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* y = positions[i, 1]
* r = radii[i]
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_i;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_x = (*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_positions.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_positions.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_positions.strides[1]) )));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":681
* # Aliases
* x = positions[i, 0]
* y = positions[i, 1] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* r = radii[i]
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_i;
__pyx_t_1 = 1;
__pyx_v_y = (*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_positions.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_positions.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_positions.strides[1]) )));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":682
* x = positions[i, 0]
* y = positions[i, 1]
* r = radii[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if r == 0:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_i;
__pyx_v_r = (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_radii.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_radii.strides[0]) )));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":684
* r = radii[i]
*
* if r == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if x == xlim[1]:
* min_nx = nx - 1
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_r == 0.0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":685
*
* if r == 0:
* if x == xlim[1]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_nx = nx - 1
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = 1;
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_x == (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_xlim.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_xlim.strides[0]) )))) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":686
* if r == 0:
* if x == xlim[1]:
* min_nx = nx - 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* min_nx = floor((x - xlim[0]) / xsize)
*/
__pyx_v_min_nx = (__pyx_v_nx - 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":685
*
* if r == 0:
* if x == xlim[1]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_nx = nx - 1
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L6;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":688
* min_nx = nx - 1
* else:
* min_nx = floor((x - xlim[0]) / xsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if y == ylim[1]:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_v_min_nx = ((Py_ssize_t)floor(((__pyx_v_x - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_xlim.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_xlim.strides[0]) )))) / __pyx_v_xsize)));
}
__pyx_L6:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":690
* min_nx = floor((x - xlim[0]) / xsize)
*
* if y == ylim[1]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_ny = ny - 1
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = 1;
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_y == (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_ylim.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_ylim.strides[0]) )))) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":691
*
* if y == ylim[1]:
* min_ny = ny - 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* min_ny = floor((y - ylim[0]) / ysize)
*/
__pyx_v_min_ny = (__pyx_v_ny - 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":690
* min_nx = floor((x - xlim[0]) / xsize)
*
* if y == ylim[1]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_ny = ny - 1
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L7;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":693
* min_ny = ny - 1
* else:
* min_ny = floor((y - ylim[0]) / ysize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if min_nx >= nx or min_nx < 0:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_v_min_ny = ((Py_ssize_t)floor(((__pyx_v_y - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_ylim.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_ylim.strides[0]) )))) / __pyx_v_ysize)));
}
__pyx_L7:;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":695
* min_ny = floor((y - ylim[0]) / ysize)
*
* if min_nx >= nx or min_nx < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* if min_ny >= ny or min_ny < 0:
*/
__pyx_t_7 = ((__pyx_v_min_nx >= __pyx_v_nx) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_7) {
} else {
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_t_7;
goto __pyx_L9_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_7 = ((__pyx_v_min_nx < 0) != 0);
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_t_7;
__pyx_L9_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":696
*
* if min_nx >= nx or min_nx < 0:
* continue # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if min_ny >= ny or min_ny < 0:
* continue
*/
goto __pyx_L3_continue;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":695
* min_ny = floor((y - ylim[0]) / ysize)
*
* if min_nx >= nx or min_nx < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* if min_ny >= ny or min_ny < 0:
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":697
* if min_nx >= nx or min_nx < 0:
* continue
* if min_ny >= ny or min_ny < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
*
*/
__pyx_t_7 = ((__pyx_v_min_ny >= __pyx_v_ny) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_7) {
} else {
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_t_7;
goto __pyx_L12_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_7 = ((__pyx_v_min_ny < 0) != 0);
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_t_7;
__pyx_L12_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":698
* continue
* if min_ny >= ny or min_ny < 0:
* continue # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* pixels[min_nx, min_ny] += 1
*/
goto __pyx_L3_continue;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":697
* if min_nx >= nx or min_nx < 0:
* continue
* if min_ny >= ny or min_ny < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
*
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":700
* continue
*
* pixels[min_nx, min_ny] += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_min_nx;
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_min_ny;
*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_pixels.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[1]) )) += 1.0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":701
*
* pixels[min_nx, min_ny] += 1
* continue # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Find minimum and maximum pixel indices over which the particle spans.
*/
goto __pyx_L3_continue;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":684
* r = radii[i]
*
* if r == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if x == xlim[1]:
* min_nx = nx - 1
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":705
* # Find minimum and maximum pixel indices over which the particle spans.
* # This corresponds to the intersected cells
* min_nx = floor((x - r - xlim[0]) / xsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* max_nx = floor((x + r - xlim[0]) / xsize)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_min_nx = ((Py_ssize_t)floor((((__pyx_v_x - __pyx_v_r) - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_xlim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_xlim.strides[0]) )))) / __pyx_v_xsize)));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":706
* # This corresponds to the intersected cells
* min_nx = floor((x - r - xlim[0]) / xsize)
* max_nx = floor((x + r - xlim[0]) / xsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* min_ny = floor((y - r - ylim[0]) / ysize)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_max_nx = ((Py_ssize_t)floor((((__pyx_v_x + __pyx_v_r) - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_xlim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_xlim.strides[0]) )))) / __pyx_v_xsize)));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":708
* max_nx = floor((x + r - xlim[0]) / xsize)
*
* min_ny = floor((y - r - ylim[0]) / ysize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* max_ny = floor((y + r - ylim[0]) / ysize)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_min_ny = ((Py_ssize_t)floor((((__pyx_v_y - __pyx_v_r) - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_ylim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_ylim.strides[0]) )))) / __pyx_v_ysize)));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":709
*
* min_ny = floor((y - r - ylim[0]) / ysize)
* max_ny = floor((y + r - ylim[0]) / ysize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # print((
*/
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_max_ny = ((Py_ssize_t)floor((((__pyx_v_y + __pyx_v_r) - (*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_ylim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_ylim.strides[0]) )))) / __pyx_v_ysize)));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":723
*
* # Check pixel indices are within the system bounds
* if min_nx >= nx: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif min_nx < 0:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_min_nx >= __pyx_v_nx) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":724
* # Check pixel indices are within the system bounds
* if min_nx >= nx:
* continue # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif min_nx < 0:
* min_nx = 0
*/
goto __pyx_L3_continue;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":723
*
* # Check pixel indices are within the system bounds
* if min_nx >= nx: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif min_nx < 0:
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":725
* if min_nx >= nx:
* continue
* elif min_nx < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_nx = 0
*
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_min_nx < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":726
* continue
* elif min_nx < 0:
* min_nx = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if max_nx < 0:
*/
__pyx_v_min_nx = 0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":725
* if min_nx >= nx:
* continue
* elif min_nx < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_nx = 0
*
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":728
* min_nx = 0
*
* if max_nx < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif max_nx >= nx:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_max_nx < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":729
*
* if max_nx < 0:
* continue # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif max_nx >= nx:
* max_nx = nx - 1
*/
goto __pyx_L3_continue;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":728
* min_nx = 0
*
* if max_nx < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif max_nx >= nx:
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":730
* if max_nx < 0:
* continue
* elif max_nx >= nx: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* max_nx = nx - 1
*
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_max_nx >= __pyx_v_nx) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":731
* continue
* elif max_nx >= nx:
* max_nx = nx - 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if min_ny >= ny:
*/
__pyx_v_max_nx = (__pyx_v_nx - 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":730
* if max_nx < 0:
* continue
* elif max_nx >= nx: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* max_nx = nx - 1
*
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":733
* max_nx = nx - 1
*
* if min_ny >= ny: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif min_ny < 0:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_min_ny >= __pyx_v_ny) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":734
*
* if min_ny >= ny:
* continue # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif min_ny < 0:
* min_ny = 0
*/
goto __pyx_L3_continue;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":733
* max_nx = nx - 1
*
* if min_ny >= ny: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif min_ny < 0:
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":735
* if min_ny >= ny:
* continue
* elif min_ny < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_ny = 0
*
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_min_ny < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":736
* continue
* elif min_ny < 0:
* min_ny = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if max_ny < 0:
*/
__pyx_v_min_ny = 0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":735
* if min_ny >= ny:
* continue
* elif min_ny < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* min_ny = 0
*
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":738
* min_ny = 0
*
* if max_ny < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif max_ny >= ny:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_max_ny < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":739
*
* if max_ny < 0:
* continue # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif max_ny >= ny:
* max_ny = ny - 1
*/
goto __pyx_L3_continue;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":738
* min_ny = 0
*
* if max_ny < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* continue
* elif max_ny >= ny:
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":740
* if max_ny < 0:
* continue
* elif max_ny >= ny: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* max_ny = ny - 1
*
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_v_max_ny >= __pyx_v_ny) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":741
* continue
* elif max_ny >= ny:
* max_ny = ny - 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # print((
*/
__pyx_v_max_ny = (__pyx_v_ny - 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":740
* if max_ny < 0:
* continue
* elif max_ny >= ny: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* max_ny = ny - 1
*
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":757
* # Iterate over all intersected pixels, computing the area covered by
* # the particle
* for j in range(min_nx, max_nx + 1): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for k in range(min_ny, max_ny + 1):
* # Find the number of pixel corners inside the particle
*/
__pyx_t_8 = (__pyx_v_max_nx + 1);
__pyx_t_9 = __pyx_t_8;
for (__pyx_t_10 = __pyx_v_min_nx; __pyx_t_10 < __pyx_t_9; __pyx_t_10+=1) {
__pyx_v_j = __pyx_t_10;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":758
* # the particle
* for j in range(min_nx, max_nx + 1):
* for k in range(min_ny, max_ny + 1): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* # Find the number of pixel corners inside the particle
* num_corners = 0
*/
__pyx_t_11 = (__pyx_v_max_ny + 1);
__pyx_t_12 = __pyx_t_11;
for (__pyx_t_13 = __pyx_v_min_ny; __pyx_t_13 < __pyx_t_12; __pyx_t_13+=1) {
__pyx_v_k = __pyx_t_13;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":760
* for k in range(min_ny, max_ny + 1):
* # Find the number of pixel corners inside the particle
* num_corners = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for l in range(4):
* corners[l] = 0
*/
__pyx_v_num_corners = 0;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":761
* # Find the number of pixel corners inside the particle
* num_corners = 0
* for l in range(4): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* corners[l] = 0
*
*/
for (__pyx_t_14 = 0; __pyx_t_14 < 4; __pyx_t_14+=1) {
__pyx_v_l = __pyx_t_14;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":762
* num_corners = 0
* for l in range(4):
* corners[l] = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Pixel centre coordinates
*/
(__pyx_v_corners[__pyx_v_l]) = 0;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":765
*
* # Pixel centre coordinates
* px = xlim[0] + (j + 0.5) * xsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* py = ylim[0] + (k + 0.5) * ysize
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_px = ((*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_xlim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_xlim.strides[0]) ))) + ((__pyx_v_j + 0.5) * __pyx_v_xsize));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":766
* # Pixel centre coordinates
* px = xlim[0] + (j + 0.5) * xsize
* py = ylim[0] + (k + 0.5) * ysize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # print((
*/
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v_py = ((*((double *) ( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_ylim.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_ylim.strides[0]) ))) + ((__pyx_v_k + 0.5) * __pyx_v_ysize));
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":780
*
* # Lower left corner
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[0] = 1
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist2((__pyx_v_px - (0.5 * __pyx_v_xsize)), (__pyx_v_py - (0.5 * __pyx_v_ysize)), __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y) < (__pyx_v_r * __pyx_v_r)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":781
* # Lower left corner
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* corners[0] = 1
*
*/
__pyx_v_num_corners = (__pyx_v_num_corners + 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":782
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1
* corners[0] = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Lower right corner
*/
(__pyx_v_corners[0]) = 1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":780
*
* # Lower left corner
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[0] = 1
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":785
*
* # Lower right corner
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[1] = 1
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist2((__pyx_v_px + (0.5 * __pyx_v_xsize)), (__pyx_v_py - (0.5 * __pyx_v_ysize)), __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y) < (__pyx_v_r * __pyx_v_r)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":786
* # Lower right corner
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* corners[1] = 1
*
*/
__pyx_v_num_corners = (__pyx_v_num_corners + 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":787
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1
* corners[1] = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Upper right corner
*/
(__pyx_v_corners[1]) = 1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":785
*
* # Lower right corner
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[1] = 1
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":790
*
* # Upper right corner
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[2] = 1
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist2((__pyx_v_px + (0.5 * __pyx_v_xsize)), (__pyx_v_py + (0.5 * __pyx_v_ysize)), __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y) < (__pyx_v_r * __pyx_v_r)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":791
* # Upper right corner
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* corners[2] = 1
*
*/
__pyx_v_num_corners = (__pyx_v_num_corners + 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":792
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1
* corners[2] = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # Upper left corner
*/
(__pyx_v_corners[2]) = 1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":790
*
* # Upper right corner
* if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[2] = 1
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":795
*
* # Upper left corner
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[3] = 1
*/
__pyx_t_6 = ((__pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_dist2((__pyx_v_px - (0.5 * __pyx_v_xsize)), (__pyx_v_py + (0.5 * __pyx_v_ysize)), __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y) < (__pyx_v_r * __pyx_v_r)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":796
* # Upper left corner
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* corners[3] = 1
*
*/
__pyx_v_num_corners = (__pyx_v_num_corners + 1);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":797
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
* num_corners += 1
* corners[3] = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* # print((
*/
(__pyx_v_corners[3]) = 1;
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":795
*
* # Upper left corner
* if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* num_corners += 1
* corners[3] = 1
*/
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":804
* # ))
*
* if num_corners == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* pixels[j, k] += zero_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 1:
*/
switch (__pyx_v_num_corners) {
case 0:
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":805
*
* if num_corners == 0:
* pixels[j, k] += zero_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif num_corners == 1:
* pixels[j, k] += one_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_j;
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_k;
*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_pixels.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[1]) )) += __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_zero_corner(__pyx_v_corners, __pyx_v_px, __pyx_v_py, __pyx_v_xsize, __pyx_v_ysize, __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y, __pyx_v_r);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":804
* # ))
*
* if num_corners == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* pixels[j, k] += zero_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 1:
*/
break;
case 1:
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":807
* pixels[j, k] += zero_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 1:
* pixels[j, k] += one_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif num_corners == 2:
* pixels[j, k] += two_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_j;
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_k;
*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_pixels.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[1]) )) += __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_one_corner(__pyx_v_corners, __pyx_v_px, __pyx_v_py, __pyx_v_xsize, __pyx_v_ysize, __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y, __pyx_v_r);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":806
* if num_corners == 0:
* pixels[j, k] += zero_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* pixels[j, k] += one_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 2:
*/
break;
case 2:
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":809
* pixels[j, k] += one_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 2:
* pixels[j, k] += two_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif num_corners == 3:
* pixels[j, k] += three_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_j;
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_k;
*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_pixels.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[1]) )) += __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_two_corner(__pyx_v_corners, __pyx_v_px, __pyx_v_py, __pyx_v_xsize, __pyx_v_ysize, __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y, __pyx_v_r);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":808
* elif num_corners == 1:
* pixels[j, k] += one_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 2: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* pixels[j, k] += two_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 3:
*/
break;
case 3:
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":811
* pixels[j, k] += two_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 3:
* pixels[j, k] += three_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif num_corners == 4:
* pixels[j, k] += four_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_j;
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_k;
*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_pixels.data + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[1]) )) += __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_three_corner(__pyx_v_corners, __pyx_v_px, __pyx_v_py, __pyx_v_xsize, __pyx_v_ysize, __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y, __pyx_v_r);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":810
* elif num_corners == 2:
* pixels[j, k] += two_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 3: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* pixels[j, k] += three_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 4:
*/
break;
case 4:
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":813
* pixels[j, k] += three_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 4:
* pixels[j, k] += four_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_j;
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_k;
*((double *) ( /* dim=1 */ (( /* dim=0 */ (__pyx_v_pixels.data + __pyx_t_2 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[0]) ) + __pyx_t_1 * __pyx_v_pixels.strides[1]) )) += __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_four_corner(__pyx_v_corners, __pyx_v_px, __pyx_v_py, __pyx_v_xsize, __pyx_v_ysize, __pyx_v_x, __pyx_v_y, __pyx_v_r);
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":812
* elif num_corners == 3:
* pixels[j, k] += three_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
* elif num_corners == 4: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* pixels[j, k] += four_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
*/
break;
default: break;
}
}
}
__pyx_L3_continue:;
}
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":599
*
*
* cpdef void circles2d_ext( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* double[:, :] pixels,
* double[:, :] positions,
*/
/* function exit code */
}
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_1circles2d_ext(PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds); /*proto*/
static char __pyx_doc_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext[] = "circles2d_ext(double[:, :] pixels, double[:, :] positions, double[:] radii, double[:] xlim, double[:] ylim) -> void\nCompute the 2D occupancy of circles of different radii.\n\n ::\n\n Function signature:\n\n void circles2d_ext(\n double[:, :] pixels,\n double[:, :] positions,\n double[:] radii,\n double[:] xlim,\n double[:] ylim,\n ) nogil\n\n This corresponds to the pixellisation of circular particles, such that\n each pixel's value corresponds to the area covered by the particle.\n\n It is important that all parameters sent to this function are initialised\n properly. Please see the parameters below, or the function *will* segfault.\n Alternatively, use the `pept.processing.occupancy2d` function which is\n more robust and initialises all parameters for you.\n\n Parameters\n ----------\n pixels: (M, N) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 2, dtype = numpy.float64]\n The 2D grid of pixels, initialised to zero. It can be created with\n `numpy.zeros((nrows, ncols))`.\n\n positions: (P, 2) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 2, dtype = numpy.float64]\n The particles' 2D positions, where all rows are formatted as\n `[x_coordinate, y_coordinate]`.\n\n radii: (P,) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 1, dtype = numpy.float64]\n The radii of each particle. It must have the same length as\n `positions`.\n\n xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 1, dtype = numpy.float64]\n The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the\n x-dimension, formatted as [xmin, xmax].\n\n ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 1, dtype = numpy.float64]\n The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the\n y-dimension, formatted as [ymin, ymax].\n\n ";
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_1circles2d_ext(PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds) {
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_pixels = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_positions = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_radii = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_xlim = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_ylim = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("circles2d_ext (wrapper)", 0);
{
static PyObject **__pyx_pyargnames[] = {&__pyx_n_s_pixels,&__pyx_n_s_positions,&__pyx_n_s_radii,&__pyx_n_s_xlim,&__pyx_n_s_ylim,0};
PyObject* values[5] = {0,0,0,0,0};
if (unlikely(__pyx_kwds)) {
Py_ssize_t kw_args;
const Py_ssize_t pos_args = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args);
switch (pos_args) {
case 5: values[4] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 4);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 4: values[3] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 3);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 3: values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2: values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1: values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 0: break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
kw_args = PyDict_Size(__pyx_kwds);
switch (pos_args) {
case 0:
if (likely((values[0] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_pixels)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1:
if (likely((values[1] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_positions)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("circles2d_ext", 1, 5, 5, 1); __PYX_ERR(0, 599, __pyx_L3_error)
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2:
if (likely((values[2] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_radii)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("circles2d_ext", 1, 5, 5, 2); __PYX_ERR(0, 599, __pyx_L3_error)
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 3:
if (likely((values[3] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_xlim)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("circles2d_ext", 1, 5, 5, 3); __PYX_ERR(0, 599, __pyx_L3_error)
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 4:
if (likely((values[4] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_ylim)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("circles2d_ext", 1, 5, 5, 4); __PYX_ERR(0, 599, __pyx_L3_error)
}
}
if (unlikely(kw_args > 0)) {
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_pyargnames, 0, values, pos_args, "circles2d_ext") < 0)) __PYX_ERR(0, 599, __pyx_L3_error)
}
} else if (PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args) != 5) {
goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
} else {
values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
values[3] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 3);
values[4] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 4);
}
__pyx_v_pixels = __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_dsds_double(values[0], PyBUF_WRITABLE); if (unlikely(!__pyx_v_pixels.memview)) __PYX_ERR(0, 600, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_v_positions = __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_dsds_double(values[1], PyBUF_WRITABLE); if (unlikely(!__pyx_v_positions.memview)) __PYX_ERR(0, 601, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_v_radii = __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_ds_double(values[2], PyBUF_WRITABLE); if (unlikely(!__pyx_v_radii.memview)) __PYX_ERR(0, 602, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_v_xlim = __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_ds_double(values[3], PyBUF_WRITABLE); if (unlikely(!__pyx_v_xlim.memview)) __PYX_ERR(0, 603, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_v_ylim = __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_ds_double(values[4], PyBUF_WRITABLE); if (unlikely(!__pyx_v_ylim.memview)) __PYX_ERR(0, 604, __pyx_L3_error)
}
goto __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done;
__pyx_L5_argtuple_error:;
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("circles2d_ext", 1, 5, 5, PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args)); __PYX_ERR(0, 599, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_L3_error:;
__Pyx_AddTraceback("pept.processing.circles_ext.circles2d_ext", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return NULL;
__pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done:;
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext(__pyx_self, __pyx_v_pixels, __pyx_v_positions, __pyx_v_radii, __pyx_v_xlim, __pyx_v_ylim);
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext(CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_self, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_pixels, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_positions, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_radii, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_xlim, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_ylim) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("circles2d_ext", 0);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_void_to_None(__pyx_f_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext(__pyx_v_pixels, __pyx_v_positions, __pyx_v_radii, __pyx_v_xlim, __pyx_v_ylim, 0)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 599, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("pept.processing.circles_ext.circles2d_ext", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&__pyx_v_pixels, 1);
__PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&__pyx_v_positions, 1);
__PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&__pyx_v_radii, 1);
__PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&__pyx_v_xlim, 1);
__PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&__pyx_v_ylim, 1);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":122
* cdef bint dtype_is_object
*
* def __cinit__(array self, tuple shape, Py_ssize_t itemsize, format not None, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mode="c", bint allocate_buffer=True):
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static int __pyx_array___cinit__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_array___cinit__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_shape = 0;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_itemsize;
PyObject *__pyx_v_format = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_v_mode = 0;
int __pyx_v_allocate_buffer;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__cinit__ (wrapper)", 0);
{
static PyObject **__pyx_pyargnames[] = {&__pyx_n_s_shape,&__pyx_n_s_itemsize,&__pyx_n_s_format,&__pyx_n_s_mode,&__pyx_n_s_allocate_buffer,0};
PyObject* values[5] = {0,0,0,0,0};
values[3] = ((PyObject *)__pyx_n_s_c);
if (unlikely(__pyx_kwds)) {
Py_ssize_t kw_args;
const Py_ssize_t pos_args = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args);
switch (pos_args) {
case 5: values[4] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 4);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 4: values[3] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 3);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 3: values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2: values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1: values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 0: break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
kw_args = PyDict_Size(__pyx_kwds);
switch (pos_args) {
case 0:
if (likely((values[0] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_shape)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1:
if (likely((values[1] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_itemsize)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__cinit__", 0, 3, 5, 1); __PYX_ERR(1, 122, __pyx_L3_error)
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2:
if (likely((values[2] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_format)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__cinit__", 0, 3, 5, 2); __PYX_ERR(1, 122, __pyx_L3_error)
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 3:
if (kw_args > 0) {
PyObject* value = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_mode);
if (value) { values[3] = value; kw_args--; }
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 4:
if (kw_args > 0) {
PyObject* value = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_allocate_buffer);
if (value) { values[4] = value; kw_args--; }
}
}
if (unlikely(kw_args > 0)) {
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_pyargnames, 0, values, pos_args, "__cinit__") < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 122, __pyx_L3_error)
}
} else {
switch (PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args)) {
case 5: values[4] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 4);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 4: values[3] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 3);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 3: values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
}
__pyx_v_shape = ((PyObject*)values[0]);
__pyx_v_itemsize = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(values[1]); if (unlikely((__pyx_v_itemsize == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 122, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_v_format = values[2];
__pyx_v_mode = values[3];
if (values[4]) {
__pyx_v_allocate_buffer = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(values[4]); if (unlikely((__pyx_v_allocate_buffer == (int)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 123, __pyx_L3_error)
} else {
/* "View.MemoryView":123
*
* def __cinit__(array self, tuple shape, Py_ssize_t itemsize, format not None,
* mode="c", bint allocate_buffer=True): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef int idx
*/
__pyx_v_allocate_buffer = ((int)1);
}
}
goto __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done;
__pyx_L5_argtuple_error:;
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__cinit__", 0, 3, 5, PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args)); __PYX_ERR(1, 122, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_L3_error:;
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__cinit__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return -1;
__pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done:;
if (unlikely(!__Pyx_ArgTypeTest(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_shape), (&PyTuple_Type), 1, "shape", 1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 122, __pyx_L1_error)
if (unlikely(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_format) == Py_None)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "Argument '%.200s' must not be None", "format"); __PYX_ERR(1, 122, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_r = __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array___cinit__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_v_shape, __pyx_v_itemsize, __pyx_v_format, __pyx_v_mode, __pyx_v_allocate_buffer);
/* "View.MemoryView":122
* cdef bint dtype_is_object
*
* def __cinit__(array self, tuple shape, Py_ssize_t itemsize, format not None, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mode="c", bint allocate_buffer=True):
*
*/
/* function exit code */
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__pyx_r = -1;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static int __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array___cinit__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_itemsize, PyObject *__pyx_v_format, PyObject *__pyx_v_mode, int __pyx_v_allocate_buffer) {
int __pyx_v_idx;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_i;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_dim;
PyObject **__pyx_v_p;
char __pyx_v_order;
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_4;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
char *__pyx_t_7;
int __pyx_t_8;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_9;
PyObject *__pyx_t_10 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_11;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__cinit__", 0);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_format);
/* "View.MemoryView":129
* cdef PyObject **p
*
* self.ndim = len(shape) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.itemsize = itemsize
*
*/
if (unlikely(__pyx_v_shape == Py_None)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "object of type 'NoneType' has no len()");
__PYX_ERR(1, 129, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_t_1 = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_v_shape); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 == ((Py_ssize_t)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 129, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_self->ndim = ((int)__pyx_t_1);
/* "View.MemoryView":130
*
* self.ndim = len(shape)
* self.itemsize = itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not self.ndim:
*/
__pyx_v_self->itemsize = __pyx_v_itemsize;
/* "View.MemoryView":132
* self.itemsize = itemsize
*
* if not self.ndim: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Empty shape tuple for cython.array")
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_v_self->ndim != 0)) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":133
*
* if not self.ndim:
* raise ValueError("Empty shape tuple for cython.array") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if itemsize <= 0:
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_tuple_, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 133, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 133, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":132
* self.itemsize = itemsize
*
* if not self.ndim: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Empty shape tuple for cython.array")
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":135
* raise ValueError("Empty shape tuple for cython.array")
*
* if itemsize <= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("itemsize <= 0 for cython.array")
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_itemsize <= 0) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":136
*
* if itemsize <= 0:
* raise ValueError("itemsize <= 0 for cython.array") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not isinstance(format, bytes):
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_tuple__2, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 136, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 136, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":135
* raise ValueError("Empty shape tuple for cython.array")
*
* if itemsize <= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("itemsize <= 0 for cython.array")
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":138
* raise ValueError("itemsize <= 0 for cython.array")
*
* if not isinstance(format, bytes): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* format = format.encode('ASCII')
* self._format = format # keep a reference to the byte string
*/
__pyx_t_2 = PyBytes_Check(__pyx_v_format);
__pyx_t_4 = ((!(__pyx_t_2 != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_4) {
/* "View.MemoryView":139
*
* if not isinstance(format, bytes):
* format = format.encode('ASCII') # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self._format = format # keep a reference to the byte string
* self.format = self._format
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_format, __pyx_n_s_encode); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 139, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && likely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_5))) {
__pyx_t_6 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_5);
if (likely(__pyx_t_6)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_5, function);
}
}
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_6) ? __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_6, __pyx_n_s_ASCII) : __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_n_s_ASCII);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 139, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_format, __pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":138
* raise ValueError("itemsize <= 0 for cython.array")
*
* if not isinstance(format, bytes): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* format = format.encode('ASCII')
* self._format = format # keep a reference to the byte string
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":140
* if not isinstance(format, bytes):
* format = format.encode('ASCII')
* self._format = format # keep a reference to the byte string # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.format = self._format
*
*/
if (!(likely(PyBytes_CheckExact(__pyx_v_format))||((__pyx_v_format) == Py_None)||(PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected %.16s, got %.200s", "bytes", Py_TYPE(__pyx_v_format)->tp_name), 0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 140, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_format;
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_self->_format);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_self->_format);
__pyx_v_self->_format = ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":141
* format = format.encode('ASCII')
* self._format = format # keep a reference to the byte string
* self.format = self._format # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
if (unlikely(__pyx_v_self->_format == Py_None)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "expected bytes, NoneType found");
__PYX_ERR(1, 141, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyBytes_AsWritableString(__pyx_v_self->_format); if (unlikely((!__pyx_t_7) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 141, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_self->format = __pyx_t_7;
/* "View.MemoryView":144
*
*
* self._shape = PyObject_Malloc(sizeof(Py_ssize_t)*self.ndim*2) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self._strides = self._shape + self.ndim
*
*/
__pyx_v_self->_shape = ((Py_ssize_t *)PyObject_Malloc((((sizeof(Py_ssize_t)) * __pyx_v_self->ndim) * 2)));
/* "View.MemoryView":145
*
* self._shape = PyObject_Malloc(sizeof(Py_ssize_t)*self.ndim*2)
* self._strides = self._shape + self.ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not self._shape:
*/
__pyx_v_self->_strides = (__pyx_v_self->_shape + __pyx_v_self->ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":147
* self._strides = self._shape + self.ndim
*
* if not self._shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate shape and strides.")
*
*/
__pyx_t_4 = ((!(__pyx_v_self->_shape != 0)) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":148
*
* if not self._shape:
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate shape and strides.") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_MemoryError, __pyx_tuple__3, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 148, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 148, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":147
* self._strides = self._shape + self.ndim
*
* if not self._shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate shape and strides.")
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":151
*
*
* for idx, dim in enumerate(shape): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if dim <= 0:
* raise ValueError("Invalid shape in axis %d: %d." % (idx, dim))
*/
__pyx_t_8 = 0;
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_shape; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
for (;;) {
if (__pyx_t_1 >= PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_3)) break;
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_5 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_1); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_1++; if (unlikely(0 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 151, __pyx_L1_error)
#else
__pyx_t_5 = PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1++; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 151, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
#endif
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(__pyx_t_5); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_9 == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 151, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_v_dim = __pyx_t_9;
__pyx_v_idx = __pyx_t_8;
__pyx_t_8 = (__pyx_t_8 + 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":152
*
* for idx, dim in enumerate(shape):
* if dim <= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Invalid shape in axis %d: %d." % (idx, dim))
* self._shape[idx] = dim
*/
__pyx_t_4 = ((__pyx_v_dim <= 0) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":153
* for idx, dim in enumerate(shape):
* if dim <= 0:
* raise ValueError("Invalid shape in axis %d: %d." % (idx, dim)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self._shape[idx] = dim
*
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(__pyx_v_idx); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 153, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__pyx_t_6 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 153, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_10 = PyTuple_New(2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_10)) __PYX_ERR(1, 153, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_5);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_10, 0, __pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_6);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_10, 1, __pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_t_6 = 0;
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyString_Format(__pyx_kp_s_Invalid_shape_in_axis_d_d, __pyx_t_10); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 153, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_10); __pyx_t_10 = 0;
__pyx_t_10 = __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_t_6); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_10)) __PYX_ERR(1, 153, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_10, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_10); __pyx_t_10 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 153, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":152
*
* for idx, dim in enumerate(shape):
* if dim <= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Invalid shape in axis %d: %d." % (idx, dim))
* self._shape[idx] = dim
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":154
* if dim <= 0:
* raise ValueError("Invalid shape in axis %d: %d." % (idx, dim))
* self._shape[idx] = dim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef char order
*/
(__pyx_v_self->_shape[__pyx_v_idx]) = __pyx_v_dim;
/* "View.MemoryView":151
*
*
* for idx, dim in enumerate(shape): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if dim <= 0:
* raise ValueError("Invalid shape in axis %d: %d." % (idx, dim))
*/
}
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":157
*
* cdef char order
* if mode == 'fortran': # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* order = b'F'
* self.mode = u'fortran'
*/
__pyx_t_4 = (__Pyx_PyString_Equals(__pyx_v_mode, __pyx_n_s_fortran, Py_EQ)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 157, __pyx_L1_error)
if (__pyx_t_4) {
/* "View.MemoryView":158
* cdef char order
* if mode == 'fortran':
* order = b'F' # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.mode = u'fortran'
* elif mode == 'c':
*/
__pyx_v_order = 'F';
/* "View.MemoryView":159
* if mode == 'fortran':
* order = b'F'
* self.mode = u'fortran' # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif mode == 'c':
* order = b'C'
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_n_u_fortran);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_n_u_fortran);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_self->mode);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_self->mode);
__pyx_v_self->mode = __pyx_n_u_fortran;
/* "View.MemoryView":157
*
* cdef char order
* if mode == 'fortran': # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* order = b'F'
* self.mode = u'fortran'
*/
goto __pyx_L10;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":160
* order = b'F'
* self.mode = u'fortran'
* elif mode == 'c': # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* order = b'C'
* self.mode = u'c'
*/
__pyx_t_4 = (__Pyx_PyString_Equals(__pyx_v_mode, __pyx_n_s_c, Py_EQ)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 160, __pyx_L1_error)
if (likely(__pyx_t_4)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":161
* self.mode = u'fortran'
* elif mode == 'c':
* order = b'C' # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.mode = u'c'
* else:
*/
__pyx_v_order = 'C';
/* "View.MemoryView":162
* elif mode == 'c':
* order = b'C'
* self.mode = u'c' # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* raise ValueError("Invalid mode, expected 'c' or 'fortran', got %s" % mode)
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_n_u_c);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_n_u_c);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_self->mode);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_self->mode);
__pyx_v_self->mode = __pyx_n_u_c;
/* "View.MemoryView":160
* order = b'F'
* self.mode = u'fortran'
* elif mode == 'c': # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* order = b'C'
* self.mode = u'c'
*/
goto __pyx_L10;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":164
* self.mode = u'c'
* else:
* raise ValueError("Invalid mode, expected 'c' or 'fortran', got %s" % mode) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* self.len = fill_contig_strides_array(self._shape, self._strides,
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyString_FormatSafe(__pyx_kp_s_Invalid_mode_expected_c_or_fortr, __pyx_v_mode); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 164, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_10 = __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_10)) __PYX_ERR(1, 164, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_10, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_10); __pyx_t_10 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 164, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_L10:;
/* "View.MemoryView":166
* raise ValueError("Invalid mode, expected 'c' or 'fortran', got %s" % mode)
*
* self.len = fill_contig_strides_array(self._shape, self._strides, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* itemsize, self.ndim, order)
*
*/
__pyx_v_self->len = __pyx_fill_contig_strides_array(__pyx_v_self->_shape, __pyx_v_self->_strides, __pyx_v_itemsize, __pyx_v_self->ndim, __pyx_v_order);
/* "View.MemoryView":169
* itemsize, self.ndim, order)
*
* self.free_data = allocate_buffer # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.dtype_is_object = format == b'O'
* if allocate_buffer:
*/
__pyx_v_self->free_data = __pyx_v_allocate_buffer;
/* "View.MemoryView":170
*
* self.free_data = allocate_buffer
* self.dtype_is_object = format == b'O' # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if allocate_buffer:
*
*/
__pyx_t_10 = PyObject_RichCompare(__pyx_v_format, __pyx_n_b_O, Py_EQ); __Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_10); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_10)) __PYX_ERR(1, 170, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_t_10); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_4 == (int)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 170, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_10); __pyx_t_10 = 0;
__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":171
* self.free_data = allocate_buffer
* self.dtype_is_object = format == b'O'
* if allocate_buffer: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_4 = (__pyx_v_allocate_buffer != 0);
if (__pyx_t_4) {
/* "View.MemoryView":174
*
*
* self.data = malloc(self.len) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not self.data:
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate array data.")
*/
__pyx_v_self->data = ((char *)malloc(__pyx_v_self->len));
/* "View.MemoryView":175
*
* self.data = malloc(self.len)
* if not self.data: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate array data.")
*
*/
__pyx_t_4 = ((!(__pyx_v_self->data != 0)) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":176
* self.data = malloc(self.len)
* if not self.data:
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate array data.") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if self.dtype_is_object:
*/
__pyx_t_10 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_MemoryError, __pyx_tuple__4, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_10)) __PYX_ERR(1, 176, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_10, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_10); __pyx_t_10 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 176, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":175
*
* self.data = malloc(self.len)
* if not self.data: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate array data.")
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":178
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate array data.")
*
* if self.dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p = self.data
* for i in range(self.len / itemsize):
*/
__pyx_t_4 = (__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object != 0);
if (__pyx_t_4) {
/* "View.MemoryView":179
*
* if self.dtype_is_object:
* p = self.data # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for i in range(self.len / itemsize):
* p[i] = Py_None
*/
__pyx_v_p = ((PyObject **)__pyx_v_self->data);
/* "View.MemoryView":180
* if self.dtype_is_object:
* p = self.data
* for i in range(self.len / itemsize): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p[i] = Py_None
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*/
if (unlikely(__pyx_v_itemsize == 0)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ZeroDivisionError, "integer division or modulo by zero");
__PYX_ERR(1, 180, __pyx_L1_error)
}
else if (sizeof(Py_ssize_t) == sizeof(long) && (!(((Py_ssize_t)-1) > 0)) && unlikely(__pyx_v_itemsize == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && unlikely(UNARY_NEG_WOULD_OVERFLOW(__pyx_v_self->len))) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError, "value too large to perform division");
__PYX_ERR(1, 180, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_self->len / __pyx_v_itemsize);
__pyx_t_9 = __pyx_t_1;
for (__pyx_t_11 = 0; __pyx_t_11 < __pyx_t_9; __pyx_t_11+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_11;
/* "View.MemoryView":181
* p = self.data
* for i in range(self.len / itemsize):
* p[i] = Py_None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*
*/
(__pyx_v_p[__pyx_v_i]) = Py_None;
/* "View.MemoryView":182
* for i in range(self.len / itemsize):
* p[i] = Py_None
* Py_INCREF(Py_None) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('getbuffer')
*/
Py_INCREF(Py_None);
}
/* "View.MemoryView":178
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate array data.")
*
* if self.dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p = self.data
* for i in range(self.len / itemsize):
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":171
* self.free_data = allocate_buffer
* self.dtype_is_object = format == b'O'
* if allocate_buffer: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":122
* cdef bint dtype_is_object
*
* def __cinit__(array self, tuple shape, Py_ssize_t itemsize, format not None, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mode="c", bint allocate_buffer=True):
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__cinit__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_format);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":185
*
* @cname('getbuffer')
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int bufmode = -1
* if self.mode == u"c":
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_array_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_array_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getbuffer__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_2__getbuffer__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((Py_buffer *)__pyx_v_info), ((int)__pyx_v_flags));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static int __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_2__getbuffer__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags) {
int __pyx_v_bufmode;
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
char *__pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_5;
int __pyx_t_6;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_7;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
if (__pyx_v_info == NULL) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_BufferError, "PyObject_GetBuffer: view==NULL argument is obsolete");
return -1;
}
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getbuffer__", 0);
__pyx_v_info->obj = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
/* "View.MemoryView":186
* @cname('getbuffer')
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags):
* cdef int bufmode = -1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.mode == u"c":
* bufmode = PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
*/
__pyx_v_bufmode = -1;
/* "View.MemoryView":187
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags):
* cdef int bufmode = -1
* if self.mode == u"c": # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* bufmode = PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* elif self.mode == u"fortran":
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__Pyx_PyUnicode_Equals(__pyx_v_self->mode, __pyx_n_u_c, Py_EQ)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 187, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":188
* cdef int bufmode = -1
* if self.mode == u"c":
* bufmode = PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif self.mode == u"fortran":
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
*/
__pyx_v_bufmode = (PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS);
/* "View.MemoryView":187
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags):
* cdef int bufmode = -1
* if self.mode == u"c": # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* bufmode = PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* elif self.mode == u"fortran":
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":189
* if self.mode == u"c":
* bufmode = PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* elif self.mode == u"fortran": # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* if not (flags & bufmode):
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__Pyx_PyUnicode_Equals(__pyx_v_self->mode, __pyx_n_u_fortran, Py_EQ)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 189, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":190
* bufmode = PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* elif self.mode == u"fortran":
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not (flags & bufmode):
* raise ValueError("Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.")
*/
__pyx_v_bufmode = (PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS);
/* "View.MemoryView":189
* if self.mode == u"c":
* bufmode = PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* elif self.mode == u"fortran": # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* if not (flags & bufmode):
*/
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":191
* elif self.mode == u"fortran":
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* if not (flags & bufmode): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.")
* info.buf = self.data
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((!((__pyx_v_flags & __pyx_v_bufmode) != 0)) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":192
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* if not (flags & bufmode):
* raise ValueError("Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.buf = self.data
* info.len = self.len
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_tuple__5, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 192, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 192, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":191
* elif self.mode == u"fortran":
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* if not (flags & bufmode): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.")
* info.buf = self.data
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":193
* if not (flags & bufmode):
* raise ValueError("Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.")
* info.buf = self.data # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.len = self.len
* info.ndim = self.ndim
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_self->data;
__pyx_v_info->buf = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":194
* raise ValueError("Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.")
* info.buf = self.data
* info.len = self.len # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.ndim = self.ndim
* info.shape = self._shape
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_self->len;
__pyx_v_info->len = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":195
* info.buf = self.data
* info.len = self.len
* info.ndim = self.ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.shape = self._shape
* info.strides = self._strides
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_v_self->ndim;
__pyx_v_info->ndim = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":196
* info.len = self.len
* info.ndim = self.ndim
* info.shape = self._shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.strides = self._strides
* info.suboffsets = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_v_self->_shape;
__pyx_v_info->shape = __pyx_t_7;
/* "View.MemoryView":197
* info.ndim = self.ndim
* info.shape = self._shape
* info.strides = self._strides # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.suboffsets = NULL
* info.itemsize = self.itemsize
*/
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_v_self->_strides;
__pyx_v_info->strides = __pyx_t_7;
/* "View.MemoryView":198
* info.shape = self._shape
* info.strides = self._strides
* info.suboffsets = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.itemsize = self.itemsize
* info.readonly = 0
*/
__pyx_v_info->suboffsets = NULL;
/* "View.MemoryView":199
* info.strides = self._strides
* info.suboffsets = NULL
* info.itemsize = self.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.readonly = 0
*
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_self->itemsize;
__pyx_v_info->itemsize = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":200
* info.suboffsets = NULL
* info.itemsize = self.itemsize
* info.readonly = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT:
*/
__pyx_v_info->readonly = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":202
* info.readonly = 0
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.format = self.format
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_flags & PyBUF_FORMAT) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":203
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT:
* info.format = self.format # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* info.format = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_self->format;
__pyx_v_info->format = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":202
* info.readonly = 0
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.format = self.format
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L5;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":205
* info.format = self.format
* else:
* info.format = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* info.obj = self
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_info->format = NULL;
}
__pyx_L5:;
/* "View.MemoryView":207
* info.format = NULL
*
* info.obj = self # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_array_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
__Pyx_GIVEREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__pyx_v_info->obj = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self);
/* "View.MemoryView":185
*
* @cname('getbuffer')
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int bufmode = -1
* if self.mode == u"c":
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__getbuffer__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
if (__pyx_v_info->obj != NULL) {
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_info->obj); __pyx_v_info->obj = 0;
}
goto __pyx_L2;
__pyx_L0:;
if (__pyx_v_info->obj == Py_None) {
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_info->obj); __pyx_v_info->obj = 0;
}
__pyx_L2:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":211
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_array_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")
*
* def __dealloc__(array self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.callback_free_data != NULL:
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static void __pyx_array___dealloc__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_array___dealloc__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__dealloc__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_4__dealloc__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
static void __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_4__dealloc__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__dealloc__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":212
*
* def __dealloc__(array self):
* if self.callback_free_data != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
* elif self.free_data:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->callback_free_data != NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":213
* def __dealloc__(array self):
* if self.callback_free_data != NULL:
* self.callback_free_data(self.data) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif self.free_data:
* if self.dtype_is_object:
*/
__pyx_v_self->callback_free_data(__pyx_v_self->data);
/* "View.MemoryView":212
*
* def __dealloc__(array self):
* if self.callback_free_data != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
* elif self.free_data:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":214
* if self.callback_free_data != NULL:
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
* elif self.free_data: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.dtype_is_object:
* refcount_objects_in_slice(self.data, self._shape,
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_self->free_data != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":215
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
* elif self.free_data:
* if self.dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* refcount_objects_in_slice(self.data, self._shape,
* self._strides, self.ndim, False)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":216
* elif self.free_data:
* if self.dtype_is_object:
* refcount_objects_in_slice(self.data, self._shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self._strides, self.ndim, False)
* free(self.data)
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice(__pyx_v_self->data, __pyx_v_self->_shape, __pyx_v_self->_strides, __pyx_v_self->ndim, 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":215
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
* elif self.free_data:
* if self.dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* refcount_objects_in_slice(self.data, self._shape,
* self._strides, self.ndim, False)
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":218
* refcount_objects_in_slice(self.data, self._shape,
* self._strides, self.ndim, False)
* free(self.data) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* PyObject_Free(self._shape)
*
*/
free(__pyx_v_self->data);
/* "View.MemoryView":214
* if self.callback_free_data != NULL:
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
* elif self.free_data: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.dtype_is_object:
* refcount_objects_in_slice(self.data, self._shape,
*/
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":219
* self._strides, self.ndim, False)
* free(self.data)
* PyObject_Free(self._shape) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
PyObject_Free(__pyx_v_self->_shape);
/* "View.MemoryView":211
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_array_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")
*
* def __dealloc__(array self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.callback_free_data != NULL:
* self.callback_free_data(self.data)
*/
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
/* "View.MemoryView":222
*
* @property
* def memview(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.get_memview()
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_7memview_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_7memview_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_7memview___get__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_7memview___get__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":223
* @property
* def memview(self):
* return self.get_memview() # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('get_memview')
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->get_memview(__pyx_v_self); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 223, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":222
*
* @property
* def memview(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.get_memview()
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.memview.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":226
*
* @cname('get_memview')
* cdef get_memview(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* flags = PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS|PyBUF_FORMAT|PyBUF_WRITABLE
* return memoryview(self, flags, self.dtype_is_object)
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_array_get_memview(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
int __pyx_v_flags;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("get_memview", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":227
* @cname('get_memview')
* cdef get_memview(self):
* flags = PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS|PyBUF_FORMAT|PyBUF_WRITABLE # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return memoryview(self, flags, self.dtype_is_object)
*
*/
__pyx_v_flags = ((PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_FORMAT) | PyBUF_WRITABLE);
/* "View.MemoryView":228
* cdef get_memview(self):
* flags = PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS|PyBUF_FORMAT|PyBUF_WRITABLE
* return memoryview(self, flags, self.dtype_is_object) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __len__(self):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(__pyx_v_flags); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 228, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 228, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 228, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
__Pyx_GIVEREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 0, ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 1, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 2, __pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_memoryview_type), __pyx_t_3, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 228, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":226
*
* @cname('get_memview')
* cdef get_memview(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* flags = PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS|PyBUF_FORMAT|PyBUF_WRITABLE
* return memoryview(self, flags, self.dtype_is_object)
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.get_memview", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":230
* return memoryview(self, flags, self.dtype_is_object)
*
* def __len__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self._shape[0]
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_array___len__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_array___len__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__len__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_6__len__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_6__len__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__len__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":231
*
* def __len__(self):
* return self._shape[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __getattr__(self, attr):
*/
__pyx_r = (__pyx_v_self->_shape[0]);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":230
* return memoryview(self, flags, self.dtype_is_object)
*
* def __len__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self._shape[0]
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":233
* return self._shape[0]
*
* def __getattr__(self, attr): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return getattr(self.memview, attr)
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_array___getattr__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_attr); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_array___getattr__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_attr) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getattr__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_8__getattr__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_attr));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_8__getattr__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_attr) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getattr__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":234
*
* def __getattr__(self, attr):
* return getattr(self.memview, attr) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __getitem__(self, item):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_n_s_memview); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 234, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_GetAttr(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_v_attr); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 234, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":233
* return self._shape[0]
*
* def __getattr__(self, attr): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return getattr(self.memview, attr)
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__getattr__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":236
* return getattr(self.memview, attr)
*
* def __getitem__(self, item): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.memview[item]
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_array___getitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_array___getitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getitem__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_10__getitem__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_item));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_10__getitem__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getitem__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":237
*
* def __getitem__(self, item):
* return self.memview[item] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __setitem__(self, item, value):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_n_s_memview); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 237, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_v_item); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 237, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":236
* return getattr(self.memview, attr)
*
* def __getitem__(self, item): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.memview[item]
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__getitem__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":239
* return self.memview[item]
*
* def __setitem__(self, item, value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.memview[item] = value
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static int __pyx_array___setitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_array___setitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setitem__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_12__setitem__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_item), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_value));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static int __pyx_array___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_12__setitem__(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_item, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setitem__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":240
*
* def __setitem__(self, item, value):
* self.memview[item] = value # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_n_s_memview); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 240, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (unlikely(PyObject_SetItem(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_v_item, __pyx_v_value) < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 240, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":239
* return self.memview[item]
*
* def __setitem__(self, item, value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.memview[item] = value
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__setitem__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_array_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_array_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_array___reduce_cython__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_array___reduce_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":2
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_tuple__6, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_1, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__reduce_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":3
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_array_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_array_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_array_2__setstate_cython__(((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v___pyx_state));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_array_2__setstate_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_tuple__7, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_1, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "(tree fragment)":3
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array.__setstate_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":244
*
* @cname("__pyx_array_new")
* cdef array array_cwrapper(tuple shape, Py_ssize_t itemsize, char *format, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* char *mode, char *buf):
* cdef array result
*/
static struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_array_new(PyObject *__pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_itemsize, char *__pyx_v_format, char *__pyx_v_mode, char *__pyx_v_buf) {
struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_result = 0;
struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("array_cwrapper", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":248
* cdef array result
*
* if buf == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'))
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_buf == NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":249
*
* if buf == NULL:
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII')) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'),
*/
__pyx_t_2 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_itemsize); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 249, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString(__pyx_v_format); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 249, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_decode_c_string(__pyx_v_mode, 0, strlen(__pyx_v_mode), NULL, NULL, PyUnicode_DecodeASCII); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 249, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_5 = PyTuple_New(4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 249, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_shape);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_shape);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 0, __pyx_v_shape);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 1, __pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 2, __pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 3, __pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_array_type), __pyx_t_5, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 249, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_v_result = ((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":248
* cdef array result
*
* if buf == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'))
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":251
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'))
* else:
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'), # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* allocate_buffer=False)
* result.data = buf
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_4 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_itemsize); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 251, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString(__pyx_v_format); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 251, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_decode_c_string(__pyx_v_mode, 0, strlen(__pyx_v_mode), NULL, NULL, PyUnicode_DecodeASCII); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 251, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_2 = PyTuple_New(4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 251, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_shape);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_shape);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, 0, __pyx_v_shape);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, 1, __pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_5);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, 2, __pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, 3, __pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":252
* else:
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'),
* allocate_buffer=False) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.data = buf
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 252, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_n_s_allocate_buffer, Py_False) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 252, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":251
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'))
* else:
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'), # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* allocate_buffer=False)
* result.data = buf
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_array_type), __pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 251, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_v_result = ((struct __pyx_array_obj *)__pyx_t_5);
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":253
* result = array(shape, itemsize, format, mode.decode('ASCII'),
* allocate_buffer=False)
* result.data = buf # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return result
*/
__pyx_v_result->data = __pyx_v_buf;
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":255
* result.data = buf
*
* return result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_r));
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result));
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_result;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":244
*
* @cname("__pyx_array_new")
* cdef array array_cwrapper(tuple shape, Py_ssize_t itemsize, char *format, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* char *mode, char *buf):
* cdef array result
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.array_cwrapper", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF((PyObject *)__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":281
* cdef class Enum(object):
* cdef object name
* def __init__(self, name): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.name = name
* def __repr__(self):
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static int __pyx_MemviewEnum___init__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_MemviewEnum___init__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_name = 0;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__init__ (wrapper)", 0);
{
static PyObject **__pyx_pyargnames[] = {&__pyx_n_s_name,0};
PyObject* values[1] = {0};
if (unlikely(__pyx_kwds)) {
Py_ssize_t kw_args;
const Py_ssize_t pos_args = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args);
switch (pos_args) {
case 1: values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 0: break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
kw_args = PyDict_Size(__pyx_kwds);
switch (pos_args) {
case 0:
if (likely((values[0] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_name)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
if (unlikely(kw_args > 0)) {
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_pyargnames, 0, values, pos_args, "__init__") < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 281, __pyx_L3_error)
}
} else if (PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args) != 1) {
goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
} else {
values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
}
__pyx_v_name = values[0];
}
goto __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done;
__pyx_L5_argtuple_error:;
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__init__", 1, 1, 1, PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args)); __PYX_ERR(1, 281, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_L3_error:;
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.Enum.__init__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return -1;
__pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done:;
__pyx_r = __pyx_MemviewEnum___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_4Enum___init__(((struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_v_name);
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static int __pyx_MemviewEnum___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_4Enum___init__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_name) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__init__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":282
* cdef object name
* def __init__(self, name):
* self.name = name # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __repr__(self):
* return self.name
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_name);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_name);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_self->name);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_self->name);
__pyx_v_self->name = __pyx_v_name;
/* "View.MemoryView":281
* cdef class Enum(object):
* cdef object name
* def __init__(self, name): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.name = name
* def __repr__(self):
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":283
* def __init__(self, name):
* self.name = name
* def __repr__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.name
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_MemviewEnum___repr__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_MemviewEnum___repr__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__repr__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_MemviewEnum___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_4Enum_2__repr__(((struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_MemviewEnum___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_4Enum_2__repr__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__repr__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":284
* self.name = name
* def __repr__(self):
* return self.name # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef generic = Enum("")
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_self->name);
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_self->name;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":283
* def __init__(self, name):
* self.name = name
* def __repr__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.name
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef tuple state
* cdef object _dict
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_MemviewEnum_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_MemviewEnum_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_MemviewEnum___reduce_cython__(((struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_MemviewEnum___reduce_cython__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_state = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_v__dict = 0;
int __pyx_v_use_setstate;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":5
* cdef object _dict
* cdef bint use_setstate
* state = (self.name,) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _dict = getattr(self, '__dict__', None)
* if _dict is not None:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = PyTuple_New(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_self->name);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_self->name);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 0, __pyx_v_self->name);
__pyx_v_state = ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":6
* cdef bint use_setstate
* state = (self.name,)
* _dict = getattr(self, '__dict__', None) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if _dict is not None:
* state += (_dict,)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_GetAttr3(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_n_s_dict, Py_None); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_v__dict = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":7
* state = (self.name,)
* _dict = getattr(self, '__dict__', None)
* if _dict is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* state += (_dict,)
* use_setstate = True
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v__dict != Py_None);
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_3) {
/* "(tree fragment)":8
* _dict = getattr(self, '__dict__', None)
* if _dict is not None:
* state += (_dict,) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* use_setstate = True
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = PyTuple_New(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 8, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v__dict);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v__dict);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 0, __pyx_v__dict);
__pyx_t_4 = PyNumber_InPlaceAdd(__pyx_v_state, __pyx_t_1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 8, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_state, ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_4));
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":9
* if _dict is not None:
* state += (_dict,)
* use_setstate = True # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* use_setstate = self.name is not None
*/
__pyx_v_use_setstate = 1;
/* "(tree fragment)":7
* state = (self.name,)
* _dict = getattr(self, '__dict__', None)
* if _dict is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* state += (_dict,)
* use_setstate = True
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":11
* use_setstate = True
* else:
* use_setstate = self.name is not None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if use_setstate:
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, None), state
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_self->name != Py_None);
__pyx_v_use_setstate = __pyx_t_3;
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "(tree fragment)":12
* else:
* use_setstate = self.name is not None
* if use_setstate: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, None), state
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_use_setstate != 0);
if (__pyx_t_3) {
/* "(tree fragment)":13
* use_setstate = self.name is not None
* if use_setstate:
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, None), state # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, state)
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_n_s_pyx_unpickle_Enum); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_1 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self))));
__Pyx_GIVEREF(((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self))));
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 0, ((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self))));
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_int_184977713);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_int_184977713);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 1, __pyx_int_184977713);
__Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(Py_None);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 2, Py_None);
__pyx_t_5 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 0, __pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 1, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_state);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_state);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 2, __pyx_v_state);
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_5;
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "(tree fragment)":12
* else:
* use_setstate = self.name is not None
* if use_setstate: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, None), state
* else:
*/
}
/* "(tree fragment)":15
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, None), state
* else:
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, state) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(self, __pyx_state)
*/
/*else*/ {
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_n_s_pyx_unpickle_Enum); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 15, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__pyx_t_1 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 15, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self))));
__Pyx_GIVEREF(((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self))));
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 0, ((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self))));
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_int_184977713);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_int_184977713);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 1, __pyx_int_184977713);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_state);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_state);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_1, 2, __pyx_v_state);
__pyx_t_4 = PyTuple_New(2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 15, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_5);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, 0, __pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, 1, __pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_4;
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef tuple state
* cdef object _dict
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.Enum.__reduce_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_state);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v__dict);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":16
* else:
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, state)
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(self, __pyx_state)
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_MemviewEnum_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_MemviewEnum_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_MemviewEnum_2__setstate_cython__(((struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v___pyx_state));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_MemviewEnum_2__setstate_cython__(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":17
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, state)
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(self, __pyx_state) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
if (!(likely(PyTuple_CheckExact(__pyx_v___pyx_state))||((__pyx_v___pyx_state) == Py_None)||(PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected %.16s, got %.200s", "tuple", Py_TYPE(__pyx_v___pyx_state)->tp_name), 0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 17, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(__pyx_v_self, ((PyObject*)__pyx_v___pyx_state)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 17, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":16
* else:
* return __pyx_unpickle_Enum, (type(self), 0xb068931, state)
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(self, __pyx_state)
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.Enum.__setstate_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":298
*
* @cname('__pyx_align_pointer')
* cdef void *align_pointer(void *memory, size_t alignment) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Align pointer memory on a given boundary"
* cdef Py_intptr_t aligned_p = memory
*/
static void *__pyx_align_pointer(void *__pyx_v_memory, size_t __pyx_v_alignment) {
Py_intptr_t __pyx_v_aligned_p;
size_t __pyx_v_offset;
void *__pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":300
* cdef void *align_pointer(void *memory, size_t alignment) nogil:
* "Align pointer memory on a given boundary"
* cdef Py_intptr_t aligned_p = memory # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef size_t offset
*
*/
__pyx_v_aligned_p = ((Py_intptr_t)__pyx_v_memory);
/* "View.MemoryView":304
*
* with cython.cdivision(True):
* offset = aligned_p % alignment # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if offset > 0:
*/
__pyx_v_offset = (__pyx_v_aligned_p % __pyx_v_alignment);
/* "View.MemoryView":306
* offset = aligned_p % alignment
*
* if offset > 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* aligned_p += alignment - offset
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_offset > 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":307
*
* if offset > 0:
* aligned_p += alignment - offset # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return aligned_p
*/
__pyx_v_aligned_p = (__pyx_v_aligned_p + (__pyx_v_alignment - __pyx_v_offset));
/* "View.MemoryView":306
* offset = aligned_p % alignment
*
* if offset > 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* aligned_p += alignment - offset
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":309
* aligned_p += alignment - offset
*
* return aligned_p # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = ((void *)__pyx_v_aligned_p);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":298
*
* @cname('__pyx_align_pointer')
* cdef void *align_pointer(void *memory, size_t alignment) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Align pointer memory on a given boundary"
* cdef Py_intptr_t aligned_p = memory
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":345
* cdef __Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo
*
* def __cinit__(memoryview self, object obj, int flags, bint dtype_is_object=False): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.obj = obj
* self.flags = flags
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static int __pyx_memoryview___cinit__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview___cinit__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_obj = 0;
int __pyx_v_flags;
int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__cinit__ (wrapper)", 0);
{
static PyObject **__pyx_pyargnames[] = {&__pyx_n_s_obj,&__pyx_n_s_flags,&__pyx_n_s_dtype_is_object,0};
PyObject* values[3] = {0,0,0};
if (unlikely(__pyx_kwds)) {
Py_ssize_t kw_args;
const Py_ssize_t pos_args = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args);
switch (pos_args) {
case 3: values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2: values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1: values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 0: break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
kw_args = PyDict_Size(__pyx_kwds);
switch (pos_args) {
case 0:
if (likely((values[0] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_obj)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1:
if (likely((values[1] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_flags)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__cinit__", 0, 2, 3, 1); __PYX_ERR(1, 345, __pyx_L3_error)
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2:
if (kw_args > 0) {
PyObject* value = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_dtype_is_object);
if (value) { values[2] = value; kw_args--; }
}
}
if (unlikely(kw_args > 0)) {
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_pyargnames, 0, values, pos_args, "__cinit__") < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 345, __pyx_L3_error)
}
} else {
switch (PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args)) {
case 3: values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2: values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
}
__pyx_v_obj = values[0];
__pyx_v_flags = __Pyx_PyInt_As_int(values[1]); if (unlikely((__pyx_v_flags == (int)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 345, __pyx_L3_error)
if (values[2]) {
__pyx_v_dtype_is_object = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(values[2]); if (unlikely((__pyx_v_dtype_is_object == (int)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 345, __pyx_L3_error)
} else {
__pyx_v_dtype_is_object = ((int)0);
}
}
goto __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done;
__pyx_L5_argtuple_error:;
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__cinit__", 0, 2, 3, PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args)); __PYX_ERR(1, 345, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_L3_error:;
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__cinit__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return -1;
__pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done:;
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview___cinit__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_v_obj, __pyx_v_flags, __pyx_v_dtype_is_object);
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static int __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview___cinit__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_obj, int __pyx_v_flags, int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__cinit__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":346
*
* def __cinit__(memoryview self, object obj, int flags, bint dtype_is_object=False):
* self.obj = obj # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.flags = flags
* if type(self) is memoryview or obj is not None:
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_obj);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_obj);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_self->obj);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_self->obj);
__pyx_v_self->obj = __pyx_v_obj;
/* "View.MemoryView":347
* def __cinit__(memoryview self, object obj, int flags, bint dtype_is_object=False):
* self.obj = obj
* self.flags = flags # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if type(self) is memoryview or obj is not None:
* __Pyx_GetBuffer(obj, &self.view, flags)
*/
__pyx_v_self->flags = __pyx_v_flags;
/* "View.MemoryView":348
* self.obj = obj
* self.flags = flags
* if type(self) is memoryview or obj is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_GetBuffer(obj, &self.view, flags)
* if self.view.obj == NULL:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self))) == ((PyObject *)__pyx_memoryview_type));
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_3) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_3;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_obj != Py_None);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_3 != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L4_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":349
* self.flags = flags
* if type(self) is memoryview or obj is not None:
* __Pyx_GetBuffer(obj, &self.view, flags) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.obj == NULL:
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = Py_None
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_GetBuffer(__pyx_v_obj, (&__pyx_v_self->view), __pyx_v_flags); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 349, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":350
* if type(self) is memoryview or obj is not None:
* __Pyx_GetBuffer(obj, &self.view, flags)
* if self.view.obj == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = Py_None
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self->view.obj) == NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":351
* __Pyx_GetBuffer(obj, &self.view, flags)
* if self.view.obj == NULL:
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = Py_None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*
*/
((Py_buffer *)(&__pyx_v_self->view))->obj = Py_None;
/* "View.MemoryView":352
* if self.view.obj == NULL:
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = Py_None
* Py_INCREF(Py_None) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* global __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used
*/
Py_INCREF(Py_None);
/* "View.MemoryView":350
* if type(self) is memoryview or obj is not None:
* __Pyx_GetBuffer(obj, &self.view, flags)
* if self.view.obj == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = Py_None
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":348
* self.obj = obj
* self.flags = flags
* if type(self) is memoryview or obj is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_GetBuffer(obj, &self.view, flags)
* if self.view.obj == NULL:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":355
*
* global __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used < THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.lock = __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used += 1
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used < 8) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":356
* global __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used < THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED:
* self.lock = __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used += 1
* if self.lock is NULL:
*/
__pyx_v_self->lock = (__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]);
/* "View.MemoryView":357
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used < THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED:
* self.lock = __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.lock is NULL:
* self.lock = PyThread_allocate_lock()
*/
__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used = (__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used + 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":355
*
* global __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used < THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.lock = __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used += 1
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":358
* self.lock = __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used += 1
* if self.lock is NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.lock = PyThread_allocate_lock()
* if self.lock is NULL:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->lock == NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":359
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used += 1
* if self.lock is NULL:
* self.lock = PyThread_allocate_lock() # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.lock is NULL:
* raise MemoryError
*/
__pyx_v_self->lock = PyThread_allocate_lock();
/* "View.MemoryView":360
* if self.lock is NULL:
* self.lock = PyThread_allocate_lock()
* if self.lock is NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->lock == NULL) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":361
* self.lock = PyThread_allocate_lock()
* if self.lock is NULL:
* raise MemoryError # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT:
*/
PyErr_NoMemory(); __PYX_ERR(1, 361, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":360
* if self.lock is NULL:
* self.lock = PyThread_allocate_lock()
* if self.lock is NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":358
* self.lock = __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used += 1
* if self.lock is NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.lock = PyThread_allocate_lock()
* if self.lock is NULL:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":363
* raise MemoryError
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.dtype_is_object = (self.view.format[0] == b'O' and self.view.format[1] == b'\0')
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_flags & PyBUF_FORMAT) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":364
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT:
* self.dtype_is_object = (self.view.format[0] == b'O' and self.view.format[1] == b'\0') # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* self.dtype_is_object = dtype_is_object
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_self->view.format[0]) == 'O') != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L11_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_self->view.format[1]) == '\x00') != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L11_bool_binop_done:;
__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":363
* raise MemoryError
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.dtype_is_object = (self.view.format[0] == b'O' and self.view.format[1] == b'\0')
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L10;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":366
* self.dtype_is_object = (self.view.format[0] == b'O' and self.view.format[1] == b'\0')
* else:
* self.dtype_is_object = dtype_is_object # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* self.acquisition_count_aligned_p = <__pyx_atomic_int *> align_pointer(
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object = __pyx_v_dtype_is_object;
}
__pyx_L10:;
/* "View.MemoryView":368
* self.dtype_is_object = dtype_is_object
*
* self.acquisition_count_aligned_p = <__pyx_atomic_int *> align_pointer( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* &self.acquisition_count[0], sizeof(__pyx_atomic_int))
* self.typeinfo = NULL
*/
__pyx_v_self->acquisition_count_aligned_p = ((__pyx_atomic_int *)__pyx_align_pointer(((void *)(&(__pyx_v_self->acquisition_count[0]))), (sizeof(__pyx_atomic_int))));
/* "View.MemoryView":370
* self.acquisition_count_aligned_p = <__pyx_atomic_int *> align_pointer(
* &self.acquisition_count[0], sizeof(__pyx_atomic_int))
* self.typeinfo = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __dealloc__(memoryview self):
*/
__pyx_v_self->typeinfo = NULL;
/* "View.MemoryView":345
* cdef __Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo
*
* def __cinit__(memoryview self, object obj, int flags, bint dtype_is_object=False): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.obj = obj
* self.flags = flags
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__cinit__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":372
* self.typeinfo = NULL
*
* def __dealloc__(memoryview self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.obj is not None:
* __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(&self.view)
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static void __pyx_memoryview___dealloc__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview___dealloc__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__dealloc__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_2__dealloc__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
static void __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_2__dealloc__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
int __pyx_v_i;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
int __pyx_t_5;
PyThread_type_lock __pyx_t_6;
PyThread_type_lock __pyx_t_7;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__dealloc__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":373
*
* def __dealloc__(memoryview self):
* if self.obj is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(&self.view)
* elif (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj == Py_None:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_self->obj != Py_None);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":374
* def __dealloc__(memoryview self):
* if self.obj is not None:
* __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(&self.view) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj == Py_None:
*
*/
__Pyx_ReleaseBuffer((&__pyx_v_self->view));
/* "View.MemoryView":373
*
* def __dealloc__(memoryview self):
* if self.obj is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(&self.view)
* elif (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj == Py_None:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":375
* if self.obj is not None:
* __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(&self.view)
* elif (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj == Py_None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((((Py_buffer *)(&__pyx_v_self->view))->obj == Py_None) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":377
* elif (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj == Py_None:
*
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_DECREF(Py_None)
*
*/
((Py_buffer *)(&__pyx_v_self->view))->obj = NULL;
/* "View.MemoryView":378
*
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = NULL
* Py_DECREF(Py_None) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef int i
*/
Py_DECREF(Py_None);
/* "View.MemoryView":375
* if self.obj is not None:
* __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(&self.view)
* elif (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj == Py_None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &self.view).obj = NULL
*/
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":382
* cdef int i
* global __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used
* if self.lock != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for i in range(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used):
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_self->lock != NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":383
* global __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used
* if self.lock != NULL:
* for i in range(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock:
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used -= 1
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used;
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_t_3;
for (__pyx_t_5 = 0; __pyx_t_5 < __pyx_t_4; __pyx_t_5+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":384
* if self.lock != NULL:
* for i in range(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used):
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used -= 1
* if i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_v_i]) == __pyx_v_self->lock) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":385
* for i in range(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used):
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock:
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used -= 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used:
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used] = (
*/
__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used = (__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used - 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":386
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock:
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used -= 1
* if i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used] = (
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i])
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":388
* if i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used:
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used] = (
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* break
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = (__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]);
__pyx_t_7 = (__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_v_i]);
/* "View.MemoryView":387
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used -= 1
* if i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used:
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used] = ( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i])
* break
*/
(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_v_i]) = __pyx_t_6;
(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used]) = __pyx_t_7;
/* "View.MemoryView":386
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock:
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used -= 1
* if i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used] = (
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i])
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":389
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used] = (
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used], __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i])
* break # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* PyThread_free_lock(self.lock)
*/
goto __pyx_L6_break;
/* "View.MemoryView":384
* if self.lock != NULL:
* for i in range(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used):
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used -= 1
* if i != __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used:
*/
}
}
/*else*/ {
/* "View.MemoryView":391
* break
* else:
* PyThread_free_lock(self.lock) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef char *get_item_pointer(memoryview self, object index) except NULL:
*/
PyThread_free_lock(__pyx_v_self->lock);
}
__pyx_L6_break:;
/* "View.MemoryView":382
* cdef int i
* global __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used
* if self.lock != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for i in range(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used):
* if __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[i] is self.lock:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":372
* self.typeinfo = NULL
*
* def __dealloc__(memoryview self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.obj is not None:
* __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(&self.view)
*/
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
/* "View.MemoryView":393
* PyThread_free_lock(self.lock)
*
* cdef char *get_item_pointer(memoryview self, object index) except NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t dim
* cdef char *itemp = self.view.buf
*/
static char *__pyx_memoryview_get_item_pointer(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_dim;
char *__pyx_v_itemp;
PyObject *__pyx_v_idx = NULL;
char *__pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_3;
PyObject *(*__pyx_t_4)(PyObject *);
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_6;
char *__pyx_t_7;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("get_item_pointer", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":395
* cdef char *get_item_pointer(memoryview self, object index) except NULL:
* cdef Py_ssize_t dim
* cdef char *itemp = self.view.buf # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for dim, idx in enumerate(index):
*/
__pyx_v_itemp = ((char *)__pyx_v_self->view.buf);
/* "View.MemoryView":397
* cdef char *itemp = self.view.buf
*
* for dim, idx in enumerate(index): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* itemp = pybuffer_index(&self.view, itemp, idx, dim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_v_index)) || PyTuple_CheckExact(__pyx_v_index)) {
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_index; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
} else {
__pyx_t_3 = -1; __pyx_t_2 = PyObject_GetIter(__pyx_v_index); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 397, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_4 = Py_TYPE(__pyx_t_2)->tp_iternext; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 397, __pyx_L1_error)
}
for (;;) {
if (likely(!__pyx_t_4)) {
if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_t_2))) {
if (__pyx_t_3 >= PyList_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_2)) break;
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_5 = PyList_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_3++; if (unlikely(0 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 397, __pyx_L1_error)
#else
__pyx_t_5 = PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3++; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 397, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
#endif
} else {
if (__pyx_t_3 >= PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_2)) break;
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_5 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_3++; if (unlikely(0 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 397, __pyx_L1_error)
#else
__pyx_t_5 = PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3++; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 397, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
#endif
}
} else {
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_t_4(__pyx_t_2);
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) {
PyObject* exc_type = PyErr_Occurred();
if (exc_type) {
if (likely(__Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(exc_type, PyExc_StopIteration))) PyErr_Clear();
else __PYX_ERR(1, 397, __pyx_L1_error)
}
break;
}
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
}
__Pyx_XDECREF_SET(__pyx_v_idx, __pyx_t_5);
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_v_dim = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_1 + 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":398
*
* for dim, idx in enumerate(index):
* itemp = pybuffer_index(&self.view, itemp, idx, dim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return itemp
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(__pyx_v_idx); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_6 == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 398, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_pybuffer_index((&__pyx_v_self->view), __pyx_v_itemp, __pyx_t_6, __pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_7 == ((char *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 398, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_itemp = __pyx_t_7;
/* "View.MemoryView":397
* cdef char *itemp = self.view.buf
*
* for dim, idx in enumerate(index): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* itemp = pybuffer_index(&self.view, itemp, idx, dim)
*
*/
}
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":400
* itemp = pybuffer_index(&self.view, itemp, idx, dim)
*
* return itemp # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_itemp;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":393
* PyThread_free_lock(self.lock)
*
* cdef char *get_item_pointer(memoryview self, object index) except NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t dim
* cdef char *itemp = self.view.buf
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.get_item_pointer", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_idx);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":403
*
*
* def __getitem__(memoryview self, object index): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if index is Ellipsis:
* return self
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___getitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___getitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getitem__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4__getitem__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_index));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4__getitem__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_have_slices = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_indices = NULL;
char *__pyx_v_itemp;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
char *__pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getitem__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":404
*
* def __getitem__(memoryview self, object index):
* if index is Ellipsis: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_index == __pyx_builtin_Ellipsis);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":405
* def __getitem__(memoryview self, object index):
* if index is Ellipsis:
* return self # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* have_slices, indices = _unellipsify(index, self.view.ndim)
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
__pyx_r = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":404
*
* def __getitem__(memoryview self, object index):
* if index is Ellipsis: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":407
* return self
*
* have_slices, indices = _unellipsify(index, self.view.ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef char *itemp
*/
__pyx_t_3 = _unellipsify(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_v_self->view.ndim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 407, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
if (likely(__pyx_t_3 != Py_None)) {
PyObject* sequence = __pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t size = __Pyx_PySequence_SIZE(sequence);
if (unlikely(size != 2)) {
if (size > 2) __Pyx_RaiseTooManyValuesError(2);
else if (size >= 0) __Pyx_RaiseNeedMoreValuesError(size);
__PYX_ERR(1, 407, __pyx_L1_error)
}
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_4 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(sequence, 0);
__pyx_t_5 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(sequence, 1);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5);
#else
__pyx_t_4 = PySequence_ITEM(sequence, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 407, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_5 = PySequence_ITEM(sequence, 1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 407, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
#endif
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
} else {
__Pyx_RaiseNoneNotIterableError(); __PYX_ERR(1, 407, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_v_have_slices = __pyx_t_4;
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_v_indices = __pyx_t_5;
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":410
*
* cdef char *itemp
* if have_slices: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return memview_slice(self, indices)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_v_have_slices); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 410, __pyx_L1_error)
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":411
* cdef char *itemp
* if have_slices:
* return memview_slice(self, indices) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* itemp = self.get_item_pointer(indices)
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_3 = ((PyObject *)__pyx_memview_slice(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_v_indices)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 411, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":410
*
* cdef char *itemp
* if have_slices: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return memview_slice(self, indices)
* else:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":413
* return memview_slice(self, indices)
* else:
* itemp = self.get_item_pointer(indices) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.convert_item_to_object(itemp)
*
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_6 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->get_item_pointer(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_v_indices); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_6 == ((char *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 413, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_itemp = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":414
* else:
* itemp = self.get_item_pointer(indices)
* return self.convert_item_to_object(itemp) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __setitem__(memoryview self, object index, object value):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_3 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->convert_item_to_object(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_v_itemp); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 414, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":403
*
*
* def __getitem__(memoryview self, object index): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if index is Ellipsis:
* return self
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__getitem__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_have_slices);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_indices);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":416
* return self.convert_item_to_object(itemp)
*
* def __setitem__(memoryview self, object index, object value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.readonly:
* raise TypeError("Cannot assign to read-only memoryview")
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static int __pyx_memoryview___setitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview___setitem__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setitem__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6__setitem__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_index), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_value));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static int __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6__setitem__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_have_slices = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_obj = NULL;
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setitem__", 0);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_index);
/* "View.MemoryView":417
*
* def __setitem__(memoryview self, object index, object value):
* if self.view.readonly: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("Cannot assign to read-only memoryview")
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_self->view.readonly != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":418
* def __setitem__(memoryview self, object index, object value):
* if self.view.readonly:
* raise TypeError("Cannot assign to read-only memoryview") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* have_slices, index = _unellipsify(index, self.view.ndim)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_tuple__8, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 418, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_2, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 418, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":417
*
* def __setitem__(memoryview self, object index, object value):
* if self.view.readonly: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("Cannot assign to read-only memoryview")
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":420
* raise TypeError("Cannot assign to read-only memoryview")
*
* have_slices, index = _unellipsify(index, self.view.ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if have_slices:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = _unellipsify(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_v_self->view.ndim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 420, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
if (likely(__pyx_t_2 != Py_None)) {
PyObject* sequence = __pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t size = __Pyx_PySequence_SIZE(sequence);
if (unlikely(size != 2)) {
if (size > 2) __Pyx_RaiseTooManyValuesError(2);
else if (size >= 0) __Pyx_RaiseNeedMoreValuesError(size);
__PYX_ERR(1, 420, __pyx_L1_error)
}
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_3 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(sequence, 0);
__pyx_t_4 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(sequence, 1);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_4);
#else
__pyx_t_3 = PySequence_ITEM(sequence, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 420, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = PySequence_ITEM(sequence, 1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 420, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
#endif
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
} else {
__Pyx_RaiseNoneNotIterableError(); __PYX_ERR(1, 420, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_v_have_slices = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":422
* have_slices, index = _unellipsify(index, self.view.ndim)
*
* if have_slices: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* obj = self.is_slice(value)
* if obj:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_v_have_slices); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 422, __pyx_L1_error)
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":423
*
* if have_slices:
* obj = self.is_slice(value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if obj:
* self.setitem_slice_assignment(self[index], obj)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->is_slice(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 423, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_v_obj = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":424
* if have_slices:
* obj = self.is_slice(value)
* if obj: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.setitem_slice_assignment(self[index], obj)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_v_obj); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 424, __pyx_L1_error)
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":425
* obj = self.is_slice(value)
* if obj:
* self.setitem_slice_assignment(self[index], obj) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* self.setitem_slice_assign_scalar(self[index], value)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_v_index); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 425, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_4 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->setitem_slice_assignment(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_t_2, __pyx_v_obj); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 425, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":424
* if have_slices:
* obj = self.is_slice(value)
* if obj: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.setitem_slice_assignment(self[index], obj)
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L5;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":427
* self.setitem_slice_assignment(self[index], obj)
* else:
* self.setitem_slice_assign_scalar(self[index], value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* self.setitem_indexed(index, value)
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_v_index); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 427, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
if (!(likely(((__pyx_t_4) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_memoryview_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 427, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_2 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->setitem_slice_assign_scalar(__pyx_v_self, ((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_t_4), __pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 427, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
}
__pyx_L5:;
/* "View.MemoryView":422
* have_slices, index = _unellipsify(index, self.view.ndim)
*
* if have_slices: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* obj = self.is_slice(value)
* if obj:
*/
goto __pyx_L4;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":429
* self.setitem_slice_assign_scalar(self[index], value)
* else:
* self.setitem_indexed(index, value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef is_slice(self, obj):
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_2 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->setitem_indexed(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_v_index, __pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 429, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
}
__pyx_L4:;
/* "View.MemoryView":416
* return self.convert_item_to_object(itemp)
*
* def __setitem__(memoryview self, object index, object value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.readonly:
* raise TypeError("Cannot assign to read-only memoryview")
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__setitem__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_have_slices);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_obj);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_index);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":431
* self.setitem_indexed(index, value)
*
* cdef is_slice(self, obj): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview):
* try:
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_is_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_obj) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_7 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_8 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_9;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("is_slice", 0);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_obj);
/* "View.MemoryView":432
*
* cdef is_slice(self, obj):
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* try:
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS,
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_TypeCheck(__pyx_v_obj, __pyx_memoryview_type);
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_t_1 != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":433
* cdef is_slice(self, obj):
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview):
* try: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS,
* self.dtype_is_object)
*/
{
__Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
__Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
__Pyx_ExceptionSave(&__pyx_t_3, &__pyx_t_4, &__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
/*try:*/ {
/* "View.MemoryView":434
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview):
* try:
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.dtype_is_object)
* except TypeError:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(((__pyx_v_self->flags & (~PyBUF_WRITABLE)) | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 434, __pyx_L4_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
/* "View.MemoryView":435
* try:
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS,
* self.dtype_is_object) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* except TypeError:
* return None
*/
__pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 435, __pyx_L4_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
/* "View.MemoryView":434
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview):
* try:
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.dtype_is_object)
* except TypeError:
*/
__pyx_t_8 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_8)) __PYX_ERR(1, 434, __pyx_L4_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_obj);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_obj);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_8, 0, __pyx_v_obj);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_6);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_8, 1, __pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_7);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_8, 2, __pyx_t_7);
__pyx_t_6 = 0;
__pyx_t_7 = 0;
__pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_memoryview_type), __pyx_t_8, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 434, __pyx_L4_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_8 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_obj, __pyx_t_7);
__pyx_t_7 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":433
* cdef is_slice(self, obj):
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview):
* try: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS,
* self.dtype_is_object)
*/
}
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
goto __pyx_L9_try_end;
__pyx_L4_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_8 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":436
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS,
* self.dtype_is_object)
* except TypeError: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return None
*
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatches(__pyx_builtin_TypeError);
if (__pyx_t_9) {
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.is_slice", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
if (__Pyx_GetException(&__pyx_t_7, &__pyx_t_8, &__pyx_t_6) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 436, __pyx_L6_except_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
/* "View.MemoryView":437
* self.dtype_is_object)
* except TypeError:
* return None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return obj
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_8 = 0;
goto __pyx_L7_except_return;
}
goto __pyx_L6_except_error;
__pyx_L6_except_error:;
/* "View.MemoryView":433
* cdef is_slice(self, obj):
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview):
* try: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS,
* self.dtype_is_object)
*/
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_ExceptionReset(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5);
goto __pyx_L1_error;
__pyx_L7_except_return:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_ExceptionReset(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L9_try_end:;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":432
*
* cdef is_slice(self, obj):
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* try:
* obj = memoryview(obj, self.flags & ~PyBUF_WRITABLE | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS,
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":439
* return None
*
* return obj # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef setitem_slice_assignment(self, dst, src):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_obj);
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_obj;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":431
* self.setitem_indexed(index, value)
*
* cdef is_slice(self, obj): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not isinstance(obj, memoryview):
* try:
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.is_slice", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_obj);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":441
* return obj
*
* cdef setitem_slice_assignment(self, dst, src): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice dst_slice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src_slice
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assignment(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_dst, PyObject *__pyx_v_src) {
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_dst_slice;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_src_slice;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_t_1;
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_4;
int __pyx_t_5;
int __pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("setitem_slice_assignment", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":445
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src_slice
*
* memoryview_copy_contents(get_slice_from_memview(src, &src_slice)[0], # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* get_slice_from_memview(dst, &dst_slice)[0],
* src.ndim, dst.ndim, self.dtype_is_object)
*/
if (!(likely(((__pyx_v_src) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(__pyx_v_src, __pyx_memoryview_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 445, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_src), (&__pyx_v_src_slice)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 == ((__Pyx_memviewslice *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 445, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":446
*
* memoryview_copy_contents(get_slice_from_memview(src, &src_slice)[0],
* get_slice_from_memview(dst, &dst_slice)[0], # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src.ndim, dst.ndim, self.dtype_is_object)
*
*/
if (!(likely(((__pyx_v_dst) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(__pyx_v_dst, __pyx_memoryview_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 446, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_dst), (&__pyx_v_dst_slice)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2 == ((__Pyx_memviewslice *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 446, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":447
* memoryview_copy_contents(get_slice_from_memview(src, &src_slice)[0],
* get_slice_from_memview(dst, &dst_slice)[0],
* src.ndim, dst.ndim, self.dtype_is_object) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef setitem_slice_assign_scalar(self, memoryview dst, value):
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_src, __pyx_n_s_ndim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 447, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyInt_As_int(__pyx_t_3); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_4 == (int)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 447, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_dst, __pyx_n_s_ndim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 447, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyInt_As_int(__pyx_t_3); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_5 == (int)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 447, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":445
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src_slice
*
* memoryview_copy_contents(get_slice_from_memview(src, &src_slice)[0], # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* get_slice_from_memview(dst, &dst_slice)[0],
* src.ndim, dst.ndim, self.dtype_is_object)
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_contents((__pyx_t_1[0]), (__pyx_t_2[0]), __pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_6 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 445, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":441
* return obj
*
* cdef setitem_slice_assignment(self, dst, src): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice dst_slice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src_slice
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.setitem_slice_assignment", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":449
* src.ndim, dst.ndim, self.dtype_is_object)
*
* cdef setitem_slice_assign_scalar(self, memoryview dst, value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int array[128]
* cdef void *tmp = NULL
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assign_scalar(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_dst, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
int __pyx_v_array[0x80];
void *__pyx_v_tmp;
void *__pyx_v_item;
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_dst_slice;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_tmp_slice;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_4;
int __pyx_t_5;
char const *__pyx_t_6;
PyObject *__pyx_t_7 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_8 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_9 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_10 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_11 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_12 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("setitem_slice_assign_scalar", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":451
* cdef setitem_slice_assign_scalar(self, memoryview dst, value):
* cdef int array[128]
* cdef void *tmp = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef void *item
*
*/
__pyx_v_tmp = NULL;
/* "View.MemoryView":456
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *dst_slice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp_slice
* dst_slice = get_slice_from_memview(dst, &tmp_slice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if self.view.itemsize > sizeof(array):
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(__pyx_v_dst, (&__pyx_v_tmp_slice)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 == ((__Pyx_memviewslice *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 456, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_dst_slice = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":458
* dst_slice = get_slice_from_memview(dst, &tmp_slice)
*
* if self.view.itemsize > sizeof(array): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tmp = PyMem_Malloc(self.view.itemsize)
* if tmp == NULL:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((((size_t)__pyx_v_self->view.itemsize) > (sizeof(__pyx_v_array))) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":459
*
* if self.view.itemsize > sizeof(array):
* tmp = PyMem_Malloc(self.view.itemsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if tmp == NULL:
* raise MemoryError
*/
__pyx_v_tmp = PyMem_Malloc(__pyx_v_self->view.itemsize);
/* "View.MemoryView":460
* if self.view.itemsize > sizeof(array):
* tmp = PyMem_Malloc(self.view.itemsize)
* if tmp == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError
* item = tmp
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_tmp == NULL) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":461
* tmp = PyMem_Malloc(self.view.itemsize)
* if tmp == NULL:
* raise MemoryError # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* item = tmp
* else:
*/
PyErr_NoMemory(); __PYX_ERR(1, 461, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":460
* if self.view.itemsize > sizeof(array):
* tmp = PyMem_Malloc(self.view.itemsize)
* if tmp == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise MemoryError
* item = tmp
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":462
* if tmp == NULL:
* raise MemoryError
* item = tmp # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* item = array
*/
__pyx_v_item = __pyx_v_tmp;
/* "View.MemoryView":458
* dst_slice = get_slice_from_memview(dst, &tmp_slice)
*
* if self.view.itemsize > sizeof(array): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tmp = PyMem_Malloc(self.view.itemsize)
* if tmp == NULL:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":464
* item = tmp
* else:
* item = array # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* try:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_item = ((void *)__pyx_v_array);
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":466
* item = array
*
* try: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.dtype_is_object:
* ( item)[0] = value
*/
/*try:*/ {
/* "View.MemoryView":467
*
* try:
* if self.dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* ( item)[0] = value
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":468
* try:
* if self.dtype_is_object:
* ( item)[0] = value # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* self.assign_item_from_object( item, value)
*/
(((PyObject **)__pyx_v_item)[0]) = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_value);
/* "View.MemoryView":467
*
* try:
* if self.dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* ( item)[0] = value
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L8;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":470
* ( item)[0] = value
* else:
* self.assign_item_from_object( item, value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_3 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->assign_item_from_object(__pyx_v_self, ((char *)__pyx_v_item), __pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 470, __pyx_L6_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
}
__pyx_L8:;
/* "View.MemoryView":474
*
*
* if self.view.suboffsets != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* assert_direct_dimensions(self.view.suboffsets, self.view.ndim)
* slice_assign_scalar(dst_slice, dst.view.ndim, self.view.itemsize,
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_self->view.suboffsets != NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":475
*
* if self.view.suboffsets != NULL:
* assert_direct_dimensions(self.view.suboffsets, self.view.ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* slice_assign_scalar(dst_slice, dst.view.ndim, self.view.itemsize,
* item, self.dtype_is_object)
*/
__pyx_t_3 = assert_direct_dimensions(__pyx_v_self->view.suboffsets, __pyx_v_self->view.ndim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 475, __pyx_L6_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":474
*
*
* if self.view.suboffsets != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* assert_direct_dimensions(self.view.suboffsets, self.view.ndim)
* slice_assign_scalar(dst_slice, dst.view.ndim, self.view.itemsize,
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":476
* if self.view.suboffsets != NULL:
* assert_direct_dimensions(self.view.suboffsets, self.view.ndim)
* slice_assign_scalar(dst_slice, dst.view.ndim, self.view.itemsize, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* item, self.dtype_is_object)
* finally:
*/
__pyx_memoryview_slice_assign_scalar(__pyx_v_dst_slice, __pyx_v_dst->view.ndim, __pyx_v_self->view.itemsize, __pyx_v_item, __pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object);
}
/* "View.MemoryView":479
* item, self.dtype_is_object)
* finally:
* PyMem_Free(tmp) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef setitem_indexed(self, index, value):
*/
/*finally:*/ {
/*normal exit:*/{
PyMem_Free(__pyx_v_tmp);
goto __pyx_L7;
}
__pyx_L6_error:;
/*exception exit:*/{
__Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
__Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
__pyx_t_7 = 0; __pyx_t_8 = 0; __pyx_t_9 = 0; __pyx_t_10 = 0; __pyx_t_11 = 0; __pyx_t_12 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
if (PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3) __Pyx_ExceptionSwap(&__pyx_t_10, &__pyx_t_11, &__pyx_t_12);
if ((PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3) || unlikely(__Pyx_GetException(&__pyx_t_7, &__pyx_t_8, &__pyx_t_9) < 0)) __Pyx_ErrFetch(&__pyx_t_7, &__pyx_t_8, &__pyx_t_9);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_11);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_12);
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_lineno; __pyx_t_5 = __pyx_clineno; __pyx_t_6 = __pyx_filename;
{
PyMem_Free(__pyx_v_tmp);
}
if (PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3) {
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_11);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_12);
__Pyx_ExceptionReset(__pyx_t_10, __pyx_t_11, __pyx_t_12);
}
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_9);
__Pyx_ErrRestore(__pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_8, __pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_7 = 0; __pyx_t_8 = 0; __pyx_t_9 = 0; __pyx_t_10 = 0; __pyx_t_11 = 0; __pyx_t_12 = 0;
__pyx_lineno = __pyx_t_4; __pyx_clineno = __pyx_t_5; __pyx_filename = __pyx_t_6;
goto __pyx_L1_error;
}
__pyx_L7:;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":449
* src.ndim, dst.ndim, self.dtype_is_object)
*
* cdef setitem_slice_assign_scalar(self, memoryview dst, value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int array[128]
* cdef void *tmp = NULL
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.setitem_slice_assign_scalar", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":481
* PyMem_Free(tmp)
*
* cdef setitem_indexed(self, index, value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef char *itemp = self.get_item_pointer(index)
* self.assign_item_from_object(itemp, value)
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_indexed(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
char *__pyx_v_itemp;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
char *__pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("setitem_indexed", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":482
*
* cdef setitem_indexed(self, index, value):
* cdef char *itemp = self.get_item_pointer(index) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.assign_item_from_object(itemp, value)
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->get_item_pointer(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_v_index); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 == ((char *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 482, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_itemp = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":483
* cdef setitem_indexed(self, index, value):
* cdef char *itemp = self.get_item_pointer(index)
* self.assign_item_from_object(itemp, value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp):
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *)__pyx_v_self->__pyx_vtab)->assign_item_from_object(__pyx_v_self, __pyx_v_itemp, __pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 483, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":481
* PyMem_Free(tmp)
*
* cdef setitem_indexed(self, index, value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef char *itemp = self.get_item_pointer(index)
* self.assign_item_from_object(itemp, value)
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.setitem_indexed", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":485
* self.assign_item_from_object(itemp, value)
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """Only used if instantiated manually by the user, or if Cython doesn't
* know how to convert the type"""
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_convert_item_to_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_struct = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_bytesitem = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_v_result = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_7 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_8;
PyObject *__pyx_t_9 = NULL;
size_t __pyx_t_10;
int __pyx_t_11;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("convert_item_to_object", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":488
* """Only used if instantiated manually by the user, or if Cython doesn't
* know how to convert the type"""
* import struct # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef bytes bytesitem
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_Import(__pyx_n_s_struct, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 488, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_v_struct = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":491
* cdef bytes bytesitem
*
* bytesitem = itemp[:self.view.itemsize] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* try:
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyBytes_FromStringAndSize(__pyx_v_itemp + 0, __pyx_v_self->view.itemsize - 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 491, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_v_bytesitem = ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":492
*
* bytesitem = itemp[:self.view.itemsize]
* try: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem)
* except struct.error:
*/
{
__Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
__Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
__Pyx_ExceptionSave(&__pyx_t_2, &__pyx_t_3, &__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
/*try:*/ {
/* "View.MemoryView":493
* bytesitem = itemp[:self.view.itemsize]
* try:
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* except struct.error:
* raise ValueError("Unable to convert item to object")
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_struct, __pyx_n_s_unpack); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 493, __pyx_L3_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString(__pyx_v_self->view.format); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 493, __pyx_L3_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_7 = NULL;
__pyx_t_8 = 0;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && likely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_5))) {
__pyx_t_7 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_5);
if (likely(__pyx_t_7)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_5, function);
__pyx_t_8 = 1;
}
}
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
if (PyFunction_Check(__pyx_t_5)) {
PyObject *__pyx_temp[3] = {__pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_6, __pyx_v_bytesitem};
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCall(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_temp+1-__pyx_t_8, 2+__pyx_t_8); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 493, __pyx_L3_error)
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
} else
#endif
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
if (__Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(__pyx_t_5)) {
PyObject *__pyx_temp[3] = {__pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_6, __pyx_v_bytesitem};
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_temp+1-__pyx_t_8, 2+__pyx_t_8); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 493, __pyx_L3_error)
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
} else
#endif
{
__pyx_t_9 = PyTuple_New(2+__pyx_t_8); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 493, __pyx_L3_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
if (__pyx_t_7) {
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_7); PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_9, 0, __pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = NULL;
}
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_6);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_9, 0+__pyx_t_8, __pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_bytesitem);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_bytesitem);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_9, 1+__pyx_t_8, __pyx_v_bytesitem);
__pyx_t_6 = 0;
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_9, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 493, __pyx_L3_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
}
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_v_result = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":492
*
* bytesitem = itemp[:self.view.itemsize]
* try: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem)
* except struct.error:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":497
* raise ValueError("Unable to convert item to object")
* else:
* if len(self.view.format) == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return result[0]
* return result
*/
/*else:*/ {
__pyx_t_10 = strlen(__pyx_v_self->view.format);
__pyx_t_11 = ((__pyx_t_10 == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_11) {
/* "View.MemoryView":498
* else:
* if len(self.view.format) == 1:
* return result[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return result
*
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_GetItemInt(__pyx_v_result, 0, long, 1, __Pyx_PyInt_From_long, 0, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 498, __pyx_L5_except_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
goto __pyx_L6_except_return;
/* "View.MemoryView":497
* raise ValueError("Unable to convert item to object")
* else:
* if len(self.view.format) == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return result[0]
* return result
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":499
* if len(self.view.format) == 1:
* return result[0]
* return result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_result);
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_result;
goto __pyx_L6_except_return;
}
__pyx_L3_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":494
* try:
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem)
* except struct.error: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Unable to convert item to object")
* else:
*/
__Pyx_ErrFetch(&__pyx_t_1, &__pyx_t_5, &__pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_struct, __pyx_n_s_error); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 494, __pyx_L5_except_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_8 = __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
__Pyx_ErrRestore(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_1 = 0; __pyx_t_5 = 0; __pyx_t_9 = 0;
if (__pyx_t_8) {
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.convert_item_to_object", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
if (__Pyx_GetException(&__pyx_t_9, &__pyx_t_5, &__pyx_t_1) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 494, __pyx_L5_except_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
/* "View.MemoryView":495
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem)
* except struct.error:
* raise ValueError("Unable to convert item to object") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* if len(self.view.format) == 1:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_tuple__9, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 495, __pyx_L5_except_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_6, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 495, __pyx_L5_except_error)
}
goto __pyx_L5_except_error;
__pyx_L5_except_error:;
/* "View.MemoryView":492
*
* bytesitem = itemp[:self.view.itemsize]
* try: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem)
* except struct.error:
*/
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_ExceptionReset(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_4);
goto __pyx_L1_error;
__pyx_L6_except_return:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_ExceptionReset(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_4);
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":485
* self.assign_item_from_object(itemp, value)
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """Only used if instantiated manually by the user, or if Cython doesn't
* know how to convert the type"""
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_9);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.convert_item_to_object", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_struct);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_bytesitem);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":501
* return result
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """Only used if instantiated manually by the user, or if Cython doesn't
* know how to convert the type"""
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_assign_item_from_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_struct = NULL;
char __pyx_v_c;
PyObject *__pyx_v_bytesvalue = 0;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_i;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_7;
PyObject *__pyx_t_8 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_9;
PyObject *__pyx_t_10 = NULL;
char *__pyx_t_11;
char *__pyx_t_12;
char *__pyx_t_13;
char *__pyx_t_14;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("assign_item_from_object", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":504
* """Only used if instantiated manually by the user, or if Cython doesn't
* know how to convert the type"""
* import struct # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef char c
* cdef bytes bytesvalue
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_Import(__pyx_n_s_struct, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 504, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_v_struct = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":509
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
*
* if isinstance(value, tuple): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, *value)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = PyTuple_Check(__pyx_v_value);
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_3) {
/* "View.MemoryView":510
*
* if isinstance(value, tuple):
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, *value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, value)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_struct, __pyx_n_s_pack); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 510, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString(__pyx_v_self->view.format); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 510, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_5 = PyTuple_New(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 510, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_5, 0, __pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PySequence_Tuple(__pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 510, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_6 = PyNumber_Add(__pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 510, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_t_6, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 510, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
if (!(likely(PyBytes_CheckExact(__pyx_t_4))||((__pyx_t_4) == Py_None)||(PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected %.16s, got %.200s", "bytes", Py_TYPE(__pyx_t_4)->tp_name), 0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 510, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_bytesvalue = ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":509
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
*
* if isinstance(value, tuple): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, *value)
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":512
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, *value)
* else:
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for i, c in enumerate(bytesvalue):
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_struct, __pyx_n_s_pack); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 512, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString(__pyx_v_self->view.format); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 512, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
__pyx_t_7 = 0;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && likely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_6))) {
__pyx_t_5 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_6);
if (likely(__pyx_t_5)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_6, function);
__pyx_t_7 = 1;
}
}
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
if (PyFunction_Check(__pyx_t_6)) {
PyObject *__pyx_temp[3] = {__pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_1, __pyx_v_value};
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCall(__pyx_t_6, __pyx_temp+1-__pyx_t_7, 2+__pyx_t_7); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 512, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
} else
#endif
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
if (__Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(__pyx_t_6)) {
PyObject *__pyx_temp[3] = {__pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_1, __pyx_v_value};
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(__pyx_t_6, __pyx_temp+1-__pyx_t_7, 2+__pyx_t_7); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 512, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
} else
#endif
{
__pyx_t_8 = PyTuple_New(2+__pyx_t_7); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_8)) __PYX_ERR(1, 512, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_8);
if (__pyx_t_5) {
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_5); PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_8, 0, __pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = NULL;
}
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_8, 0+__pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_value);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_value);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_8, 1+__pyx_t_7, __pyx_v_value);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_t_6, __pyx_t_8, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 512, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_8 = 0;
}
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
if (!(likely(PyBytes_CheckExact(__pyx_t_4))||((__pyx_t_4) == Py_None)||(PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected %.16s, got %.200s", "bytes", Py_TYPE(__pyx_t_4)->tp_name), 0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 512, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_bytesvalue = ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":514
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, value)
*
* for i, c in enumerate(bytesvalue): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* itemp[i] = c
*
*/
__pyx_t_9 = 0;
if (unlikely(__pyx_v_bytesvalue == Py_None)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "'NoneType' is not iterable");
__PYX_ERR(1, 514, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_bytesvalue);
__pyx_t_10 = __pyx_v_bytesvalue;
__pyx_t_12 = PyBytes_AS_STRING(__pyx_t_10);
__pyx_t_13 = (__pyx_t_12 + PyBytes_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_10));
for (__pyx_t_14 = __pyx_t_12; __pyx_t_14 < __pyx_t_13; __pyx_t_14++) {
__pyx_t_11 = __pyx_t_14;
__pyx_v_c = (__pyx_t_11[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":515
*
* for i, c in enumerate(bytesvalue):
* itemp[i] = c # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('getbuffer')
*/
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_9;
/* "View.MemoryView":514
* bytesvalue = struct.pack(self.view.format, value)
*
* for i, c in enumerate(bytesvalue): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* itemp[i] = c
*
*/
__pyx_t_9 = (__pyx_t_9 + 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":515
*
* for i, c in enumerate(bytesvalue):
* itemp[i] = c # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('getbuffer')
*/
(__pyx_v_itemp[__pyx_v_i]) = __pyx_v_c;
}
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_10); __pyx_t_10 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":501
* return result
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """Only used if instantiated manually by the user, or if Cython doesn't
* know how to convert the type"""
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_10);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.assign_item_from_object", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_struct);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_bytesvalue);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":518
*
* @cname('getbuffer')
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE and self.view.readonly:
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview")
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_memoryview_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_memoryview_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getbuffer__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8__getbuffer__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((Py_buffer *)__pyx_v_info), ((int)__pyx_v_flags));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static int __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8__getbuffer__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_4;
char *__pyx_t_5;
void *__pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_t_7;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_8;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
if (__pyx_v_info == NULL) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_BufferError, "PyObject_GetBuffer: view==NULL argument is obsolete");
return -1;
}
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__getbuffer__", 0);
__pyx_v_info->obj = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
/* "View.MemoryView":519
* @cname('getbuffer')
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags):
* if flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE and self.view.readonly: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview")
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_self->view.readonly != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L4_bool_binop_done:;
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":520
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags):
* if flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE and self.view.readonly:
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if flags & PyBUF_ND:
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_tuple__10, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 520, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 520, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":519
* @cname('getbuffer')
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags):
* if flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE and self.view.readonly: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview")
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":522
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview")
*
* if flags & PyBUF_ND: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.shape = self.view.shape
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_flags & PyBUF_ND) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":523
*
* if flags & PyBUF_ND:
* info.shape = self.view.shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* info.shape = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_self->view.shape;
__pyx_v_info->shape = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":522
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview")
*
* if flags & PyBUF_ND: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.shape = self.view.shape
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L6;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":525
* info.shape = self.view.shape
* else:
* info.shape = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if flags & PyBUF_STRIDES:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_info->shape = NULL;
}
__pyx_L6:;
/* "View.MemoryView":527
* info.shape = NULL
*
* if flags & PyBUF_STRIDES: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.strides = self.view.strides
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_flags & PyBUF_STRIDES) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":528
*
* if flags & PyBUF_STRIDES:
* info.strides = self.view.strides # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* info.strides = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_self->view.strides;
__pyx_v_info->strides = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":527
* info.shape = NULL
*
* if flags & PyBUF_STRIDES: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.strides = self.view.strides
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L7;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":530
* info.strides = self.view.strides
* else:
* info.strides = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if flags & PyBUF_INDIRECT:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_info->strides = NULL;
}
__pyx_L7:;
/* "View.MemoryView":532
* info.strides = NULL
*
* if flags & PyBUF_INDIRECT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.suboffsets = self.view.suboffsets
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_flags & PyBUF_INDIRECT) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":533
*
* if flags & PyBUF_INDIRECT:
* info.suboffsets = self.view.suboffsets # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* info.suboffsets = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_self->view.suboffsets;
__pyx_v_info->suboffsets = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":532
* info.strides = NULL
*
* if flags & PyBUF_INDIRECT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.suboffsets = self.view.suboffsets
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L8;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":535
* info.suboffsets = self.view.suboffsets
* else:
* info.suboffsets = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_info->suboffsets = NULL;
}
__pyx_L8:;
/* "View.MemoryView":537
* info.suboffsets = NULL
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.format = self.view.format
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_flags & PyBUF_FORMAT) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":538
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT:
* info.format = self.view.format # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* info.format = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_self->view.format;
__pyx_v_info->format = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":537
* info.suboffsets = NULL
*
* if flags & PyBUF_FORMAT: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.format = self.view.format
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L9;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":540
* info.format = self.view.format
* else:
* info.format = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* info.buf = self.view.buf
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_info->format = NULL;
}
__pyx_L9:;
/* "View.MemoryView":542
* info.format = NULL
*
* info.buf = self.view.buf # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.ndim = self.view.ndim
* info.itemsize = self.view.itemsize
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_v_self->view.buf;
__pyx_v_info->buf = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":543
*
* info.buf = self.view.buf
* info.ndim = self.view.ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.itemsize = self.view.itemsize
* info.len = self.view.len
*/
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_v_self->view.ndim;
__pyx_v_info->ndim = __pyx_t_7;
/* "View.MemoryView":544
* info.buf = self.view.buf
* info.ndim = self.view.ndim
* info.itemsize = self.view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.len = self.view.len
* info.readonly = self.view.readonly
*/
__pyx_t_8 = __pyx_v_self->view.itemsize;
__pyx_v_info->itemsize = __pyx_t_8;
/* "View.MemoryView":545
* info.ndim = self.view.ndim
* info.itemsize = self.view.itemsize
* info.len = self.view.len # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.readonly = self.view.readonly
* info.obj = self
*/
__pyx_t_8 = __pyx_v_self->view.len;
__pyx_v_info->len = __pyx_t_8;
/* "View.MemoryView":546
* info.itemsize = self.view.itemsize
* info.len = self.view.len
* info.readonly = self.view.readonly # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.obj = self
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_self->view.readonly;
__pyx_v_info->readonly = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":547
* info.len = self.view.len
* info.readonly = self.view.readonly
* info.obj = self # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_memoryview_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
__Pyx_GIVEREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self));
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__pyx_v_info->obj = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self);
/* "View.MemoryView":518
*
* @cname('getbuffer')
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE and self.view.readonly:
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview")
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__getbuffer__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
if (__pyx_v_info->obj != NULL) {
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_info->obj); __pyx_v_info->obj = 0;
}
goto __pyx_L2;
__pyx_L0:;
if (__pyx_v_info->obj == Py_None) {
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_info->obj);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_info->obj); __pyx_v_info->obj = 0;
}
__pyx_L2:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":553
*
* @property
* def T(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef _memoryviewslice result = memoryview_copy(self)
* transpose_memslice(&result.from_slice)
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_1T_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_1T_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_1T___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_1T___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_result = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":554
* @property
* def T(self):
* cdef _memoryviewslice result = memoryview_copy(self) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* transpose_memslice(&result.from_slice)
* return result
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_object(__pyx_v_self); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 554, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (!(likely(((__pyx_t_1) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_memoryviewslice_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 554, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_result = ((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":555
* def T(self):
* cdef _memoryviewslice result = memoryview_copy(self)
* transpose_memslice(&result.from_slice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return result
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_memslice_transpose((&__pyx_v_result->from_slice)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2 == ((int)0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 555, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":556
* cdef _memoryviewslice result = memoryview_copy(self)
* transpose_memslice(&result.from_slice)
* return result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result));
__pyx_r = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":553
*
* @property
* def T(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef _memoryviewslice result = memoryview_copy(self)
* transpose_memslice(&result.from_slice)
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.T.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":559
*
* @property
* def base(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.obj
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4base_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4base_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4base___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4base___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":560
* @property
* def base(self):
* return self.obj # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_self->obj);
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_self->obj;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":559
*
* @property
* def base(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.obj
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":563
*
* @property
* def shape(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return tuple([length for length in self.view.shape[:self.view.ndim]])
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_5shape_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_5shape_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_5shape___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_5shape___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_length;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_4;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":564
* @property
* def shape(self):
* return tuple([length for length in self.view.shape[:self.view.ndim]]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = PyList_New(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 564, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_self->view.shape + __pyx_v_self->view.ndim);
for (__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_self->view.shape; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4++) {
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_4;
__pyx_v_length = (__pyx_t_2[0]);
__pyx_t_5 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_length); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 564, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ListComp_Append(__pyx_t_1, (PyObject*)__pyx_t_5))) __PYX_ERR(1, 564, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
}
__pyx_t_5 = PyList_AsTuple(((PyObject*)__pyx_t_1)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 564, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_5;
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":563
*
* @property
* def shape(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return tuple([length for length in self.view.shape[:self.view.ndim]])
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.shape.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":567
*
* @property
* def strides(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.strides == NULL:
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_7strides_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_7strides_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_7strides___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_7strides___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_stride;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_5;
PyObject *__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":568
* @property
* def strides(self):
* if self.view.strides == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* raise ValueError("Buffer view does not expose strides")
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->view.strides == NULL) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":570
* if self.view.strides == NULL:
*
* raise ValueError("Buffer view does not expose strides") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return tuple([stride for stride in self.view.strides[:self.view.ndim]])
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_tuple__11, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 570, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_2, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 570, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":568
* @property
* def strides(self):
* if self.view.strides == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* raise ValueError("Buffer view does not expose strides")
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":572
* raise ValueError("Buffer view does not expose strides")
*
* return tuple([stride for stride in self.view.strides[:self.view.ndim]]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = PyList_New(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 572, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_4 = (__pyx_v_self->view.strides + __pyx_v_self->view.ndim);
for (__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_self->view.strides; __pyx_t_5 < __pyx_t_4; __pyx_t_5++) {
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_5;
__pyx_v_stride = (__pyx_t_3[0]);
__pyx_t_6 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_stride); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 572, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ListComp_Append(__pyx_t_2, (PyObject*)__pyx_t_6))) __PYX_ERR(1, 572, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
}
__pyx_t_6 = PyList_AsTuple(((PyObject*)__pyx_t_2)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 572, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_6;
__pyx_t_6 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":567
*
* @property
* def strides(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.strides == NULL:
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.strides.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":575
*
* @property
* def suboffsets(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.suboffsets == NULL:
* return (-1,) * self.view.ndim
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10suboffsets_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10suboffsets_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10suboffsets___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10suboffsets___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_suboffset;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_5;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":576
* @property
* def suboffsets(self):
* if self.view.suboffsets == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return (-1,) * self.view.ndim
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->view.suboffsets == NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":577
* def suboffsets(self):
* if self.view.suboffsets == NULL:
* return (-1,) * self.view.ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return tuple([suboffset for suboffset in self.view.suboffsets[:self.view.ndim]])
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(__pyx_v_self->view.ndim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 577, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = PyNumber_Multiply(__pyx_tuple__12, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 577, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":576
* @property
* def suboffsets(self):
* if self.view.suboffsets == NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return (-1,) * self.view.ndim
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":579
* return (-1,) * self.view.ndim
*
* return tuple([suboffset for suboffset in self.view.suboffsets[:self.view.ndim]]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_3 = PyList_New(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 579, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_5 = (__pyx_v_self->view.suboffsets + __pyx_v_self->view.ndim);
for (__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_v_self->view.suboffsets; __pyx_t_6 < __pyx_t_5; __pyx_t_6++) {
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_t_6;
__pyx_v_suboffset = (__pyx_t_4[0]);
__pyx_t_2 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_suboffset); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 579, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ListComp_Append(__pyx_t_3, (PyObject*)__pyx_t_2))) __PYX_ERR(1, 579, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
}
__pyx_t_2 = PyList_AsTuple(((PyObject*)__pyx_t_3)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 579, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":575
*
* @property
* def suboffsets(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.suboffsets == NULL:
* return (-1,) * self.view.ndim
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.suboffsets.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":582
*
* @property
* def ndim(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.view.ndim
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4ndim_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4ndim_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4ndim___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4ndim___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":583
* @property
* def ndim(self):
* return self.view.ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(__pyx_v_self->view.ndim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 583, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":582
*
* @property
* def ndim(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.view.ndim
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.ndim.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":586
*
* @property
* def itemsize(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.view.itemsize
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8itemsize_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8itemsize_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8itemsize___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8itemsize___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":587
* @property
* def itemsize(self):
* return self.view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_self->view.itemsize); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 587, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":586
*
* @property
* def itemsize(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.view.itemsize
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.itemsize.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":590
*
* @property
* def nbytes(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.size * self.view.itemsize
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6nbytes_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6nbytes_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6nbytes___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6nbytes___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":591
* @property
* def nbytes(self):
* return self.size * self.view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_n_s_size); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 591, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_self->view.itemsize); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 591, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = PyNumber_Multiply(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 591, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":590
*
* @property
* def nbytes(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.size * self.view.itemsize
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.nbytes.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":594
*
* @property
* def size(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self._size is None:
* result = 1
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4size_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4size_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4size___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4size___get__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_result = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_length = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_5;
PyObject *__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":595
* @property
* def size(self):
* if self._size is None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result = 1
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_self->_size == Py_None);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":596
* def size(self):
* if self._size is None:
* result = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for length in self.view.shape[:self.view.ndim]:
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_int_1);
__pyx_v_result = __pyx_int_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":598
* result = 1
*
* for length in self.view.shape[:self.view.ndim]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result *= length
*
*/
__pyx_t_4 = (__pyx_v_self->view.shape + __pyx_v_self->view.ndim);
for (__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_self->view.shape; __pyx_t_5 < __pyx_t_4; __pyx_t_5++) {
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_5;
__pyx_t_6 = PyInt_FromSsize_t((__pyx_t_3[0])); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 598, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_XDECREF_SET(__pyx_v_length, __pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_6 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":599
*
* for length in self.view.shape[:self.view.ndim]:
* result *= length # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* self._size = result
*/
__pyx_t_6 = PyNumber_InPlaceMultiply(__pyx_v_result, __pyx_v_length); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 599, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_v_result, __pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_6 = 0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":601
* result *= length
*
* self._size = result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return self._size
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_self->_size);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_self->_size);
__pyx_v_self->_size = __pyx_v_result;
/* "View.MemoryView":595
* @property
* def size(self):
* if self._size is None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result = 1
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":603
* self._size = result
*
* return self._size # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __len__(self):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_self->_size);
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_self->_size;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":594
*
* @property
* def size(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self._size is None:
* result = 1
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.size.__get__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_length);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":605
* return self._size
*
* def __len__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.ndim >= 1:
* return self.view.shape[0]
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_memoryview___len__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_memoryview___len__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__len__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10__len__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10__len__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__len__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":606
*
* def __len__(self):
* if self.view.ndim >= 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.view.shape[0]
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->view.ndim >= 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":607
* def __len__(self):
* if self.view.ndim >= 1:
* return self.view.shape[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return 0
*/
__pyx_r = (__pyx_v_self->view.shape[0]);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":606
*
* def __len__(self):
* if self.view.ndim >= 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.view.shape[0]
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":609
* return self.view.shape[0]
*
* return 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __repr__(self):
*/
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":605
* return self._size
*
* def __len__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.view.ndim >= 1:
* return self.view.shape[0]
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":611
* return 0
*
* def __repr__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__,
* id(self))
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___repr__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___repr__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__repr__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_12__repr__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_12__repr__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__repr__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":612
*
* def __repr__(self):
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* id(self))
*
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_n_s_base); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 612, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_n_s_class); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 612, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_n_s_name_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 612, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":613
* def __repr__(self):
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__,
* id(self)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __str__(self):
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_builtin_id, ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 613, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
/* "View.MemoryView":612
*
* def __repr__(self):
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* id(self))
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = PyTuple_New(2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 612, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 0, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 1, __pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyString_Format(__pyx_kp_s_MemoryView_of_r_at_0x_x, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 612, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":611
* return 0
*
* def __repr__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__,
* id(self))
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__repr__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":615
* id(self))
*
* def __str__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__,)
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___str__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___str__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__str__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_14__str__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_14__str__(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__str__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":616
*
* def __str__(self):
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__,) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_n_s_base); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 616, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_t_1, __pyx_n_s_class); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 616, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_n_s_name_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 616, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = PyTuple_New(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 616, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, 0, __pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyString_Format(__pyx_kp_s_MemoryView_of_r_object, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 616, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":615
* id(self))
*
* def __str__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return "" % (self.base.__class__.__name__,)
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__str__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":619
*
*
* def is_c_contig(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_is_c_contig(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_is_c_contig(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("is_c_contig (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_16is_c_contig(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_16is_c_contig(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_mslice;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_tmp;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("is_c_contig", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":622
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
* mslice = get_slice_from_memview(self, &tmp) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'C', self.view.ndim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(__pyx_v_self, (&__pyx_v_tmp)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 == ((__Pyx_memviewslice *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 622, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_mslice = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":623
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
* mslice = get_slice_from_memview(self, &tmp)
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'C', self.view.ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def is_f_contig(self):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(__pyx_memviewslice_is_contig((__pyx_v_mslice[0]), 'C', __pyx_v_self->view.ndim)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 623, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":619
*
*
* def is_c_contig(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.is_c_contig", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":625
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'C', self.view.ndim)
*
* def is_f_contig(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_is_f_contig(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_is_f_contig(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("is_f_contig (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_18is_f_contig(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_18is_f_contig(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_mslice;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_tmp;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("is_f_contig", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":628
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
* mslice = get_slice_from_memview(self, &tmp) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'F', self.view.ndim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(__pyx_v_self, (&__pyx_v_tmp)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 == ((__Pyx_memviewslice *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 628, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_mslice = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":629
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
* mslice = get_slice_from_memview(self, &tmp)
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'F', self.view.ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def copy(self):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(__pyx_memviewslice_is_contig((__pyx_v_mslice[0]), 'F', __pyx_v_self->view.ndim)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 629, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":625
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'C', self.view.ndim)
*
* def is_f_contig(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.is_f_contig", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":631
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'F', self.view.ndim)
*
* def copy(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice mslice
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("copy (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_20copy(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_20copy(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_mslice;
int __pyx_v_flags;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("copy", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":633
* def copy(self):
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice mslice
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* slice_copy(self, &mslice)
*/
__pyx_v_flags = (__pyx_v_self->flags & (~PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS));
/* "View.MemoryView":635
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS
*
* slice_copy(self, &mslice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mslice = slice_copy_contig(&mslice, "c", self.view.ndim,
* self.view.itemsize,
*/
__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(__pyx_v_self, (&__pyx_v_mslice));
/* "View.MemoryView":636
*
* slice_copy(self, &mslice)
* mslice = slice_copy_contig(&mslice, "c", self.view.ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.view.itemsize,
* flags|PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS,
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_new_contig((&__pyx_v_mslice), ((char *)"c"), __pyx_v_self->view.ndim, __pyx_v_self->view.itemsize, (__pyx_v_flags | PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS), __pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 636, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_mslice = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":641
* self.dtype_is_object)
*
* return memoryview_copy_from_slice(self, &mslice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def copy_fortran(self):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice(__pyx_v_self, (&__pyx_v_mslice)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 641, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":631
* return slice_is_contig(mslice[0], 'F', self.view.ndim)
*
* def copy(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice mslice
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.copy", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":643
* return memoryview_copy_from_slice(self, &mslice)
*
* def copy_fortran(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src, dst
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_fortran(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_fortran(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("copy_fortran (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_22copy_fortran(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_22copy_fortran(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_src;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_dst;
int __pyx_v_flags;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("copy_fortran", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":645
* def copy_fortran(self):
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src, dst
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* slice_copy(self, &src)
*/
__pyx_v_flags = (__pyx_v_self->flags & (~PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS));
/* "View.MemoryView":647
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS
*
* slice_copy(self, &src) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst = slice_copy_contig(&src, "fortran", self.view.ndim,
* self.view.itemsize,
*/
__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(__pyx_v_self, (&__pyx_v_src));
/* "View.MemoryView":648
*
* slice_copy(self, &src)
* dst = slice_copy_contig(&src, "fortran", self.view.ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.view.itemsize,
* flags|PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS,
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_new_contig((&__pyx_v_src), ((char *)"fortran"), __pyx_v_self->view.ndim, __pyx_v_self->view.itemsize, (__pyx_v_flags | PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS), __pyx_v_self->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 648, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_dst = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":653
* self.dtype_is_object)
*
* return memoryview_copy_from_slice(self, &dst) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice(__pyx_v_self, (&__pyx_v_dst)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 653, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":643
* return memoryview_copy_from_slice(self, &mslice)
*
* def copy_fortran(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src, dst
* cdef int flags = self.flags & ~PyBUF_C_CONTIGUOUS
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.copy_fortran", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryview_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryview_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_memoryview___reduce_cython__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryview___reduce_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":2
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_tuple__13, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_1, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__reduce_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":3
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryview_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryview_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_memoryview_2__setstate_cython__(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v___pyx_state));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryview_2__setstate_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_tuple__14, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_1, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "(tree fragment)":3
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview.__setstate_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":657
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_new')
* cdef memoryview_cwrapper(object o, int flags, bint dtype_is_object, __Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef memoryview result = memoryview(o, flags, dtype_is_object)
* result.typeinfo = typeinfo
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_new(PyObject *__pyx_v_o, int __pyx_v_flags, int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, __Pyx_TypeInfo *__pyx_v_typeinfo) {
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_result = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("memoryview_cwrapper", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":658
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_new')
* cdef memoryview_cwrapper(object o, int flags, bint dtype_is_object, __Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo):
* cdef memoryview result = memoryview(o, flags, dtype_is_object) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.typeinfo = typeinfo
* return result
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(__pyx_v_flags); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 658, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(__pyx_v_dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 658, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 658, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_o);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_o);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 0, __pyx_v_o);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 1, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 2, __pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_memoryview_type), __pyx_t_3, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 658, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_v_result = ((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":659
* cdef memoryview_cwrapper(object o, int flags, bint dtype_is_object, __Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo):
* cdef memoryview result = memoryview(o, flags, dtype_is_object)
* result.typeinfo = typeinfo # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return result
*
*/
__pyx_v_result->typeinfo = __pyx_v_typeinfo;
/* "View.MemoryView":660
* cdef memoryview result = memoryview(o, flags, dtype_is_object)
* result.typeinfo = typeinfo
* return result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_check')
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result));
__pyx_r = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":657
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_new')
* cdef memoryview_cwrapper(object o, int flags, bint dtype_is_object, __Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef memoryview result = memoryview(o, flags, dtype_is_object)
* result.typeinfo = typeinfo
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview_cwrapper", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":663
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_check')
* cdef inline bint memoryview_check(object o): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return isinstance(o, memoryview)
*
*/
static CYTHON_INLINE int __pyx_memoryview_check(PyObject *__pyx_v_o) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("memoryview_check", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":664
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_check')
* cdef inline bint memoryview_check(object o):
* return isinstance(o, memoryview) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef tuple _unellipsify(object index, int ndim):
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_TypeCheck(__pyx_v_o, __pyx_memoryview_type);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":663
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_check')
* cdef inline bint memoryview_check(object o): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return isinstance(o, memoryview)
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":666
* return isinstance(o, memoryview)
*
* cdef tuple _unellipsify(object index, int ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """
* Replace all ellipses with full slices and fill incomplete indices with
*/
static PyObject *_unellipsify(PyObject *__pyx_v_index, int __pyx_v_ndim) {
PyObject *__pyx_v_tup = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_result = NULL;
int __pyx_v_have_slices;
int __pyx_v_seen_ellipsis;
CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_v_idx = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_v_item = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_nslices;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_5;
PyObject *(*__pyx_t_6)(PyObject *);
PyObject *__pyx_t_7 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_8;
int __pyx_t_9;
int __pyx_t_10;
PyObject *__pyx_t_11 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("_unellipsify", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":671
* full slices.
* """
* if not isinstance(index, tuple): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tup = (index,)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = PyTuple_Check(__pyx_v_index);
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_t_1 != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":672
* """
* if not isinstance(index, tuple):
* tup = (index,) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* tup = index
*/
__pyx_t_3 = PyTuple_New(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 672, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_index);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_v_index);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 0, __pyx_v_index);
__pyx_v_tup = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":671
* full slices.
* """
* if not isinstance(index, tuple): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tup = (index,)
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":674
* tup = (index,)
* else:
* tup = index # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result = []
*/
/*else*/ {
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_index);
__pyx_v_tup = __pyx_v_index;
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":676
* tup = index
*
* result = [] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* have_slices = False
* seen_ellipsis = False
*/
__pyx_t_3 = PyList_New(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 676, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_v_result = ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":677
*
* result = []
* have_slices = False # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* seen_ellipsis = False
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup):
*/
__pyx_v_have_slices = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":678
* result = []
* have_slices = False
* seen_ellipsis = False # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup):
* if item is Ellipsis:
*/
__pyx_v_seen_ellipsis = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":679
* have_slices = False
* seen_ellipsis = False
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if item is Ellipsis:
* if not seen_ellipsis:
*/
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_int_0);
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_int_0;
if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_v_tup)) || PyTuple_CheckExact(__pyx_v_tup)) {
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_tup; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
} else {
__pyx_t_5 = -1; __pyx_t_4 = PyObject_GetIter(__pyx_v_tup); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_6 = Py_TYPE(__pyx_t_4)->tp_iternext; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
}
for (;;) {
if (likely(!__pyx_t_6)) {
if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_t_4))) {
if (__pyx_t_5 >= PyList_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_4)) break;
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_7 = PyList_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_5++; if (unlikely(0 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
#else
__pyx_t_7 = PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5++; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
#endif
} else {
if (__pyx_t_5 >= PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_4)) break;
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_7 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_5++; if (unlikely(0 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
#else
__pyx_t_7 = PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5++; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
#endif
}
} else {
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_t_6(__pyx_t_4);
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) {
PyObject* exc_type = PyErr_Occurred();
if (exc_type) {
if (likely(__Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(exc_type, PyExc_StopIteration))) PyErr_Clear();
else __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
}
break;
}
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
}
__Pyx_XDECREF_SET(__pyx_v_item, __pyx_t_7);
__pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF_SET(__pyx_v_idx, __pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyInt_AddObjC(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_int_1, 1, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 679, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_7;
__pyx_t_7 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":680
* seen_ellipsis = False
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup):
* if item is Ellipsis: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not seen_ellipsis:
* result.extend([slice(None)] * (ndim - len(tup) + 1))
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_item == __pyx_builtin_Ellipsis);
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":681
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup):
* if item is Ellipsis:
* if not seen_ellipsis: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.extend([slice(None)] * (ndim - len(tup) + 1))
* seen_ellipsis = True
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((!(__pyx_v_seen_ellipsis != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":682
* if item is Ellipsis:
* if not seen_ellipsis:
* result.extend([slice(None)] * (ndim - len(tup) + 1)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* seen_ellipsis = True
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_8 = PyObject_Length(__pyx_v_tup); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_8 == ((Py_ssize_t)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 682, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_7 = PyList_New(1 * ((((__pyx_v_ndim - __pyx_t_8) + 1)<0) ? 0:((__pyx_v_ndim - __pyx_t_8) + 1))); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 682, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
{ Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp;
for (__pyx_temp=0; __pyx_temp < ((__pyx_v_ndim - __pyx_t_8) + 1); __pyx_temp++) {
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_slice__15);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_slice__15);
PyList_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_7, __pyx_temp, __pyx_slice__15);
}
}
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyList_Extend(__pyx_v_result, __pyx_t_7); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_9 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 682, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":683
* if not seen_ellipsis:
* result.extend([slice(None)] * (ndim - len(tup) + 1))
* seen_ellipsis = True # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* result.append(slice(None))
*/
__pyx_v_seen_ellipsis = 1;
/* "View.MemoryView":681
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup):
* if item is Ellipsis:
* if not seen_ellipsis: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.extend([slice(None)] * (ndim - len(tup) + 1))
* seen_ellipsis = True
*/
goto __pyx_L7;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":685
* seen_ellipsis = True
* else:
* result.append(slice(None)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* have_slices = True
* else:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyList_Append(__pyx_v_result, __pyx_slice__15); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_9 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 685, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_L7:;
/* "View.MemoryView":686
* else:
* result.append(slice(None))
* have_slices = True # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* if not isinstance(item, slice) and not PyIndex_Check(item):
*/
__pyx_v_have_slices = 1;
/* "View.MemoryView":680
* seen_ellipsis = False
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup):
* if item is Ellipsis: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not seen_ellipsis:
* result.extend([slice(None)] * (ndim - len(tup) + 1))
*/
goto __pyx_L6;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":688
* have_slices = True
* else:
* if not isinstance(item, slice) and not PyIndex_Check(item): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("Cannot index with type '%s'" % type(item))
*
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_2 = PySlice_Check(__pyx_v_item);
__pyx_t_10 = ((!(__pyx_t_2 != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_10) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_10;
goto __pyx_L9_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_10 = ((!(PyIndex_Check(__pyx_v_item) != 0)) != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_10;
__pyx_L9_bool_binop_done:;
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":689
* else:
* if not isinstance(item, slice) and not PyIndex_Check(item):
* raise TypeError("Cannot index with type '%s'" % type(item)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* have_slices = have_slices or isinstance(item, slice)
*/
__pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyString_FormatSafe(__pyx_kp_s_Cannot_index_with_type_s, ((PyObject *)Py_TYPE(__pyx_v_item))); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 689, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
__pyx_t_11 = __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_t_7); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_11)) __PYX_ERR(1, 689, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_11);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_11, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_11); __pyx_t_11 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 689, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":688
* have_slices = True
* else:
* if not isinstance(item, slice) and not PyIndex_Check(item): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("Cannot index with type '%s'" % type(item))
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":691
* raise TypeError("Cannot index with type '%s'" % type(item))
*
* have_slices = have_slices or isinstance(item, slice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.append(item)
*
*/
__pyx_t_10 = (__pyx_v_have_slices != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_10) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_10;
goto __pyx_L11_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_10 = PySlice_Check(__pyx_v_item);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_10 != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_L11_bool_binop_done:;
__pyx_v_have_slices = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":692
*
* have_slices = have_slices or isinstance(item, slice)
* result.append(item) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* nslices = ndim - len(result)
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyList_Append(__pyx_v_result, __pyx_v_item); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_9 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 692, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_L6:;
/* "View.MemoryView":679
* have_slices = False
* seen_ellipsis = False
* for idx, item in enumerate(tup): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if item is Ellipsis:
* if not seen_ellipsis:
*/
}
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":694
* result.append(item)
*
* nslices = ndim - len(result) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if nslices:
* result.extend([slice(None)] * nslices)
*/
__pyx_t_5 = PyList_GET_SIZE(__pyx_v_result); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_5 == ((Py_ssize_t)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 694, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_nslices = (__pyx_v_ndim - __pyx_t_5);
/* "View.MemoryView":695
*
* nslices = ndim - len(result)
* if nslices: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.extend([slice(None)] * nslices)
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_nslices != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":696
* nslices = ndim - len(result)
* if nslices:
* result.extend([slice(None)] * nslices) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return have_slices or nslices, tuple(result)
*/
__pyx_t_3 = PyList_New(1 * ((__pyx_v_nslices<0) ? 0:__pyx_v_nslices)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 696, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
{ Py_ssize_t __pyx_temp;
for (__pyx_temp=0; __pyx_temp < __pyx_v_nslices; __pyx_temp++) {
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_slice__15);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_slice__15);
PyList_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_temp, __pyx_slice__15);
}
}
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyList_Extend(__pyx_v_result, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_9 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 696, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":695
*
* nslices = ndim - len(result)
* if nslices: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.extend([slice(None)] * nslices)
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":698
* result.extend([slice(None)] * nslices)
*
* return have_slices or nslices, tuple(result) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *suboffsets, int ndim):
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
if (!__pyx_v_have_slices) {
} else {
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(__pyx_v_have_slices); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 698, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_4;
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
goto __pyx_L14_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_4 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_nslices); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 698, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_4;
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_L14_bool_binop_done:;
__pyx_t_4 = PyList_AsTuple(__pyx_v_result); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 698, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_11 = PyTuple_New(2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_11)) __PYX_ERR(1, 698, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_11);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_11, 0, __pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_4);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_11, 1, __pyx_t_4);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_r = ((PyObject*)__pyx_t_11);
__pyx_t_11 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":666
* return isinstance(o, memoryview)
*
* cdef tuple _unellipsify(object index, int ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """
* Replace all ellipses with full slices and fill incomplete indices with
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_11);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._unellipsify", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_tup);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_idx);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_item);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":700
* return have_slices or nslices, tuple(result)
*
* cdef assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *suboffsets, int ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for suboffset in suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0:
*/
static PyObject *assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_suboffsets, int __pyx_v_ndim) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_suboffset;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_1;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("assert_direct_dimensions", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":701
*
* cdef assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *suboffsets, int ndim):
* for suboffset in suboffsets[:ndim]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if suboffset >= 0:
* raise ValueError("Indirect dimensions not supported")
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_suboffsets + __pyx_v_ndim);
for (__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_suboffsets; __pyx_t_3 < __pyx_t_2; __pyx_t_3++) {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_v_suboffset = (__pyx_t_1[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":702
* cdef assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *suboffsets, int ndim):
* for suboffset in suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Indirect dimensions not supported")
*
*/
__pyx_t_4 = ((__pyx_v_suboffset >= 0) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":703
* for suboffset in suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0:
* raise ValueError("Indirect dimensions not supported") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_tuple__16, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 703, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_5, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 703, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":702
* cdef assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *suboffsets, int ndim):
* for suboffset in suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise ValueError("Indirect dimensions not supported")
*
*/
}
}
/* "View.MemoryView":700
* return have_slices or nslices, tuple(result)
*
* cdef assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *suboffsets, int ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for suboffset in suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0:
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.assert_direct_dimensions", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":710
*
* @cname('__pyx_memview_slice')
* cdef memoryview memview_slice(memoryview memview, object indices): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int new_ndim = 0, suboffset_dim = -1, dim
* cdef bint negative_step
*/
static struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_memview_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_memview, PyObject *__pyx_v_indices) {
int __pyx_v_new_ndim;
int __pyx_v_suboffset_dim;
int __pyx_v_dim;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_src;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_dst;
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_p_src;
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_memviewsliceobj = 0;
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_p_dst;
int *__pyx_v_p_suboffset_dim;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_start;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_stop;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_step;
int __pyx_v_have_start;
int __pyx_v_have_stop;
int __pyx_v_have_step;
PyObject *__pyx_v_index = NULL;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_t_4;
char *__pyx_t_5;
int __pyx_t_6;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_7;
PyObject *(*__pyx_t_8)(PyObject *);
PyObject *__pyx_t_9 = NULL;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_10;
int __pyx_t_11;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_12;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("memview_slice", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":711
* @cname('__pyx_memview_slice')
* cdef memoryview memview_slice(memoryview memview, object indices):
* cdef int new_ndim = 0, suboffset_dim = -1, dim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef bint negative_step
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice src, dst
*/
__pyx_v_new_ndim = 0;
__pyx_v_suboffset_dim = -1;
/* "View.MemoryView":718
*
*
* memset(&dst, 0, sizeof(dst)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef _memoryviewslice memviewsliceobj
*/
(void)(memset((&__pyx_v_dst), 0, (sizeof(__pyx_v_dst))));
/* "View.MemoryView":722
* cdef _memoryviewslice memviewsliceobj
*
* assert memview.view.ndim > 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
*/
#ifndef CYTHON_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS
if (unlikely(!Py_OptimizeFlag)) {
if (unlikely(!((__pyx_v_memview->view.ndim > 0) != 0))) {
PyErr_SetNone(PyExc_AssertionError);
__PYX_ERR(1, 722, __pyx_L1_error)
}
}
#endif
/* "View.MemoryView":724
* assert memview.view.ndim > 0
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memviewsliceobj = memview
* p_src = &memviewsliceobj.from_slice
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_TypeCheck(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview), __pyx_memoryviewslice_type);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":725
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* memviewsliceobj = memview # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_src = &memviewsliceobj.from_slice
* else:
*/
if (!(likely(((((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview)) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview), __pyx_memoryviewslice_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 725, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_3 = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_v_memviewsliceobj = ((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":726
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* memviewsliceobj = memview
* p_src = &memviewsliceobj.from_slice # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* slice_copy(memview, &src)
*/
__pyx_v_p_src = (&__pyx_v_memviewsliceobj->from_slice);
/* "View.MemoryView":724
* assert memview.view.ndim > 0
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memviewsliceobj = memview
* p_src = &memviewsliceobj.from_slice
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":728
* p_src = &memviewsliceobj.from_slice
* else:
* slice_copy(memview, &src) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_src = &src
*
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(__pyx_v_memview, (&__pyx_v_src));
/* "View.MemoryView":729
* else:
* slice_copy(memview, &src)
* p_src = &src # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_v_p_src = (&__pyx_v_src);
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":735
*
*
* dst.memview = p_src.memview # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.data = p_src.data
*
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_p_src->memview;
__pyx_v_dst.memview = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":736
*
* dst.memview = p_src.memview
* dst.data = p_src.data # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_p_src->data;
__pyx_v_dst.data = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":741
*
*
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *p_dst = &dst # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int *p_suboffset_dim = &suboffset_dim
* cdef Py_ssize_t start, stop, step
*/
__pyx_v_p_dst = (&__pyx_v_dst);
/* "View.MemoryView":742
*
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *p_dst = &dst
* cdef int *p_suboffset_dim = &suboffset_dim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t start, stop, step
* cdef bint have_start, have_stop, have_step
*/
__pyx_v_p_suboffset_dim = (&__pyx_v_suboffset_dim);
/* "View.MemoryView":746
* cdef bint have_start, have_stop, have_step
*
* for dim, index in enumerate(indices): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if PyIndex_Check(index):
* slice_memviewslice(
*/
__pyx_t_6 = 0;
if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_v_indices)) || PyTuple_CheckExact(__pyx_v_indices)) {
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_indices; __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__pyx_t_8 = NULL;
} else {
__pyx_t_7 = -1; __pyx_t_3 = PyObject_GetIter(__pyx_v_indices); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 746, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_8 = Py_TYPE(__pyx_t_3)->tp_iternext; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_8)) __PYX_ERR(1, 746, __pyx_L1_error)
}
for (;;) {
if (likely(!__pyx_t_8)) {
if (likely(PyList_CheckExact(__pyx_t_3))) {
if (__pyx_t_7 >= PyList_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_3)) break;
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_9 = PyList_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_7); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_7++; if (unlikely(0 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 746, __pyx_L1_error)
#else
__pyx_t_9 = PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7++; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 746, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
#endif
} else {
if (__pyx_t_7 >= PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_t_3)) break;
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
__pyx_t_9 = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_7); __Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_7++; if (unlikely(0 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 746, __pyx_L1_error)
#else
__pyx_t_9 = PySequence_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7++; if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 746, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
#endif
}
} else {
__pyx_t_9 = __pyx_t_8(__pyx_t_3);
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) {
PyObject* exc_type = PyErr_Occurred();
if (exc_type) {
if (likely(__Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(exc_type, PyExc_StopIteration))) PyErr_Clear();
else __PYX_ERR(1, 746, __pyx_L1_error)
}
break;
}
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
}
__Pyx_XDECREF_SET(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_9 = 0;
__pyx_v_dim = __pyx_t_6;
__pyx_t_6 = (__pyx_t_6 + 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":747
*
* for dim, index in enumerate(indices):
* if PyIndex_Check(index): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* slice_memviewslice(
* p_dst, p_src.shape[dim], p_src.strides[dim], p_src.suboffsets[dim],
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (PyIndex_Check(__pyx_v_index) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":751
* p_dst, p_src.shape[dim], p_src.strides[dim], p_src.suboffsets[dim],
* dim, new_ndim, p_suboffset_dim,
* index, 0, 0, # start, stop, step # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* 0, 0, 0, # have_{start,stop,step}
* False)
*/
__pyx_t_10 = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(__pyx_v_index); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_10 == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 751, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":748
* for dim, index in enumerate(indices):
* if PyIndex_Check(index):
* slice_memviewslice( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_dst, p_src.shape[dim], p_src.strides[dim], p_src.suboffsets[dim],
* dim, new_ndim, p_suboffset_dim,
*/
__pyx_t_11 = __pyx_memoryview_slice_memviewslice(__pyx_v_p_dst, (__pyx_v_p_src->shape[__pyx_v_dim]), (__pyx_v_p_src->strides[__pyx_v_dim]), (__pyx_v_p_src->suboffsets[__pyx_v_dim]), __pyx_v_dim, __pyx_v_new_ndim, __pyx_v_p_suboffset_dim, __pyx_t_10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_11 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 748, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":747
*
* for dim, index in enumerate(indices):
* if PyIndex_Check(index): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* slice_memviewslice(
* p_dst, p_src.shape[dim], p_src.strides[dim], p_src.suboffsets[dim],
*/
goto __pyx_L6;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":754
* 0, 0, 0, # have_{start,stop,step}
* False)
* elif index is None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_dst.shape[new_ndim] = 1
* p_dst.strides[new_ndim] = 0
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_index == Py_None);
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":755
* False)
* elif index is None:
* p_dst.shape[new_ndim] = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_dst.strides[new_ndim] = 0
* p_dst.suboffsets[new_ndim] = -1
*/
(__pyx_v_p_dst->shape[__pyx_v_new_ndim]) = 1;
/* "View.MemoryView":756
* elif index is None:
* p_dst.shape[new_ndim] = 1
* p_dst.strides[new_ndim] = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_dst.suboffsets[new_ndim] = -1
* new_ndim += 1
*/
(__pyx_v_p_dst->strides[__pyx_v_new_ndim]) = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":757
* p_dst.shape[new_ndim] = 1
* p_dst.strides[new_ndim] = 0
* p_dst.suboffsets[new_ndim] = -1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* new_ndim += 1
* else:
*/
(__pyx_v_p_dst->suboffsets[__pyx_v_new_ndim]) = -1L;
/* "View.MemoryView":758
* p_dst.strides[new_ndim] = 0
* p_dst.suboffsets[new_ndim] = -1
* new_ndim += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* start = index.start or 0
*/
__pyx_v_new_ndim = (__pyx_v_new_ndim + 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":754
* 0, 0, 0, # have_{start,stop,step}
* False)
* elif index is None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_dst.shape[new_ndim] = 1
* p_dst.strides[new_ndim] = 0
*/
goto __pyx_L6;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":760
* new_ndim += 1
* else:
* start = index.start or 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop = index.stop or 0
* step = index.step or 0
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_n_s_start); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 760, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_t_9); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 760, __pyx_L1_error)
if (!__pyx_t_1) {
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
} else {
__pyx_t_12 = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(__pyx_t_9); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_12 == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 760, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_10 = __pyx_t_12;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
goto __pyx_L7_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_10 = 0;
__pyx_L7_bool_binop_done:;
__pyx_v_start = __pyx_t_10;
/* "View.MemoryView":761
* else:
* start = index.start or 0
* stop = index.stop or 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* step = index.step or 0
*
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_n_s_stop); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 761, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_t_9); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 761, __pyx_L1_error)
if (!__pyx_t_1) {
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
} else {
__pyx_t_12 = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(__pyx_t_9); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_12 == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 761, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_10 = __pyx_t_12;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
goto __pyx_L9_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_10 = 0;
__pyx_L9_bool_binop_done:;
__pyx_v_stop = __pyx_t_10;
/* "View.MemoryView":762
* start = index.start or 0
* stop = index.stop or 0
* step = index.step or 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* have_start = index.start is not None
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_n_s_step); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 762, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(__pyx_t_9); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1 < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 762, __pyx_L1_error)
if (!__pyx_t_1) {
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
} else {
__pyx_t_12 = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(__pyx_t_9); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_12 == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 762, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_10 = __pyx_t_12;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
goto __pyx_L11_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_10 = 0;
__pyx_L11_bool_binop_done:;
__pyx_v_step = __pyx_t_10;
/* "View.MemoryView":764
* step = index.step or 0
*
* have_start = index.start is not None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* have_stop = index.stop is not None
* have_step = index.step is not None
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_n_s_start); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 764, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_9 != Py_None);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
__pyx_v_have_start = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":765
*
* have_start = index.start is not None
* have_stop = index.stop is not None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* have_step = index.step is not None
*
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_n_s_stop); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 765, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_9 != Py_None);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
__pyx_v_have_stop = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":766
* have_start = index.start is not None
* have_stop = index.stop is not None
* have_step = index.step is not None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* slice_memviewslice(
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_v_index, __pyx_n_s_step); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 766, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_9);
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_9 != Py_None);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_9); __pyx_t_9 = 0;
__pyx_v_have_step = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":768
* have_step = index.step is not None
*
* slice_memviewslice( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* p_dst, p_src.shape[dim], p_src.strides[dim], p_src.suboffsets[dim],
* dim, new_ndim, p_suboffset_dim,
*/
__pyx_t_11 = __pyx_memoryview_slice_memviewslice(__pyx_v_p_dst, (__pyx_v_p_src->shape[__pyx_v_dim]), (__pyx_v_p_src->strides[__pyx_v_dim]), (__pyx_v_p_src->suboffsets[__pyx_v_dim]), __pyx_v_dim, __pyx_v_new_ndim, __pyx_v_p_suboffset_dim, __pyx_v_start, __pyx_v_stop, __pyx_v_step, __pyx_v_have_start, __pyx_v_have_stop, __pyx_v_have_step, 1); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_11 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 768, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":774
* have_start, have_stop, have_step,
* True)
* new_ndim += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
*/
__pyx_v_new_ndim = (__pyx_v_new_ndim + 1);
}
__pyx_L6:;
/* "View.MemoryView":746
* cdef bint have_start, have_stop, have_step
*
* for dim, index in enumerate(indices): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if PyIndex_Check(index):
* slice_memviewslice(
*/
}
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":776
* new_ndim += 1
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim,
* memviewsliceobj.to_object_func,
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_TypeCheck(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview), __pyx_memoryviewslice_type);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":777
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memviewsliceobj.to_object_func,
* memviewsliceobj.to_dtype_func,
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_r));
/* "View.MemoryView":778
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim,
* memviewsliceobj.to_object_func, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memviewsliceobj.to_dtype_func,
* memview.dtype_is_object)
*/
if (unlikely(!__pyx_v_memviewsliceobj)) { __Pyx_RaiseUnboundLocalError("memviewsliceobj"); __PYX_ERR(1, 778, __pyx_L1_error) }
/* "View.MemoryView":779
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim,
* memviewsliceobj.to_object_func,
* memviewsliceobj.to_dtype_func, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memview.dtype_is_object)
* else:
*/
if (unlikely(!__pyx_v_memviewsliceobj)) { __Pyx_RaiseUnboundLocalError("memviewsliceobj"); __PYX_ERR(1, 779, __pyx_L1_error) }
/* "View.MemoryView":777
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memviewsliceobj.to_object_func,
* memviewsliceobj.to_dtype_func,
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_fromslice(__pyx_v_dst, __pyx_v_new_ndim, __pyx_v_memviewsliceobj->to_object_func, __pyx_v_memviewsliceobj->to_dtype_func, __pyx_v_memview->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 777, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
if (!(likely(((__pyx_t_3) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_memoryview_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 777, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_r = ((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":776
* new_ndim += 1
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim,
* memviewsliceobj.to_object_func,
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":782
* memview.dtype_is_object)
* else:
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim, NULL, NULL, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memview.dtype_is_object)
*
*/
/*else*/ {
__Pyx_XDECREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_r));
/* "View.MemoryView":783
* else:
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim, NULL, NULL,
* memview.dtype_is_object) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_fromslice(__pyx_v_dst, __pyx_v_new_ndim, NULL, NULL, __pyx_v_memview->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 782, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
/* "View.MemoryView":782
* memview.dtype_is_object)
* else:
* return memoryview_fromslice(dst, new_ndim, NULL, NULL, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memview.dtype_is_object)
*
*/
if (!(likely(((__pyx_t_3) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_memoryview_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 782, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_r = ((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":710
*
* @cname('__pyx_memview_slice')
* cdef memoryview memview_slice(memoryview memview, object indices): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int new_ndim = 0, suboffset_dim = -1, dim
* cdef bint negative_step
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_9);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memview_slice", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memviewsliceobj);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_index);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF((PyObject *)__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":807
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_memviewslice')
* cdef int slice_memviewslice( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *dst,
* Py_ssize_t shape, Py_ssize_t stride, Py_ssize_t suboffset,
*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_slice_memviewslice(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_dst, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_stride, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_suboffset, int __pyx_v_dim, int __pyx_v_new_ndim, int *__pyx_v_suboffset_dim, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_start, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_stop, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_step, int __pyx_v_have_start, int __pyx_v_have_stop, int __pyx_v_have_step, int __pyx_v_is_slice) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_new_shape;
int __pyx_v_negative_step;
int __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":827
* cdef bint negative_step
*
* if not is_slice: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if start < 0:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((!(__pyx_v_is_slice != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":829
* if not is_slice:
*
* if start < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start += shape
* if not 0 <= start < shape:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_start < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":830
*
* if start < 0:
* start += shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not 0 <= start < shape:
* _err_dim(IndexError, "Index out of bounds (axis %d)", dim)
*/
__pyx_v_start = (__pyx_v_start + __pyx_v_shape);
/* "View.MemoryView":829
* if not is_slice:
*
* if start < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start += shape
* if not 0 <= start < shape:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":831
* if start < 0:
* start += shape
* if not 0 <= start < shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err_dim(IndexError, "Index out of bounds (axis %d)", dim)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (0 <= __pyx_v_start);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_start < __pyx_v_shape);
}
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_t_1 != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":832
* start += shape
* if not 0 <= start < shape:
* _err_dim(IndexError, "Index out of bounds (axis %d)", dim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_err_dim(__pyx_builtin_IndexError, ((char *)"Index out of bounds (axis %d)"), __pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_3 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 832, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":831
* if start < 0:
* start += shape
* if not 0 <= start < shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err_dim(IndexError, "Index out of bounds (axis %d)", dim)
* else:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":827
* cdef bint negative_step
*
* if not is_slice: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if start < 0:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":835
* else:
*
* negative_step = have_step != 0 and step < 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if have_step and step == 0:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_have_step != 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
} else {
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_1;
goto __pyx_L6_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_step < 0) != 0);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_L6_bool_binop_done:;
__pyx_v_negative_step = __pyx_t_2;
/* "View.MemoryView":837
* negative_step = have_step != 0 and step < 0
*
* if have_step and step == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Step may not be zero (axis %d)", dim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_have_step != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
} else {
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_1;
goto __pyx_L9_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_step == 0) != 0);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_L9_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":838
*
* if have_step and step == 0:
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Step may not be zero (axis %d)", dim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_err_dim(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, ((char *)"Step may not be zero (axis %d)"), __pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_3 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 838, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":837
* negative_step = have_step != 0 and step < 0
*
* if have_step and step == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Step may not be zero (axis %d)", dim)
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":841
*
*
* if have_start: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if start < 0:
* start += shape
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_have_start != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":842
*
* if have_start:
* if start < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start += shape
* if start < 0:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_start < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":843
* if have_start:
* if start < 0:
* start += shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if start < 0:
* start = 0
*/
__pyx_v_start = (__pyx_v_start + __pyx_v_shape);
/* "View.MemoryView":844
* if start < 0:
* start += shape
* if start < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start = 0
* elif start >= shape:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_start < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":845
* start += shape
* if start < 0:
* start = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif start >= shape:
* if negative_step:
*/
__pyx_v_start = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":844
* if start < 0:
* start += shape
* if start < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start = 0
* elif start >= shape:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":842
*
* if have_start:
* if start < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start += shape
* if start < 0:
*/
goto __pyx_L12;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":846
* if start < 0:
* start = 0
* elif start >= shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if negative_step:
* start = shape - 1
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_start >= __pyx_v_shape) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":847
* start = 0
* elif start >= shape:
* if negative_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start = shape - 1
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_negative_step != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":848
* elif start >= shape:
* if negative_step:
* start = shape - 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* start = shape
*/
__pyx_v_start = (__pyx_v_shape - 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":847
* start = 0
* elif start >= shape:
* if negative_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start = shape - 1
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L14;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":850
* start = shape - 1
* else:
* start = shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* if negative_step:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_start = __pyx_v_shape;
}
__pyx_L14:;
/* "View.MemoryView":846
* if start < 0:
* start = 0
* elif start >= shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if negative_step:
* start = shape - 1
*/
}
__pyx_L12:;
/* "View.MemoryView":841
*
*
* if have_start: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if start < 0:
* start += shape
*/
goto __pyx_L11;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":852
* start = shape
* else:
* if negative_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start = shape - 1
* else:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_negative_step != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":853
* else:
* if negative_step:
* start = shape - 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* start = 0
*/
__pyx_v_start = (__pyx_v_shape - 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":852
* start = shape
* else:
* if negative_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* start = shape - 1
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L15;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":855
* start = shape - 1
* else:
* start = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if have_stop:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_start = 0;
}
__pyx_L15:;
}
__pyx_L11:;
/* "View.MemoryView":857
* start = 0
*
* if have_stop: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if stop < 0:
* stop += shape
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_have_stop != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":858
*
* if have_stop:
* if stop < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop += shape
* if stop < 0:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_stop < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":859
* if have_stop:
* if stop < 0:
* stop += shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if stop < 0:
* stop = 0
*/
__pyx_v_stop = (__pyx_v_stop + __pyx_v_shape);
/* "View.MemoryView":860
* if stop < 0:
* stop += shape
* if stop < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop = 0
* elif stop > shape:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_stop < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":861
* stop += shape
* if stop < 0:
* stop = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif stop > shape:
* stop = shape
*/
__pyx_v_stop = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":860
* if stop < 0:
* stop += shape
* if stop < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop = 0
* elif stop > shape:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":858
*
* if have_stop:
* if stop < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop += shape
* if stop < 0:
*/
goto __pyx_L17;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":862
* if stop < 0:
* stop = 0
* elif stop > shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop = shape
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_stop > __pyx_v_shape) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":863
* stop = 0
* elif stop > shape:
* stop = shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* if negative_step:
*/
__pyx_v_stop = __pyx_v_shape;
/* "View.MemoryView":862
* if stop < 0:
* stop = 0
* elif stop > shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop = shape
* else:
*/
}
__pyx_L17:;
/* "View.MemoryView":857
* start = 0
*
* if have_stop: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if stop < 0:
* stop += shape
*/
goto __pyx_L16;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":865
* stop = shape
* else:
* if negative_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop = -1
* else:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_negative_step != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":866
* else:
* if negative_step:
* stop = -1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* stop = shape
*/
__pyx_v_stop = -1L;
/* "View.MemoryView":865
* stop = shape
* else:
* if negative_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stop = -1
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L19;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":868
* stop = -1
* else:
* stop = shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not have_step:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_stop = __pyx_v_shape;
}
__pyx_L19:;
}
__pyx_L16:;
/* "View.MemoryView":870
* stop = shape
*
* if not have_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* step = 1
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_v_have_step != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":871
*
* if not have_step:
* step = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_v_step = 1;
/* "View.MemoryView":870
* stop = shape
*
* if not have_step: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* step = 1
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":875
*
* with cython.cdivision(True):
* new_shape = (stop - start) // step # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if (stop - start) - step * new_shape:
*/
__pyx_v_new_shape = ((__pyx_v_stop - __pyx_v_start) / __pyx_v_step);
/* "View.MemoryView":877
* new_shape = (stop - start) // step
*
* if (stop - start) - step * new_shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* new_shape += 1
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_stop - __pyx_v_start) - (__pyx_v_step * __pyx_v_new_shape)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":878
*
* if (stop - start) - step * new_shape:
* new_shape += 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if new_shape < 0:
*/
__pyx_v_new_shape = (__pyx_v_new_shape + 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":877
* new_shape = (stop - start) // step
*
* if (stop - start) - step * new_shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* new_shape += 1
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":880
* new_shape += 1
*
* if new_shape < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* new_shape = 0
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_new_shape < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":881
*
* if new_shape < 0:
* new_shape = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_v_new_shape = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":880
* new_shape += 1
*
* if new_shape < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* new_shape = 0
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":884
*
*
* dst.strides[new_ndim] = stride * step # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.shape[new_ndim] = new_shape
* dst.suboffsets[new_ndim] = suboffset
*/
(__pyx_v_dst->strides[__pyx_v_new_ndim]) = (__pyx_v_stride * __pyx_v_step);
/* "View.MemoryView":885
*
* dst.strides[new_ndim] = stride * step
* dst.shape[new_ndim] = new_shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.suboffsets[new_ndim] = suboffset
*
*/
(__pyx_v_dst->shape[__pyx_v_new_ndim]) = __pyx_v_new_shape;
/* "View.MemoryView":886
* dst.strides[new_ndim] = stride * step
* dst.shape[new_ndim] = new_shape
* dst.suboffsets[new_ndim] = suboffset # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
(__pyx_v_dst->suboffsets[__pyx_v_new_ndim]) = __pyx_v_suboffset;
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":889
*
*
* if suboffset_dim[0] < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.data += start * stride
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_suboffset_dim[0]) < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":890
*
* if suboffset_dim[0] < 0:
* dst.data += start * stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* dst.suboffsets[suboffset_dim[0]] += start * stride
*/
__pyx_v_dst->data = (__pyx_v_dst->data + (__pyx_v_start * __pyx_v_stride));
/* "View.MemoryView":889
*
*
* if suboffset_dim[0] < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.data += start * stride
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L23;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":892
* dst.data += start * stride
* else:
* dst.suboffsets[suboffset_dim[0]] += start * stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if suboffset >= 0:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_suboffset_dim[0]);
(__pyx_v_dst->suboffsets[__pyx_t_3]) = ((__pyx_v_dst->suboffsets[__pyx_t_3]) + (__pyx_v_start * __pyx_v_stride));
}
__pyx_L23:;
/* "View.MemoryView":894
* dst.suboffsets[suboffset_dim[0]] += start * stride
*
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not is_slice:
* if new_ndim == 0:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_suboffset >= 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":895
*
* if suboffset >= 0:
* if not is_slice: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if new_ndim == 0:
* dst.data = ( dst.data)[0] + suboffset
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_v_is_slice != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":896
* if suboffset >= 0:
* if not is_slice:
* if new_ndim == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.data = ( dst.data)[0] + suboffset
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_new_ndim == 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":897
* if not is_slice:
* if new_ndim == 0:
* dst.data = ( dst.data)[0] + suboffset # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* _err_dim(IndexError, "All dimensions preceding dimension %d "
*/
__pyx_v_dst->data = ((((char **)__pyx_v_dst->data)[0]) + __pyx_v_suboffset);
/* "View.MemoryView":896
* if suboffset >= 0:
* if not is_slice:
* if new_ndim == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.data = ( dst.data)[0] + suboffset
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L26;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":899
* dst.data = ( dst.data)[0] + suboffset
* else:
* _err_dim(IndexError, "All dimensions preceding dimension %d " # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "must be indexed and not sliced", dim)
* else:
*/
/*else*/ {
/* "View.MemoryView":900
* else:
* _err_dim(IndexError, "All dimensions preceding dimension %d "
* "must be indexed and not sliced", dim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* suboffset_dim[0] = new_ndim
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_err_dim(__pyx_builtin_IndexError, ((char *)"All dimensions preceding dimension %d must be indexed and not sliced"), __pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_3 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 899, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_L26:;
/* "View.MemoryView":895
*
* if suboffset >= 0:
* if not is_slice: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if new_ndim == 0:
* dst.data = ( dst.data)[0] + suboffset
*/
goto __pyx_L25;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":902
* "must be indexed and not sliced", dim)
* else:
* suboffset_dim[0] = new_ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return 0
*/
/*else*/ {
(__pyx_v_suboffset_dim[0]) = __pyx_v_new_ndim;
}
__pyx_L25:;
/* "View.MemoryView":894
* dst.suboffsets[suboffset_dim[0]] += start * stride
*
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not is_slice:
* if new_ndim == 0:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":904
* suboffset_dim[0] = new_ndim
*
* return 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":807
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_memviewslice')
* cdef int slice_memviewslice( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *dst,
* Py_ssize_t shape, Py_ssize_t stride, Py_ssize_t suboffset,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
{
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.slice_memviewslice", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
}
__pyx_r = -1;
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":910
*
* @cname('__pyx_pybuffer_index')
* cdef char *pybuffer_index(Py_buffer *view, char *bufp, Py_ssize_t index, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t dim) except NULL:
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, stride, suboffset = -1
*/
static char *__pyx_pybuffer_index(Py_buffer *__pyx_v_view, char *__pyx_v_bufp, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_index, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_dim) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_shape;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_stride;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_suboffset;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_itemsize;
char *__pyx_v_resultp;
char *__pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("pybuffer_index", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":912
* cdef char *pybuffer_index(Py_buffer *view, char *bufp, Py_ssize_t index,
* Py_ssize_t dim) except NULL:
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, stride, suboffset = -1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t itemsize = view.itemsize
* cdef char *resultp
*/
__pyx_v_suboffset = -1L;
/* "View.MemoryView":913
* Py_ssize_t dim) except NULL:
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, stride, suboffset = -1
* cdef Py_ssize_t itemsize = view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef char *resultp
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_view->itemsize;
__pyx_v_itemsize = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":916
* cdef char *resultp
*
* if view.ndim == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* shape = view.len / itemsize
* stride = itemsize
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_view->ndim == 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":917
*
* if view.ndim == 0:
* shape = view.len / itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stride = itemsize
* else:
*/
if (unlikely(__pyx_v_itemsize == 0)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ZeroDivisionError, "integer division or modulo by zero");
__PYX_ERR(1, 917, __pyx_L1_error)
}
else if (sizeof(Py_ssize_t) == sizeof(long) && (!(((Py_ssize_t)-1) > 0)) && unlikely(__pyx_v_itemsize == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && unlikely(UNARY_NEG_WOULD_OVERFLOW(__pyx_v_view->len))) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError, "value too large to perform division");
__PYX_ERR(1, 917, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_v_shape = (__pyx_v_view->len / __pyx_v_itemsize);
/* "View.MemoryView":918
* if view.ndim == 0:
* shape = view.len / itemsize
* stride = itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* shape = view.shape[dim]
*/
__pyx_v_stride = __pyx_v_itemsize;
/* "View.MemoryView":916
* cdef char *resultp
*
* if view.ndim == 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* shape = view.len / itemsize
* stride = itemsize
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":920
* stride = itemsize
* else:
* shape = view.shape[dim] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stride = view.strides[dim]
* if view.suboffsets != NULL:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_shape = (__pyx_v_view->shape[__pyx_v_dim]);
/* "View.MemoryView":921
* else:
* shape = view.shape[dim]
* stride = view.strides[dim] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if view.suboffsets != NULL:
* suboffset = view.suboffsets[dim]
*/
__pyx_v_stride = (__pyx_v_view->strides[__pyx_v_dim]);
/* "View.MemoryView":922
* shape = view.shape[dim]
* stride = view.strides[dim]
* if view.suboffsets != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* suboffset = view.suboffsets[dim]
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_view->suboffsets != NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":923
* stride = view.strides[dim]
* if view.suboffsets != NULL:
* suboffset = view.suboffsets[dim] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if index < 0:
*/
__pyx_v_suboffset = (__pyx_v_view->suboffsets[__pyx_v_dim]);
/* "View.MemoryView":922
* shape = view.shape[dim]
* stride = view.strides[dim]
* if view.suboffsets != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* suboffset = view.suboffsets[dim]
*
*/
}
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":925
* suboffset = view.suboffsets[dim]
*
* if index < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* index += view.shape[dim]
* if index < 0:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_index < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":926
*
* if index < 0:
* index += view.shape[dim] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if index < 0:
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*/
__pyx_v_index = (__pyx_v_index + (__pyx_v_view->shape[__pyx_v_dim]));
/* "View.MemoryView":927
* if index < 0:
* index += view.shape[dim]
* if index < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_index < 0) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":928
* index += view.shape[dim]
* if index < 0:
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if index >= shape:
*/
__pyx_t_3 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 928, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyString_Format(__pyx_kp_s_Out_of_bounds_on_buffer_access_a, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 928, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_builtin_IndexError, __pyx_t_4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 928, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 928, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":927
* if index < 0:
* index += view.shape[dim]
* if index < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":925
* suboffset = view.suboffsets[dim]
*
* if index < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* index += view.shape[dim]
* if index < 0:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":930
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*
* if index >= shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_index >= __pyx_v_shape) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":931
*
* if index >= shape:
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* resultp = bufp + index * stride
*/
__pyx_t_3 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 931, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyString_Format(__pyx_kp_s_Out_of_bounds_on_buffer_access_a, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 931, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_builtin_IndexError, __pyx_t_4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 931, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 931, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":930
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*
* if index >= shape: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":933
* raise IndexError("Out of bounds on buffer access (axis %d)" % dim)
*
* resultp = bufp + index * stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if suboffset >= 0:
* resultp = ( resultp)[0] + suboffset
*/
__pyx_v_resultp = (__pyx_v_bufp + (__pyx_v_index * __pyx_v_stride));
/* "View.MemoryView":934
*
* resultp = bufp + index * stride
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* resultp = ( resultp)[0] + suboffset
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_suboffset >= 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":935
* resultp = bufp + index * stride
* if suboffset >= 0:
* resultp = ( resultp)[0] + suboffset # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return resultp
*/
__pyx_v_resultp = ((((char **)__pyx_v_resultp)[0]) + __pyx_v_suboffset);
/* "View.MemoryView":934
*
* resultp = bufp + index * stride
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* resultp = ( resultp)[0] + suboffset
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":937
* resultp = ( resultp)[0] + suboffset
*
* return resultp # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_resultp;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":910
*
* @cname('__pyx_pybuffer_index')
* cdef char *pybuffer_index(Py_buffer *view, char *bufp, Py_ssize_t index, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t dim) except NULL:
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, stride, suboffset = -1
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.pybuffer_index", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":943
*
* @cname('__pyx_memslice_transpose')
* cdef int transpose_memslice(__Pyx_memviewslice *memslice) nogil except 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int ndim = memslice.memview.view.ndim
*
*/
static int __pyx_memslice_transpose(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_memslice) {
int __pyx_v_ndim;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_shape;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_strides;
int __pyx_v_i;
int __pyx_v_j;
int __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_2;
long __pyx_t_3;
long __pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_5;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_t_7;
int __pyx_t_8;
int __pyx_t_9;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":944
* @cname('__pyx_memslice_transpose')
* cdef int transpose_memslice(__Pyx_memviewslice *memslice) nogil except 0:
* cdef int ndim = memslice.memview.view.ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t *shape = memslice.shape
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_memslice->memview->view.ndim;
__pyx_v_ndim = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":946
* cdef int ndim = memslice.memview.view.ndim
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t *shape = memslice.shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t *strides = memslice.strides
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_memslice->shape;
__pyx_v_shape = __pyx_t_2;
/* "View.MemoryView":947
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t *shape = memslice.shape
* cdef Py_ssize_t *strides = memslice.strides # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_memslice->strides;
__pyx_v_strides = __pyx_t_2;
/* "View.MemoryView":951
*
* cdef int i, j
* for i in range(ndim / 2): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* j = ndim - 1 - i
* strides[i], strides[j] = strides[j], strides[i]
*/
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_ndim / 2);
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_t_3;
for (__pyx_t_1 = 0; __pyx_t_1 < __pyx_t_4; __pyx_t_1+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":952
* cdef int i, j
* for i in range(ndim / 2):
* j = ndim - 1 - i # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* strides[i], strides[j] = strides[j], strides[i]
* shape[i], shape[j] = shape[j], shape[i]
*/
__pyx_v_j = ((__pyx_v_ndim - 1) - __pyx_v_i);
/* "View.MemoryView":953
* for i in range(ndim / 2):
* j = ndim - 1 - i
* strides[i], strides[j] = strides[j], strides[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* shape[i], shape[j] = shape[j], shape[i]
*
*/
__pyx_t_5 = (__pyx_v_strides[__pyx_v_j]);
__pyx_t_6 = (__pyx_v_strides[__pyx_v_i]);
(__pyx_v_strides[__pyx_v_i]) = __pyx_t_5;
(__pyx_v_strides[__pyx_v_j]) = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":954
* j = ndim - 1 - i
* strides[i], strides[j] = strides[j], strides[i]
* shape[i], shape[j] = shape[j], shape[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if memslice.suboffsets[i] >= 0 or memslice.suboffsets[j] >= 0:
*/
__pyx_t_6 = (__pyx_v_shape[__pyx_v_j]);
__pyx_t_5 = (__pyx_v_shape[__pyx_v_i]);
(__pyx_v_shape[__pyx_v_i]) = __pyx_t_6;
(__pyx_v_shape[__pyx_v_j]) = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":956
* shape[i], shape[j] = shape[j], shape[i]
*
* if memslice.suboffsets[i] >= 0 or memslice.suboffsets[j] >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err(ValueError, "Cannot transpose memoryview with indirect dimensions")
*
*/
__pyx_t_8 = (((__pyx_v_memslice->suboffsets[__pyx_v_i]) >= 0) != 0);
if (!__pyx_t_8) {
} else {
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_t_8;
goto __pyx_L6_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_8 = (((__pyx_v_memslice->suboffsets[__pyx_v_j]) >= 0) != 0);
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_t_8;
__pyx_L6_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_7) {
/* "View.MemoryView":957
*
* if memslice.suboffsets[i] >= 0 or memslice.suboffsets[j] >= 0:
* _err(ValueError, "Cannot transpose memoryview with indirect dimensions") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return 1
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __pyx_memoryview_err(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, ((char *)"Cannot transpose memoryview with indirect dimensions")); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_9 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 957, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":956
* shape[i], shape[j] = shape[j], shape[i]
*
* if memslice.suboffsets[i] >= 0 or memslice.suboffsets[j] >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err(ValueError, "Cannot transpose memoryview with indirect dimensions")
*
*/
}
}
/* "View.MemoryView":959
* _err(ValueError, "Cannot transpose memoryview with indirect dimensions")
*
* return 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = 1;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":943
*
* @cname('__pyx_memslice_transpose')
* cdef int transpose_memslice(__Pyx_memviewslice *memslice) nogil except 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int ndim = memslice.memview.view.ndim
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
{
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.transpose_memslice", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
}
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":976
* cdef int (*to_dtype_func)(char *, object) except 0
*
* def __dealloc__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&self.from_slice, 1)
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static void __pyx_memoryviewslice___dealloc__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryviewslice___dealloc__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__dealloc__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_memoryviewslice___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice___dealloc__(((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
static void __pyx_memoryviewslice___pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice___dealloc__(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__dealloc__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":977
*
* def __dealloc__(self):
* __PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&self.from_slice, 1) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp):
*/
__PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW((&__pyx_v_self->from_slice), 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":976
* cdef int (*to_dtype_func)(char *, object) except 0
*
* def __dealloc__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&self.from_slice, 1)
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
/* "View.MemoryView":979
* __PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&self.from_slice, 1)
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.to_object_func != NULL:
* return self.to_object_func(itemp)
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_convert_item_to_object(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("convert_item_to_object", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":980
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp):
* if self.to_object_func != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.to_object_func(itemp)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->to_object_func != NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":981
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp):
* if self.to_object_func != NULL:
* return self.to_object_func(itemp) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* return memoryview.convert_item_to_object(self, itemp)
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_self->to_object_func(__pyx_v_itemp); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 981, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":980
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp):
* if self.to_object_func != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.to_object_func(itemp)
* else:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":983
* return self.to_object_func(itemp)
* else:
* return memoryview.convert_item_to_object(self, itemp) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value):
*/
/*else*/ {
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_memoryview_convert_item_to_object(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_v_itemp); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 983, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":979
* __PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&self.from_slice, 1)
*
* cdef convert_item_to_object(self, char *itemp): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.to_object_func != NULL:
* return self.to_object_func(itemp)
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._memoryviewslice.convert_item_to_object", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":985
* return memoryview.convert_item_to_object(self, itemp)
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.to_dtype_func != NULL:
* self.to_dtype_func(itemp, value)
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_assign_item_from_object(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp, PyObject *__pyx_v_value) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("assign_item_from_object", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":986
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value):
* if self.to_dtype_func != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.to_dtype_func(itemp, value)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_self->to_dtype_func != NULL) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":987
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value):
* if self.to_dtype_func != NULL:
* self.to_dtype_func(itemp, value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* memoryview.assign_item_from_object(self, itemp, value)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_self->to_dtype_func(__pyx_v_itemp, __pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_2 == ((int)0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 987, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":986
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value):
* if self.to_dtype_func != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* self.to_dtype_func(itemp, value)
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":989
* self.to_dtype_func(itemp, value)
* else:
* memoryview.assign_item_from_object(self, itemp, value) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @property
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_assign_item_from_object(((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_self), __pyx_v_itemp, __pyx_v_value); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 989, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":985
* return memoryview.convert_item_to_object(self, itemp)
*
* cdef assign_item_from_object(self, char *itemp, object value): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if self.to_dtype_func != NULL:
* self.to_dtype_func(itemp, value)
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._memoryviewslice.assign_item_from_object", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":992
*
* @property
* def base(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.from_object
*
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice_4base_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice_4base_1__get__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice_4base___get__(((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice_4base___get__(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__get__", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":993
* @property
* def base(self):
* return self.from_object # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_memoryview_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_self->from_object);
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_self->from_object;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":992
*
* @property
* def base(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return self.from_object
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryviewslice_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryviewslice_1__reduce_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *unused) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_memoryviewslice___reduce_cython__(((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_v_self));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryviewslice___reduce_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__reduce_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":2
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_tuple__17, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_1, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __reduce_cython__(self): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._memoryviewslice.__reduce_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":3
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryviewslice_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryviewslice_3__setstate_cython__(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__ (wrapper)", 0);
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf___pyx_memoryviewslice_2__setstate_cython__(((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_v_self), ((PyObject *)__pyx_v___pyx_state));
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf___pyx_memoryviewslice_2__setstate_cython__(CYTHON_UNUSED struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__setstate_cython__", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(__pyx_builtin_TypeError, __pyx_tuple__18, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_1, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "(tree fragment)":3
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._memoryviewslice.__setstate_cython__", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":999
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_fromslice')
* cdef memoryview_fromslice(__Pyx_memviewslice memviewslice, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* int ndim,
* object (*to_object_func)(char *),
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_fromslice(__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_memviewslice, int __pyx_v_ndim, PyObject *(*__pyx_v_to_object_func)(char *), int (*__pyx_v_to_dtype_func)(char *, PyObject *), int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object) {
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_result = 0;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_suboffset;
PyObject *__pyx_v_length = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
__Pyx_TypeInfo *__pyx_t_4;
Py_buffer __pyx_t_5;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_6;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_7;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_8;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_9;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("memoryview_fromslice", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1007
* cdef _memoryviewslice result
*
* if memviewslice.memview == Py_None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return None
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memviewslice.memview) == Py_None) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1008
*
* if memviewslice.memview == Py_None:
* return None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1007
* cdef _memoryviewslice result
*
* if memviewslice.memview == Py_None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return None
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1013
*
*
* result = _memoryviewslice(None, 0, dtype_is_object) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result.from_slice = memviewslice
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(__pyx_v_dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1013, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1013, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(Py_None);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 0, Py_None);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_int_0);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_int_0);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 1, __pyx_int_0);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_3, 2, __pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_memoryviewslice_type), __pyx_t_3, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1013, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_v_result = ((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1015
* result = _memoryviewslice(None, 0, dtype_is_object)
*
* result.from_slice = memviewslice # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __PYX_INC_MEMVIEW(&memviewslice, 1)
*
*/
__pyx_v_result->from_slice = __pyx_v_memviewslice;
/* "View.MemoryView":1016
*
* result.from_slice = memviewslice
* __PYX_INC_MEMVIEW(&memviewslice, 1) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result.from_object = ( memviewslice.memview).base
*/
__PYX_INC_MEMVIEW((&__pyx_v_memviewslice), 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":1018
* __PYX_INC_MEMVIEW(&memviewslice, 1)
*
* result.from_object = ( memviewslice.memview).base # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.typeinfo = memviewslice.memview.typeinfo
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memviewslice.memview), __pyx_n_s_base); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1018, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v_result->from_object);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v_result->from_object);
__pyx_v_result->from_object = __pyx_t_2;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1019
*
* result.from_object = ( memviewslice.memview).base
* result.typeinfo = memviewslice.memview.typeinfo # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result.view = memviewslice.memview.view
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_memviewslice.memview->typeinfo;
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.typeinfo = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1021
* result.typeinfo = memviewslice.memview.typeinfo
*
* result.view = memviewslice.memview.view # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.view.buf = memviewslice.data
* result.view.ndim = ndim
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_memviewslice.memview->view;
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":1022
*
* result.view = memviewslice.memview.view
* result.view.buf = memviewslice.data # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.view.ndim = ndim
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &result.view).obj = Py_None
*/
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.buf = ((void *)__pyx_v_memviewslice.data);
/* "View.MemoryView":1023
* result.view = memviewslice.memview.view
* result.view.buf = memviewslice.data
* result.view.ndim = ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &result.view).obj = Py_None
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*/
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.ndim = __pyx_v_ndim;
/* "View.MemoryView":1024
* result.view.buf = memviewslice.data
* result.view.ndim = ndim
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &result.view).obj = Py_None # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*
*/
((Py_buffer *)(&__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view))->obj = Py_None;
/* "View.MemoryView":1025
* result.view.ndim = ndim
* (<__pyx_buffer *> &result.view).obj = Py_None
* Py_INCREF(Py_None) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if (memviewslice.memview).flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE:
*/
Py_INCREF(Py_None);
/* "View.MemoryView":1027
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*
* if (memviewslice.memview).flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_memviewslice.memview)->flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1028
*
* if (memviewslice.memview).flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE:
* result.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* result.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS_RO
*/
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS;
/* "View.MemoryView":1027
* Py_INCREF(Py_None)
*
* if (memviewslice.memview).flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L4;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1030
* result.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS
* else:
* result.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS_RO # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result.view.shape = result.from_slice.shape
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS_RO;
}
__pyx_L4:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1032
* result.flags = PyBUF_RECORDS_RO
*
* result.view.shape = result.from_slice.shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.view.strides = result.from_slice.strides
*
*/
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.shape = ((Py_ssize_t *)__pyx_v_result->from_slice.shape);
/* "View.MemoryView":1033
*
* result.view.shape = result.from_slice.shape
* result.view.strides = result.from_slice.strides # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.strides = ((Py_ssize_t *)__pyx_v_result->from_slice.strides);
/* "View.MemoryView":1036
*
*
* result.view.suboffsets = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for suboffset in result.from_slice.suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0:
*/
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.suboffsets = NULL;
/* "View.MemoryView":1037
*
* result.view.suboffsets = NULL
* for suboffset in result.from_slice.suboffsets[:ndim]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if suboffset >= 0:
* result.view.suboffsets = result.from_slice.suboffsets
*/
__pyx_t_7 = (__pyx_v_result->from_slice.suboffsets + __pyx_v_ndim);
for (__pyx_t_8 = __pyx_v_result->from_slice.suboffsets; __pyx_t_8 < __pyx_t_7; __pyx_t_8++) {
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_t_8;
__pyx_v_suboffset = (__pyx_t_6[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1038
* result.view.suboffsets = NULL
* for suboffset in result.from_slice.suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.view.suboffsets = result.from_slice.suboffsets
* break
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_suboffset >= 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1039
* for suboffset in result.from_slice.suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0:
* result.view.suboffsets = result.from_slice.suboffsets # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* break
*
*/
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.suboffsets = ((Py_ssize_t *)__pyx_v_result->from_slice.suboffsets);
/* "View.MemoryView":1040
* if suboffset >= 0:
* result.view.suboffsets = result.from_slice.suboffsets
* break # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result.view.len = result.view.itemsize
*/
goto __pyx_L6_break;
/* "View.MemoryView":1038
* result.view.suboffsets = NULL
* for suboffset in result.from_slice.suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.view.suboffsets = result.from_slice.suboffsets
* break
*/
}
}
__pyx_L6_break:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1042
* break
*
* result.view.len = result.view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for length in result.view.shape[:ndim]:
* result.view.len *= length
*/
__pyx_t_9 = __pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.itemsize;
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.len = __pyx_t_9;
/* "View.MemoryView":1043
*
* result.view.len = result.view.itemsize
* for length in result.view.shape[:ndim]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.view.len *= length
*
*/
__pyx_t_7 = (__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.shape + __pyx_v_ndim);
for (__pyx_t_8 = __pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.shape; __pyx_t_8 < __pyx_t_7; __pyx_t_8++) {
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_t_8;
__pyx_t_2 = PyInt_FromSsize_t((__pyx_t_6[0])); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1043, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF_SET(__pyx_v_length, __pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1044
* result.view.len = result.view.itemsize
* for length in result.view.shape[:ndim]:
* result.view.len *= length # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result.to_object_func = to_object_func
*/
__pyx_t_2 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.len); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1044, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = PyNumber_InPlaceMultiply(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_v_length); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1044, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_9 = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(__pyx_t_3); if (unlikely((__pyx_t_9 == (Py_ssize_t)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 1044, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__pyx_v_result->__pyx_base.view.len = __pyx_t_9;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1046
* result.view.len *= length
*
* result.to_object_func = to_object_func # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* result.to_dtype_func = to_dtype_func
*
*/
__pyx_v_result->to_object_func = __pyx_v_to_object_func;
/* "View.MemoryView":1047
*
* result.to_object_func = to_object_func
* result.to_dtype_func = to_dtype_func # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return result
*/
__pyx_v_result->to_dtype_func = __pyx_v_to_dtype_func;
/* "View.MemoryView":1049
* result.to_dtype_func = to_dtype_func
*
* return result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview')
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result));
__pyx_r = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":999
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_fromslice')
* cdef memoryview_fromslice(__Pyx_memviewslice memviewslice, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* int ndim,
* object (*to_object_func)(char *),
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview_fromslice", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF((PyObject *)__pyx_v_result);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_length);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1052
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview')
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *get_slice_from_memview(memoryview memview, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice) except NULL:
* cdef _memoryviewslice obj
*/
static __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_memview, __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_mslice) {
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_obj = 0;
__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("get_slice_from_memview", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1055
* __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice) except NULL:
* cdef _memoryviewslice obj
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* obj = memview
* return &obj.from_slice
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_TypeCheck(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview), __pyx_memoryviewslice_type);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1056
* cdef _memoryviewslice obj
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* obj = memview # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return &obj.from_slice
* else:
*/
if (!(likely(((((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview)) == Py_None) || likely(__Pyx_TypeTest(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview), __pyx_memoryviewslice_type))))) __PYX_ERR(1, 1056, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_3 = ((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_v_obj = ((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1057
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* obj = memview
* return &obj.from_slice # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* slice_copy(memview, mslice)
*/
__pyx_r = (&__pyx_v_obj->from_slice);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1055
* __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice) except NULL:
* cdef _memoryviewslice obj
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* obj = memview
* return &obj.from_slice
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1059
* return &obj.from_slice
* else:
* slice_copy(memview, mslice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return mslice
*
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(__pyx_v_memview, __pyx_v_mslice);
/* "View.MemoryView":1060
* else:
* slice_copy(memview, mslice)
* return mslice # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy')
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_mslice;
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1052
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview')
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice *get_slice_from_memview(memoryview memview, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *mslice) except NULL:
* cdef _memoryviewslice obj
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.get_slice_from_memview", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF((PyObject *)__pyx_v_obj);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1063
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy')
* cdef void slice_copy(memoryview memview, __Pyx_memviewslice *dst): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int dim
* cdef (Py_ssize_t*) shape, strides, suboffsets
*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_memview, __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_dst) {
int __pyx_v_dim;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_shape;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_strides;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_suboffsets;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_5;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("slice_copy", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1067
* cdef (Py_ssize_t*) shape, strides, suboffsets
*
* shape = memview.view.shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* strides = memview.view.strides
* suboffsets = memview.view.suboffsets
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_memview->view.shape;
__pyx_v_shape = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1068
*
* shape = memview.view.shape
* strides = memview.view.strides # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* suboffsets = memview.view.suboffsets
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_memview->view.strides;
__pyx_v_strides = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1069
* shape = memview.view.shape
* strides = memview.view.strides
* suboffsets = memview.view.suboffsets # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* dst.memview = <__pyx_memoryview *> memview
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_memview->view.suboffsets;
__pyx_v_suboffsets = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1071
* suboffsets = memview.view.suboffsets
*
* dst.memview = <__pyx_memoryview *> memview # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.data = memview.view.buf
*
*/
__pyx_v_dst->memview = ((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)__pyx_v_memview);
/* "View.MemoryView":1072
*
* dst.memview = <__pyx_memoryview *> memview
* dst.data = memview.view.buf # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for dim in range(memview.view.ndim):
*/
__pyx_v_dst->data = ((char *)__pyx_v_memview->view.buf);
/* "View.MemoryView":1074
* dst.data = memview.view.buf
*
* for dim in range(memview.view.ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.shape[dim] = shape[dim]
* dst.strides[dim] = strides[dim]
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_memview->view.ndim;
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_2;
for (__pyx_t_4 = 0; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4+=1) {
__pyx_v_dim = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1075
*
* for dim in range(memview.view.ndim):
* dst.shape[dim] = shape[dim] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.strides[dim] = strides[dim]
* dst.suboffsets[dim] = suboffsets[dim] if suboffsets else -1
*/
(__pyx_v_dst->shape[__pyx_v_dim]) = (__pyx_v_shape[__pyx_v_dim]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1076
* for dim in range(memview.view.ndim):
* dst.shape[dim] = shape[dim]
* dst.strides[dim] = strides[dim] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.suboffsets[dim] = suboffsets[dim] if suboffsets else -1
*
*/
(__pyx_v_dst->strides[__pyx_v_dim]) = (__pyx_v_strides[__pyx_v_dim]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1077
* dst.shape[dim] = shape[dim]
* dst.strides[dim] = strides[dim]
* dst.suboffsets[dim] = suboffsets[dim] if suboffsets else -1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_object')
*/
if ((__pyx_v_suboffsets != 0)) {
__pyx_t_5 = (__pyx_v_suboffsets[__pyx_v_dim]);
} else {
__pyx_t_5 = -1L;
}
(__pyx_v_dst->suboffsets[__pyx_v_dim]) = __pyx_t_5;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1063
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy')
* cdef void slice_copy(memoryview memview, __Pyx_memviewslice *dst): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int dim
* cdef (Py_ssize_t*) shape, strides, suboffsets
*/
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1080
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_object')
* cdef memoryview_copy(memoryview memview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Create a new memoryview object"
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice memviewslice
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_memview) {
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_memviewslice;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("memoryview_copy", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1083
* "Create a new memoryview object"
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice memviewslice
* slice_copy(memview, &memviewslice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return memoryview_copy_from_slice(memview, &memviewslice)
*
*/
__pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(__pyx_v_memview, (&__pyx_v_memviewslice));
/* "View.MemoryView":1084
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice memviewslice
* slice_copy(memview, &memviewslice)
* return memoryview_copy_from_slice(memview, &memviewslice) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice')
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice(__pyx_v_memview, (&__pyx_v_memviewslice)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1084, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1080
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_object')
* cdef memoryview_copy(memoryview memview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Create a new memoryview object"
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice memviewslice
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview_copy", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1087
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice')
* cdef memoryview_copy_from_slice(memoryview memview, __Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """
* Create a new memoryview object from a given memoryview object and slice.
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_memview, __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_memviewslice) {
PyObject *(*__pyx_v_to_object_func)(char *);
int (*__pyx_v_to_dtype_func)(char *, PyObject *);
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
PyObject *(*__pyx_t_3)(char *);
int (*__pyx_t_4)(char *, PyObject *);
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("memoryview_copy_from_slice", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1094
* cdef int (*to_dtype_func)(char *, object) except 0
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* to_object_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_object_func
* to_dtype_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_dtype_func
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_TypeCheck(((PyObject *)__pyx_v_memview), __pyx_memoryviewslice_type);
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1095
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* to_object_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_object_func # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* to_dtype_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_dtype_func
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_3 = ((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_v_memview)->to_object_func;
__pyx_v_to_object_func = __pyx_t_3;
/* "View.MemoryView":1096
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice):
* to_object_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_object_func
* to_dtype_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_dtype_func # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* to_object_func = NULL
*/
__pyx_t_4 = ((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)__pyx_v_memview)->to_dtype_func;
__pyx_v_to_dtype_func = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1094
* cdef int (*to_dtype_func)(char *, object) except 0
*
* if isinstance(memview, _memoryviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* to_object_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_object_func
* to_dtype_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_dtype_func
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1098
* to_dtype_func = (<_memoryviewslice> memview).to_dtype_func
* else:
* to_object_func = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* to_dtype_func = NULL
*
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_v_to_object_func = NULL;
/* "View.MemoryView":1099
* else:
* to_object_func = NULL
* to_dtype_func = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return memoryview_fromslice(memviewslice[0], memview.view.ndim,
*/
__pyx_v_to_dtype_func = NULL;
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1101
* to_dtype_func = NULL
*
* return memoryview_fromslice(memviewslice[0], memview.view.ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* to_object_func, to_dtype_func,
* memview.dtype_is_object)
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
/* "View.MemoryView":1103
* return memoryview_fromslice(memviewslice[0], memview.view.ndim,
* to_object_func, to_dtype_func,
* memview.dtype_is_object) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_memoryview_fromslice((__pyx_v_memviewslice[0]), __pyx_v_memview->view.ndim, __pyx_v_to_object_func, __pyx_v_to_dtype_func, __pyx_v_memview->dtype_is_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1101, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_5);
__pyx_r = __pyx_t_5;
__pyx_t_5 = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1087
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice')
* cdef memoryview_copy_from_slice(memoryview memview, __Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """
* Create a new memoryview object from a given memoryview object and slice.
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview_copy_from_slice", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1109
*
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t arg) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if arg < 0:
* return -arg
*/
static Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_arg) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1110
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t arg) nogil:
* if arg < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return -arg
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_arg < 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1111
* cdef Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t arg) nogil:
* if arg < 0:
* return -arg # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* return arg
*/
__pyx_r = (-__pyx_v_arg);
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1110
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t arg) nogil:
* if arg < 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return -arg
* else:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1113
* return -arg
* else:
* return arg # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_get_best_slice_order')
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_arg;
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1109
*
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t arg) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if arg < 0:
* return -arg
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1116
*
* @cname('__pyx_get_best_slice_order')
* cdef char get_best_order(__Pyx_memviewslice *mslice, int ndim) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """
* Figure out the best memory access order for a given slice.
*/
static char __pyx_get_best_slice_order(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_mslice, int __pyx_v_ndim) {
int __pyx_v_i;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_c_stride;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_f_stride;
char __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1121
* """
* cdef int i
* cdef Py_ssize_t c_stride = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t f_stride = 0
*
*/
__pyx_v_c_stride = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1122
* cdef int i
* cdef Py_ssize_t c_stride = 0
* cdef Py_ssize_t f_stride = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
*/
__pyx_v_f_stride = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1124
* cdef Py_ssize_t f_stride = 0
*
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1:
* c_stride = mslice.strides[i]
*/
for (__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_ndim - 1); __pyx_t_1 > -1; __pyx_t_1-=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1125
*
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* c_stride = mslice.strides[i]
* break
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_mslice->shape[__pyx_v_i]) > 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1126
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1:
* c_stride = mslice.strides[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* break
*
*/
__pyx_v_c_stride = (__pyx_v_mslice->strides[__pyx_v_i]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1127
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1:
* c_stride = mslice.strides[i]
* break # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for i in range(ndim):
*/
goto __pyx_L4_break;
/* "View.MemoryView":1125
*
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* c_stride = mslice.strides[i]
* break
*/
}
}
__pyx_L4_break:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1129
* break
*
* for i in range(ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1:
* f_stride = mslice.strides[i]
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_ndim;
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_1;
for (__pyx_t_4 = 0; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1130
*
* for i in range(ndim):
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* f_stride = mslice.strides[i]
* break
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_mslice->shape[__pyx_v_i]) > 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1131
* for i in range(ndim):
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1:
* f_stride = mslice.strides[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* break
*
*/
__pyx_v_f_stride = (__pyx_v_mslice->strides[__pyx_v_i]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1132
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1:
* f_stride = mslice.strides[i]
* break # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if abs_py_ssize_t(c_stride) <= abs_py_ssize_t(f_stride):
*/
goto __pyx_L7_break;
/* "View.MemoryView":1130
*
* for i in range(ndim):
* if mslice.shape[i] > 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* f_stride = mslice.strides[i]
* break
*/
}
}
__pyx_L7_break:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1134
* break
*
* if abs_py_ssize_t(c_stride) <= abs_py_ssize_t(f_stride): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return 'C'
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((abs_py_ssize_t(__pyx_v_c_stride) <= abs_py_ssize_t(__pyx_v_f_stride)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1135
*
* if abs_py_ssize_t(c_stride) <= abs_py_ssize_t(f_stride):
* return 'C' # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* return 'F'
*/
__pyx_r = 'C';
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1134
* break
*
* if abs_py_ssize_t(c_stride) <= abs_py_ssize_t(f_stride): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return 'C'
* else:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1137
* return 'C'
* else:
* return 'F' # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cython.cdivision(True)
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_r = 'F';
goto __pyx_L0;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1116
*
* @cname('__pyx_get_best_slice_order')
* cdef char get_best_order(__Pyx_memviewslice *mslice, int ndim) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* """
* Figure out the best memory access order for a given slice.
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1140
*
* @cython.cdivision(True)
* cdef void _copy_strided_to_strided(char *src_data, Py_ssize_t *src_strides, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* char *dst_data, Py_ssize_t *dst_strides,
* Py_ssize_t *src_shape, Py_ssize_t *dst_shape,
*/
static void _copy_strided_to_strided(char *__pyx_v_src_data, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_src_strides, char *__pyx_v_dst_data, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_dst_strides, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_src_shape, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_dst_shape, int __pyx_v_ndim, size_t __pyx_v_itemsize) {
CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_i;
CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_src_extent;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_dst_extent;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_src_stride;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_dst_stride;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_4;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_5;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":1147
*
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
* cdef Py_ssize_t src_extent = src_shape[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_extent = dst_shape[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t src_stride = src_strides[0]
*/
__pyx_v_src_extent = (__pyx_v_src_shape[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1148
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
* cdef Py_ssize_t src_extent = src_shape[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_extent = dst_shape[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t src_stride = src_strides[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_stride = dst_strides[0]
*/
__pyx_v_dst_extent = (__pyx_v_dst_shape[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1149
* cdef Py_ssize_t src_extent = src_shape[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_extent = dst_shape[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t src_stride = src_strides[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_stride = dst_strides[0]
*
*/
__pyx_v_src_stride = (__pyx_v_src_strides[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1150
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_extent = dst_shape[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t src_stride = src_strides[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_stride = dst_strides[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if ndim == 1:
*/
__pyx_v_dst_stride = (__pyx_v_dst_strides[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1152
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_stride = dst_strides[0]
*
* if ndim == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if (src_stride > 0 and dst_stride > 0 and
* src_stride == itemsize == dst_stride):
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_ndim == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1153
*
* if ndim == 1:
* if (src_stride > 0 and dst_stride > 0 and # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src_stride == itemsize == dst_stride):
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize * dst_extent)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_src_stride > 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L5_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_dst_stride > 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
} else {
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_2;
goto __pyx_L5_bool_binop_done;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1154
* if ndim == 1:
* if (src_stride > 0 and dst_stride > 0 and
* src_stride == itemsize == dst_stride): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize * dst_extent)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((size_t)__pyx_v_src_stride) == __pyx_v_itemsize);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_itemsize == ((size_t)__pyx_v_dst_stride));
}
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_L5_bool_binop_done:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1153
*
* if ndim == 1:
* if (src_stride > 0 and dst_stride > 0 and # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src_stride == itemsize == dst_stride):
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize * dst_extent)
*/
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1155
* if (src_stride > 0 and dst_stride > 0 and
* src_stride == itemsize == dst_stride):
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize * dst_extent) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* for i in range(dst_extent):
*/
(void)(memcpy(__pyx_v_dst_data, __pyx_v_src_data, (__pyx_v_itemsize * __pyx_v_dst_extent)));
/* "View.MemoryView":1153
*
* if ndim == 1:
* if (src_stride > 0 and dst_stride > 0 and # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src_stride == itemsize == dst_stride):
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize * dst_extent)
*/
goto __pyx_L4;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1157
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize * dst_extent)
* else:
* for i in range(dst_extent): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize)
* src_data += src_stride
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_dst_extent;
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_t_4;
for (__pyx_t_6 = 0; __pyx_t_6 < __pyx_t_5; __pyx_t_6+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":1158
* else:
* for i in range(dst_extent):
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src_data += src_stride
* dst_data += dst_stride
*/
(void)(memcpy(__pyx_v_dst_data, __pyx_v_src_data, __pyx_v_itemsize));
/* "View.MemoryView":1159
* for i in range(dst_extent):
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize)
* src_data += src_stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst_data += dst_stride
* else:
*/
__pyx_v_src_data = (__pyx_v_src_data + __pyx_v_src_stride);
/* "View.MemoryView":1160
* memcpy(dst_data, src_data, itemsize)
* src_data += src_stride
* dst_data += dst_stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* for i in range(dst_extent):
*/
__pyx_v_dst_data = (__pyx_v_dst_data + __pyx_v_dst_stride);
}
}
__pyx_L4:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1152
* cdef Py_ssize_t dst_stride = dst_strides[0]
*
* if ndim == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if (src_stride > 0 and dst_stride > 0 and
* src_stride == itemsize == dst_stride):
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1162
* dst_data += dst_stride
* else:
* for i in range(dst_extent): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _copy_strided_to_strided(src_data, src_strides + 1,
* dst_data, dst_strides + 1,
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_dst_extent;
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_t_4;
for (__pyx_t_6 = 0; __pyx_t_6 < __pyx_t_5; __pyx_t_6+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":1163
* else:
* for i in range(dst_extent):
* _copy_strided_to_strided(src_data, src_strides + 1, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst_data, dst_strides + 1,
* src_shape + 1, dst_shape + 1,
*/
_copy_strided_to_strided(__pyx_v_src_data, (__pyx_v_src_strides + 1), __pyx_v_dst_data, (__pyx_v_dst_strides + 1), (__pyx_v_src_shape + 1), (__pyx_v_dst_shape + 1), (__pyx_v_ndim - 1), __pyx_v_itemsize);
/* "View.MemoryView":1167
* src_shape + 1, dst_shape + 1,
* ndim - 1, itemsize)
* src_data += src_stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst_data += dst_stride
*
*/
__pyx_v_src_data = (__pyx_v_src_data + __pyx_v_src_stride);
/* "View.MemoryView":1168
* ndim - 1, itemsize)
* src_data += src_stride
* dst_data += dst_stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef void copy_strided_to_strided(__Pyx_memviewslice *src,
*/
__pyx_v_dst_data = (__pyx_v_dst_data + __pyx_v_dst_stride);
}
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1140
*
* @cython.cdivision(True)
* cdef void _copy_strided_to_strided(char *src_data, Py_ssize_t *src_strides, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* char *dst_data, Py_ssize_t *dst_strides,
* Py_ssize_t *src_shape, Py_ssize_t *dst_shape,
*/
/* function exit code */
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1170
* dst_data += dst_stride
*
* cdef void copy_strided_to_strided(__Pyx_memviewslice *src, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *dst,
* int ndim, size_t itemsize) nogil:
*/
static void copy_strided_to_strided(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_src, __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_dst, int __pyx_v_ndim, size_t __pyx_v_itemsize) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1173
* __Pyx_memviewslice *dst,
* int ndim, size_t itemsize) nogil:
* _copy_strided_to_strided(src.data, src.strides, dst.data, dst.strides, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src.shape, dst.shape, ndim, itemsize)
*
*/
_copy_strided_to_strided(__pyx_v_src->data, __pyx_v_src->strides, __pyx_v_dst->data, __pyx_v_dst->strides, __pyx_v_src->shape, __pyx_v_dst->shape, __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_itemsize);
/* "View.MemoryView":1170
* dst_data += dst_stride
*
* cdef void copy_strided_to_strided(__Pyx_memviewslice *src, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *dst,
* int ndim, size_t itemsize) nogil:
*/
/* function exit code */
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1177
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_get_size')
* cdef Py_ssize_t slice_get_size(__Pyx_memviewslice *src, int ndim) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Return the size of the memory occupied by the slice in number of bytes"
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, size = src.memview.view.itemsize
*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_memoryview_slice_get_size(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_src, int __pyx_v_ndim) {
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_shape;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_size;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_r;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t *__pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1179
* cdef Py_ssize_t slice_get_size(__Pyx_memviewslice *src, int ndim) nogil:
* "Return the size of the memory occupied by the slice in number of bytes"
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, size = src.memview.view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for shape in src.shape[:ndim]:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_src->memview->view.itemsize;
__pyx_v_size = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1181
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, size = src.memview.view.itemsize
*
* for shape in src.shape[:ndim]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* size *= shape
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_v_src->shape + __pyx_v_ndim);
for (__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_src->shape; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4++) {
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_4;
__pyx_v_shape = (__pyx_t_2[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1182
*
* for shape in src.shape[:ndim]:
* size *= shape # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return size
*/
__pyx_v_size = (__pyx_v_size * __pyx_v_shape);
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1184
* size *= shape
*
* return size # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_fill_contig_strides_array')
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_size;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1177
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_get_size')
* cdef Py_ssize_t slice_get_size(__Pyx_memviewslice *src, int ndim) nogil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Return the size of the memory occupied by the slice in number of bytes"
* cdef Py_ssize_t shape, size = src.memview.view.itemsize
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1187
*
* @cname('__pyx_fill_contig_strides_array')
* cdef Py_ssize_t fill_contig_strides_array( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *shape, Py_ssize_t *strides, Py_ssize_t stride,
* int ndim, char order) nogil:
*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_fill_contig_strides_array(Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_strides, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_stride, int __pyx_v_ndim, char __pyx_v_order) {
int __pyx_v_idx;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_r;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1196
* cdef int idx
*
* if order == 'F': # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for idx in range(ndim):
* strides[idx] = stride
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_order == 'F') != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1197
*
* if order == 'F':
* for idx in range(ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* strides[idx] = stride
* stride *= shape[idx]
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_ndim;
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_2;
for (__pyx_t_4 = 0; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4+=1) {
__pyx_v_idx = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1198
* if order == 'F':
* for idx in range(ndim):
* strides[idx] = stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stride *= shape[idx]
* else:
*/
(__pyx_v_strides[__pyx_v_idx]) = __pyx_v_stride;
/* "View.MemoryView":1199
* for idx in range(ndim):
* strides[idx] = stride
* stride *= shape[idx] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* for idx in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
*/
__pyx_v_stride = (__pyx_v_stride * (__pyx_v_shape[__pyx_v_idx]));
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1196
* cdef int idx
*
* if order == 'F': # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for idx in range(ndim):
* strides[idx] = stride
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1201
* stride *= shape[idx]
* else:
* for idx in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* strides[idx] = stride
* stride *= shape[idx]
*/
/*else*/ {
for (__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_ndim - 1); __pyx_t_2 > -1; __pyx_t_2-=1) {
__pyx_v_idx = __pyx_t_2;
/* "View.MemoryView":1202
* else:
* for idx in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
* strides[idx] = stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* stride *= shape[idx]
*
*/
(__pyx_v_strides[__pyx_v_idx]) = __pyx_v_stride;
/* "View.MemoryView":1203
* for idx in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
* strides[idx] = stride
* stride *= shape[idx] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return stride
*/
__pyx_v_stride = (__pyx_v_stride * (__pyx_v_shape[__pyx_v_idx]));
}
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1205
* stride *= shape[idx]
*
* return stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_data_to_temp')
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_stride;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1187
*
* @cname('__pyx_fill_contig_strides_array')
* cdef Py_ssize_t fill_contig_strides_array( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *shape, Py_ssize_t *strides, Py_ssize_t stride,
* int ndim, char order) nogil:
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1208
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_data_to_temp')
* cdef void *copy_data_to_temp(__Pyx_memviewslice *src, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *tmpslice,
* char order,
*/
static void *__pyx_memoryview_copy_data_to_temp(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_src, __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_tmpslice, char __pyx_v_order, int __pyx_v_ndim) {
int __pyx_v_i;
void *__pyx_v_result;
size_t __pyx_v_itemsize;
size_t __pyx_v_size;
void *__pyx_r;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_t_4;
int __pyx_t_5;
int __pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1219
* cdef void *result
*
* cdef size_t itemsize = src.memview.view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef size_t size = slice_get_size(src, ndim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_src->memview->view.itemsize;
__pyx_v_itemsize = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1220
*
* cdef size_t itemsize = src.memview.view.itemsize
* cdef size_t size = slice_get_size(src, ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* result = malloc(size)
*/
__pyx_v_size = __pyx_memoryview_slice_get_size(__pyx_v_src, __pyx_v_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1222
* cdef size_t size = slice_get_size(src, ndim)
*
* result = malloc(size) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if not result:
* _err(MemoryError, NULL)
*/
__pyx_v_result = malloc(__pyx_v_size);
/* "View.MemoryView":1223
*
* result = malloc(size)
* if not result: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err(MemoryError, NULL)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_v_result != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1224
* result = malloc(size)
* if not result:
* _err(MemoryError, NULL) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_memoryview_err(__pyx_builtin_MemoryError, NULL); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_3 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 1224, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":1223
*
* result = malloc(size)
* if not result: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err(MemoryError, NULL)
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1227
*
*
* tmpslice.data = result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tmpslice.memview = src.memview
* for i in range(ndim):
*/
__pyx_v_tmpslice->data = ((char *)__pyx_v_result);
/* "View.MemoryView":1228
*
* tmpslice.data = result
* tmpslice.memview = src.memview # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for i in range(ndim):
* tmpslice.shape[i] = src.shape[i]
*/
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_src->memview;
__pyx_v_tmpslice->memview = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1229
* tmpslice.data = result
* tmpslice.memview = src.memview
* for i in range(ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tmpslice.shape[i] = src.shape[i]
* tmpslice.suboffsets[i] = -1
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_ndim;
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_t_3;
for (__pyx_t_6 = 0; __pyx_t_6 < __pyx_t_5; __pyx_t_6+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":1230
* tmpslice.memview = src.memview
* for i in range(ndim):
* tmpslice.shape[i] = src.shape[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tmpslice.suboffsets[i] = -1
*
*/
(__pyx_v_tmpslice->shape[__pyx_v_i]) = (__pyx_v_src->shape[__pyx_v_i]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1231
* for i in range(ndim):
* tmpslice.shape[i] = src.shape[i]
* tmpslice.suboffsets[i] = -1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* fill_contig_strides_array(&tmpslice.shape[0], &tmpslice.strides[0], itemsize,
*/
(__pyx_v_tmpslice->suboffsets[__pyx_v_i]) = -1L;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1233
* tmpslice.suboffsets[i] = -1
*
* fill_contig_strides_array(&tmpslice.shape[0], &tmpslice.strides[0], itemsize, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* ndim, order)
*
*/
(void)(__pyx_fill_contig_strides_array((&(__pyx_v_tmpslice->shape[0])), (&(__pyx_v_tmpslice->strides[0])), __pyx_v_itemsize, __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_order));
/* "View.MemoryView":1237
*
*
* for i in range(ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if tmpslice.shape[i] == 1:
* tmpslice.strides[i] = 0
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_ndim;
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_t_3;
for (__pyx_t_6 = 0; __pyx_t_6 < __pyx_t_5; __pyx_t_6+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_6;
/* "View.MemoryView":1238
*
* for i in range(ndim):
* if tmpslice.shape[i] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tmpslice.strides[i] = 0
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_tmpslice->shape[__pyx_v_i]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1239
* for i in range(ndim):
* if tmpslice.shape[i] == 1:
* tmpslice.strides[i] = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if slice_is_contig(src[0], order, ndim):
*/
(__pyx_v_tmpslice->strides[__pyx_v_i]) = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1238
*
* for i in range(ndim):
* if tmpslice.shape[i] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* tmpslice.strides[i] = 0
*
*/
}
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1241
* tmpslice.strides[i] = 0
*
* if slice_is_contig(src[0], order, ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memcpy(result, src.data, size)
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_memviewslice_is_contig((__pyx_v_src[0]), __pyx_v_order, __pyx_v_ndim) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1242
*
* if slice_is_contig(src[0], order, ndim):
* memcpy(result, src.data, size) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* copy_strided_to_strided(src, tmpslice, ndim, itemsize)
*/
(void)(memcpy(__pyx_v_result, __pyx_v_src->data, __pyx_v_size));
/* "View.MemoryView":1241
* tmpslice.strides[i] = 0
*
* if slice_is_contig(src[0], order, ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memcpy(result, src.data, size)
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L9;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1244
* memcpy(result, src.data, size)
* else:
* copy_strided_to_strided(src, tmpslice, ndim, itemsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return result
*/
/*else*/ {
copy_strided_to_strided(__pyx_v_src, __pyx_v_tmpslice, __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_itemsize);
}
__pyx_L9:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1246
* copy_strided_to_strided(src, tmpslice, ndim, itemsize)
*
* return result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_r = __pyx_v_result;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1208
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_data_to_temp')
* cdef void *copy_data_to_temp(__Pyx_memviewslice *src, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice *tmpslice,
* char order,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
{
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.copy_data_to_temp", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
}
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1251
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err_extents')
* cdef int _err_extents(int i, Py_ssize_t extent1, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t extent2) except -1 with gil:
* raise ValueError("got differing extents in dimension %d (got %d and %d)" %
*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err_extents(int __pyx_v_i, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_extent1, Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_extent2) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("_err_extents", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1254
* Py_ssize_t extent2) except -1 with gil:
* raise ValueError("got differing extents in dimension %d (got %d and %d)" %
* (i, extent1, extent2)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err_dim')
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(__pyx_v_i); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1254, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_2 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_extent1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1254, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = PyInt_FromSsize_t(__pyx_v_extent2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1254, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = PyTuple_New(3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1254, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, 0, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_2);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, 1, __pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_3);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_4, 2, __pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1253
* cdef int _err_extents(int i, Py_ssize_t extent1,
* Py_ssize_t extent2) except -1 with gil:
* raise ValueError("got differing extents in dimension %d (got %d and %d)" % # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* (i, extent1, extent2))
*
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyString_Format(__pyx_kp_s_got_differing_extents_in_dimensi, __pyx_t_4); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1253, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1253, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_4, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 1253, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":1251
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err_extents')
* cdef int _err_extents(int i, Py_ssize_t extent1, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t extent2) except -1 with gil:
* raise ValueError("got differing extents in dimension %d (got %d and %d)" %
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._err_extents", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1257
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err_dim')
* cdef int _err_dim(object error, char *msg, int dim) except -1 with gil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii') % dim)
*
*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err_dim(PyObject *__pyx_v_error, char *__pyx_v_msg, int __pyx_v_dim) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("_err_dim", 0);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_error);
/* "View.MemoryView":1258
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err_dim')
* cdef int _err_dim(object error, char *msg, int dim) except -1 with gil:
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii') % dim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err')
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_decode_c_string(__pyx_v_msg, 0, strlen(__pyx_v_msg), NULL, NULL, PyUnicode_DecodeASCII); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1258, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(__pyx_v_dim); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1258, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__pyx_t_4 = PyUnicode_Format(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_3); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1258, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_error);
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_error; __pyx_t_2 = NULL;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && unlikely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_3))) {
__pyx_t_2 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_3);
if (likely(__pyx_t_2)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_3, function);
}
}
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_2) ? __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_4) : __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1258, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_1, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 1258, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":1257
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err_dim')
* cdef int _err_dim(object error, char *msg, int dim) except -1 with gil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii') % dim)
*
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._err_dim", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_error);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1261
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err')
* cdef int _err(object error, char *msg) except -1 with gil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if msg != NULL:
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii'))
*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err(PyObject *__pyx_v_error, char *__pyx_v_msg) {
int __pyx_r;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("_err", 0);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_error);
/* "View.MemoryView":1262
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err')
* cdef int _err(object error, char *msg) except -1 with gil:
* if msg != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii'))
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_msg != NULL) != 0);
if (unlikely(__pyx_t_1)) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1263
* cdef int _err(object error, char *msg) except -1 with gil:
* if msg != NULL:
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii')) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* raise error
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_decode_c_string(__pyx_v_msg, 0, strlen(__pyx_v_msg), NULL, NULL, PyUnicode_DecodeASCII); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1263, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v_error);
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_error; __pyx_t_5 = NULL;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && unlikely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_4))) {
__pyx_t_5 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_4);
if (likely(__pyx_t_5)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_4, function);
}
}
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_t_5) ? __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_3) : __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_t_4, __pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1263, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_2, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 1263, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":1262
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err')
* cdef int _err(object error, char *msg) except -1 with gil:
* if msg != NULL: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii'))
* else:
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1265
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii'))
* else:
* raise error # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_contents')
*/
/*else*/ {
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_v_error, 0, 0, 0);
__PYX_ERR(1, 1265, __pyx_L1_error)
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1261
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_err')
* cdef int _err(object error, char *msg) except -1 with gil: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if msg != NULL:
* raise error(msg.decode('ascii'))
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView._err", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = -1;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v_error);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1268
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_contents')
* cdef int memoryview_copy_contents(__Pyx_memviewslice src, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice dst,
* int src_ndim, int dst_ndim,
*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_copy_contents(__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_src, __Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_dst, int __pyx_v_src_ndim, int __pyx_v_dst_ndim, int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object) {
void *__pyx_v_tmpdata;
size_t __pyx_v_itemsize;
int __pyx_v_i;
char __pyx_v_order;
int __pyx_v_broadcasting;
int __pyx_v_direct_copy;
__Pyx_memviewslice __pyx_v_tmp;
int __pyx_v_ndim;
int __pyx_r;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
int __pyx_t_5;
int __pyx_t_6;
void *__pyx_t_7;
int __pyx_t_8;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1276
* Check for overlapping memory and verify the shapes.
* """
* cdef void *tmpdata = NULL # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef size_t itemsize = src.memview.view.itemsize
* cdef int i
*/
__pyx_v_tmpdata = NULL;
/* "View.MemoryView":1277
* """
* cdef void *tmpdata = NULL
* cdef size_t itemsize = src.memview.view.itemsize # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef int i
* cdef char order = get_best_order(&src, src_ndim)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_src.memview->view.itemsize;
__pyx_v_itemsize = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1279
* cdef size_t itemsize = src.memview.view.itemsize
* cdef int i
* cdef char order = get_best_order(&src, src_ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef bint broadcasting = False
* cdef bint direct_copy = False
*/
__pyx_v_order = __pyx_get_best_slice_order((&__pyx_v_src), __pyx_v_src_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1280
* cdef int i
* cdef char order = get_best_order(&src, src_ndim)
* cdef bint broadcasting = False # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef bint direct_copy = False
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*/
__pyx_v_broadcasting = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1281
* cdef char order = get_best_order(&src, src_ndim)
* cdef bint broadcasting = False
* cdef bint direct_copy = False # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*
*/
__pyx_v_direct_copy = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1284
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*
* if src_ndim < dst_ndim: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* broadcast_leading(&src, src_ndim, dst_ndim)
* elif dst_ndim < src_ndim:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_src_ndim < __pyx_v_dst_ndim) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1285
*
* if src_ndim < dst_ndim:
* broadcast_leading(&src, src_ndim, dst_ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif dst_ndim < src_ndim:
* broadcast_leading(&dst, dst_ndim, src_ndim)
*/
__pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading((&__pyx_v_src), __pyx_v_src_ndim, __pyx_v_dst_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1284
* cdef __Pyx_memviewslice tmp
*
* if src_ndim < dst_ndim: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* broadcast_leading(&src, src_ndim, dst_ndim)
* elif dst_ndim < src_ndim:
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1286
* if src_ndim < dst_ndim:
* broadcast_leading(&src, src_ndim, dst_ndim)
* elif dst_ndim < src_ndim: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* broadcast_leading(&dst, dst_ndim, src_ndim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((__pyx_v_dst_ndim < __pyx_v_src_ndim) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1287
* broadcast_leading(&src, src_ndim, dst_ndim)
* elif dst_ndim < src_ndim:
* broadcast_leading(&dst, dst_ndim, src_ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef int ndim = max(src_ndim, dst_ndim)
*/
__pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading((&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_dst_ndim, __pyx_v_src_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1286
* if src_ndim < dst_ndim:
* broadcast_leading(&src, src_ndim, dst_ndim)
* elif dst_ndim < src_ndim: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* broadcast_leading(&dst, dst_ndim, src_ndim)
*
*/
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1289
* broadcast_leading(&dst, dst_ndim, src_ndim)
*
* cdef int ndim = max(src_ndim, dst_ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for i in range(ndim):
*/
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_v_dst_ndim;
__pyx_t_4 = __pyx_v_src_ndim;
if (((__pyx_t_3 > __pyx_t_4) != 0)) {
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_t_3;
} else {
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_t_4;
}
__pyx_v_ndim = __pyx_t_5;
/* "View.MemoryView":1291
* cdef int ndim = max(src_ndim, dst_ndim)
*
* for i in range(ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if src.shape[i] != dst.shape[i]:
* if src.shape[i] == 1:
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_v_ndim;
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_5;
for (__pyx_t_4 = 0; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1292
*
* for i in range(ndim):
* if src.shape[i] != dst.shape[i]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if src.shape[i] == 1:
* broadcasting = True
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_src.shape[__pyx_v_i]) != (__pyx_v_dst.shape[__pyx_v_i])) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1293
* for i in range(ndim):
* if src.shape[i] != dst.shape[i]:
* if src.shape[i] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* broadcasting = True
* src.strides[i] = 0
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_src.shape[__pyx_v_i]) == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1294
* if src.shape[i] != dst.shape[i]:
* if src.shape[i] == 1:
* broadcasting = True # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src.strides[i] = 0
* else:
*/
__pyx_v_broadcasting = 1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1295
* if src.shape[i] == 1:
* broadcasting = True
* src.strides[i] = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* _err_extents(i, dst.shape[i], src.shape[i])
*/
(__pyx_v_src.strides[__pyx_v_i]) = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1293
* for i in range(ndim):
* if src.shape[i] != dst.shape[i]:
* if src.shape[i] == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* broadcasting = True
* src.strides[i] = 0
*/
goto __pyx_L7;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1297
* src.strides[i] = 0
* else:
* _err_extents(i, dst.shape[i], src.shape[i]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if src.suboffsets[i] >= 0:
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_memoryview_err_extents(__pyx_v_i, (__pyx_v_dst.shape[__pyx_v_i]), (__pyx_v_src.shape[__pyx_v_i])); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_6 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 1297, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_L7:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1292
*
* for i in range(ndim):
* if src.shape[i] != dst.shape[i]: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if src.shape[i] == 1:
* broadcasting = True
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1299
* _err_extents(i, dst.shape[i], src.shape[i])
*
* if src.suboffsets[i] >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Dimension %d is not direct", i)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (((__pyx_v_src.suboffsets[__pyx_v_i]) >= 0) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1300
*
* if src.suboffsets[i] >= 0:
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Dimension %d is not direct", i) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if slices_overlap(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize):
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __pyx_memoryview_err_dim(__pyx_builtin_ValueError, ((char *)"Dimension %d is not direct"), __pyx_v_i); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_6 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 1300, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":1299
* _err_extents(i, dst.shape[i], src.shape[i])
*
* if src.suboffsets[i] >= 0: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Dimension %d is not direct", i)
*
*/
}
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1302
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Dimension %d is not direct", i)
*
* if slices_overlap(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not slice_is_contig(src, order, ndim):
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_slices_overlap((&__pyx_v_src), (&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_itemsize) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1304
* if slices_overlap(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize):
*
* if not slice_is_contig(src, order, ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* order = get_best_order(&dst, ndim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(__pyx_v_src, __pyx_v_order, __pyx_v_ndim) != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1305
*
* if not slice_is_contig(src, order, ndim):
* order = get_best_order(&dst, ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* tmpdata = copy_data_to_temp(&src, &tmp, order, ndim)
*/
__pyx_v_order = __pyx_get_best_slice_order((&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1304
* if slices_overlap(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize):
*
* if not slice_is_contig(src, order, ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* order = get_best_order(&dst, ndim)
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1307
* order = get_best_order(&dst, ndim)
*
* tmpdata = copy_data_to_temp(&src, &tmp, order, ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* src = tmp
*
*/
__pyx_t_7 = __pyx_memoryview_copy_data_to_temp((&__pyx_v_src), (&__pyx_v_tmp), __pyx_v_order, __pyx_v_ndim); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_7 == ((void *)NULL))) __PYX_ERR(1, 1307, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_v_tmpdata = __pyx_t_7;
/* "View.MemoryView":1308
*
* tmpdata = copy_data_to_temp(&src, &tmp, order, ndim)
* src = tmp # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not broadcasting:
*/
__pyx_v_src = __pyx_v_tmp;
/* "View.MemoryView":1302
* _err_dim(ValueError, "Dimension %d is not direct", i)
*
* if slices_overlap(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not slice_is_contig(src, order, ndim):
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1310
* src = tmp
*
* if not broadcasting: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = ((!(__pyx_v_broadcasting != 0)) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1313
*
*
* if slice_is_contig(src, 'C', ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'C', ndim)
* elif slice_is_contig(src, 'F', ndim):
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(__pyx_v_src, 'C', __pyx_v_ndim) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1314
*
* if slice_is_contig(src, 'C', ndim):
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'C', ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* elif slice_is_contig(src, 'F', ndim):
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'F', ndim)
*/
__pyx_v_direct_copy = __pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(__pyx_v_dst, 'C', __pyx_v_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1313
*
*
* if slice_is_contig(src, 'C', ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'C', ndim)
* elif slice_is_contig(src, 'F', ndim):
*/
goto __pyx_L12;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1315
* if slice_is_contig(src, 'C', ndim):
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'C', ndim)
* elif slice_is_contig(src, 'F', ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'F', ndim)
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(__pyx_v_src, 'F', __pyx_v_ndim) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1316
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'C', ndim)
* elif slice_is_contig(src, 'F', ndim):
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'F', ndim) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if direct_copy:
*/
__pyx_v_direct_copy = __pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(__pyx_v_dst, 'F', __pyx_v_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1315
* if slice_is_contig(src, 'C', ndim):
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'C', ndim)
* elif slice_is_contig(src, 'F', ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'F', ndim)
*
*/
}
__pyx_L12:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1318
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'F', ndim)
*
* if direct_copy: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_direct_copy != 0);
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1320
* if direct_copy:
*
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memcpy(dst.data, src.data, slice_get_size(&src, ndim))
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying((&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, __pyx_v_ndim, 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1321
*
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
* memcpy(dst.data, src.data, slice_get_size(&src, ndim)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
* free(tmpdata)
*/
(void)(memcpy(__pyx_v_dst.data, __pyx_v_src.data, __pyx_memoryview_slice_get_size((&__pyx_v_src), __pyx_v_ndim)));
/* "View.MemoryView":1322
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
* memcpy(dst.data, src.data, slice_get_size(&src, ndim))
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* free(tmpdata)
* return 0
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying((&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, __pyx_v_ndim, 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":1323
* memcpy(dst.data, src.data, slice_get_size(&src, ndim))
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
* free(tmpdata) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return 0
*
*/
free(__pyx_v_tmpdata);
/* "View.MemoryView":1324
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
* free(tmpdata)
* return 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if order == 'F' == get_best_order(&dst, ndim):
*/
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1318
* direct_copy = slice_is_contig(dst, 'F', ndim)
*
* if direct_copy: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1310
* src = tmp
*
* if not broadcasting: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1326
* return 0
*
* if order == 'F' == get_best_order(&dst, ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_2 = (__pyx_v_order == 'F');
if (__pyx_t_2) {
__pyx_t_2 = ('F' == __pyx_get_best_slice_order((&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_ndim));
}
__pyx_t_8 = (__pyx_t_2 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_8) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1329
*
*
* transpose_memslice(&src) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* transpose_memslice(&dst)
*
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_memslice_transpose((&__pyx_v_src)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_5 == ((int)0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 1329, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":1330
*
* transpose_memslice(&src)
* transpose_memslice(&dst) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
*/
__pyx_t_5 = __pyx_memslice_transpose((&__pyx_v_dst)); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_5 == ((int)0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 1330, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "View.MemoryView":1326
* return 0
*
* if order == 'F' == get_best_order(&dst, ndim): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1332
* transpose_memslice(&dst)
*
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* copy_strided_to_strided(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize)
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying((&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, __pyx_v_ndim, 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1333
*
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
* copy_strided_to_strided(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
*
*/
copy_strided_to_strided((&__pyx_v_src), (&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_itemsize);
/* "View.MemoryView":1334
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
* copy_strided_to_strided(&src, &dst, ndim, itemsize)
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* free(tmpdata)
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying((&__pyx_v_dst), __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, __pyx_v_ndim, 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":1336
* refcount_copying(&dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
*
* free(tmpdata) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return 0
*
*/
free(__pyx_v_tmpdata);
/* "View.MemoryView":1337
*
* free(tmpdata)
* return 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading')
*/
__pyx_r = 0;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "View.MemoryView":1268
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_copy_contents')
* cdef int memoryview_copy_contents(__Pyx_memviewslice src, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __Pyx_memviewslice dst,
* int src_ndim, int dst_ndim,
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
{
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.memoryview_copy_contents", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
}
__pyx_r = -1;
__pyx_L0:;
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1340
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading')
* cdef void broadcast_leading(__Pyx_memviewslice *mslice, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* int ndim,
* int ndim_other) nogil:
*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_mslice, int __pyx_v_ndim, int __pyx_v_ndim_other) {
int __pyx_v_i;
int __pyx_v_offset;
int __pyx_t_1;
int __pyx_t_2;
int __pyx_t_3;
/* "View.MemoryView":1344
* int ndim_other) nogil:
* cdef int i
* cdef int offset = ndim_other - ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
*/
__pyx_v_offset = (__pyx_v_ndim_other - __pyx_v_ndim);
/* "View.MemoryView":1346
* cdef int offset = ndim_other - ndim
*
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mslice.shape[i + offset] = mslice.shape[i]
* mslice.strides[i + offset] = mslice.strides[i]
*/
for (__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_ndim - 1); __pyx_t_1 > -1; __pyx_t_1-=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1347
*
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
* mslice.shape[i + offset] = mslice.shape[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mslice.strides[i + offset] = mslice.strides[i]
* mslice.suboffsets[i + offset] = mslice.suboffsets[i]
*/
(__pyx_v_mslice->shape[(__pyx_v_i + __pyx_v_offset)]) = (__pyx_v_mslice->shape[__pyx_v_i]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1348
* for i in range(ndim - 1, -1, -1):
* mslice.shape[i + offset] = mslice.shape[i]
* mslice.strides[i + offset] = mslice.strides[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mslice.suboffsets[i + offset] = mslice.suboffsets[i]
*
*/
(__pyx_v_mslice->strides[(__pyx_v_i + __pyx_v_offset)]) = (__pyx_v_mslice->strides[__pyx_v_i]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1349
* mslice.shape[i + offset] = mslice.shape[i]
* mslice.strides[i + offset] = mslice.strides[i]
* mslice.suboffsets[i + offset] = mslice.suboffsets[i] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* for i in range(offset):
*/
(__pyx_v_mslice->suboffsets[(__pyx_v_i + __pyx_v_offset)]) = (__pyx_v_mslice->suboffsets[__pyx_v_i]);
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1351
* mslice.suboffsets[i + offset] = mslice.suboffsets[i]
*
* for i in range(offset): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mslice.shape[i] = 1
* mslice.strides[i] = mslice.strides[0]
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_v_offset;
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_1;
for (__pyx_t_3 = 0; __pyx_t_3 < __pyx_t_2; __pyx_t_3+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_3;
/* "View.MemoryView":1352
*
* for i in range(offset):
* mslice.shape[i] = 1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mslice.strides[i] = mslice.strides[0]
* mslice.suboffsets[i] = -1
*/
(__pyx_v_mslice->shape[__pyx_v_i]) = 1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1353
* for i in range(offset):
* mslice.shape[i] = 1
* mslice.strides[i] = mslice.strides[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* mslice.suboffsets[i] = -1
*
*/
(__pyx_v_mslice->strides[__pyx_v_i]) = (__pyx_v_mslice->strides[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1354
* mslice.shape[i] = 1
* mslice.strides[i] = mslice.strides[0]
* mslice.suboffsets[i] = -1 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
(__pyx_v_mslice->suboffsets[__pyx_v_i]) = -1L;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1340
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading')
* cdef void broadcast_leading(__Pyx_memviewslice *mslice, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* int ndim,
* int ndim_other) nogil:
*/
/* function exit code */
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1362
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying')
* cdef void refcount_copying(__Pyx_memviewslice *dst, bint dtype_is_object, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* int ndim, bint inc) nogil:
*
*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_dst, int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, int __pyx_v_ndim, int __pyx_v_inc) {
int __pyx_t_1;
/* "View.MemoryView":1366
*
*
* if dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(dst.data, dst.shape,
* dst.strides, ndim, inc)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_dtype_is_object != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1367
*
* if dtype_is_object:
* refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(dst.data, dst.shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* dst.strides, ndim, inc)
*
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(__pyx_v_dst->data, __pyx_v_dst->shape, __pyx_v_dst->strides, __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_inc);
/* "View.MemoryView":1366
*
*
* if dtype_is_object: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(dst.data, dst.shape,
* dst.strides, ndim, inc)
*/
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1362
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying')
* cdef void refcount_copying(__Pyx_memviewslice *dst, bint dtype_is_object, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* int ndim, bint inc) nogil:
*
*/
/* function exit code */
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1371
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil')
* cdef void refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(char *data, Py_ssize_t *shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *strides, int ndim,
* bint inc) with gil:
*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(char *__pyx_v_data, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_strides, int __pyx_v_ndim, int __pyx_v_inc) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure();
#endif
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1374
* Py_ssize_t *strides, int ndim,
* bint inc) with gil:
* refcount_objects_in_slice(data, shape, strides, ndim, inc) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice')
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice(__pyx_v_data, __pyx_v_shape, __pyx_v_strides, __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_inc);
/* "View.MemoryView":1371
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil')
* cdef void refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(char *data, Py_ssize_t *shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *strides, int ndim,
* bint inc) with gil:
*/
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
__Pyx_PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);
#endif
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1377
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice')
* cdef void refcount_objects_in_slice(char *data, Py_ssize_t *shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *strides, int ndim, bint inc):
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice(char *__pyx_v_data, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_strides, int __pyx_v_ndim, int __pyx_v_inc) {
CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_i;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_1;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("refcount_objects_in_slice", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1381
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
*
* for i in range(shape[0]): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if ndim == 1:
* if inc:
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v_shape[0]);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_1;
for (__pyx_t_3 = 0; __pyx_t_3 < __pyx_t_2; __pyx_t_3+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_3;
/* "View.MemoryView":1382
*
* for i in range(shape[0]):
* if ndim == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if inc:
* Py_INCREF(( data)[0])
*/
__pyx_t_4 = ((__pyx_v_ndim == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_4) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1383
* for i in range(shape[0]):
* if ndim == 1:
* if inc: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_INCREF(( data)[0])
* else:
*/
__pyx_t_4 = (__pyx_v_inc != 0);
if (__pyx_t_4) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1384
* if ndim == 1:
* if inc:
* Py_INCREF(( data)[0]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* Py_DECREF(( data)[0])
*/
Py_INCREF((((PyObject **)__pyx_v_data)[0]));
/* "View.MemoryView":1383
* for i in range(shape[0]):
* if ndim == 1:
* if inc: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_INCREF(( data)[0])
* else:
*/
goto __pyx_L6;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1386
* Py_INCREF(( data)[0])
* else:
* Py_DECREF(( data)[0]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* refcount_objects_in_slice(data, shape + 1, strides + 1,
*/
/*else*/ {
Py_DECREF((((PyObject **)__pyx_v_data)[0]));
}
__pyx_L6:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1382
*
* for i in range(shape[0]):
* if ndim == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if inc:
* Py_INCREF(( data)[0])
*/
goto __pyx_L5;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1388
* Py_DECREF(( data)[0])
* else:
* refcount_objects_in_slice(data, shape + 1, strides + 1, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* ndim - 1, inc)
*
*/
/*else*/ {
/* "View.MemoryView":1389
* else:
* refcount_objects_in_slice(data, shape + 1, strides + 1,
* ndim - 1, inc) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* data += strides[0]
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice(__pyx_v_data, (__pyx_v_shape + 1), (__pyx_v_strides + 1), (__pyx_v_ndim - 1), __pyx_v_inc);
}
__pyx_L5:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1391
* ndim - 1, inc)
*
* data += strides[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_v_data = (__pyx_v_data + (__pyx_v_strides[0]));
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1377
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice')
* cdef void refcount_objects_in_slice(char *data, Py_ssize_t *shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *strides, int ndim, bint inc):
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
*/
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1397
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_assign_scalar')
* cdef void slice_assign_scalar(__Pyx_memviewslice *dst, int ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* size_t itemsize, void *item,
* bint dtype_is_object) nogil:
*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_slice_assign_scalar(__Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_v_dst, int __pyx_v_ndim, size_t __pyx_v_itemsize, void *__pyx_v_item, int __pyx_v_dtype_is_object) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1400
* size_t itemsize, void *item,
* bint dtype_is_object) nogil:
* refcount_copying(dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _slice_assign_scalar(dst.data, dst.shape, dst.strides, ndim,
* itemsize, item)
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying(__pyx_v_dst, __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, __pyx_v_ndim, 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":1401
* bint dtype_is_object) nogil:
* refcount_copying(dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, False)
* _slice_assign_scalar(dst.data, dst.shape, dst.strides, ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* itemsize, item)
* refcount_copying(dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True)
*/
__pyx_memoryview__slice_assign_scalar(__pyx_v_dst->data, __pyx_v_dst->shape, __pyx_v_dst->strides, __pyx_v_ndim, __pyx_v_itemsize, __pyx_v_item);
/* "View.MemoryView":1403
* _slice_assign_scalar(dst.data, dst.shape, dst.strides, ndim,
* itemsize, item)
* refcount_copying(dst, dtype_is_object, ndim, True) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying(__pyx_v_dst, __pyx_v_dtype_is_object, __pyx_v_ndim, 1);
/* "View.MemoryView":1397
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview_slice_assign_scalar')
* cdef void slice_assign_scalar(__Pyx_memviewslice *dst, int ndim, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* size_t itemsize, void *item,
* bint dtype_is_object) nogil:
*/
/* function exit code */
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1407
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview__slice_assign_scalar')
* cdef void _slice_assign_scalar(char *data, Py_ssize_t *shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *strides, int ndim,
* size_t itemsize, void *item) nogil:
*/
static void __pyx_memoryview__slice_assign_scalar(char *__pyx_v_data, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_shape, Py_ssize_t *__pyx_v_strides, int __pyx_v_ndim, size_t __pyx_v_itemsize, void *__pyx_v_item) {
CYTHON_UNUSED Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_i;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_stride;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_v_extent;
int __pyx_t_1;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_3;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1411
* size_t itemsize, void *item) nogil:
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
* cdef Py_ssize_t stride = strides[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef Py_ssize_t extent = shape[0]
*
*/
__pyx_v_stride = (__pyx_v_strides[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1412
* cdef Py_ssize_t i
* cdef Py_ssize_t stride = strides[0]
* cdef Py_ssize_t extent = shape[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if ndim == 1:
*/
__pyx_v_extent = (__pyx_v_shape[0]);
/* "View.MemoryView":1414
* cdef Py_ssize_t extent = shape[0]
*
* if ndim == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for i in range(extent):
* memcpy(data, item, itemsize)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v_ndim == 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "View.MemoryView":1415
*
* if ndim == 1:
* for i in range(extent): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* memcpy(data, item, itemsize)
* data += stride
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_extent;
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_2;
for (__pyx_t_4 = 0; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1416
* if ndim == 1:
* for i in range(extent):
* memcpy(data, item, itemsize) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* data += stride
* else:
*/
(void)(memcpy(__pyx_v_data, __pyx_v_item, __pyx_v_itemsize));
/* "View.MemoryView":1417
* for i in range(extent):
* memcpy(data, item, itemsize)
* data += stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* for i in range(extent):
*/
__pyx_v_data = (__pyx_v_data + __pyx_v_stride);
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1414
* cdef Py_ssize_t extent = shape[0]
*
* if ndim == 1: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* for i in range(extent):
* memcpy(data, item, itemsize)
*/
goto __pyx_L3;
}
/* "View.MemoryView":1419
* data += stride
* else:
* for i in range(extent): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* _slice_assign_scalar(data, shape + 1, strides + 1,
* ndim - 1, itemsize, item)
*/
/*else*/ {
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v_extent;
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_t_2;
for (__pyx_t_4 = 0; __pyx_t_4 < __pyx_t_3; __pyx_t_4+=1) {
__pyx_v_i = __pyx_t_4;
/* "View.MemoryView":1420
* else:
* for i in range(extent):
* _slice_assign_scalar(data, shape + 1, strides + 1, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* ndim - 1, itemsize, item)
* data += stride
*/
__pyx_memoryview__slice_assign_scalar(__pyx_v_data, (__pyx_v_shape + 1), (__pyx_v_strides + 1), (__pyx_v_ndim - 1), __pyx_v_itemsize, __pyx_v_item);
/* "View.MemoryView":1422
* _slice_assign_scalar(data, shape + 1, strides + 1,
* ndim - 1, itemsize, item)
* data += stride # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_v_data = (__pyx_v_data + __pyx_v_stride);
}
}
__pyx_L3:;
/* "View.MemoryView":1407
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview__slice_assign_scalar')
* cdef void _slice_assign_scalar(char *data, Py_ssize_t *shape, # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* Py_ssize_t *strides, int ndim,
* size_t itemsize, void *item) nogil:
*/
/* function exit code */
}
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __pyx_unpickle_Enum(__pyx_type, long __pyx_checksum, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef object __pyx_PickleError
* cdef object __pyx_result
*/
/* Python wrapper */
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_1__pyx_unpickle_Enum(PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds); /*proto*/
static PyMethodDef __pyx_mdef_15View_dot_MemoryView_1__pyx_unpickle_Enum = {"__pyx_unpickle_Enum", (PyCFunction)(void*)(PyCFunctionWithKeywords)__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_1__pyx_unpickle_Enum, METH_VARARGS|METH_KEYWORDS, 0};
static PyObject *__pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_1__pyx_unpickle_Enum(PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_args, PyObject *__pyx_kwds) {
PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_type = 0;
long __pyx_v___pyx_checksum;
PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state = 0;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_r = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__pyx_unpickle_Enum (wrapper)", 0);
{
static PyObject **__pyx_pyargnames[] = {&__pyx_n_s_pyx_type,&__pyx_n_s_pyx_checksum,&__pyx_n_s_pyx_state,0};
PyObject* values[3] = {0,0,0};
if (unlikely(__pyx_kwds)) {
Py_ssize_t kw_args;
const Py_ssize_t pos_args = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args);
switch (pos_args) {
case 3: values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2: values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1: values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 0: break;
default: goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
}
kw_args = PyDict_Size(__pyx_kwds);
switch (pos_args) {
case 0:
if (likely((values[0] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_pyx_type)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 1:
if (likely((values[1] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_pyx_checksum)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__pyx_unpickle_Enum", 1, 3, 3, 1); __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2:
if (likely((values[2] = __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_n_s_pyx_state)) != 0)) kw_args--;
else {
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__pyx_unpickle_Enum", 1, 3, 3, 2); __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
}
}
if (unlikely(kw_args > 0)) {
if (unlikely(__Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(__pyx_kwds, __pyx_pyargnames, 0, values, pos_args, "__pyx_unpickle_Enum") < 0)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
}
} else if (PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args) != 3) {
goto __pyx_L5_argtuple_error;
} else {
values[0] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 0);
values[1] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 1);
values[2] = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__pyx_args, 2);
}
__pyx_v___pyx_type = values[0];
__pyx_v___pyx_checksum = __Pyx_PyInt_As_long(values[1]); if (unlikely((__pyx_v___pyx_checksum == (long)-1) && PyErr_Occurred())) __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_v___pyx_state = values[2];
}
goto __pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done;
__pyx_L5_argtuple_error:;
__Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid("__pyx_unpickle_Enum", 1, 3, 3, PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_args)); __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L3_error)
__pyx_L3_error:;
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.__pyx_unpickle_Enum", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return NULL;
__pyx_L4_argument_unpacking_done:;
__pyx_r = __pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView___pyx_unpickle_Enum(__pyx_self, __pyx_v___pyx_type, __pyx_v___pyx_checksum, __pyx_v___pyx_state);
/* function exit code */
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_pf_15View_dot_MemoryView___pyx_unpickle_Enum(CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *__pyx_self, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_type, long __pyx_v___pyx_checksum, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_PickleError = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_result = 0;
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_t_1;
PyObject *__pyx_t_2 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_3 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_5 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_6;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__pyx_unpickle_Enum", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* cdef object __pyx_PickleError
* cdef object __pyx_result
* if __pyx_checksum != 0xb068931: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* from pickle import PickleError as __pyx_PickleError
* raise __pyx_PickleError("Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))" % __pyx_checksum)
*/
__pyx_t_1 = ((__pyx_v___pyx_checksum != 0xb068931) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_1) {
/* "(tree fragment)":5
* cdef object __pyx_result
* if __pyx_checksum != 0xb068931:
* from pickle import PickleError as __pyx_PickleError # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* raise __pyx_PickleError("Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))" % __pyx_checksum)
* __pyx_result = Enum.__new__(__pyx_type)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = PyList_New(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_n_s_PickleError);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_n_s_PickleError);
PyList_SET_ITEM(__pyx_t_2, 0, __pyx_n_s_PickleError);
__pyx_t_3 = __Pyx_Import(__pyx_n_s_pickle, __pyx_t_2, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_ImportFrom(__pyx_t_3, __pyx_n_s_PickleError); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 5, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_v___pyx_PickleError = __pyx_t_2;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":6
* if __pyx_checksum != 0xb068931:
* from pickle import PickleError as __pyx_PickleError
* raise __pyx_PickleError("Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))" % __pyx_checksum) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_result = Enum.__new__(__pyx_type)
* if __pyx_state is not None:
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyInt_From_long(__pyx_v___pyx_checksum); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_PyString_Format(__pyx_kp_s_Incompatible_checksums_s_vs_0xb0, __pyx_t_2); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v___pyx_PickleError);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_v___pyx_PickleError; __pyx_t_5 = NULL;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && unlikely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_2))) {
__pyx_t_5 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_2);
if (likely(__pyx_t_5)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_2, function);
}
}
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_5) ? __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_5, __pyx_t_4) : __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5); __pyx_t_5 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__Pyx_Raise(__pyx_t_3, 0, 0, 0);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
__PYX_ERR(1, 6, __pyx_L1_error)
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* cdef object __pyx_PickleError
* cdef object __pyx_result
* if __pyx_checksum != 0xb068931: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* from pickle import PickleError as __pyx_PickleError
* raise __pyx_PickleError("Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))" % __pyx_checksum)
*/
}
/* "(tree fragment)":7
* from pickle import PickleError as __pyx_PickleError
* raise __pyx_PickleError("Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))" % __pyx_checksum)
* __pyx_result = Enum.__new__(__pyx_type) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if __pyx_state is not None:
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state)
*/
__pyx_t_2 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_MemviewEnum_type), __pyx_n_s_new); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 7, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_2);
__pyx_t_4 = NULL;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && likely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_2))) {
__pyx_t_4 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_2);
if (likely(__pyx_t_4)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_2, function);
}
}
__pyx_t_3 = (__pyx_t_4) ? __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_t_4, __pyx_v___pyx_type) : __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_t_2, __pyx_v___pyx_type);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4); __pyx_t_4 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 7, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_2); __pyx_t_2 = 0;
__pyx_v___pyx_result = __pyx_t_3;
__pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":8
* raise __pyx_PickleError("Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))" % __pyx_checksum)
* __pyx_result = Enum.__new__(__pyx_type)
* if __pyx_state is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state)
* return __pyx_result
*/
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_v___pyx_state != Py_None);
__pyx_t_6 = (__pyx_t_1 != 0);
if (__pyx_t_6) {
/* "(tree fragment)":9
* __pyx_result = Enum.__new__(__pyx_type)
* if __pyx_state is not None:
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* return __pyx_result
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state):
*/
if (!(likely(PyTuple_CheckExact(__pyx_v___pyx_state))||((__pyx_v___pyx_state) == Py_None)||(PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "Expected %.16s, got %.200s", "tuple", Py_TYPE(__pyx_v___pyx_state)->tp_name), 0))) __PYX_ERR(1, 9, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_3 = __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(((struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)__pyx_v___pyx_result), ((PyObject*)__pyx_v___pyx_state)); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 9, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_3); __pyx_t_3 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":8
* raise __pyx_PickleError("Incompatible checksums (%s vs 0xb068931 = (name))" % __pyx_checksum)
* __pyx_result = Enum.__new__(__pyx_type)
* if __pyx_state is not None: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state)
* return __pyx_result
*/
}
/* "(tree fragment)":10
* if __pyx_state is not None:
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state)
* return __pyx_result # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state):
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0]
*/
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_v___pyx_result);
__pyx_r = __pyx_v___pyx_result;
goto __pyx_L0;
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __pyx_unpickle_Enum(__pyx_type, long __pyx_checksum, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef object __pyx_PickleError
* cdef object __pyx_result
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_2);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_3);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_4);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_5);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.__pyx_unpickle_Enum", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = NULL;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v___pyx_PickleError);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_v___pyx_result);
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
/* "(tree fragment)":11
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state)
* return __pyx_result
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0]
* if len(__pyx_state) > 1 and hasattr(__pyx_result, '__dict__'):
*/
static PyObject *__pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *__pyx_v___pyx_result, PyObject *__pyx_v___pyx_state) {
PyObject *__pyx_r = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
int __pyx_t_2;
Py_ssize_t __pyx_t_3;
int __pyx_t_4;
int __pyx_t_5;
PyObject *__pyx_t_6 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_7 = NULL;
PyObject *__pyx_t_8 = NULL;
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state", 0);
/* "(tree fragment)":12
* return __pyx_result
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state):
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0] # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* if len(__pyx_state) > 1 and hasattr(__pyx_result, '__dict__'):
* __pyx_result.__dict__.update(__pyx_state[1])
*/
if (unlikely(__pyx_v___pyx_state == Py_None)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "'NoneType' object is not subscriptable");
__PYX_ERR(1, 12, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple(__pyx_v___pyx_state, 0, long, 1, __Pyx_PyInt_From_long, 0, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 12, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_v___pyx_result->name);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_v___pyx_result->name);
__pyx_v___pyx_result->name = __pyx_t_1;
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":13
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state):
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0]
* if len(__pyx_state) > 1 and hasattr(__pyx_result, '__dict__'): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_result.__dict__.update(__pyx_state[1])
*/
if (unlikely(__pyx_v___pyx_state == Py_None)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "object of type 'NoneType' has no len()");
__PYX_ERR(1, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_t_3 = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__pyx_v___pyx_state); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_3 == ((Py_ssize_t)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_4 = ((__pyx_t_3 > 1) != 0);
if (__pyx_t_4) {
} else {
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_4;
goto __pyx_L4_bool_binop_done;
}
__pyx_t_4 = __Pyx_HasAttr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v___pyx_result), __pyx_n_s_dict); if (unlikely(__pyx_t_4 == ((int)-1))) __PYX_ERR(1, 13, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_t_5 = (__pyx_t_4 != 0);
__pyx_t_2 = __pyx_t_5;
__pyx_L4_bool_binop_done:;
if (__pyx_t_2) {
/* "(tree fragment)":14
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0]
* if len(__pyx_state) > 1 and hasattr(__pyx_result, '__dict__'):
* __pyx_result.__dict__.update(__pyx_state[1]) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(((PyObject *)__pyx_v___pyx_result), __pyx_n_s_dict); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 14, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_7 = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_t_6, __pyx_n_s_update); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 14, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
if (unlikely(__pyx_v___pyx_state == Py_None)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "'NoneType' object is not subscriptable");
__PYX_ERR(1, 14, __pyx_L1_error)
}
__pyx_t_6 = __Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple(__pyx_v___pyx_state, 1, long, 1, __Pyx_PyInt_From_long, 0, 0, 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 14, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_6);
__pyx_t_8 = NULL;
if (CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS && likely(PyMethod_Check(__pyx_t_7))) {
__pyx_t_8 = PyMethod_GET_SELF(__pyx_t_7);
if (likely(__pyx_t_8)) {
PyObject* function = PyMethod_GET_FUNCTION(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_INCREF(function);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(__pyx_t_7, function);
}
}
__pyx_t_1 = (__pyx_t_8) ? __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(__pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_8, __pyx_t_6) : __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(__pyx_t_7, __pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_8); __pyx_t_8 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_6); __pyx_t_6 = 0;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 14, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_7); __pyx_t_7 = 0;
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":13
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state):
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0]
* if len(__pyx_state) > 1 and hasattr(__pyx_result, '__dict__'): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_result.__dict__.update(__pyx_state[1])
*/
}
/* "(tree fragment)":11
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state)
* return __pyx_result
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0]
* if len(__pyx_state) > 1 and hasattr(__pyx_result, '__dict__'):
*/
/* function exit code */
__pyx_r = Py_None; __Pyx_INCREF(Py_None);
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_6);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_7);
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_8);
__Pyx_AddTraceback("View.MemoryView.__pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
__pyx_r = 0;
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_XGIVEREF(__pyx_r);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return __pyx_r;
}
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array __pyx_vtable_array;
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new_array(PyTypeObject *t, PyObject *a, PyObject *k) {
struct __pyx_array_obj *p;
PyObject *o;
if (likely((t->tp_flags & Py_TPFLAGS_IS_ABSTRACT) == 0)) {
o = (*t->tp_alloc)(t, 0);
} else {
o = (PyObject *) PyBaseObject_Type.tp_new(t, __pyx_empty_tuple, 0);
}
if (unlikely(!o)) return 0;
p = ((struct __pyx_array_obj *)o);
p->__pyx_vtab = __pyx_vtabptr_array;
p->mode = ((PyObject*)Py_None); Py_INCREF(Py_None);
p->_format = ((PyObject*)Py_None); Py_INCREF(Py_None);
if (unlikely(__pyx_array___cinit__(o, a, k) < 0)) goto bad;
return o;
bad:
Py_DECREF(o); o = 0;
return NULL;
}
static void __pyx_tp_dealloc_array(PyObject *o) {
struct __pyx_array_obj *p = (struct __pyx_array_obj *)o;
#if CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
if (unlikely(PyType_HasFeature(Py_TYPE(o), Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE) && Py_TYPE(o)->tp_finalize) && (!PyType_IS_GC(Py_TYPE(o)) || !_PyGC_FINALIZED(o))) {
if (PyObject_CallFinalizerFromDealloc(o)) return;
}
#endif
{
PyObject *etype, *eval, *etb;
PyErr_Fetch(&etype, &eval, &etb);
__Pyx_SET_REFCNT(o, Py_REFCNT(o) + 1);
__pyx_array___dealloc__(o);
__Pyx_SET_REFCNT(o, Py_REFCNT(o) - 1);
PyErr_Restore(etype, eval, etb);
}
Py_CLEAR(p->mode);
Py_CLEAR(p->_format);
(*Py_TYPE(o)->tp_free)(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_sq_item_array(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i) {
PyObject *r;
PyObject *x = PyInt_FromSsize_t(i); if(!x) return 0;
r = Py_TYPE(o)->tp_as_mapping->mp_subscript(o, x);
Py_DECREF(x);
return r;
}
static int __pyx_mp_ass_subscript_array(PyObject *o, PyObject *i, PyObject *v) {
if (v) {
return __pyx_array___setitem__(o, i, v);
}
else {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_NotImplementedError,
"Subscript deletion not supported by %.200s", Py_TYPE(o)->tp_name);
return -1;
}
}
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_getattro_array(PyObject *o, PyObject *n) {
PyObject *v = __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr(o, n);
if (!v && PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_AttributeError)) {
PyErr_Clear();
v = __pyx_array___getattr__(o, n);
}
return v;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_array_memview(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_5array_7memview_1__get__(o);
}
static PyMethodDef __pyx_methods_array[] = {
{"__getattr__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_array___getattr__, METH_O|METH_COEXIST, 0},
{"__reduce_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_array_1__reduce_cython__, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"__setstate_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_array_3__setstate_cython__, METH_O, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static struct PyGetSetDef __pyx_getsets_array[] = {
{(char *)"memview", __pyx_getprop___pyx_array_memview, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static PySequenceMethods __pyx_tp_as_sequence_array = {
__pyx_array___len__, /*sq_length*/
0, /*sq_concat*/
0, /*sq_repeat*/
__pyx_sq_item_array, /*sq_item*/
0, /*sq_slice*/
0, /*sq_ass_item*/
0, /*sq_ass_slice*/
0, /*sq_contains*/
0, /*sq_inplace_concat*/
0, /*sq_inplace_repeat*/
};
static PyMappingMethods __pyx_tp_as_mapping_array = {
__pyx_array___len__, /*mp_length*/
__pyx_array___getitem__, /*mp_subscript*/
__pyx_mp_ass_subscript_array, /*mp_ass_subscript*/
};
static PyBufferProcs __pyx_tp_as_buffer_array = {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getreadbuffer*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getwritebuffer*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getsegcount*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getcharbuffer*/
#endif
__pyx_array_getbuffer, /*bf_getbuffer*/
0, /*bf_releasebuffer*/
};
static PyTypeObject __pyx_type___pyx_array = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(0, 0)
"pept.processing.circles_ext.array", /*tp_name*/
sizeof(struct __pyx_array_obj), /*tp_basicsize*/
0, /*tp_itemsize*/
__pyx_tp_dealloc_array, /*tp_dealloc*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_vectorcall_offset*/
#endif
0, /*tp_getattr*/
0, /*tp_setattr*/
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*tp_compare*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
0, /*tp_as_async*/
#endif
0, /*tp_repr*/
0, /*tp_as_number*/
&__pyx_tp_as_sequence_array, /*tp_as_sequence*/
&__pyx_tp_as_mapping_array, /*tp_as_mapping*/
0, /*tp_hash*/
0, /*tp_call*/
0, /*tp_str*/
__pyx_tp_getattro_array, /*tp_getattro*/
0, /*tp_setattro*/
&__pyx_tp_as_buffer_array, /*tp_as_buffer*/
Py_TPFLAGS_DEFAULT|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_VERSION_TAG|Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER|Py_TPFLAGS_BASETYPE, /*tp_flags*/
0, /*tp_doc*/
0, /*tp_traverse*/
0, /*tp_clear*/
0, /*tp_richcompare*/
0, /*tp_weaklistoffset*/
0, /*tp_iter*/
0, /*tp_iternext*/
__pyx_methods_array, /*tp_methods*/
0, /*tp_members*/
__pyx_getsets_array, /*tp_getset*/
0, /*tp_base*/
0, /*tp_dict*/
0, /*tp_descr_get*/
0, /*tp_descr_set*/
0, /*tp_dictoffset*/
0, /*tp_init*/
0, /*tp_alloc*/
__pyx_tp_new_array, /*tp_new*/
0, /*tp_free*/
0, /*tp_is_gc*/
0, /*tp_bases*/
0, /*tp_mro*/
0, /*tp_cache*/
0, /*tp_subclasses*/
0, /*tp_weaklist*/
0, /*tp_del*/
0, /*tp_version_tag*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030400a1
0, /*tp_finalize*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b1
0, /*tp_vectorcall*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4 && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03090000
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
};
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new_Enum(PyTypeObject *t, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *a, CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *k) {
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *p;
PyObject *o;
if (likely((t->tp_flags & Py_TPFLAGS_IS_ABSTRACT) == 0)) {
o = (*t->tp_alloc)(t, 0);
} else {
o = (PyObject *) PyBaseObject_Type.tp_new(t, __pyx_empty_tuple, 0);
}
if (unlikely(!o)) return 0;
p = ((struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)o);
p->name = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
return o;
}
static void __pyx_tp_dealloc_Enum(PyObject *o) {
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *p = (struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)o;
#if CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
if (unlikely(PyType_HasFeature(Py_TYPE(o), Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE) && Py_TYPE(o)->tp_finalize) && !_PyGC_FINALIZED(o)) {
if (PyObject_CallFinalizerFromDealloc(o)) return;
}
#endif
PyObject_GC_UnTrack(o);
Py_CLEAR(p->name);
(*Py_TYPE(o)->tp_free)(o);
}
static int __pyx_tp_traverse_Enum(PyObject *o, visitproc v, void *a) {
int e;
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *p = (struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)o;
if (p->name) {
e = (*v)(p->name, a); if (e) return e;
}
return 0;
}
static int __pyx_tp_clear_Enum(PyObject *o) {
PyObject* tmp;
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *p = (struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *)o;
tmp = ((PyObject*)p->name);
p->name = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
Py_XDECREF(tmp);
return 0;
}
static PyMethodDef __pyx_methods_Enum[] = {
{"__reduce_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_MemviewEnum_1__reduce_cython__, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"__setstate_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_MemviewEnum_3__setstate_cython__, METH_O, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static PyTypeObject __pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(0, 0)
"pept.processing.circles_ext.Enum", /*tp_name*/
sizeof(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj), /*tp_basicsize*/
0, /*tp_itemsize*/
__pyx_tp_dealloc_Enum, /*tp_dealloc*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_vectorcall_offset*/
#endif
0, /*tp_getattr*/
0, /*tp_setattr*/
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*tp_compare*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
0, /*tp_as_async*/
#endif
__pyx_MemviewEnum___repr__, /*tp_repr*/
0, /*tp_as_number*/
0, /*tp_as_sequence*/
0, /*tp_as_mapping*/
0, /*tp_hash*/
0, /*tp_call*/
0, /*tp_str*/
0, /*tp_getattro*/
0, /*tp_setattro*/
0, /*tp_as_buffer*/
Py_TPFLAGS_DEFAULT|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_VERSION_TAG|Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER|Py_TPFLAGS_BASETYPE|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_GC, /*tp_flags*/
0, /*tp_doc*/
__pyx_tp_traverse_Enum, /*tp_traverse*/
__pyx_tp_clear_Enum, /*tp_clear*/
0, /*tp_richcompare*/
0, /*tp_weaklistoffset*/
0, /*tp_iter*/
0, /*tp_iternext*/
__pyx_methods_Enum, /*tp_methods*/
0, /*tp_members*/
0, /*tp_getset*/
0, /*tp_base*/
0, /*tp_dict*/
0, /*tp_descr_get*/
0, /*tp_descr_set*/
0, /*tp_dictoffset*/
__pyx_MemviewEnum___init__, /*tp_init*/
0, /*tp_alloc*/
__pyx_tp_new_Enum, /*tp_new*/
0, /*tp_free*/
0, /*tp_is_gc*/
0, /*tp_bases*/
0, /*tp_mro*/
0, /*tp_cache*/
0, /*tp_subclasses*/
0, /*tp_weaklist*/
0, /*tp_del*/
0, /*tp_version_tag*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030400a1
0, /*tp_finalize*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b1
0, /*tp_vectorcall*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4 && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03090000
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview __pyx_vtable_memoryview;
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new_memoryview(PyTypeObject *t, PyObject *a, PyObject *k) {
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *p;
PyObject *o;
if (likely((t->tp_flags & Py_TPFLAGS_IS_ABSTRACT) == 0)) {
o = (*t->tp_alloc)(t, 0);
} else {
o = (PyObject *) PyBaseObject_Type.tp_new(t, __pyx_empty_tuple, 0);
}
if (unlikely(!o)) return 0;
p = ((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)o);
p->__pyx_vtab = __pyx_vtabptr_memoryview;
p->obj = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
p->_size = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
p->_array_interface = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
p->view.obj = NULL;
if (unlikely(__pyx_memoryview___cinit__(o, a, k) < 0)) goto bad;
return o;
bad:
Py_DECREF(o); o = 0;
return NULL;
}
static void __pyx_tp_dealloc_memoryview(PyObject *o) {
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *p = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)o;
#if CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
if (unlikely(PyType_HasFeature(Py_TYPE(o), Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE) && Py_TYPE(o)->tp_finalize) && !_PyGC_FINALIZED(o)) {
if (PyObject_CallFinalizerFromDealloc(o)) return;
}
#endif
PyObject_GC_UnTrack(o);
{
PyObject *etype, *eval, *etb;
PyErr_Fetch(&etype, &eval, &etb);
__Pyx_SET_REFCNT(o, Py_REFCNT(o) + 1);
__pyx_memoryview___dealloc__(o);
__Pyx_SET_REFCNT(o, Py_REFCNT(o) - 1);
PyErr_Restore(etype, eval, etb);
}
Py_CLEAR(p->obj);
Py_CLEAR(p->_size);
Py_CLEAR(p->_array_interface);
(*Py_TYPE(o)->tp_free)(o);
}
static int __pyx_tp_traverse_memoryview(PyObject *o, visitproc v, void *a) {
int e;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *p = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)o;
if (p->obj) {
e = (*v)(p->obj, a); if (e) return e;
}
if (p->_size) {
e = (*v)(p->_size, a); if (e) return e;
}
if (p->_array_interface) {
e = (*v)(p->_array_interface, a); if (e) return e;
}
if (p->view.obj) {
e = (*v)(p->view.obj, a); if (e) return e;
}
return 0;
}
static int __pyx_tp_clear_memoryview(PyObject *o) {
PyObject* tmp;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *p = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)o;
tmp = ((PyObject*)p->obj);
p->obj = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
Py_XDECREF(tmp);
tmp = ((PyObject*)p->_size);
p->_size = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
Py_XDECREF(tmp);
tmp = ((PyObject*)p->_array_interface);
p->_array_interface = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
Py_XDECREF(tmp);
Py_CLEAR(p->view.obj);
return 0;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_sq_item_memoryview(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i) {
PyObject *r;
PyObject *x = PyInt_FromSsize_t(i); if(!x) return 0;
r = Py_TYPE(o)->tp_as_mapping->mp_subscript(o, x);
Py_DECREF(x);
return r;
}
static int __pyx_mp_ass_subscript_memoryview(PyObject *o, PyObject *i, PyObject *v) {
if (v) {
return __pyx_memoryview___setitem__(o, i, v);
}
else {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_NotImplementedError,
"Subscript deletion not supported by %.200s", Py_TYPE(o)->tp_name);
return -1;
}
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_T(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_1T_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_base(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4base_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_shape(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_5shape_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_strides(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_7strides_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_suboffsets(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_10suboffsets_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_ndim(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4ndim_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_itemsize(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_8itemsize_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_nbytes(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_6nbytes_1__get__(o);
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_size(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_10memoryview_4size_1__get__(o);
}
static PyMethodDef __pyx_methods_memoryview[] = {
{"is_c_contig", (PyCFunction)__pyx_memoryview_is_c_contig, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"is_f_contig", (PyCFunction)__pyx_memoryview_is_f_contig, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"copy", (PyCFunction)__pyx_memoryview_copy, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"copy_fortran", (PyCFunction)__pyx_memoryview_copy_fortran, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"__reduce_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryview_1__reduce_cython__, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"__setstate_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryview_3__setstate_cython__, METH_O, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static struct PyGetSetDef __pyx_getsets_memoryview[] = {
{(char *)"T", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_T, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"base", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_base, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"shape", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_shape, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"strides", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_strides, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"suboffsets", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_suboffsets, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"ndim", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_ndim, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"itemsize", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_itemsize, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"nbytes", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_nbytes, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{(char *)"size", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryview_size, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static PySequenceMethods __pyx_tp_as_sequence_memoryview = {
__pyx_memoryview___len__, /*sq_length*/
0, /*sq_concat*/
0, /*sq_repeat*/
__pyx_sq_item_memoryview, /*sq_item*/
0, /*sq_slice*/
0, /*sq_ass_item*/
0, /*sq_ass_slice*/
0, /*sq_contains*/
0, /*sq_inplace_concat*/
0, /*sq_inplace_repeat*/
};
static PyMappingMethods __pyx_tp_as_mapping_memoryview = {
__pyx_memoryview___len__, /*mp_length*/
__pyx_memoryview___getitem__, /*mp_subscript*/
__pyx_mp_ass_subscript_memoryview, /*mp_ass_subscript*/
};
static PyBufferProcs __pyx_tp_as_buffer_memoryview = {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getreadbuffer*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getwritebuffer*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getsegcount*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*bf_getcharbuffer*/
#endif
__pyx_memoryview_getbuffer, /*bf_getbuffer*/
0, /*bf_releasebuffer*/
};
static PyTypeObject __pyx_type___pyx_memoryview = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(0, 0)
"pept.processing.circles_ext.memoryview", /*tp_name*/
sizeof(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj), /*tp_basicsize*/
0, /*tp_itemsize*/
__pyx_tp_dealloc_memoryview, /*tp_dealloc*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_vectorcall_offset*/
#endif
0, /*tp_getattr*/
0, /*tp_setattr*/
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*tp_compare*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
0, /*tp_as_async*/
#endif
__pyx_memoryview___repr__, /*tp_repr*/
0, /*tp_as_number*/
&__pyx_tp_as_sequence_memoryview, /*tp_as_sequence*/
&__pyx_tp_as_mapping_memoryview, /*tp_as_mapping*/
0, /*tp_hash*/
0, /*tp_call*/
__pyx_memoryview___str__, /*tp_str*/
0, /*tp_getattro*/
0, /*tp_setattro*/
&__pyx_tp_as_buffer_memoryview, /*tp_as_buffer*/
Py_TPFLAGS_DEFAULT|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_VERSION_TAG|Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER|Py_TPFLAGS_BASETYPE|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_GC, /*tp_flags*/
0, /*tp_doc*/
__pyx_tp_traverse_memoryview, /*tp_traverse*/
__pyx_tp_clear_memoryview, /*tp_clear*/
0, /*tp_richcompare*/
0, /*tp_weaklistoffset*/
0, /*tp_iter*/
0, /*tp_iternext*/
__pyx_methods_memoryview, /*tp_methods*/
0, /*tp_members*/
__pyx_getsets_memoryview, /*tp_getset*/
0, /*tp_base*/
0, /*tp_dict*/
0, /*tp_descr_get*/
0, /*tp_descr_set*/
0, /*tp_dictoffset*/
0, /*tp_init*/
0, /*tp_alloc*/
__pyx_tp_new_memoryview, /*tp_new*/
0, /*tp_free*/
0, /*tp_is_gc*/
0, /*tp_bases*/
0, /*tp_mro*/
0, /*tp_cache*/
0, /*tp_subclasses*/
0, /*tp_weaklist*/
0, /*tp_del*/
0, /*tp_version_tag*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030400a1
0, /*tp_finalize*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b1
0, /*tp_vectorcall*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4 && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03090000
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct__memoryviewslice __pyx_vtable__memoryviewslice;
static PyObject *__pyx_tp_new__memoryviewslice(PyTypeObject *t, PyObject *a, PyObject *k) {
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *p;
PyObject *o = __pyx_tp_new_memoryview(t, a, k);
if (unlikely(!o)) return 0;
p = ((struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)o);
p->__pyx_base.__pyx_vtab = (struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview*)__pyx_vtabptr__memoryviewslice;
p->from_object = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
p->from_slice.memview = NULL;
return o;
}
static void __pyx_tp_dealloc__memoryviewslice(PyObject *o) {
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *p = (struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)o;
#if CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
if (unlikely(PyType_HasFeature(Py_TYPE(o), Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE) && Py_TYPE(o)->tp_finalize) && !_PyGC_FINALIZED(o)) {
if (PyObject_CallFinalizerFromDealloc(o)) return;
}
#endif
PyObject_GC_UnTrack(o);
{
PyObject *etype, *eval, *etb;
PyErr_Fetch(&etype, &eval, &etb);
__Pyx_SET_REFCNT(o, Py_REFCNT(o) + 1);
__pyx_memoryviewslice___dealloc__(o);
__Pyx_SET_REFCNT(o, Py_REFCNT(o) - 1);
PyErr_Restore(etype, eval, etb);
}
Py_CLEAR(p->from_object);
PyObject_GC_Track(o);
__pyx_tp_dealloc_memoryview(o);
}
static int __pyx_tp_traverse__memoryviewslice(PyObject *o, visitproc v, void *a) {
int e;
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *p = (struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)o;
e = __pyx_tp_traverse_memoryview(o, v, a); if (e) return e;
if (p->from_object) {
e = (*v)(p->from_object, a); if (e) return e;
}
return 0;
}
static int __pyx_tp_clear__memoryviewslice(PyObject *o) {
PyObject* tmp;
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *p = (struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *)o;
__pyx_tp_clear_memoryview(o);
tmp = ((PyObject*)p->from_object);
p->from_object = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
Py_XDECREF(tmp);
__PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(&p->from_slice, 1);
return 0;
}
static PyObject *__pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryviewslice_base(PyObject *o, CYTHON_UNUSED void *x) {
return __pyx_pw_15View_dot_MemoryView_16_memoryviewslice_4base_1__get__(o);
}
static PyMethodDef __pyx_methods__memoryviewslice[] = {
{"__reduce_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryviewslice_1__reduce_cython__, METH_NOARGS, 0},
{"__setstate_cython__", (PyCFunction)__pyx_pw___pyx_memoryviewslice_3__setstate_cython__, METH_O, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static struct PyGetSetDef __pyx_getsets__memoryviewslice[] = {
{(char *)"base", __pyx_getprop___pyx_memoryviewslice_base, 0, (char *)0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static PyTypeObject __pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(0, 0)
"pept.processing.circles_ext._memoryviewslice", /*tp_name*/
sizeof(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj), /*tp_basicsize*/
0, /*tp_itemsize*/
__pyx_tp_dealloc__memoryviewslice, /*tp_dealloc*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4
0, /*tp_vectorcall_offset*/
#endif
0, /*tp_getattr*/
0, /*tp_setattr*/
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
0, /*tp_compare*/
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
0, /*tp_as_async*/
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
__pyx_memoryview___repr__, /*tp_repr*/
#else
0, /*tp_repr*/
#endif
0, /*tp_as_number*/
0, /*tp_as_sequence*/
0, /*tp_as_mapping*/
0, /*tp_hash*/
0, /*tp_call*/
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
__pyx_memoryview___str__, /*tp_str*/
#else
0, /*tp_str*/
#endif
0, /*tp_getattro*/
0, /*tp_setattro*/
0, /*tp_as_buffer*/
Py_TPFLAGS_DEFAULT|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_VERSION_TAG|Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER|Py_TPFLAGS_BASETYPE|Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_GC, /*tp_flags*/
"Internal class for passing memoryview slices to Python", /*tp_doc*/
__pyx_tp_traverse__memoryviewslice, /*tp_traverse*/
__pyx_tp_clear__memoryviewslice, /*tp_clear*/
0, /*tp_richcompare*/
0, /*tp_weaklistoffset*/
0, /*tp_iter*/
0, /*tp_iternext*/
__pyx_methods__memoryviewslice, /*tp_methods*/
0, /*tp_members*/
__pyx_getsets__memoryviewslice, /*tp_getset*/
0, /*tp_base*/
0, /*tp_dict*/
0, /*tp_descr_get*/
0, /*tp_descr_set*/
0, /*tp_dictoffset*/
0, /*tp_init*/
0, /*tp_alloc*/
__pyx_tp_new__memoryviewslice, /*tp_new*/
0, /*tp_free*/
0, /*tp_is_gc*/
0, /*tp_bases*/
0, /*tp_mro*/
0, /*tp_cache*/
0, /*tp_subclasses*/
0, /*tp_weaklist*/
0, /*tp_del*/
0, /*tp_version_tag*/
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030400a1
0, /*tp_finalize*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b1
0, /*tp_vectorcall*/
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800b4 && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03090000
0, /*tp_print*/
#endif
};
static PyMethodDef __pyx_methods[] = {
{"circles2d_ext", (PyCFunction)(void*)(PyCFunctionWithKeywords)__pyx_pw_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_1circles2d_ext, METH_VARARGS|METH_KEYWORDS, __pyx_doc_4pept_10processing_11circles_ext_circles2d_ext},
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#if CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
static PyObject* __pyx_pymod_create(PyObject *spec, PyModuleDef *def); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_pymod_exec_circles_ext(PyObject* module); /*proto*/
static PyModuleDef_Slot __pyx_moduledef_slots[] = {
{Py_mod_create, (void*)__pyx_pymod_create},
{Py_mod_exec, (void*)__pyx_pymod_exec_circles_ext},
{0, NULL}
};
#endif
static struct PyModuleDef __pyx_moduledef = {
PyModuleDef_HEAD_INIT,
"circles_ext",
0, /* m_doc */
#if CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
0, /* m_size */
#else
-1, /* m_size */
#endif
__pyx_methods /* m_methods */,
#if CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
__pyx_moduledef_slots, /* m_slots */
#else
NULL, /* m_reload */
#endif
NULL, /* m_traverse */
NULL, /* m_clear */
NULL /* m_free */
};
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_SMALL_CODE
#if defined(__clang__)
#define CYTHON_SMALL_CODE
#elif defined(__GNUC__) && (__GNUC__ > 4 || (__GNUC__ == 4 && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= 3))
#define CYTHON_SMALL_CODE __attribute__((cold))
#else
#define CYTHON_SMALL_CODE
#endif
#endif
static __Pyx_StringTabEntry __pyx_string_tab[] = {
{&__pyx_n_s_ASCII, __pyx_k_ASCII, sizeof(__pyx_k_ASCII), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Buffer_view_does_not_expose_stri, __pyx_k_Buffer_view_does_not_expose_stri, sizeof(__pyx_k_Buffer_view_does_not_expose_stri), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Can_only_create_a_buffer_that_is, __pyx_k_Can_only_create_a_buffer_that_is, sizeof(__pyx_k_Can_only_create_a_buffer_that_is), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Cannot_assign_to_read_only_memor, __pyx_k_Cannot_assign_to_read_only_memor, sizeof(__pyx_k_Cannot_assign_to_read_only_memor), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Cannot_create_writable_memory_vi, __pyx_k_Cannot_create_writable_memory_vi, sizeof(__pyx_k_Cannot_create_writable_memory_vi), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Cannot_index_with_type_s, __pyx_k_Cannot_index_with_type_s, sizeof(__pyx_k_Cannot_index_with_type_s), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_Ellipsis, __pyx_k_Ellipsis, sizeof(__pyx_k_Ellipsis), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Empty_shape_tuple_for_cython_arr, __pyx_k_Empty_shape_tuple_for_cython_arr, sizeof(__pyx_k_Empty_shape_tuple_for_cython_arr), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Incompatible_checksums_s_vs_0xb0, __pyx_k_Incompatible_checksums_s_vs_0xb0, sizeof(__pyx_k_Incompatible_checksums_s_vs_0xb0), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_IndexError, __pyx_k_IndexError, sizeof(__pyx_k_IndexError), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Indirect_dimensions_not_supporte, __pyx_k_Indirect_dimensions_not_supporte, sizeof(__pyx_k_Indirect_dimensions_not_supporte), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Invalid_mode_expected_c_or_fortr, __pyx_k_Invalid_mode_expected_c_or_fortr, sizeof(__pyx_k_Invalid_mode_expected_c_or_fortr), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Invalid_shape_in_axis_d_d, __pyx_k_Invalid_shape_in_axis_d_d, sizeof(__pyx_k_Invalid_shape_in_axis_d_d), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_MemoryError, __pyx_k_MemoryError, sizeof(__pyx_k_MemoryError), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_MemoryView_of_r_at_0x_x, __pyx_k_MemoryView_of_r_at_0x_x, sizeof(__pyx_k_MemoryView_of_r_at_0x_x), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_MemoryView_of_r_object, __pyx_k_MemoryView_of_r_object, sizeof(__pyx_k_MemoryView_of_r_object), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_b_O, __pyx_k_O, sizeof(__pyx_k_O), 0, 0, 0, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Out_of_bounds_on_buffer_access_a, __pyx_k_Out_of_bounds_on_buffer_access_a, sizeof(__pyx_k_Out_of_bounds_on_buffer_access_a), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_PickleError, __pyx_k_PickleError, sizeof(__pyx_k_PickleError), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_TypeError, __pyx_k_TypeError, sizeof(__pyx_k_TypeError), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_Unable_to_convert_item_to_object, __pyx_k_Unable_to_convert_item_to_object, sizeof(__pyx_k_Unable_to_convert_item_to_object), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_ValueError, __pyx_k_ValueError, sizeof(__pyx_k_ValueError), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_View_MemoryView, __pyx_k_View_MemoryView, sizeof(__pyx_k_View_MemoryView), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_allocate_buffer, __pyx_k_allocate_buffer, sizeof(__pyx_k_allocate_buffer), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_base, __pyx_k_base, sizeof(__pyx_k_base), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_c, __pyx_k_c, sizeof(__pyx_k_c), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_u_c, __pyx_k_c, sizeof(__pyx_k_c), 0, 1, 0, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_class, __pyx_k_class, sizeof(__pyx_k_class), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_cline_in_traceback, __pyx_k_cline_in_traceback, sizeof(__pyx_k_cline_in_traceback), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_contiguous_and_direct, __pyx_k_contiguous_and_direct, sizeof(__pyx_k_contiguous_and_direct), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_contiguous_and_indirect, __pyx_k_contiguous_and_indirect, sizeof(__pyx_k_contiguous_and_indirect), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_dict, __pyx_k_dict, sizeof(__pyx_k_dict), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_dtype_is_object, __pyx_k_dtype_is_object, sizeof(__pyx_k_dtype_is_object), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_encode, __pyx_k_encode, sizeof(__pyx_k_encode), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_enumerate, __pyx_k_enumerate, sizeof(__pyx_k_enumerate), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_error, __pyx_k_error, sizeof(__pyx_k_error), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_flags, __pyx_k_flags, sizeof(__pyx_k_flags), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_format, __pyx_k_format, sizeof(__pyx_k_format), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_fortran, __pyx_k_fortran, sizeof(__pyx_k_fortran), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_u_fortran, __pyx_k_fortran, sizeof(__pyx_k_fortran), 0, 1, 0, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_getstate, __pyx_k_getstate, sizeof(__pyx_k_getstate), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_got_differing_extents_in_dimensi, __pyx_k_got_differing_extents_in_dimensi, sizeof(__pyx_k_got_differing_extents_in_dimensi), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_id, __pyx_k_id, sizeof(__pyx_k_id), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_import, __pyx_k_import, sizeof(__pyx_k_import), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_itemsize, __pyx_k_itemsize, sizeof(__pyx_k_itemsize), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_itemsize_0_for_cython_array, __pyx_k_itemsize_0_for_cython_array, sizeof(__pyx_k_itemsize_0_for_cython_array), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_main, __pyx_k_main, sizeof(__pyx_k_main), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_memview, __pyx_k_memview, sizeof(__pyx_k_memview), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_mode, __pyx_k_mode, sizeof(__pyx_k_mode), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_name, __pyx_k_name, sizeof(__pyx_k_name), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_name_2, __pyx_k_name_2, sizeof(__pyx_k_name_2), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_ndim, __pyx_k_ndim, sizeof(__pyx_k_ndim), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_new, __pyx_k_new, sizeof(__pyx_k_new), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non, __pyx_k_no_default___reduce___due_to_non, sizeof(__pyx_k_no_default___reduce___due_to_non), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_obj, __pyx_k_obj, sizeof(__pyx_k_obj), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pack, __pyx_k_pack, sizeof(__pyx_k_pack), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pickle, __pyx_k_pickle, sizeof(__pyx_k_pickle), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pixels, __pyx_k_pixels, sizeof(__pyx_k_pixels), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_positions, __pyx_k_positions, sizeof(__pyx_k_positions), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_PickleError, __pyx_k_pyx_PickleError, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_PickleError), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_checksum, __pyx_k_pyx_checksum, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_checksum), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_getbuffer, __pyx_k_pyx_getbuffer, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_getbuffer), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_result, __pyx_k_pyx_result, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_result), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_state, __pyx_k_pyx_state, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_state), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_type, __pyx_k_pyx_type, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_type), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_unpickle_Enum, __pyx_k_pyx_unpickle_Enum, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_unpickle_Enum), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_pyx_vtable, __pyx_k_pyx_vtable, sizeof(__pyx_k_pyx_vtable), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_radii, __pyx_k_radii, sizeof(__pyx_k_radii), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_range, __pyx_k_range, sizeof(__pyx_k_range), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_reduce, __pyx_k_reduce, sizeof(__pyx_k_reduce), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_reduce_cython, __pyx_k_reduce_cython, sizeof(__pyx_k_reduce_cython), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_reduce_ex, __pyx_k_reduce_ex, sizeof(__pyx_k_reduce_ex), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_setstate, __pyx_k_setstate, sizeof(__pyx_k_setstate), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_setstate_cython, __pyx_k_setstate_cython, sizeof(__pyx_k_setstate_cython), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_shape, __pyx_k_shape, sizeof(__pyx_k_shape), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_size, __pyx_k_size, sizeof(__pyx_k_size), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_start, __pyx_k_start, sizeof(__pyx_k_start), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_step, __pyx_k_step, sizeof(__pyx_k_step), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_stop, __pyx_k_stop, sizeof(__pyx_k_stop), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_strided_and_direct, __pyx_k_strided_and_direct, sizeof(__pyx_k_strided_and_direct), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_strided_and_direct_or_indirect, __pyx_k_strided_and_direct_or_indirect, sizeof(__pyx_k_strided_and_direct_or_indirect), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_strided_and_indirect, __pyx_k_strided_and_indirect, sizeof(__pyx_k_strided_and_indirect), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_stringsource, __pyx_k_stringsource, sizeof(__pyx_k_stringsource), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_struct, __pyx_k_struct, sizeof(__pyx_k_struct), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_test, __pyx_k_test, sizeof(__pyx_k_test), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_kp_s_unable_to_allocate_array_data, __pyx_k_unable_to_allocate_array_data, sizeof(__pyx_k_unable_to_allocate_array_data), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_kp_s_unable_to_allocate_shape_and_str, __pyx_k_unable_to_allocate_shape_and_str, sizeof(__pyx_k_unable_to_allocate_shape_and_str), 0, 0, 1, 0},
{&__pyx_n_s_unpack, __pyx_k_unpack, sizeof(__pyx_k_unpack), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_update, __pyx_k_update, sizeof(__pyx_k_update), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_xlim, __pyx_k_xlim, sizeof(__pyx_k_xlim), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{&__pyx_n_s_ylim, __pyx_k_ylim, sizeof(__pyx_k_ylim), 0, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_InitCachedBuiltins(void) {
__pyx_builtin_range = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_range); if (!__pyx_builtin_range) __PYX_ERR(0, 678, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_builtin_ValueError = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_ValueError); if (!__pyx_builtin_ValueError) __PYX_ERR(1, 133, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_builtin_MemoryError = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_MemoryError); if (!__pyx_builtin_MemoryError) __PYX_ERR(1, 148, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_builtin_enumerate = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_enumerate); if (!__pyx_builtin_enumerate) __PYX_ERR(1, 151, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_builtin_TypeError = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_TypeError); if (!__pyx_builtin_TypeError) __PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_builtin_Ellipsis = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_Ellipsis); if (!__pyx_builtin_Ellipsis) __PYX_ERR(1, 404, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_builtin_id = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_id); if (!__pyx_builtin_id) __PYX_ERR(1, 613, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_builtin_IndexError = __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(__pyx_n_s_IndexError); if (!__pyx_builtin_IndexError) __PYX_ERR(1, 832, __pyx_L1_error)
return 0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
return -1;
}
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_InitCachedConstants(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_InitCachedConstants", 0);
/* "View.MemoryView":133
*
* if not self.ndim:
* raise ValueError("Empty shape tuple for cython.array") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if itemsize <= 0:
*/
__pyx_tuple_ = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_Empty_shape_tuple_for_cython_arr); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple_)) __PYX_ERR(1, 133, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple_);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple_);
/* "View.MemoryView":136
*
* if itemsize <= 0:
* raise ValueError("itemsize <= 0 for cython.array") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if not isinstance(format, bytes):
*/
__pyx_tuple__2 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_itemsize_0_for_cython_array); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__2)) __PYX_ERR(1, 136, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__2);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__2);
/* "View.MemoryView":148
*
* if not self._shape:
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate shape and strides.") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_tuple__3 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_unable_to_allocate_shape_and_str); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__3)) __PYX_ERR(1, 148, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__3);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__3);
/* "View.MemoryView":176
* self.data = malloc(self.len)
* if not self.data:
* raise MemoryError("unable to allocate array data.") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if self.dtype_is_object:
*/
__pyx_tuple__4 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_unable_to_allocate_array_data); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__4)) __PYX_ERR(1, 176, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__4);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__4);
/* "View.MemoryView":192
* bufmode = PyBUF_F_CONTIGUOUS | PyBUF_ANY_CONTIGUOUS
* if not (flags & bufmode):
* raise ValueError("Can only create a buffer that is contiguous in memory.") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* info.buf = self.data
* info.len = self.len
*/
__pyx_tuple__5 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_Can_only_create_a_buffer_that_is); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__5)) __PYX_ERR(1, 192, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__5);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__5);
/* "(tree fragment)":2
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
__pyx_tuple__6 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__6)) __PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__6);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__6);
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_tuple__7 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__7)) __PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__7);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__7);
/* "View.MemoryView":418
* def __setitem__(memoryview self, object index, object value):
* if self.view.readonly:
* raise TypeError("Cannot assign to read-only memoryview") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* have_slices, index = _unellipsify(index, self.view.ndim)
*/
__pyx_tuple__8 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_Cannot_assign_to_read_only_memor); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__8)) __PYX_ERR(1, 418, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__8);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__8);
/* "View.MemoryView":495
* result = struct.unpack(self.view.format, bytesitem)
* except struct.error:
* raise ValueError("Unable to convert item to object") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* else:
* if len(self.view.format) == 1:
*/
__pyx_tuple__9 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_Unable_to_convert_item_to_object); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__9)) __PYX_ERR(1, 495, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__9);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__9);
/* "View.MemoryView":520
* def __getbuffer__(self, Py_buffer *info, int flags):
* if flags & PyBUF_WRITABLE and self.view.readonly:
* raise ValueError("Cannot create writable memory view from read-only memoryview") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* if flags & PyBUF_ND:
*/
__pyx_tuple__10 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_Cannot_create_writable_memory_vi); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__10)) __PYX_ERR(1, 520, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__10);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__10);
/* "View.MemoryView":570
* if self.view.strides == NULL:
*
* raise ValueError("Buffer view does not expose strides") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return tuple([stride for stride in self.view.strides[:self.view.ndim]])
*/
__pyx_tuple__11 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_Buffer_view_does_not_expose_stri); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__11)) __PYX_ERR(1, 570, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__11);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__11);
/* "View.MemoryView":577
* def suboffsets(self):
* if self.view.suboffsets == NULL:
* return (-1,) * self.view.ndim # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* return tuple([suboffset for suboffset in self.view.suboffsets[:self.view.ndim]])
*/
__pyx_tuple__12 = PyTuple_New(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__12)) __PYX_ERR(1, 577, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__12);
__Pyx_INCREF(__pyx_int_neg_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_int_neg_1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(__pyx_tuple__12, 0, __pyx_int_neg_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__12);
/* "(tree fragment)":2
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
__pyx_tuple__13 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__13)) __PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__13);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__13);
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_tuple__14 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__14)) __PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__14);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__14);
/* "View.MemoryView":682
* if item is Ellipsis:
* if not seen_ellipsis:
* result.extend([slice(None)] * (ndim - len(tup) + 1)) # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* seen_ellipsis = True
* else:
*/
__pyx_slice__15 = PySlice_New(Py_None, Py_None, Py_None); if (unlikely(!__pyx_slice__15)) __PYX_ERR(1, 682, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_slice__15);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_slice__15);
/* "View.MemoryView":703
* for suboffset in suboffsets[:ndim]:
* if suboffset >= 0:
* raise ValueError("Indirect dimensions not supported") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_tuple__16 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_Indirect_dimensions_not_supporte); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__16)) __PYX_ERR(1, 703, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__16);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__16);
/* "(tree fragment)":2
* def __reduce_cython__(self):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
*/
__pyx_tuple__17 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__17)) __PYX_ERR(1, 2, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__17);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__17);
/* "(tree fragment)":4
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__")
* def __setstate_cython__(self, __pyx_state):
* raise TypeError("no default __reduce__ due to non-trivial __cinit__") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*/
__pyx_tuple__18 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_no_default___reduce___due_to_non); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__18)) __PYX_ERR(1, 4, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__18);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__18);
/* "View.MemoryView":286
* return self.name
*
* cdef generic = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef strided = Enum("") # default
* cdef indirect = Enum("")
*/
__pyx_tuple__19 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_strided_and_direct_or_indirect); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__19)) __PYX_ERR(1, 286, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__19);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__19);
/* "View.MemoryView":287
*
* cdef generic = Enum("")
* cdef strided = Enum("") # default # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef indirect = Enum("")
*
*/
__pyx_tuple__20 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_strided_and_direct); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__20)) __PYX_ERR(1, 287, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__20);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__20);
/* "View.MemoryView":288
* cdef generic = Enum("")
* cdef strided = Enum("") # default
* cdef indirect = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_tuple__21 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_strided_and_indirect); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__21)) __PYX_ERR(1, 288, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__21);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__21);
/* "View.MemoryView":291
*
*
* cdef contiguous = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef indirect_contiguous = Enum("")
*
*/
__pyx_tuple__22 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_contiguous_and_direct); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__22)) __PYX_ERR(1, 291, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__22);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__22);
/* "View.MemoryView":292
*
* cdef contiguous = Enum("")
* cdef indirect_contiguous = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_tuple__23 = PyTuple_Pack(1, __pyx_kp_s_contiguous_and_indirect); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__23)) __PYX_ERR(1, 292, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__23);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__23);
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __pyx_unpickle_Enum(__pyx_type, long __pyx_checksum, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef object __pyx_PickleError
* cdef object __pyx_result
*/
__pyx_tuple__24 = PyTuple_Pack(5, __pyx_n_s_pyx_type, __pyx_n_s_pyx_checksum, __pyx_n_s_pyx_state, __pyx_n_s_pyx_PickleError, __pyx_n_s_pyx_result); if (unlikely(!__pyx_tuple__24)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_tuple__24);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_tuple__24);
__pyx_codeobj__25 = (PyObject*)__Pyx_PyCode_New(3, 0, 5, 0, CO_OPTIMIZED|CO_NEWLOCALS, __pyx_empty_bytes, __pyx_empty_tuple, __pyx_empty_tuple, __pyx_tuple__24, __pyx_empty_tuple, __pyx_empty_tuple, __pyx_kp_s_stringsource, __pyx_n_s_pyx_unpickle_Enum, 1, __pyx_empty_bytes); if (unlikely(!__pyx_codeobj__25)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return -1;
}
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_InitGlobals(void) {
if (__Pyx_InitStrings(__pyx_string_tab) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error);
__pyx_int_0 = PyInt_FromLong(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_int_0)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_int_1 = PyInt_FromLong(1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_int_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_int_184977713 = PyInt_FromLong(184977713L); if (unlikely(!__pyx_int_184977713)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_int_neg_1 = PyInt_FromLong(-1); if (unlikely(!__pyx_int_neg_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
return 0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
return -1;
}
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_modinit_global_init_code(void); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_modinit_variable_export_code(void); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_modinit_function_export_code(void); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_modinit_type_init_code(void); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_modinit_type_import_code(void); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_modinit_variable_import_code(void); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_modinit_function_import_code(void); /*proto*/
static int __Pyx_modinit_global_init_code(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_modinit_global_init_code", 0);
/*--- Global init code ---*/
generic = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
strided = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
indirect = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
contiguous = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
indirect_contiguous = Py_None; Py_INCREF(Py_None);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
}
static int __Pyx_modinit_variable_export_code(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_modinit_variable_export_code", 0);
/*--- Variable export code ---*/
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
}
static int __Pyx_modinit_function_export_code(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_modinit_function_export_code", 0);
/*--- Function export code ---*/
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
}
static int __Pyx_modinit_type_init_code(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_modinit_type_init_code", 0);
/*--- Type init code ---*/
__pyx_vtabptr_array = &__pyx_vtable_array;
__pyx_vtable_array.get_memview = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_array_obj *))__pyx_array_get_memview;
if (PyType_Ready(&__pyx_type___pyx_array) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 105, __pyx_L1_error)
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800B1
__pyx_type___pyx_array.tp_print = 0;
#endif
if (__Pyx_SetVtable(__pyx_type___pyx_array.tp_dict, __pyx_vtabptr_array) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 105, __pyx_L1_error)
if (__Pyx_setup_reduce((PyObject*)&__pyx_type___pyx_array) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 105, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_array_type = &__pyx_type___pyx_array;
if (PyType_Ready(&__pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 279, __pyx_L1_error)
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800B1
__pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum.tp_print = 0;
#endif
if ((CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP) && likely(!__pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum.tp_dictoffset && __pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum.tp_getattro == PyObject_GenericGetAttr)) {
__pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum.tp_getattro = __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr;
}
if (__Pyx_setup_reduce((PyObject*)&__pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 279, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_MemviewEnum_type = &__pyx_type___pyx_MemviewEnum;
__pyx_vtabptr_memoryview = &__pyx_vtable_memoryview;
__pyx_vtable_memoryview.get_item_pointer = (char *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *))__pyx_memoryview_get_item_pointer;
__pyx_vtable_memoryview.is_slice = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *))__pyx_memoryview_is_slice;
__pyx_vtable_memoryview.setitem_slice_assignment = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *, PyObject *))__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assignment;
__pyx_vtable_memoryview.setitem_slice_assign_scalar = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *))__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assign_scalar;
__pyx_vtable_memoryview.setitem_indexed = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *, PyObject *))__pyx_memoryview_setitem_indexed;
__pyx_vtable_memoryview.convert_item_to_object = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *))__pyx_memoryview_convert_item_to_object;
__pyx_vtable_memoryview.assign_item_from_object = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *, PyObject *))__pyx_memoryview_assign_item_from_object;
if (PyType_Ready(&__pyx_type___pyx_memoryview) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 330, __pyx_L1_error)
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800B1
__pyx_type___pyx_memoryview.tp_print = 0;
#endif
if ((CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP) && likely(!__pyx_type___pyx_memoryview.tp_dictoffset && __pyx_type___pyx_memoryview.tp_getattro == PyObject_GenericGetAttr)) {
__pyx_type___pyx_memoryview.tp_getattro = __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr;
}
if (__Pyx_SetVtable(__pyx_type___pyx_memoryview.tp_dict, __pyx_vtabptr_memoryview) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 330, __pyx_L1_error)
if (__Pyx_setup_reduce((PyObject*)&__pyx_type___pyx_memoryview) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 330, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_memoryview_type = &__pyx_type___pyx_memoryview;
__pyx_vtabptr__memoryviewslice = &__pyx_vtable__memoryviewslice;
__pyx_vtable__memoryviewslice.__pyx_base = *__pyx_vtabptr_memoryview;
__pyx_vtable__memoryviewslice.__pyx_base.convert_item_to_object = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *))__pyx_memoryviewslice_convert_item_to_object;
__pyx_vtable__memoryviewslice.__pyx_base.assign_item_from_object = (PyObject *(*)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *, PyObject *))__pyx_memoryviewslice_assign_item_from_object;
__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice.tp_base = __pyx_memoryview_type;
if (PyType_Ready(&__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 965, __pyx_L1_error)
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800B1
__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice.tp_print = 0;
#endif
if ((CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP) && likely(!__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice.tp_dictoffset && __pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice.tp_getattro == PyObject_GenericGetAttr)) {
__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice.tp_getattro = __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr;
}
if (__Pyx_SetVtable(__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice.tp_dict, __pyx_vtabptr__memoryviewslice) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 965, __pyx_L1_error)
if (__Pyx_setup_reduce((PyObject*)&__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 965, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_memoryviewslice_type = &__pyx_type___pyx_memoryviewslice;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return -1;
}
static int __Pyx_modinit_type_import_code(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_modinit_type_import_code", 0);
/*--- Type import code ---*/
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
}
static int __Pyx_modinit_variable_import_code(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_modinit_variable_import_code", 0);
/*--- Variable import code ---*/
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
}
static int __Pyx_modinit_function_import_code(void) {
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_modinit_function_import_code", 0);
/*--- Function import code ---*/
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return 0;
}
#ifndef CYTHON_NO_PYINIT_EXPORT
#define __Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC PyMODINIT_FUNC
#elif PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define __Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC extern "C" void
#else
#define __Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC void
#endif
#else
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define __Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC extern "C" PyObject *
#else
#define __Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC PyObject *
#endif
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
__Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC initcircles_ext(void) CYTHON_SMALL_CODE; /*proto*/
__Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC initcircles_ext(void)
#else
__Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC PyInit_circles_ext(void) CYTHON_SMALL_CODE; /*proto*/
__Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC PyInit_circles_ext(void)
#if CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
{
return PyModuleDef_Init(&__pyx_moduledef);
}
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_check_single_interpreter(void) {
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030700A1
static PY_INT64_T main_interpreter_id = -1;
PY_INT64_T current_id = PyInterpreterState_GetID(PyThreadState_Get()->interp);
if (main_interpreter_id == -1) {
main_interpreter_id = current_id;
return (unlikely(current_id == -1)) ? -1 : 0;
} else if (unlikely(main_interpreter_id != current_id))
#else
static PyInterpreterState *main_interpreter = NULL;
PyInterpreterState *current_interpreter = PyThreadState_Get()->interp;
if (!main_interpreter) {
main_interpreter = current_interpreter;
} else if (unlikely(main_interpreter != current_interpreter))
#endif
{
PyErr_SetString(
PyExc_ImportError,
"Interpreter change detected - this module can only be loaded into one interpreter per process.");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __Pyx_copy_spec_to_module(PyObject *spec, PyObject *moddict, const char* from_name, const char* to_name, int allow_none) {
PyObject *value = PyObject_GetAttrString(spec, from_name);
int result = 0;
if (likely(value)) {
if (allow_none || value != Py_None) {
result = PyDict_SetItemString(moddict, to_name, value);
}
Py_DECREF(value);
} else if (PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_AttributeError)) {
PyErr_Clear();
} else {
result = -1;
}
return result;
}
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE PyObject* __pyx_pymod_create(PyObject *spec, CYTHON_UNUSED PyModuleDef *def) {
PyObject *module = NULL, *moddict, *modname;
if (__Pyx_check_single_interpreter())
return NULL;
if (__pyx_m)
return __Pyx_NewRef(__pyx_m);
modname = PyObject_GetAttrString(spec, "name");
if (unlikely(!modname)) goto bad;
module = PyModule_NewObject(modname);
Py_DECREF(modname);
if (unlikely(!module)) goto bad;
moddict = PyModule_GetDict(module);
if (unlikely(!moddict)) goto bad;
if (unlikely(__Pyx_copy_spec_to_module(spec, moddict, "loader", "__loader__", 1) < 0)) goto bad;
if (unlikely(__Pyx_copy_spec_to_module(spec, moddict, "origin", "__file__", 1) < 0)) goto bad;
if (unlikely(__Pyx_copy_spec_to_module(spec, moddict, "parent", "__package__", 1) < 0)) goto bad;
if (unlikely(__Pyx_copy_spec_to_module(spec, moddict, "submodule_search_locations", "__path__", 0) < 0)) goto bad;
return module;
bad:
Py_XDECREF(module);
return NULL;
}
static CYTHON_SMALL_CODE int __pyx_pymod_exec_circles_ext(PyObject *__pyx_pyinit_module)
#endif
#endif
{
PyObject *__pyx_t_1 = NULL;
static PyThread_type_lock __pyx_t_2[8];
int __pyx_lineno = 0;
const char *__pyx_filename = NULL;
int __pyx_clineno = 0;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
#if CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
if (__pyx_m) {
if (__pyx_m == __pyx_pyinit_module) return 0;
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_RuntimeError, "Module 'circles_ext' has already been imported. Re-initialisation is not supported.");
return -1;
}
#elif PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
if (__pyx_m) return __Pyx_NewRef(__pyx_m);
#endif
#if CYTHON_REFNANNY
__Pyx_RefNanny = __Pyx_RefNannyImportAPI("refnanny");
if (!__Pyx_RefNanny) {
PyErr_Clear();
__Pyx_RefNanny = __Pyx_RefNannyImportAPI("Cython.Runtime.refnanny");
if (!__Pyx_RefNanny)
Py_FatalError("failed to import 'refnanny' module");
}
#endif
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__Pyx_PyMODINIT_FUNC PyInit_circles_ext(void)", 0);
if (__Pyx_check_binary_version() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#ifdef __Pxy_PyFrame_Initialize_Offsets
__Pxy_PyFrame_Initialize_Offsets();
#endif
__pyx_empty_tuple = PyTuple_New(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_empty_tuple)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_empty_bytes = PyBytes_FromStringAndSize("", 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_empty_bytes)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__pyx_empty_unicode = PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize("", 0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_empty_unicode)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#ifdef __Pyx_CyFunction_USED
if (__pyx_CyFunction_init() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
#ifdef __Pyx_FusedFunction_USED
if (__pyx_FusedFunction_init() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
#ifdef __Pyx_Coroutine_USED
if (__pyx_Coroutine_init() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
#ifdef __Pyx_Generator_USED
if (__pyx_Generator_init() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
#ifdef __Pyx_AsyncGen_USED
if (__pyx_AsyncGen_init() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
#ifdef __Pyx_StopAsyncIteration_USED
if (__pyx_StopAsyncIteration_init() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
/*--- Library function declarations ---*/
/*--- Threads initialization code ---*/
#if defined(__PYX_FORCE_INIT_THREADS) && __PYX_FORCE_INIT_THREADS
#ifdef WITH_THREAD /* Python build with threading support? */
PyEval_InitThreads();
#endif
#endif
/*--- Module creation code ---*/
#if CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
__pyx_m = __pyx_pyinit_module;
Py_INCREF(__pyx_m);
#else
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
__pyx_m = Py_InitModule4("circles_ext", __pyx_methods, 0, 0, PYTHON_API_VERSION); Py_XINCREF(__pyx_m);
#else
__pyx_m = PyModule_Create(&__pyx_moduledef);
#endif
if (unlikely(!__pyx_m)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
__pyx_d = PyModule_GetDict(__pyx_m); if (unlikely(!__pyx_d)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
Py_INCREF(__pyx_d);
__pyx_b = PyImport_AddModule(__Pyx_BUILTIN_MODULE_NAME); if (unlikely(!__pyx_b)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
Py_INCREF(__pyx_b);
__pyx_cython_runtime = PyImport_AddModule((char *) "cython_runtime"); if (unlikely(!__pyx_cython_runtime)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
Py_INCREF(__pyx_cython_runtime);
if (PyObject_SetAttrString(__pyx_m, "__builtins__", __pyx_b) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error);
/*--- Initialize various global constants etc. ---*/
if (__Pyx_InitGlobals() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 && (__PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII || __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT)
if (__Pyx_init_sys_getdefaultencoding_params() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
if (__pyx_module_is_main_pept__processing__circles_ext) {
if (PyObject_SetAttr(__pyx_m, __pyx_n_s_name_2, __pyx_n_s_main) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
}
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
{
PyObject *modules = PyImport_GetModuleDict(); if (unlikely(!modules)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
if (!PyDict_GetItemString(modules, "pept.processing.circles_ext")) {
if (unlikely(PyDict_SetItemString(modules, "pept.processing.circles_ext", __pyx_m) < 0)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
}
}
#endif
/*--- Builtin init code ---*/
if (__Pyx_InitCachedBuiltins() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
/*--- Constants init code ---*/
if (__Pyx_InitCachedConstants() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
/*--- Global type/function init code ---*/
(void)__Pyx_modinit_global_init_code();
(void)__Pyx_modinit_variable_export_code();
(void)__Pyx_modinit_function_export_code();
if (unlikely(__Pyx_modinit_type_init_code() < 0)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
(void)__Pyx_modinit_type_import_code();
(void)__Pyx_modinit_variable_import_code();
(void)__Pyx_modinit_function_import_code();
/*--- Execution code ---*/
#if defined(__Pyx_Generator_USED) || defined(__Pyx_Coroutine_USED)
if (__Pyx_patch_abc() < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
#endif
/* "pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx":1
* # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(0); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_d, __pyx_n_s_test, __pyx_t_1) < 0) __PYX_ERR(0, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":209
* info.obj = self
*
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_array_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* def __dealloc__(array self):
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_capsule_create(((void *)(&__pyx_array_getbuffer)), ((char *)"getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 209, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (PyDict_SetItem((PyObject *)__pyx_array_type->tp_dict, __pyx_n_s_pyx_getbuffer, __pyx_t_1) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 209, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
PyType_Modified(__pyx_array_type);
/* "View.MemoryView":286
* return self.name
*
* cdef generic = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef strided = Enum("") # default
* cdef indirect = Enum("")
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_MemviewEnum_type), __pyx_tuple__19, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 286, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(generic);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(generic, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":287
*
* cdef generic = Enum("")
* cdef strided = Enum("") # default # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef indirect = Enum("")
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_MemviewEnum_type), __pyx_tuple__20, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 287, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(strided);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(strided, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":288
* cdef generic = Enum("")
* cdef strided = Enum("") # default
* cdef indirect = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_MemviewEnum_type), __pyx_tuple__21, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 288, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(indirect);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(indirect, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":291
*
*
* cdef contiguous = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef indirect_contiguous = Enum("")
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_MemviewEnum_type), __pyx_tuple__22, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 291, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(contiguous);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(contiguous, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":292
*
* cdef contiguous = Enum("")
* cdef indirect_contiguous = Enum("") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(((PyObject *)__pyx_MemviewEnum_type), __pyx_tuple__23, NULL); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 292, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_XGOTREF(indirect_contiguous);
__Pyx_DECREF_SET(indirect_contiguous, __pyx_t_1);
__Pyx_GIVEREF(__pyx_t_1);
__pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":316
*
* DEF THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED = 8
* cdef int __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used = 0 # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef PyThread_type_lock[THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED] __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks = [
* PyThread_allocate_lock(),
*/
__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used = 0;
/* "View.MemoryView":317
* DEF THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED = 8
* cdef int __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used = 0
* cdef PyThread_type_lock[THREAD_LOCKS_PREALLOCATED] __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks = [ # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* PyThread_allocate_lock(),
* PyThread_allocate_lock(),
*/
__pyx_t_2[0] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
__pyx_t_2[1] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
__pyx_t_2[2] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
__pyx_t_2[3] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
__pyx_t_2[4] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
__pyx_t_2[5] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
__pyx_t_2[6] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
__pyx_t_2[7] = PyThread_allocate_lock();
memcpy(&(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[0]), __pyx_t_2, sizeof(__pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[0]) * (8));
/* "View.MemoryView":549
* info.obj = self
*
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_memoryview_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_capsule_create(((void *)(&__pyx_memoryview_getbuffer)), ((char *)"getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 549, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (PyDict_SetItem((PyObject *)__pyx_memoryview_type->tp_dict, __pyx_n_s_pyx_getbuffer, __pyx_t_1) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 549, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
PyType_Modified(__pyx_memoryview_type);
/* "View.MemoryView":995
* return self.from_object
*
* __pyx_getbuffer = capsule( &__pyx_memoryview_getbuffer, "getbuffer(obj, view, flags)") # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
*
*/
__pyx_t_1 = __pyx_capsule_create(((void *)(&__pyx_memoryview_getbuffer)), ((char *)"getbuffer(obj, view, flags)")); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 995, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (PyDict_SetItem((PyObject *)__pyx_memoryviewslice_type->tp_dict, __pyx_n_s_pyx_getbuffer, __pyx_t_1) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 995, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
PyType_Modified(__pyx_memoryviewslice_type);
/* "(tree fragment)":1
* def __pyx_unpickle_Enum(__pyx_type, long __pyx_checksum, __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef object __pyx_PickleError
* cdef object __pyx_result
*/
__pyx_t_1 = PyCFunction_NewEx(&__pyx_mdef_15View_dot_MemoryView_1__pyx_unpickle_Enum, NULL, __pyx_n_s_View_MemoryView); if (unlikely(!__pyx_t_1)) __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_GOTREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (PyDict_SetItem(__pyx_d, __pyx_n_s_pyx_unpickle_Enum, __pyx_t_1) < 0) __PYX_ERR(1, 1, __pyx_L1_error)
__Pyx_DECREF(__pyx_t_1); __pyx_t_1 = 0;
/* "(tree fragment)":11
* __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state( __pyx_result, __pyx_state)
* return __pyx_result
* cdef __pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(Enum __pyx_result, tuple __pyx_state): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* __pyx_result.name = __pyx_state[0]
* if len(__pyx_state) > 1 and hasattr(__pyx_result, '__dict__'):
*/
/*--- Wrapped vars code ---*/
goto __pyx_L0;
__pyx_L1_error:;
__Pyx_XDECREF(__pyx_t_1);
if (__pyx_m) {
if (__pyx_d) {
__Pyx_AddTraceback("init pept.processing.circles_ext", __pyx_clineno, __pyx_lineno, __pyx_filename);
}
Py_CLEAR(__pyx_m);
} else if (!PyErr_Occurred()) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ImportError, "init pept.processing.circles_ext");
}
__pyx_L0:;
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
#if CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
return (__pyx_m != NULL) ? 0 : -1;
#elif PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
return __pyx_m;
#else
return;
#endif
}
/* --- Runtime support code --- */
/* Refnanny */
#if CYTHON_REFNANNY
static __Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct *__Pyx_RefNannyImportAPI(const char *modname) {
PyObject *m = NULL, *p = NULL;
void *r = NULL;
m = PyImport_ImportModule(modname);
if (!m) goto end;
p = PyObject_GetAttrString(m, "RefNannyAPI");
if (!p) goto end;
r = PyLong_AsVoidPtr(p);
end:
Py_XDECREF(p);
Py_XDECREF(m);
return (__Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct *)r;
}
#endif
/* PyObjectGetAttrStr */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name) {
PyTypeObject* tp = Py_TYPE(obj);
if (likely(tp->tp_getattro))
return tp->tp_getattro(obj, attr_name);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(tp->tp_getattr))
return tp->tp_getattr(obj, PyString_AS_STRING(attr_name));
#endif
return PyObject_GetAttr(obj, attr_name);
}
#endif
/* GetBuiltinName */
static PyObject *__Pyx_GetBuiltinName(PyObject *name) {
PyObject* result = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_b, name);
if (unlikely(!result)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_NameError,
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
"name '%U' is not defined", name);
#else
"name '%.200s' is not defined", PyString_AS_STRING(name));
#endif
}
return result;
}
/* RaiseArgTupleInvalid */
static void __Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid(
const char* func_name,
int exact,
Py_ssize_t num_min,
Py_ssize_t num_max,
Py_ssize_t num_found)
{
Py_ssize_t num_expected;
const char *more_or_less;
if (num_found < num_min) {
num_expected = num_min;
more_or_less = "at least";
} else {
num_expected = num_max;
more_or_less = "at most";
}
if (exact) {
more_or_less = "exactly";
}
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError,
"%.200s() takes %.8s %" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "d positional argument%.1s (%" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "d given)",
func_name, more_or_less, num_expected,
(num_expected == 1) ? "" : "s", num_found);
}
/* RaiseDoubleKeywords */
static void __Pyx_RaiseDoubleKeywordsError(
const char* func_name,
PyObject* kw_name)
{
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError,
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
"%s() got multiple values for keyword argument '%U'", func_name, kw_name);
#else
"%s() got multiple values for keyword argument '%s'", func_name,
PyString_AsString(kw_name));
#endif
}
/* ParseKeywords */
static int __Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(
PyObject *kwds,
PyObject **argnames[],
PyObject *kwds2,
PyObject *values[],
Py_ssize_t num_pos_args,
const char* function_name)
{
PyObject *key = 0, *value = 0;
Py_ssize_t pos = 0;
PyObject*** name;
PyObject*** first_kw_arg = argnames + num_pos_args;
while (PyDict_Next(kwds, &pos, &key, &value)) {
name = first_kw_arg;
while (*name && (**name != key)) name++;
if (*name) {
values[name-argnames] = value;
continue;
}
name = first_kw_arg;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(PyString_Check(key))) {
while (*name) {
if ((CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY || PyString_GET_SIZE(**name) == PyString_GET_SIZE(key))
&& _PyString_Eq(**name, key)) {
values[name-argnames] = value;
break;
}
name++;
}
if (*name) continue;
else {
PyObject*** argname = argnames;
while (argname != first_kw_arg) {
if ((**argname == key) || (
(CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY || PyString_GET_SIZE(**argname) == PyString_GET_SIZE(key))
&& _PyString_Eq(**argname, key))) {
goto arg_passed_twice;
}
argname++;
}
}
} else
#endif
if (likely(PyUnicode_Check(key))) {
while (*name) {
int cmp = (**name == key) ? 0 :
#if !CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
(__Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(**name) != __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(key)) ? 1 :
#endif
PyUnicode_Compare(**name, key);
if (cmp < 0 && unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) goto bad;
if (cmp == 0) {
values[name-argnames] = value;
break;
}
name++;
}
if (*name) continue;
else {
PyObject*** argname = argnames;
while (argname != first_kw_arg) {
int cmp = (**argname == key) ? 0 :
#if !CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
(__Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(**argname) != __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(key)) ? 1 :
#endif
PyUnicode_Compare(**argname, key);
if (cmp < 0 && unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) goto bad;
if (cmp == 0) goto arg_passed_twice;
argname++;
}
}
} else
goto invalid_keyword_type;
if (kwds2) {
if (unlikely(PyDict_SetItem(kwds2, key, value))) goto bad;
} else {
goto invalid_keyword;
}
}
return 0;
arg_passed_twice:
__Pyx_RaiseDoubleKeywordsError(function_name, key);
goto bad;
invalid_keyword_type:
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError,
"%.200s() keywords must be strings", function_name);
goto bad;
invalid_keyword:
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError,
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
"%.200s() got an unexpected keyword argument '%.200s'",
function_name, PyString_AsString(key));
#else
"%s() got an unexpected keyword argument '%U'",
function_name, key);
#endif
bad:
return -1;
}
/* MemviewSliceInit */
static int
__Pyx_init_memviewslice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview,
int ndim,
__Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice,
int memview_is_new_reference)
{
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int i, retval=-1;
Py_buffer *buf = &memview->view;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("init_memviewslice", 0);
if (unlikely(memviewslice->memview || memviewslice->data)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"memviewslice is already initialized!");
goto fail;
}
if (buf->strides) {
for (i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
memviewslice->strides[i] = buf->strides[i];
}
} else {
Py_ssize_t stride = buf->itemsize;
for (i = ndim - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
memviewslice->strides[i] = stride;
stride *= buf->shape[i];
}
}
for (i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
memviewslice->shape[i] = buf->shape[i];
if (buf->suboffsets) {
memviewslice->suboffsets[i] = buf->suboffsets[i];
} else {
memviewslice->suboffsets[i] = -1;
}
}
memviewslice->memview = memview;
memviewslice->data = (char *)buf->buf;
if (__pyx_add_acquisition_count(memview) == 0 && !memview_is_new_reference) {
Py_INCREF(memview);
}
retval = 0;
goto no_fail;
fail:
memviewslice->memview = 0;
memviewslice->data = 0;
retval = -1;
no_fail:
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return retval;
}
#ifndef Py_NO_RETURN
#define Py_NO_RETURN
#endif
static void __pyx_fatalerror(const char *fmt, ...) Py_NO_RETURN {
va_list vargs;
char msg[200];
#ifdef HAVE_STDARG_PROTOTYPES
va_start(vargs, fmt);
#else
va_start(vargs);
#endif
vsnprintf(msg, 200, fmt, vargs);
va_end(vargs);
Py_FatalError(msg);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int
__pyx_add_acquisition_count_locked(__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count,
PyThread_type_lock lock)
{
int result;
PyThread_acquire_lock(lock, 1);
result = (*acquisition_count)++;
PyThread_release_lock(lock);
return result;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int
__pyx_sub_acquisition_count_locked(__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count,
PyThread_type_lock lock)
{
int result;
PyThread_acquire_lock(lock, 1);
result = (*acquisition_count)--;
PyThread_release_lock(lock);
return result;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void
__Pyx_INC_MEMVIEW(__Pyx_memviewslice *memslice, int have_gil, int lineno)
{
int first_time;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview = memslice->memview;
if (unlikely(!memview || (PyObject *) memview == Py_None))
return;
if (unlikely(__pyx_get_slice_count(memview) < 0))
__pyx_fatalerror("Acquisition count is %d (line %d)",
__pyx_get_slice_count(memview), lineno);
first_time = __pyx_add_acquisition_count(memview) == 0;
if (unlikely(first_time)) {
if (have_gil) {
Py_INCREF((PyObject *) memview);
} else {
PyGILState_STATE _gilstate = PyGILState_Ensure();
Py_INCREF((PyObject *) memview);
PyGILState_Release(_gilstate);
}
}
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_XDEC_MEMVIEW(__Pyx_memviewslice *memslice,
int have_gil, int lineno) {
int last_time;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview = memslice->memview;
if (unlikely(!memview || (PyObject *) memview == Py_None)) {
memslice->memview = NULL;
return;
}
if (unlikely(__pyx_get_slice_count(memview) <= 0))
__pyx_fatalerror("Acquisition count is %d (line %d)",
__pyx_get_slice_count(memview), lineno);
last_time = __pyx_sub_acquisition_count(memview) == 1;
memslice->data = NULL;
if (unlikely(last_time)) {
if (have_gil) {
Py_CLEAR(memslice->memview);
} else {
PyGILState_STATE _gilstate = PyGILState_Ensure();
Py_CLEAR(memslice->memview);
PyGILState_Release(_gilstate);
}
} else {
memslice->memview = NULL;
}
}
/* ArgTypeTest */
static int __Pyx__ArgTypeTest(PyObject *obj, PyTypeObject *type, const char *name, int exact)
{
if (unlikely(!type)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_SystemError, "Missing type object");
return 0;
}
else if (exact) {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION == 2
if ((type == &PyBaseString_Type) && likely(__Pyx_PyBaseString_CheckExact(obj))) return 1;
#endif
}
else {
if (likely(__Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, type))) return 1;
}
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError,
"Argument '%.200s' has incorrect type (expected %.200s, got %.200s)",
name, type->tp_name, Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_name);
return 0;
}
/* PyObjectCall */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_Call(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg, PyObject *kw) {
PyObject *result;
ternaryfunc call = func->ob_type->tp_call;
if (unlikely(!call))
return PyObject_Call(func, arg, kw);
if (unlikely(Py_EnterRecursiveCall((char*)" while calling a Python object")))
return NULL;
result = (*call)(func, arg, kw);
Py_LeaveRecursiveCall();
if (unlikely(!result) && unlikely(!PyErr_Occurred())) {
PyErr_SetString(
PyExc_SystemError,
"NULL result without error in PyObject_Call");
}
return result;
}
#endif
/* PyErrFetchRestore */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb) {
PyObject *tmp_type, *tmp_value, *tmp_tb;
tmp_type = tstate->curexc_type;
tmp_value = tstate->curexc_value;
tmp_tb = tstate->curexc_traceback;
tstate->curexc_type = type;
tstate->curexc_value = value;
tstate->curexc_traceback = tb;
Py_XDECREF(tmp_type);
Py_XDECREF(tmp_value);
Py_XDECREF(tmp_tb);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb) {
*type = tstate->curexc_type;
*value = tstate->curexc_value;
*tb = tstate->curexc_traceback;
tstate->curexc_type = 0;
tstate->curexc_value = 0;
tstate->curexc_traceback = 0;
}
#endif
/* RaiseException */
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
static void __Pyx_Raise(PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb,
CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject *cause) {
__Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
Py_XINCREF(type);
if (!value || value == Py_None)
value = NULL;
else
Py_INCREF(value);
if (!tb || tb == Py_None)
tb = NULL;
else {
Py_INCREF(tb);
if (!PyTraceBack_Check(tb)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"raise: arg 3 must be a traceback or None");
goto raise_error;
}
}
if (PyType_Check(type)) {
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
if (!value) {
Py_INCREF(Py_None);
value = Py_None;
}
#endif
PyErr_NormalizeException(&type, &value, &tb);
} else {
if (value) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"instance exception may not have a separate value");
goto raise_error;
}
value = type;
type = (PyObject*) Py_TYPE(type);
Py_INCREF(type);
if (!PyType_IsSubtype((PyTypeObject *)type, (PyTypeObject *)PyExc_BaseException)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"raise: exception class must be a subclass of BaseException");
goto raise_error;
}
}
__Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
__Pyx_ErrRestore(type, value, tb);
return;
raise_error:
Py_XDECREF(value);
Py_XDECREF(type);
Py_XDECREF(tb);
return;
}
#else
static void __Pyx_Raise(PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb, PyObject *cause) {
PyObject* owned_instance = NULL;
if (tb == Py_None) {
tb = 0;
} else if (tb && !PyTraceBack_Check(tb)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"raise: arg 3 must be a traceback or None");
goto bad;
}
if (value == Py_None)
value = 0;
if (PyExceptionInstance_Check(type)) {
if (value) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"instance exception may not have a separate value");
goto bad;
}
value = type;
type = (PyObject*) Py_TYPE(value);
} else if (PyExceptionClass_Check(type)) {
PyObject *instance_class = NULL;
if (value && PyExceptionInstance_Check(value)) {
instance_class = (PyObject*) Py_TYPE(value);
if (instance_class != type) {
int is_subclass = PyObject_IsSubclass(instance_class, type);
if (!is_subclass) {
instance_class = NULL;
} else if (unlikely(is_subclass == -1)) {
goto bad;
} else {
type = instance_class;
}
}
}
if (!instance_class) {
PyObject *args;
if (!value)
args = PyTuple_New(0);
else if (PyTuple_Check(value)) {
Py_INCREF(value);
args = value;
} else
args = PyTuple_Pack(1, value);
if (!args)
goto bad;
owned_instance = PyObject_Call(type, args, NULL);
Py_DECREF(args);
if (!owned_instance)
goto bad;
value = owned_instance;
if (!PyExceptionInstance_Check(value)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError,
"calling %R should have returned an instance of "
"BaseException, not %R",
type, Py_TYPE(value));
goto bad;
}
}
} else {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"raise: exception class must be a subclass of BaseException");
goto bad;
}
if (cause) {
PyObject *fixed_cause;
if (cause == Py_None) {
fixed_cause = NULL;
} else if (PyExceptionClass_Check(cause)) {
fixed_cause = PyObject_CallObject(cause, NULL);
if (fixed_cause == NULL)
goto bad;
} else if (PyExceptionInstance_Check(cause)) {
fixed_cause = cause;
Py_INCREF(fixed_cause);
} else {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"exception causes must derive from "
"BaseException");
goto bad;
}
PyException_SetCause(value, fixed_cause);
}
PyErr_SetObject(type, value);
if (tb) {
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
PyObject *tmp_type, *tmp_value, *tmp_tb;
PyErr_Fetch(&tmp_type, &tmp_value, &tmp_tb);
Py_INCREF(tb);
PyErr_Restore(tmp_type, tmp_value, tb);
Py_XDECREF(tmp_tb);
#else
PyThreadState *tstate = __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current;
PyObject* tmp_tb = tstate->curexc_traceback;
if (tb != tmp_tb) {
Py_INCREF(tb);
tstate->curexc_traceback = tb;
Py_XDECREF(tmp_tb);
}
#endif
}
bad:
Py_XDECREF(owned_instance);
return;
}
#endif
/* PyCFunctionFastCall */
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject * __Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(PyObject *func_obj, PyObject **args, Py_ssize_t nargs) {
PyCFunctionObject *func = (PyCFunctionObject*)func_obj;
PyCFunction meth = PyCFunction_GET_FUNCTION(func);
PyObject *self = PyCFunction_GET_SELF(func);
int flags = PyCFunction_GET_FLAGS(func);
assert(PyCFunction_Check(func));
assert(METH_FASTCALL == (flags & ~(METH_CLASS | METH_STATIC | METH_COEXIST | METH_KEYWORDS | METH_STACKLESS)));
assert(nargs >= 0);
assert(nargs == 0 || args != NULL);
/* _PyCFunction_FastCallDict() must not be called with an exception set,
because it may clear it (directly or indirectly) and so the
caller loses its exception */
assert(!PyErr_Occurred());
if ((PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030700A0) || unlikely(flags & METH_KEYWORDS)) {
return (*((__Pyx_PyCFunctionFastWithKeywords)(void*)meth)) (self, args, nargs, NULL);
} else {
return (*((__Pyx_PyCFunctionFast)(void*)meth)) (self, args, nargs);
}
}
#endif
/* PyFunctionFastCall */
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
static PyObject* __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallNoKw(PyCodeObject *co, PyObject **args, Py_ssize_t na,
PyObject *globals) {
PyFrameObject *f;
PyThreadState *tstate = __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current;
PyObject **fastlocals;
Py_ssize_t i;
PyObject *result;
assert(globals != NULL);
/* XXX Perhaps we should create a specialized
PyFrame_New() that doesn't take locals, but does
take builtins without sanity checking them.
*/
assert(tstate != NULL);
f = PyFrame_New(tstate, co, globals, NULL);
if (f == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
fastlocals = __Pyx_PyFrame_GetLocalsplus(f);
for (i = 0; i < na; i++) {
Py_INCREF(*args);
fastlocals[i] = *args++;
}
result = PyEval_EvalFrameEx(f,0);
++tstate->recursion_depth;
Py_DECREF(f);
--tstate->recursion_depth;
return result;
}
#if 1 || PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030600B1
static PyObject *__Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallDict(PyObject *func, PyObject **args, Py_ssize_t nargs, PyObject *kwargs) {
PyCodeObject *co = (PyCodeObject *)PyFunction_GET_CODE(func);
PyObject *globals = PyFunction_GET_GLOBALS(func);
PyObject *argdefs = PyFunction_GET_DEFAULTS(func);
PyObject *closure;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
PyObject *kwdefs;
#endif
PyObject *kwtuple, **k;
PyObject **d;
Py_ssize_t nd;
Py_ssize_t nk;
PyObject *result;
assert(kwargs == NULL || PyDict_Check(kwargs));
nk = kwargs ? PyDict_Size(kwargs) : 0;
if (Py_EnterRecursiveCall((char*)" while calling a Python object")) {
return NULL;
}
if (
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
co->co_kwonlyargcount == 0 &&
#endif
likely(kwargs == NULL || nk == 0) &&
co->co_flags == (CO_OPTIMIZED | CO_NEWLOCALS | CO_NOFREE)) {
if (argdefs == NULL && co->co_argcount == nargs) {
result = __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallNoKw(co, args, nargs, globals);
goto done;
}
else if (nargs == 0 && argdefs != NULL
&& co->co_argcount == Py_SIZE(argdefs)) {
/* function called with no arguments, but all parameters have
a default value: use default values as arguments .*/
args = &PyTuple_GET_ITEM(argdefs, 0);
result =__Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallNoKw(co, args, Py_SIZE(argdefs), globals);
goto done;
}
}
if (kwargs != NULL) {
Py_ssize_t pos, i;
kwtuple = PyTuple_New(2 * nk);
if (kwtuple == NULL) {
result = NULL;
goto done;
}
k = &PyTuple_GET_ITEM(kwtuple, 0);
pos = i = 0;
while (PyDict_Next(kwargs, &pos, &k[i], &k[i+1])) {
Py_INCREF(k[i]);
Py_INCREF(k[i+1]);
i += 2;
}
nk = i / 2;
}
else {
kwtuple = NULL;
k = NULL;
}
closure = PyFunction_GET_CLOSURE(func);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
kwdefs = PyFunction_GET_KW_DEFAULTS(func);
#endif
if (argdefs != NULL) {
d = &PyTuple_GET_ITEM(argdefs, 0);
nd = Py_SIZE(argdefs);
}
else {
d = NULL;
nd = 0;
}
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
result = PyEval_EvalCodeEx((PyObject*)co, globals, (PyObject *)NULL,
args, (int)nargs,
k, (int)nk,
d, (int)nd, kwdefs, closure);
#else
result = PyEval_EvalCodeEx(co, globals, (PyObject *)NULL,
args, (int)nargs,
k, (int)nk,
d, (int)nd, closure);
#endif
Py_XDECREF(kwtuple);
done:
Py_LeaveRecursiveCall();
return result;
}
#endif
#endif
/* PyObjectCall2Args */
static CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(PyObject* function, PyObject* arg1, PyObject* arg2) {
PyObject *args, *result = NULL;
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
if (PyFunction_Check(function)) {
PyObject *args[2] = {arg1, arg2};
return __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCall(function, args, 2);
}
#endif
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
if (__Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(function)) {
PyObject *args[2] = {arg1, arg2};
return __Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(function, args, 2);
}
#endif
args = PyTuple_New(2);
if (unlikely(!args)) goto done;
Py_INCREF(arg1);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(args, 0, arg1);
Py_INCREF(arg2);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(args, 1, arg2);
Py_INCREF(function);
result = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(function, args, NULL);
Py_DECREF(args);
Py_DECREF(function);
done:
return result;
}
/* PyObjectCallMethO */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_CallMethO(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg) {
PyObject *self, *result;
PyCFunction cfunc;
cfunc = PyCFunction_GET_FUNCTION(func);
self = PyCFunction_GET_SELF(func);
if (unlikely(Py_EnterRecursiveCall((char*)" while calling a Python object")))
return NULL;
result = cfunc(self, arg);
Py_LeaveRecursiveCall();
if (unlikely(!result) && unlikely(!PyErr_Occurred())) {
PyErr_SetString(
PyExc_SystemError,
"NULL result without error in PyObject_Call");
}
return result;
}
#endif
/* PyObjectCallOneArg */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static PyObject* __Pyx__PyObject_CallOneArg(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg) {
PyObject *result;
PyObject *args = PyTuple_New(1);
if (unlikely(!args)) return NULL;
Py_INCREF(arg);
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(args, 0, arg);
result = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(func, args, NULL);
Py_DECREF(args);
return result;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg) {
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
if (PyFunction_Check(func)) {
return __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCall(func, &arg, 1);
}
#endif
if (likely(PyCFunction_Check(func))) {
if (likely(PyCFunction_GET_FLAGS(func) & METH_O)) {
return __Pyx_PyObject_CallMethO(func, arg);
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
} else if (__Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(func)) {
return __Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(func, &arg, 1);
#endif
}
}
return __Pyx__PyObject_CallOneArg(func, arg);
}
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg) {
PyObject *result;
PyObject *args = PyTuple_Pack(1, arg);
if (unlikely(!args)) return NULL;
result = __Pyx_PyObject_Call(func, args, NULL);
Py_DECREF(args);
return result;
}
#endif
/* BytesEquals */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyBytes_Equals(PyObject* s1, PyObject* s2, int equals) {
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
return PyObject_RichCompareBool(s1, s2, equals);
#else
if (s1 == s2) {
return (equals == Py_EQ);
} else if (PyBytes_CheckExact(s1) & PyBytes_CheckExact(s2)) {
const char *ps1, *ps2;
Py_ssize_t length = PyBytes_GET_SIZE(s1);
if (length != PyBytes_GET_SIZE(s2))
return (equals == Py_NE);
ps1 = PyBytes_AS_STRING(s1);
ps2 = PyBytes_AS_STRING(s2);
if (ps1[0] != ps2[0]) {
return (equals == Py_NE);
} else if (length == 1) {
return (equals == Py_EQ);
} else {
int result;
#if CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
Py_hash_t hash1, hash2;
hash1 = ((PyBytesObject*)s1)->ob_shash;
hash2 = ((PyBytesObject*)s2)->ob_shash;
if (hash1 != hash2 && hash1 != -1 && hash2 != -1) {
return (equals == Py_NE);
}
#endif
result = memcmp(ps1, ps2, (size_t)length);
return (equals == Py_EQ) ? (result == 0) : (result != 0);
}
} else if ((s1 == Py_None) & PyBytes_CheckExact(s2)) {
return (equals == Py_NE);
} else if ((s2 == Py_None) & PyBytes_CheckExact(s1)) {
return (equals == Py_NE);
} else {
int result;
PyObject* py_result = PyObject_RichCompare(s1, s2, equals);
if (!py_result)
return -1;
result = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(py_result);
Py_DECREF(py_result);
return result;
}
#endif
}
/* UnicodeEquals */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyUnicode_Equals(PyObject* s1, PyObject* s2, int equals) {
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
return PyObject_RichCompareBool(s1, s2, equals);
#else
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
PyObject* owned_ref = NULL;
#endif
int s1_is_unicode, s2_is_unicode;
if (s1 == s2) {
goto return_eq;
}
s1_is_unicode = PyUnicode_CheckExact(s1);
s2_is_unicode = PyUnicode_CheckExact(s2);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if ((s1_is_unicode & (!s2_is_unicode)) && PyString_CheckExact(s2)) {
owned_ref = PyUnicode_FromObject(s2);
if (unlikely(!owned_ref))
return -1;
s2 = owned_ref;
s2_is_unicode = 1;
} else if ((s2_is_unicode & (!s1_is_unicode)) && PyString_CheckExact(s1)) {
owned_ref = PyUnicode_FromObject(s1);
if (unlikely(!owned_ref))
return -1;
s1 = owned_ref;
s1_is_unicode = 1;
} else if (((!s2_is_unicode) & (!s1_is_unicode))) {
return __Pyx_PyBytes_Equals(s1, s2, equals);
}
#endif
if (s1_is_unicode & s2_is_unicode) {
Py_ssize_t length;
int kind;
void *data1, *data2;
if (unlikely(__Pyx_PyUnicode_READY(s1) < 0) || unlikely(__Pyx_PyUnicode_READY(s2) < 0))
return -1;
length = __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(s1);
if (length != __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(s2)) {
goto return_ne;
}
#if CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
{
Py_hash_t hash1, hash2;
#if CYTHON_PEP393_ENABLED
hash1 = ((PyASCIIObject*)s1)->hash;
hash2 = ((PyASCIIObject*)s2)->hash;
#else
hash1 = ((PyUnicodeObject*)s1)->hash;
hash2 = ((PyUnicodeObject*)s2)->hash;
#endif
if (hash1 != hash2 && hash1 != -1 && hash2 != -1) {
goto return_ne;
}
}
#endif
kind = __Pyx_PyUnicode_KIND(s1);
if (kind != __Pyx_PyUnicode_KIND(s2)) {
goto return_ne;
}
data1 = __Pyx_PyUnicode_DATA(s1);
data2 = __Pyx_PyUnicode_DATA(s2);
if (__Pyx_PyUnicode_READ(kind, data1, 0) != __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ(kind, data2, 0)) {
goto return_ne;
} else if (length == 1) {
goto return_eq;
} else {
int result = memcmp(data1, data2, (size_t)(length * kind));
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
Py_XDECREF(owned_ref);
#endif
return (equals == Py_EQ) ? (result == 0) : (result != 0);
}
} else if ((s1 == Py_None) & s2_is_unicode) {
goto return_ne;
} else if ((s2 == Py_None) & s1_is_unicode) {
goto return_ne;
} else {
int result;
PyObject* py_result = PyObject_RichCompare(s1, s2, equals);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
Py_XDECREF(owned_ref);
#endif
if (!py_result)
return -1;
result = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(py_result);
Py_DECREF(py_result);
return result;
}
return_eq:
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
Py_XDECREF(owned_ref);
#endif
return (equals == Py_EQ);
return_ne:
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
Py_XDECREF(owned_ref);
#endif
return (equals == Py_NE);
#endif
}
/* GetAttr */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetAttr(PyObject *o, PyObject *n) {
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
if (likely(PyUnicode_Check(n)))
#else
if (likely(PyString_Check(n)))
#endif
return __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(o, n);
#endif
return PyObject_GetAttr(o, n);
}
/* GetItemInt */
static PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(PyObject *o, PyObject* j) {
PyObject *r;
if (!j) return NULL;
r = PyObject_GetItem(o, j);
Py_DECREF(j);
return r;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_List_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED int wraparound,
CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED int boundscheck) {
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
Py_ssize_t wrapped_i = i;
if (wraparound & unlikely(i < 0)) {
wrapped_i += PyList_GET_SIZE(o);
}
if ((!boundscheck) || likely(__Pyx_is_valid_index(wrapped_i, PyList_GET_SIZE(o)))) {
PyObject *r = PyList_GET_ITEM(o, wrapped_i);
Py_INCREF(r);
return r;
}
return __Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(o, PyInt_FromSsize_t(i));
#else
return PySequence_GetItem(o, i);
#endif
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED int wraparound,
CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED int boundscheck) {
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
Py_ssize_t wrapped_i = i;
if (wraparound & unlikely(i < 0)) {
wrapped_i += PyTuple_GET_SIZE(o);
}
if ((!boundscheck) || likely(__Pyx_is_valid_index(wrapped_i, PyTuple_GET_SIZE(o)))) {
PyObject *r = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(o, wrapped_i);
Py_INCREF(r);
return r;
}
return __Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(o, PyInt_FromSsize_t(i));
#else
return PySequence_GetItem(o, i);
#endif
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i, int is_list,
CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED int wraparound,
CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED int boundscheck) {
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS && !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS && CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
if (is_list || PyList_CheckExact(o)) {
Py_ssize_t n = ((!wraparound) | likely(i >= 0)) ? i : i + PyList_GET_SIZE(o);
if ((!boundscheck) || (likely(__Pyx_is_valid_index(n, PyList_GET_SIZE(o))))) {
PyObject *r = PyList_GET_ITEM(o, n);
Py_INCREF(r);
return r;
}
}
else if (PyTuple_CheckExact(o)) {
Py_ssize_t n = ((!wraparound) | likely(i >= 0)) ? i : i + PyTuple_GET_SIZE(o);
if ((!boundscheck) || likely(__Pyx_is_valid_index(n, PyTuple_GET_SIZE(o)))) {
PyObject *r = PyTuple_GET_ITEM(o, n);
Py_INCREF(r);
return r;
}
} else {
PySequenceMethods *m = Py_TYPE(o)->tp_as_sequence;
if (likely(m && m->sq_item)) {
if (wraparound && unlikely(i < 0) && likely(m->sq_length)) {
Py_ssize_t l = m->sq_length(o);
if (likely(l >= 0)) {
i += l;
} else {
if (!PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_OverflowError))
return NULL;
PyErr_Clear();
}
}
return m->sq_item(o, i);
}
}
#else
if (is_list || PySequence_Check(o)) {
return PySequence_GetItem(o, i);
}
#endif
return __Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(o, PyInt_FromSsize_t(i));
}
/* ObjectGetItem */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
static PyObject *__Pyx_PyObject_GetIndex(PyObject *obj, PyObject* index) {
PyObject *runerr;
Py_ssize_t key_value;
PySequenceMethods *m = Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_as_sequence;
if (unlikely(!(m && m->sq_item))) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "'%.200s' object is not subscriptable", Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_name);
return NULL;
}
key_value = __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(index);
if (likely(key_value != -1 || !(runerr = PyErr_Occurred()))) {
return __Pyx_GetItemInt_Fast(obj, key_value, 0, 1, 1);
}
if (PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(runerr, PyExc_OverflowError)) {
PyErr_Clear();
PyErr_Format(PyExc_IndexError, "cannot fit '%.200s' into an index-sized integer", Py_TYPE(index)->tp_name);
}
return NULL;
}
static PyObject *__Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(PyObject *obj, PyObject* key) {
PyMappingMethods *m = Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_as_mapping;
if (likely(m && m->mp_subscript)) {
return m->mp_subscript(obj, key);
}
return __Pyx_PyObject_GetIndex(obj, key);
}
#endif
/* decode_c_string */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_decode_c_string(
const char* cstring, Py_ssize_t start, Py_ssize_t stop,
const char* encoding, const char* errors,
PyObject* (*decode_func)(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors)) {
Py_ssize_t length;
if (unlikely((start < 0) | (stop < 0))) {
size_t slen = strlen(cstring);
if (unlikely(slen > (size_t) PY_SSIZE_T_MAX)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"c-string too long to convert to Python");
return NULL;
}
length = (Py_ssize_t) slen;
if (start < 0) {
start += length;
if (start < 0)
start = 0;
}
if (stop < 0)
stop += length;
}
if (unlikely(stop <= start))
return __Pyx_NewRef(__pyx_empty_unicode);
length = stop - start;
cstring += start;
if (decode_func) {
return decode_func(cstring, length, errors);
} else {
return PyUnicode_Decode(cstring, length, encoding, errors);
}
}
/* PyErrExceptionMatches */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
static int __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatchesTuple(PyObject *exc_type, PyObject *tuple) {
Py_ssize_t i, n;
n = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(tuple);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
for (i=0; icurexc_type;
if (exc_type == err) return 1;
if (unlikely(!exc_type)) return 0;
if (unlikely(PyTuple_Check(err)))
return __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatchesTuple(exc_type, err);
return __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(exc_type, err);
}
#endif
/* GetAttr3 */
static PyObject *__Pyx_GetAttr3Default(PyObject *d) {
__Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
__Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
if (unlikely(!__Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_AttributeError)))
return NULL;
__Pyx_PyErr_Clear();
Py_INCREF(d);
return d;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetAttr3(PyObject *o, PyObject *n, PyObject *d) {
PyObject *r = __Pyx_GetAttr(o, n);
return (likely(r)) ? r : __Pyx_GetAttr3Default(d);
}
/* PyDictVersioning */
#if CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS && CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
static CYTHON_INLINE PY_UINT64_T __Pyx_get_tp_dict_version(PyObject *obj) {
PyObject *dict = Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_dict;
return likely(dict) ? __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict) : 0;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PY_UINT64_T __Pyx_get_object_dict_version(PyObject *obj) {
PyObject **dictptr = NULL;
Py_ssize_t offset = Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_dictoffset;
if (offset) {
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
dictptr = (likely(offset > 0)) ? (PyObject **) ((char *)obj + offset) : _PyObject_GetDictPtr(obj);
#else
dictptr = _PyObject_GetDictPtr(obj);
#endif
}
return (dictptr && *dictptr) ? __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(*dictptr) : 0;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_object_dict_version_matches(PyObject* obj, PY_UINT64_T tp_dict_version, PY_UINT64_T obj_dict_version) {
PyObject *dict = Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_dict;
if (unlikely(!dict) || unlikely(tp_dict_version != __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict)))
return 0;
return obj_dict_version == __Pyx_get_object_dict_version(obj);
}
#endif
/* GetModuleGlobalName */
#if CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
static PyObject *__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(PyObject *name, PY_UINT64_T *dict_version, PyObject **dict_cached_value)
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(PyObject *name)
#endif
{
PyObject *result;
#if !CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON && PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030500A1
result = _PyDict_GetItem_KnownHash(__pyx_d, name, ((PyASCIIObject *) name)->hash);
__PYX_UPDATE_DICT_CACHE(__pyx_d, result, *dict_cached_value, *dict_version)
if (likely(result)) {
return __Pyx_NewRef(result);
} else if (unlikely(PyErr_Occurred())) {
return NULL;
}
#else
result = PyDict_GetItem(__pyx_d, name);
__PYX_UPDATE_DICT_CACHE(__pyx_d, result, *dict_cached_value, *dict_version)
if (likely(result)) {
return __Pyx_NewRef(result);
}
#endif
#else
result = PyObject_GetItem(__pyx_d, name);
__PYX_UPDATE_DICT_CACHE(__pyx_d, result, *dict_cached_value, *dict_version)
if (likely(result)) {
return __Pyx_NewRef(result);
}
PyErr_Clear();
#endif
return __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(name);
}
/* RaiseTooManyValuesToUnpack */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseTooManyValuesError(Py_ssize_t expected) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"too many values to unpack (expected %" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "d)", expected);
}
/* RaiseNeedMoreValuesToUnpack */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseNeedMoreValuesError(Py_ssize_t index) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"need more than %" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "d value%.1s to unpack",
index, (index == 1) ? "" : "s");
}
/* RaiseNoneIterError */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseNoneNotIterableError(void) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, "'NoneType' object is not iterable");
}
/* ExtTypeTest */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_TypeTest(PyObject *obj, PyTypeObject *type) {
if (unlikely(!type)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_SystemError, "Missing type object");
return 0;
}
if (likely(__Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, type)))
return 1;
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "Cannot convert %.200s to %.200s",
Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_name, type->tp_name);
return 0;
}
/* GetTopmostException */
#if CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
static _PyErr_StackItem *
__Pyx_PyErr_GetTopmostException(PyThreadState *tstate)
{
_PyErr_StackItem *exc_info = tstate->exc_info;
while ((exc_info->exc_type == NULL || exc_info->exc_type == Py_None) &&
exc_info->previous_item != NULL)
{
exc_info = exc_info->previous_item;
}
return exc_info;
}
#endif
/* SaveResetException */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionSave(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb) {
#if CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
_PyErr_StackItem *exc_info = __Pyx_PyErr_GetTopmostException(tstate);
*type = exc_info->exc_type;
*value = exc_info->exc_value;
*tb = exc_info->exc_traceback;
#else
*type = tstate->exc_type;
*value = tstate->exc_value;
*tb = tstate->exc_traceback;
#endif
Py_XINCREF(*type);
Py_XINCREF(*value);
Py_XINCREF(*tb);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionReset(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb) {
PyObject *tmp_type, *tmp_value, *tmp_tb;
#if CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
_PyErr_StackItem *exc_info = tstate->exc_info;
tmp_type = exc_info->exc_type;
tmp_value = exc_info->exc_value;
tmp_tb = exc_info->exc_traceback;
exc_info->exc_type = type;
exc_info->exc_value = value;
exc_info->exc_traceback = tb;
#else
tmp_type = tstate->exc_type;
tmp_value = tstate->exc_value;
tmp_tb = tstate->exc_traceback;
tstate->exc_type = type;
tstate->exc_value = value;
tstate->exc_traceback = tb;
#endif
Py_XDECREF(tmp_type);
Py_XDECREF(tmp_value);
Py_XDECREF(tmp_tb);
}
#endif
/* GetException */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
static int __Pyx__GetException(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb)
#else
static int __Pyx_GetException(PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb)
#endif
{
PyObject *local_type, *local_value, *local_tb;
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
PyObject *tmp_type, *tmp_value, *tmp_tb;
local_type = tstate->curexc_type;
local_value = tstate->curexc_value;
local_tb = tstate->curexc_traceback;
tstate->curexc_type = 0;
tstate->curexc_value = 0;
tstate->curexc_traceback = 0;
#else
PyErr_Fetch(&local_type, &local_value, &local_tb);
#endif
PyErr_NormalizeException(&local_type, &local_value, &local_tb);
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
if (unlikely(tstate->curexc_type))
#else
if (unlikely(PyErr_Occurred()))
#endif
goto bad;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
if (local_tb) {
if (unlikely(PyException_SetTraceback(local_value, local_tb) < 0))
goto bad;
}
#endif
Py_XINCREF(local_tb);
Py_XINCREF(local_type);
Py_XINCREF(local_value);
*type = local_type;
*value = local_value;
*tb = local_tb;
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#if CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
{
_PyErr_StackItem *exc_info = tstate->exc_info;
tmp_type = exc_info->exc_type;
tmp_value = exc_info->exc_value;
tmp_tb = exc_info->exc_traceback;
exc_info->exc_type = local_type;
exc_info->exc_value = local_value;
exc_info->exc_traceback = local_tb;
}
#else
tmp_type = tstate->exc_type;
tmp_value = tstate->exc_value;
tmp_tb = tstate->exc_traceback;
tstate->exc_type = local_type;
tstate->exc_value = local_value;
tstate->exc_traceback = local_tb;
#endif
Py_XDECREF(tmp_type);
Py_XDECREF(tmp_value);
Py_XDECREF(tmp_tb);
#else
PyErr_SetExcInfo(local_type, local_value, local_tb);
#endif
return 0;
bad:
*type = 0;
*value = 0;
*tb = 0;
Py_XDECREF(local_type);
Py_XDECREF(local_value);
Py_XDECREF(local_tb);
return -1;
}
/* SwapException */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionSwap(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb) {
PyObject *tmp_type, *tmp_value, *tmp_tb;
#if CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
_PyErr_StackItem *exc_info = tstate->exc_info;
tmp_type = exc_info->exc_type;
tmp_value = exc_info->exc_value;
tmp_tb = exc_info->exc_traceback;
exc_info->exc_type = *type;
exc_info->exc_value = *value;
exc_info->exc_traceback = *tb;
#else
tmp_type = tstate->exc_type;
tmp_value = tstate->exc_value;
tmp_tb = tstate->exc_traceback;
tstate->exc_type = *type;
tstate->exc_value = *value;
tstate->exc_traceback = *tb;
#endif
*type = tmp_type;
*value = tmp_value;
*tb = tmp_tb;
}
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ExceptionSwap(PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb) {
PyObject *tmp_type, *tmp_value, *tmp_tb;
PyErr_GetExcInfo(&tmp_type, &tmp_value, &tmp_tb);
PyErr_SetExcInfo(*type, *value, *tb);
*type = tmp_type;
*value = tmp_value;
*tb = tmp_tb;
}
#endif
/* Import */
static PyObject *__Pyx_Import(PyObject *name, PyObject *from_list, int level) {
PyObject *empty_list = 0;
PyObject *module = 0;
PyObject *global_dict = 0;
PyObject *empty_dict = 0;
PyObject *list;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
PyObject *py_import;
py_import = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_b, __pyx_n_s_import);
if (!py_import)
goto bad;
#endif
if (from_list)
list = from_list;
else {
empty_list = PyList_New(0);
if (!empty_list)
goto bad;
list = empty_list;
}
global_dict = PyModule_GetDict(__pyx_m);
if (!global_dict)
goto bad;
empty_dict = PyDict_New();
if (!empty_dict)
goto bad;
{
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
if (level == -1) {
if ((1) && (strchr(__Pyx_MODULE_NAME, '.'))) {
module = PyImport_ImportModuleLevelObject(
name, global_dict, empty_dict, list, 1);
if (!module) {
if (!PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_ImportError))
goto bad;
PyErr_Clear();
}
}
level = 0;
}
#endif
if (!module) {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
PyObject *py_level = PyInt_FromLong(level);
if (!py_level)
goto bad;
module = PyObject_CallFunctionObjArgs(py_import,
name, global_dict, empty_dict, list, py_level, (PyObject *)NULL);
Py_DECREF(py_level);
#else
module = PyImport_ImportModuleLevelObject(
name, global_dict, empty_dict, list, level);
#endif
}
}
bad:
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
Py_XDECREF(py_import);
#endif
Py_XDECREF(empty_list);
Py_XDECREF(empty_dict);
return module;
}
/* FastTypeChecks */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static int __Pyx_InBases(PyTypeObject *a, PyTypeObject *b) {
while (a) {
a = a->tp_base;
if (a == b)
return 1;
}
return b == &PyBaseObject_Type;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_IsSubtype(PyTypeObject *a, PyTypeObject *b) {
PyObject *mro;
if (a == b) return 1;
mro = a->tp_mro;
if (likely(mro)) {
Py_ssize_t i, n;
n = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(mro);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (PyTuple_GET_ITEM(mro, i) == (PyObject *)b)
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
return __Pyx_InBases(a, b);
}
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION == 2
static int __Pyx_inner_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches2(PyObject *err, PyObject* exc_type1, PyObject* exc_type2) {
PyObject *exception, *value, *tb;
int res;
__Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
__Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
__Pyx_ErrFetch(&exception, &value, &tb);
res = exc_type1 ? PyObject_IsSubclass(err, exc_type1) : 0;
if (unlikely(res == -1)) {
PyErr_WriteUnraisable(err);
res = 0;
}
if (!res) {
res = PyObject_IsSubclass(err, exc_type2);
if (unlikely(res == -1)) {
PyErr_WriteUnraisable(err);
res = 0;
}
}
__Pyx_ErrRestore(exception, value, tb);
return res;
}
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_inner_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches2(PyObject *err, PyObject* exc_type1, PyObject *exc_type2) {
int res = exc_type1 ? __Pyx_IsSubtype((PyTypeObject*)err, (PyTypeObject*)exc_type1) : 0;
if (!res) {
res = __Pyx_IsSubtype((PyTypeObject*)err, (PyTypeObject*)exc_type2);
}
return res;
}
#endif
static int __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatchesTuple(PyObject *exc_type, PyObject *tuple) {
Py_ssize_t i, n;
assert(PyExceptionClass_Check(exc_type));
n = PyTuple_GET_SIZE(tuple);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
for (i=0; i= 0 || (x^b) >= 0))
return PyInt_FromLong(x);
return PyLong_Type.tp_as_number->nb_add(op1, op2);
}
#endif
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
if (likely(PyLong_CheckExact(op1))) {
const long b = intval;
long a, x;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
const PY_LONG_LONG llb = intval;
PY_LONG_LONG lla, llx;
#endif
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)op1)->ob_digit;
const Py_ssize_t size = Py_SIZE(op1);
if (likely(__Pyx_sst_abs(size) <= 1)) {
a = likely(size) ? digits[0] : 0;
if (size == -1) a = -a;
} else {
switch (size) {
case -2:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
a = -(long) (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0]));
break;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (8 * sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
lla = -(PY_LONG_LONG) (((((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[0]));
goto long_long;
#endif
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
a = (long) (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0]));
break;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (8 * sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
lla = (PY_LONG_LONG) (((((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[0]));
goto long_long;
#endif
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case -3:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
a = -(long) (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0]));
break;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (8 * sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
lla = -(PY_LONG_LONG) (((((((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[0]));
goto long_long;
#endif
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
a = (long) (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0]));
break;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (8 * sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
lla = (PY_LONG_LONG) (((((((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[0]));
goto long_long;
#endif
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case -4:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
a = -(long) (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0]));
break;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (8 * sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
lla = -(PY_LONG_LONG) (((((((((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[0]));
goto long_long;
#endif
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
a = (long) (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0]));
break;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (8 * sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
lla = (PY_LONG_LONG) (((((((((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)digits[0]));
goto long_long;
#endif
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
default: return PyLong_Type.tp_as_number->nb_add(op1, op2);
}
}
x = a + b;
return PyLong_FromLong(x);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
long_long:
llx = lla + llb;
return PyLong_FromLongLong(llx);
#endif
}
#endif
if (PyFloat_CheckExact(op1)) {
const long b = intval;
double a = PyFloat_AS_DOUBLE(op1);
double result;
PyFPE_START_PROTECT("add", return NULL)
result = ((double)a) + (double)b;
PyFPE_END_PROTECT(result)
return PyFloat_FromDouble(result);
}
return (inplace ? PyNumber_InPlaceAdd : PyNumber_Add)(op1, op2);
}
#endif
/* None */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseUnboundLocalError(const char *varname) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_UnboundLocalError, "local variable '%s' referenced before assignment", varname);
}
/* ImportFrom */
static PyObject* __Pyx_ImportFrom(PyObject* module, PyObject* name) {
PyObject* value = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(module, name);
if (unlikely(!value) && PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_AttributeError)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ImportError,
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
"cannot import name %.230s", PyString_AS_STRING(name));
#else
"cannot import name %S", name);
#endif
}
return value;
}
/* HasAttr */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_HasAttr(PyObject *o, PyObject *n) {
PyObject *r;
if (unlikely(!__Pyx_PyBaseString_Check(n))) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"hasattr(): attribute name must be string");
return -1;
}
r = __Pyx_GetAttr(o, n);
if (unlikely(!r)) {
PyErr_Clear();
return 0;
} else {
Py_DECREF(r);
return 1;
}
}
/* PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03070000
static PyObject *__Pyx_RaiseGenericGetAttributeError(PyTypeObject *tp, PyObject *attr_name) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_AttributeError,
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
"'%.50s' object has no attribute '%U'",
tp->tp_name, attr_name);
#else
"'%.50s' object has no attribute '%.400s'",
tp->tp_name, PyString_AS_STRING(attr_name));
#endif
return NULL;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name) {
PyObject *descr;
PyTypeObject *tp = Py_TYPE(obj);
if (unlikely(!PyString_Check(attr_name))) {
return PyObject_GenericGetAttr(obj, attr_name);
}
assert(!tp->tp_dictoffset);
descr = _PyType_Lookup(tp, attr_name);
if (unlikely(!descr)) {
return __Pyx_RaiseGenericGetAttributeError(tp, attr_name);
}
Py_INCREF(descr);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(PyType_HasFeature(Py_TYPE(descr), Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_CLASS)))
#endif
{
descrgetfunc f = Py_TYPE(descr)->tp_descr_get;
if (unlikely(f)) {
PyObject *res = f(descr, obj, (PyObject *)tp);
Py_DECREF(descr);
return res;
}
}
return descr;
}
#endif
/* PyObject_GenericGetAttr */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03070000
static PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name) {
if (unlikely(Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_dictoffset)) {
return PyObject_GenericGetAttr(obj, attr_name);
}
return __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict(obj, attr_name);
}
#endif
/* SetVTable */
static int __Pyx_SetVtable(PyObject *dict, void *vtable) {
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x02070000
PyObject *ob = PyCapsule_New(vtable, 0, 0);
#else
PyObject *ob = PyCObject_FromVoidPtr(vtable, 0);
#endif
if (!ob)
goto bad;
if (PyDict_SetItem(dict, __pyx_n_s_pyx_vtable, ob) < 0)
goto bad;
Py_DECREF(ob);
return 0;
bad:
Py_XDECREF(ob);
return -1;
}
/* PyObjectGetAttrStrNoError */
static void __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr_ClearAttributeError(void) {
__Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
__Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
if (likely(__Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatches(PyExc_AttributeError)))
__Pyx_PyErr_Clear();
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStrNoError(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name) {
PyObject *result;
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON && CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030700B1
PyTypeObject* tp = Py_TYPE(obj);
if (likely(tp->tp_getattro == PyObject_GenericGetAttr)) {
return _PyObject_GenericGetAttrWithDict(obj, attr_name, NULL, 1);
}
#endif
result = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(obj, attr_name);
if (unlikely(!result)) {
__Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr_ClearAttributeError();
}
return result;
}
/* SetupReduce */
static int __Pyx_setup_reduce_is_named(PyObject* meth, PyObject* name) {
int ret;
PyObject *name_attr;
name_attr = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(meth, __pyx_n_s_name_2);
if (likely(name_attr)) {
ret = PyObject_RichCompareBool(name_attr, name, Py_EQ);
} else {
ret = -1;
}
if (unlikely(ret < 0)) {
PyErr_Clear();
ret = 0;
}
Py_XDECREF(name_attr);
return ret;
}
static int __Pyx_setup_reduce(PyObject* type_obj) {
int ret = 0;
PyObject *object_reduce = NULL;
PyObject *object_reduce_ex = NULL;
PyObject *reduce = NULL;
PyObject *reduce_ex = NULL;
PyObject *reduce_cython = NULL;
PyObject *setstate = NULL;
PyObject *setstate_cython = NULL;
#if CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
if (_PyType_Lookup((PyTypeObject*)type_obj, __pyx_n_s_getstate)) goto __PYX_GOOD;
#else
if (PyObject_HasAttr(type_obj, __pyx_n_s_getstate)) goto __PYX_GOOD;
#endif
#if CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
object_reduce_ex = _PyType_Lookup(&PyBaseObject_Type, __pyx_n_s_reduce_ex); if (!object_reduce_ex) goto __PYX_BAD;
#else
object_reduce_ex = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr((PyObject*)&PyBaseObject_Type, __pyx_n_s_reduce_ex); if (!object_reduce_ex) goto __PYX_BAD;
#endif
reduce_ex = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(type_obj, __pyx_n_s_reduce_ex); if (unlikely(!reduce_ex)) goto __PYX_BAD;
if (reduce_ex == object_reduce_ex) {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
object_reduce = _PyType_Lookup(&PyBaseObject_Type, __pyx_n_s_reduce); if (!object_reduce) goto __PYX_BAD;
#else
object_reduce = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr((PyObject*)&PyBaseObject_Type, __pyx_n_s_reduce); if (!object_reduce) goto __PYX_BAD;
#endif
reduce = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(type_obj, __pyx_n_s_reduce); if (unlikely(!reduce)) goto __PYX_BAD;
if (reduce == object_reduce || __Pyx_setup_reduce_is_named(reduce, __pyx_n_s_reduce_cython)) {
reduce_cython = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStrNoError(type_obj, __pyx_n_s_reduce_cython);
if (likely(reduce_cython)) {
ret = PyDict_SetItem(((PyTypeObject*)type_obj)->tp_dict, __pyx_n_s_reduce, reduce_cython); if (unlikely(ret < 0)) goto __PYX_BAD;
ret = PyDict_DelItem(((PyTypeObject*)type_obj)->tp_dict, __pyx_n_s_reduce_cython); if (unlikely(ret < 0)) goto __PYX_BAD;
} else if (reduce == object_reduce || PyErr_Occurred()) {
goto __PYX_BAD;
}
setstate = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(type_obj, __pyx_n_s_setstate);
if (!setstate) PyErr_Clear();
if (!setstate || __Pyx_setup_reduce_is_named(setstate, __pyx_n_s_setstate_cython)) {
setstate_cython = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStrNoError(type_obj, __pyx_n_s_setstate_cython);
if (likely(setstate_cython)) {
ret = PyDict_SetItem(((PyTypeObject*)type_obj)->tp_dict, __pyx_n_s_setstate, setstate_cython); if (unlikely(ret < 0)) goto __PYX_BAD;
ret = PyDict_DelItem(((PyTypeObject*)type_obj)->tp_dict, __pyx_n_s_setstate_cython); if (unlikely(ret < 0)) goto __PYX_BAD;
} else if (!setstate || PyErr_Occurred()) {
goto __PYX_BAD;
}
}
PyType_Modified((PyTypeObject*)type_obj);
}
}
goto __PYX_GOOD;
__PYX_BAD:
if (!PyErr_Occurred())
PyErr_Format(PyExc_RuntimeError, "Unable to initialize pickling for %s", ((PyTypeObject*)type_obj)->tp_name);
ret = -1;
__PYX_GOOD:
#if !CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
Py_XDECREF(object_reduce);
Py_XDECREF(object_reduce_ex);
#endif
Py_XDECREF(reduce);
Py_XDECREF(reduce_ex);
Py_XDECREF(reduce_cython);
Py_XDECREF(setstate);
Py_XDECREF(setstate_cython);
return ret;
}
/* CLineInTraceback */
#ifndef CYTHON_CLINE_IN_TRACEBACK
static int __Pyx_CLineForTraceback(CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED PyThreadState *tstate, int c_line) {
PyObject *use_cline;
PyObject *ptype, *pvalue, *ptraceback;
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
PyObject **cython_runtime_dict;
#endif
if (unlikely(!__pyx_cython_runtime)) {
return c_line;
}
__Pyx_ErrFetchInState(tstate, &ptype, &pvalue, &ptraceback);
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
cython_runtime_dict = _PyObject_GetDictPtr(__pyx_cython_runtime);
if (likely(cython_runtime_dict)) {
__PYX_PY_DICT_LOOKUP_IF_MODIFIED(
use_cline, *cython_runtime_dict,
__Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(*cython_runtime_dict, __pyx_n_s_cline_in_traceback))
} else
#endif
{
PyObject *use_cline_obj = __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(__pyx_cython_runtime, __pyx_n_s_cline_in_traceback);
if (use_cline_obj) {
use_cline = PyObject_Not(use_cline_obj) ? Py_False : Py_True;
Py_DECREF(use_cline_obj);
} else {
PyErr_Clear();
use_cline = NULL;
}
}
if (!use_cline) {
c_line = 0;
PyObject_SetAttr(__pyx_cython_runtime, __pyx_n_s_cline_in_traceback, Py_False);
}
else if (use_cline == Py_False || (use_cline != Py_True && PyObject_Not(use_cline) != 0)) {
c_line = 0;
}
__Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(tstate, ptype, pvalue, ptraceback);
return c_line;
}
#endif
/* CodeObjectCache */
static int __pyx_bisect_code_objects(__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry* entries, int count, int code_line) {
int start = 0, mid = 0, end = count - 1;
if (end >= 0 && code_line > entries[end].code_line) {
return count;
}
while (start < end) {
mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
if (code_line < entries[mid].code_line) {
end = mid;
} else if (code_line > entries[mid].code_line) {
start = mid + 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
if (code_line <= entries[mid].code_line) {
return mid;
} else {
return mid + 1;
}
}
static PyCodeObject *__pyx_find_code_object(int code_line) {
PyCodeObject* code_object;
int pos;
if (unlikely(!code_line) || unlikely(!__pyx_code_cache.entries)) {
return NULL;
}
pos = __pyx_bisect_code_objects(__pyx_code_cache.entries, __pyx_code_cache.count, code_line);
if (unlikely(pos >= __pyx_code_cache.count) || unlikely(__pyx_code_cache.entries[pos].code_line != code_line)) {
return NULL;
}
code_object = __pyx_code_cache.entries[pos].code_object;
Py_INCREF(code_object);
return code_object;
}
static void __pyx_insert_code_object(int code_line, PyCodeObject* code_object) {
int pos, i;
__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry* entries = __pyx_code_cache.entries;
if (unlikely(!code_line)) {
return;
}
if (unlikely(!entries)) {
entries = (__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry*)PyMem_Malloc(64*sizeof(__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry));
if (likely(entries)) {
__pyx_code_cache.entries = entries;
__pyx_code_cache.max_count = 64;
__pyx_code_cache.count = 1;
entries[0].code_line = code_line;
entries[0].code_object = code_object;
Py_INCREF(code_object);
}
return;
}
pos = __pyx_bisect_code_objects(__pyx_code_cache.entries, __pyx_code_cache.count, code_line);
if ((pos < __pyx_code_cache.count) && unlikely(__pyx_code_cache.entries[pos].code_line == code_line)) {
PyCodeObject* tmp = entries[pos].code_object;
entries[pos].code_object = code_object;
Py_DECREF(tmp);
return;
}
if (__pyx_code_cache.count == __pyx_code_cache.max_count) {
int new_max = __pyx_code_cache.max_count + 64;
entries = (__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry*)PyMem_Realloc(
__pyx_code_cache.entries, ((size_t)new_max) * sizeof(__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry));
if (unlikely(!entries)) {
return;
}
__pyx_code_cache.entries = entries;
__pyx_code_cache.max_count = new_max;
}
for (i=__pyx_code_cache.count; i>pos; i--) {
entries[i] = entries[i-1];
}
entries[pos].code_line = code_line;
entries[pos].code_object = code_object;
__pyx_code_cache.count++;
Py_INCREF(code_object);
}
/* AddTraceback */
#include "compile.h"
#include "frameobject.h"
#include "traceback.h"
static PyCodeObject* __Pyx_CreateCodeObjectForTraceback(
const char *funcname, int c_line,
int py_line, const char *filename) {
PyCodeObject *py_code = 0;
PyObject *py_srcfile = 0;
PyObject *py_funcname = 0;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
py_srcfile = PyString_FromString(filename);
#else
py_srcfile = PyUnicode_FromString(filename);
#endif
if (!py_srcfile) goto bad;
if (c_line) {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
py_funcname = PyString_FromFormat( "%s (%s:%d)", funcname, __pyx_cfilenm, c_line);
#else
py_funcname = PyUnicode_FromFormat( "%s (%s:%d)", funcname, __pyx_cfilenm, c_line);
#endif
}
else {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
py_funcname = PyString_FromString(funcname);
#else
py_funcname = PyUnicode_FromString(funcname);
#endif
}
if (!py_funcname) goto bad;
py_code = __Pyx_PyCode_New(
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
__pyx_empty_bytes, /*PyObject *code,*/
__pyx_empty_tuple, /*PyObject *consts,*/
__pyx_empty_tuple, /*PyObject *names,*/
__pyx_empty_tuple, /*PyObject *varnames,*/
__pyx_empty_tuple, /*PyObject *freevars,*/
__pyx_empty_tuple, /*PyObject *cellvars,*/
py_srcfile, /*PyObject *filename,*/
py_funcname, /*PyObject *name,*/
py_line,
__pyx_empty_bytes /*PyObject *lnotab*/
);
Py_DECREF(py_srcfile);
Py_DECREF(py_funcname);
return py_code;
bad:
Py_XDECREF(py_srcfile);
Py_XDECREF(py_funcname);
return NULL;
}
static void __Pyx_AddTraceback(const char *funcname, int c_line,
int py_line, const char *filename) {
PyCodeObject *py_code = 0;
PyFrameObject *py_frame = 0;
PyThreadState *tstate = __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current;
if (c_line) {
c_line = __Pyx_CLineForTraceback(tstate, c_line);
}
py_code = __pyx_find_code_object(c_line ? -c_line : py_line);
if (!py_code) {
py_code = __Pyx_CreateCodeObjectForTraceback(
funcname, c_line, py_line, filename);
if (!py_code) goto bad;
__pyx_insert_code_object(c_line ? -c_line : py_line, py_code);
}
py_frame = PyFrame_New(
tstate, /*PyThreadState *tstate,*/
py_code, /*PyCodeObject *code,*/
__pyx_d, /*PyObject *globals,*/
0 /*PyObject *locals*/
);
if (!py_frame) goto bad;
__Pyx_PyFrame_SetLineNumber(py_frame, py_line);
PyTraceBack_Here(py_frame);
bad:
Py_XDECREF(py_code);
Py_XDECREF(py_frame);
}
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
static int __Pyx_GetBuffer(PyObject *obj, Py_buffer *view, int flags) {
if (PyObject_CheckBuffer(obj)) return PyObject_GetBuffer(obj, view, flags);
if (__Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, __pyx_array_type)) return __pyx_array_getbuffer(obj, view, flags);
if (__Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, __pyx_memoryview_type)) return __pyx_memoryview_getbuffer(obj, view, flags);
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError, "'%.200s' does not have the buffer interface", Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_name);
return -1;
}
static void __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(Py_buffer *view) {
PyObject *obj = view->obj;
if (!obj) return;
if (PyObject_CheckBuffer(obj)) {
PyBuffer_Release(view);
return;
}
if ((0)) {}
view->obj = NULL;
Py_DECREF(obj);
}
#endif
/* MemviewSliceIsContig */
static int
__pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(const __Pyx_memviewslice mvs, char order, int ndim)
{
int i, index, step, start;
Py_ssize_t itemsize = mvs.memview->view.itemsize;
if (order == 'F') {
step = 1;
start = 0;
} else {
step = -1;
start = ndim - 1;
}
for (i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
index = start + step * i;
if (mvs.suboffsets[index] >= 0 || mvs.strides[index] != itemsize)
return 0;
itemsize *= mvs.shape[index];
}
return 1;
}
/* OverlappingSlices */
static void
__pyx_get_array_memory_extents(__Pyx_memviewslice *slice,
void **out_start, void **out_end,
int ndim, size_t itemsize)
{
char *start, *end;
int i;
start = end = slice->data;
for (i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
Py_ssize_t stride = slice->strides[i];
Py_ssize_t extent = slice->shape[i];
if (extent == 0) {
*out_start = *out_end = start;
return;
} else {
if (stride > 0)
end += stride * (extent - 1);
else
start += stride * (extent - 1);
}
}
*out_start = start;
*out_end = end + itemsize;
}
static int
__pyx_slices_overlap(__Pyx_memviewslice *slice1,
__Pyx_memviewslice *slice2,
int ndim, size_t itemsize)
{
void *start1, *end1, *start2, *end2;
__pyx_get_array_memory_extents(slice1, &start1, &end1, ndim, itemsize);
__pyx_get_array_memory_extents(slice2, &start2, &end2, ndim, itemsize);
return (start1 < end2) && (start2 < end1);
}
/* Capsule */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *
__pyx_capsule_create(void *p, CYTHON_UNUSED const char *sig)
{
PyObject *cobj;
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x02070000
cobj = PyCapsule_New(p, sig, NULL);
#else
cobj = PyCObject_FromVoidPtr(p, NULL);
#endif
return cobj;
}
/* IsLittleEndian */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_Is_Little_Endian(void)
{
union {
uint32_t u32;
uint8_t u8[4];
} S;
S.u32 = 0x01020304;
return S.u8[0] == 4;
}
/* BufferFormatCheck */
static void __Pyx_BufFmt_Init(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx,
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem* stack,
__Pyx_TypeInfo* type) {
stack[0].field = &ctx->root;
stack[0].parent_offset = 0;
ctx->root.type = type;
ctx->root.name = "buffer dtype";
ctx->root.offset = 0;
ctx->head = stack;
ctx->head->field = &ctx->root;
ctx->fmt_offset = 0;
ctx->head->parent_offset = 0;
ctx->new_packmode = '@';
ctx->enc_packmode = '@';
ctx->new_count = 1;
ctx->enc_count = 0;
ctx->enc_type = 0;
ctx->is_complex = 0;
ctx->is_valid_array = 0;
ctx->struct_alignment = 0;
while (type->typegroup == 'S') {
++ctx->head;
ctx->head->field = type->fields;
ctx->head->parent_offset = 0;
type = type->fields->type;
}
}
static int __Pyx_BufFmt_ParseNumber(const char** ts) {
int count;
const char* t = *ts;
if (*t < '0' || *t > '9') {
return -1;
} else {
count = *t++ - '0';
while (*t >= '0' && *t <= '9') {
count *= 10;
count += *t++ - '0';
}
}
*ts = t;
return count;
}
static int __Pyx_BufFmt_ExpectNumber(const char **ts) {
int number = __Pyx_BufFmt_ParseNumber(ts);
if (number == -1)
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,\
"Does not understand character buffer dtype format string ('%c')", **ts);
return number;
}
static void __Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseUnexpectedChar(char ch) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Unexpected format string character: '%c'", ch);
}
static const char* __Pyx_BufFmt_DescribeTypeChar(char ch, int is_complex) {
switch (ch) {
case '?': return "'bool'";
case 'c': return "'char'";
case 'b': return "'signed char'";
case 'B': return "'unsigned char'";
case 'h': return "'short'";
case 'H': return "'unsigned short'";
case 'i': return "'int'";
case 'I': return "'unsigned int'";
case 'l': return "'long'";
case 'L': return "'unsigned long'";
case 'q': return "'long long'";
case 'Q': return "'unsigned long long'";
case 'f': return (is_complex ? "'complex float'" : "'float'");
case 'd': return (is_complex ? "'complex double'" : "'double'");
case 'g': return (is_complex ? "'complex long double'" : "'long double'");
case 'T': return "a struct";
case 'O': return "Python object";
case 'P': return "a pointer";
case 's': case 'p': return "a string";
case 0: return "end";
default: return "unparseable format string";
}
}
static size_t __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToStandardSize(char ch, int is_complex) {
switch (ch) {
case '?': case 'c': case 'b': case 'B': case 's': case 'p': return 1;
case 'h': case 'H': return 2;
case 'i': case 'I': case 'l': case 'L': return 4;
case 'q': case 'Q': return 8;
case 'f': return (is_complex ? 8 : 4);
case 'd': return (is_complex ? 16 : 8);
case 'g': {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError, "Python does not define a standard format string size for long double ('g')..");
return 0;
}
case 'O': case 'P': return sizeof(void*);
default:
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseUnexpectedChar(ch);
return 0;
}
}
static size_t __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToNativeSize(char ch, int is_complex) {
switch (ch) {
case '?': case 'c': case 'b': case 'B': case 's': case 'p': return 1;
case 'h': case 'H': return sizeof(short);
case 'i': case 'I': return sizeof(int);
case 'l': case 'L': return sizeof(long);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
case 'q': case 'Q': return sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG);
#endif
case 'f': return sizeof(float) * (is_complex ? 2 : 1);
case 'd': return sizeof(double) * (is_complex ? 2 : 1);
case 'g': return sizeof(long double) * (is_complex ? 2 : 1);
case 'O': case 'P': return sizeof(void*);
default: {
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseUnexpectedChar(ch);
return 0;
}
}
}
typedef struct { char c; short x; } __Pyx_st_short;
typedef struct { char c; int x; } __Pyx_st_int;
typedef struct { char c; long x; } __Pyx_st_long;
typedef struct { char c; float x; } __Pyx_st_float;
typedef struct { char c; double x; } __Pyx_st_double;
typedef struct { char c; long double x; } __Pyx_st_longdouble;
typedef struct { char c; void *x; } __Pyx_st_void_p;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
typedef struct { char c; PY_LONG_LONG x; } __Pyx_st_longlong;
#endif
static size_t __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToAlignment(char ch, CYTHON_UNUSED int is_complex) {
switch (ch) {
case '?': case 'c': case 'b': case 'B': case 's': case 'p': return 1;
case 'h': case 'H': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_short) - sizeof(short);
case 'i': case 'I': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_int) - sizeof(int);
case 'l': case 'L': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_long) - sizeof(long);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
case 'q': case 'Q': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_longlong) - sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG);
#endif
case 'f': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_float) - sizeof(float);
case 'd': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_double) - sizeof(double);
case 'g': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_longdouble) - sizeof(long double);
case 'P': case 'O': return sizeof(__Pyx_st_void_p) - sizeof(void*);
default:
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseUnexpectedChar(ch);
return 0;
}
}
/* These are for computing the padding at the end of the struct to align
on the first member of the struct. This will probably the same as above,
but we don't have any guarantees.
*/
typedef struct { short x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_short;
typedef struct { int x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_int;
typedef struct { long x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_long;
typedef struct { float x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_float;
typedef struct { double x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_double;
typedef struct { long double x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_longdouble;
typedef struct { void *x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_void_p;
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
typedef struct { PY_LONG_LONG x; char c; } __Pyx_pad_longlong;
#endif
static size_t __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToPadding(char ch, CYTHON_UNUSED int is_complex) {
switch (ch) {
case '?': case 'c': case 'b': case 'B': case 's': case 'p': return 1;
case 'h': case 'H': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_short) - sizeof(short);
case 'i': case 'I': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_int) - sizeof(int);
case 'l': case 'L': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_long) - sizeof(long);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
case 'q': case 'Q': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_longlong) - sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG);
#endif
case 'f': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_float) - sizeof(float);
case 'd': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_double) - sizeof(double);
case 'g': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_longdouble) - sizeof(long double);
case 'P': case 'O': return sizeof(__Pyx_pad_void_p) - sizeof(void*);
default:
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseUnexpectedChar(ch);
return 0;
}
}
static char __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToGroup(char ch, int is_complex) {
switch (ch) {
case 'c':
return 'H';
case 'b': case 'h': case 'i':
case 'l': case 'q': case 's': case 'p':
return 'I';
case '?': case 'B': case 'H': case 'I': case 'L': case 'Q':
return 'U';
case 'f': case 'd': case 'g':
return (is_complex ? 'C' : 'R');
case 'O':
return 'O';
case 'P':
return 'P';
default: {
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseUnexpectedChar(ch);
return 0;
}
}
}
static void __Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseExpected(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx) {
if (ctx->head == NULL || ctx->head->field == &ctx->root) {
const char* expected;
const char* quote;
if (ctx->head == NULL) {
expected = "end";
quote = "";
} else {
expected = ctx->head->field->type->name;
quote = "'";
}
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer dtype mismatch, expected %s%s%s but got %s",
quote, expected, quote,
__Pyx_BufFmt_DescribeTypeChar(ctx->enc_type, ctx->is_complex));
} else {
__Pyx_StructField* field = ctx->head->field;
__Pyx_StructField* parent = (ctx->head - 1)->field;
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer dtype mismatch, expected '%s' but got %s in '%s.%s'",
field->type->name, __Pyx_BufFmt_DescribeTypeChar(ctx->enc_type, ctx->is_complex),
parent->type->name, field->name);
}
}
static int __Pyx_BufFmt_ProcessTypeChunk(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx) {
char group;
size_t size, offset, arraysize = 1;
if (ctx->enc_type == 0) return 0;
if (ctx->head->field->type->arraysize[0]) {
int i, ndim = 0;
if (ctx->enc_type == 's' || ctx->enc_type == 'p') {
ctx->is_valid_array = ctx->head->field->type->ndim == 1;
ndim = 1;
if (ctx->enc_count != ctx->head->field->type->arraysize[0]) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Expected a dimension of size %zu, got %zu",
ctx->head->field->type->arraysize[0], ctx->enc_count);
return -1;
}
}
if (!ctx->is_valid_array) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError, "Expected %d dimensions, got %d",
ctx->head->field->type->ndim, ndim);
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < ctx->head->field->type->ndim; i++) {
arraysize *= ctx->head->field->type->arraysize[i];
}
ctx->is_valid_array = 0;
ctx->enc_count = 1;
}
group = __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToGroup(ctx->enc_type, ctx->is_complex);
do {
__Pyx_StructField* field = ctx->head->field;
__Pyx_TypeInfo* type = field->type;
if (ctx->enc_packmode == '@' || ctx->enc_packmode == '^') {
size = __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToNativeSize(ctx->enc_type, ctx->is_complex);
} else {
size = __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToStandardSize(ctx->enc_type, ctx->is_complex);
}
if (ctx->enc_packmode == '@') {
size_t align_at = __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToAlignment(ctx->enc_type, ctx->is_complex);
size_t align_mod_offset;
if (align_at == 0) return -1;
align_mod_offset = ctx->fmt_offset % align_at;
if (align_mod_offset > 0) ctx->fmt_offset += align_at - align_mod_offset;
if (ctx->struct_alignment == 0)
ctx->struct_alignment = __Pyx_BufFmt_TypeCharToPadding(ctx->enc_type,
ctx->is_complex);
}
if (type->size != size || type->typegroup != group) {
if (type->typegroup == 'C' && type->fields != NULL) {
size_t parent_offset = ctx->head->parent_offset + field->offset;
++ctx->head;
ctx->head->field = type->fields;
ctx->head->parent_offset = parent_offset;
continue;
}
if ((type->typegroup == 'H' || group == 'H') && type->size == size) {
} else {
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseExpected(ctx);
return -1;
}
}
offset = ctx->head->parent_offset + field->offset;
if (ctx->fmt_offset != offset) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer dtype mismatch; next field is at offset %" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "d but %" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "d expected",
(Py_ssize_t)ctx->fmt_offset, (Py_ssize_t)offset);
return -1;
}
ctx->fmt_offset += size;
if (arraysize)
ctx->fmt_offset += (arraysize - 1) * size;
--ctx->enc_count;
while (1) {
if (field == &ctx->root) {
ctx->head = NULL;
if (ctx->enc_count != 0) {
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseExpected(ctx);
return -1;
}
break;
}
ctx->head->field = ++field;
if (field->type == NULL) {
--ctx->head;
field = ctx->head->field;
continue;
} else if (field->type->typegroup == 'S') {
size_t parent_offset = ctx->head->parent_offset + field->offset;
if (field->type->fields->type == NULL) continue;
field = field->type->fields;
++ctx->head;
ctx->head->field = field;
ctx->head->parent_offset = parent_offset;
break;
} else {
break;
}
}
} while (ctx->enc_count);
ctx->enc_type = 0;
ctx->is_complex = 0;
return 0;
}
static PyObject *
__pyx_buffmt_parse_array(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx, const char** tsp)
{
const char *ts = *tsp;
int i = 0, number, ndim;
++ts;
if (ctx->new_count != 1) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"Cannot handle repeated arrays in format string");
return NULL;
}
if (__Pyx_BufFmt_ProcessTypeChunk(ctx) == -1) return NULL;
ndim = ctx->head->field->type->ndim;
while (*ts && *ts != ')') {
switch (*ts) {
case ' ': case '\f': case '\r': case '\n': case '\t': case '\v': continue;
default: break;
}
number = __Pyx_BufFmt_ExpectNumber(&ts);
if (number == -1) return NULL;
if (i < ndim && (size_t) number != ctx->head->field->type->arraysize[i])
return PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Expected a dimension of size %zu, got %d",
ctx->head->field->type->arraysize[i], number);
if (*ts != ',' && *ts != ')')
return PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Expected a comma in format string, got '%c'", *ts);
if (*ts == ',') ts++;
i++;
}
if (i != ndim)
return PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError, "Expected %d dimension(s), got %d",
ctx->head->field->type->ndim, i);
if (!*ts) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"Unexpected end of format string, expected ')'");
return NULL;
}
ctx->is_valid_array = 1;
ctx->new_count = 1;
*tsp = ++ts;
return Py_None;
}
static const char* __Pyx_BufFmt_CheckString(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx, const char* ts) {
int got_Z = 0;
while (1) {
switch(*ts) {
case 0:
if (ctx->enc_type != 0 && ctx->head == NULL) {
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseExpected(ctx);
return NULL;
}
if (__Pyx_BufFmt_ProcessTypeChunk(ctx) == -1) return NULL;
if (ctx->head != NULL) {
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseExpected(ctx);
return NULL;
}
return ts;
case ' ':
case '\r':
case '\n':
++ts;
break;
case '<':
if (!__Pyx_Is_Little_Endian()) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError, "Little-endian buffer not supported on big-endian compiler");
return NULL;
}
ctx->new_packmode = '=';
++ts;
break;
case '>':
case '!':
if (__Pyx_Is_Little_Endian()) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError, "Big-endian buffer not supported on little-endian compiler");
return NULL;
}
ctx->new_packmode = '=';
++ts;
break;
case '=':
case '@':
case '^':
ctx->new_packmode = *ts++;
break;
case 'T':
{
const char* ts_after_sub;
size_t i, struct_count = ctx->new_count;
size_t struct_alignment = ctx->struct_alignment;
ctx->new_count = 1;
++ts;
if (*ts != '{') {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError, "Buffer acquisition: Expected '{' after 'T'");
return NULL;
}
if (__Pyx_BufFmt_ProcessTypeChunk(ctx) == -1) return NULL;
ctx->enc_type = 0;
ctx->enc_count = 0;
ctx->struct_alignment = 0;
++ts;
ts_after_sub = ts;
for (i = 0; i != struct_count; ++i) {
ts_after_sub = __Pyx_BufFmt_CheckString(ctx, ts);
if (!ts_after_sub) return NULL;
}
ts = ts_after_sub;
if (struct_alignment) ctx->struct_alignment = struct_alignment;
}
break;
case '}':
{
size_t alignment = ctx->struct_alignment;
++ts;
if (__Pyx_BufFmt_ProcessTypeChunk(ctx) == -1) return NULL;
ctx->enc_type = 0;
if (alignment && ctx->fmt_offset % alignment) {
ctx->fmt_offset += alignment - (ctx->fmt_offset % alignment);
}
}
return ts;
case 'x':
if (__Pyx_BufFmt_ProcessTypeChunk(ctx) == -1) return NULL;
ctx->fmt_offset += ctx->new_count;
ctx->new_count = 1;
ctx->enc_count = 0;
ctx->enc_type = 0;
ctx->enc_packmode = ctx->new_packmode;
++ts;
break;
case 'Z':
got_Z = 1;
++ts;
if (*ts != 'f' && *ts != 'd' && *ts != 'g') {
__Pyx_BufFmt_RaiseUnexpectedChar('Z');
return NULL;
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case '?': case 'c': case 'b': case 'B': case 'h': case 'H': case 'i': case 'I':
case 'l': case 'L': case 'q': case 'Q':
case 'f': case 'd': case 'g':
case 'O': case 'p':
if ((ctx->enc_type == *ts) && (got_Z == ctx->is_complex) &&
(ctx->enc_packmode == ctx->new_packmode) && (!ctx->is_valid_array)) {
ctx->enc_count += ctx->new_count;
ctx->new_count = 1;
got_Z = 0;
++ts;
break;
}
CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH;
case 's':
if (__Pyx_BufFmt_ProcessTypeChunk(ctx) == -1) return NULL;
ctx->enc_count = ctx->new_count;
ctx->enc_packmode = ctx->new_packmode;
ctx->enc_type = *ts;
ctx->is_complex = got_Z;
++ts;
ctx->new_count = 1;
got_Z = 0;
break;
case ':':
++ts;
while(*ts != ':') ++ts;
++ts;
break;
case '(':
if (!__pyx_buffmt_parse_array(ctx, &ts)) return NULL;
break;
default:
{
int number = __Pyx_BufFmt_ExpectNumber(&ts);
if (number == -1) return NULL;
ctx->new_count = (size_t)number;
}
}
}
}
/* TypeInfoCompare */
static int
__pyx_typeinfo_cmp(__Pyx_TypeInfo *a, __Pyx_TypeInfo *b)
{
int i;
if (!a || !b)
return 0;
if (a == b)
return 1;
if (a->size != b->size || a->typegroup != b->typegroup ||
a->is_unsigned != b->is_unsigned || a->ndim != b->ndim) {
if (a->typegroup == 'H' || b->typegroup == 'H') {
return a->size == b->size;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
if (a->ndim) {
for (i = 0; i < a->ndim; i++)
if (a->arraysize[i] != b->arraysize[i])
return 0;
}
if (a->typegroup == 'S') {
if (a->flags != b->flags)
return 0;
if (a->fields || b->fields) {
if (!(a->fields && b->fields))
return 0;
for (i = 0; a->fields[i].type && b->fields[i].type; i++) {
__Pyx_StructField *field_a = a->fields + i;
__Pyx_StructField *field_b = b->fields + i;
if (field_a->offset != field_b->offset ||
!__pyx_typeinfo_cmp(field_a->type, field_b->type))
return 0;
}
return !a->fields[i].type && !b->fields[i].type;
}
}
return 1;
}
/* MemviewSliceValidateAndInit */
static int
__pyx_check_strides(Py_buffer *buf, int dim, int ndim, int spec)
{
if (buf->shape[dim] <= 1)
return 1;
if (buf->strides) {
if (spec & __Pyx_MEMVIEW_CONTIG) {
if (spec & (__Pyx_MEMVIEW_PTR|__Pyx_MEMVIEW_FULL)) {
if (unlikely(buf->strides[dim] != sizeof(void *))) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer is not indirectly contiguous "
"in dimension %d.", dim);
goto fail;
}
} else if (unlikely(buf->strides[dim] != buf->itemsize)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer and memoryview are not contiguous "
"in the same dimension.");
goto fail;
}
}
if (spec & __Pyx_MEMVIEW_FOLLOW) {
Py_ssize_t stride = buf->strides[dim];
if (stride < 0)
stride = -stride;
if (unlikely(stride < buf->itemsize)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer and memoryview are not contiguous "
"in the same dimension.");
goto fail;
}
}
} else {
if (unlikely(spec & __Pyx_MEMVIEW_CONTIG && dim != ndim - 1)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"C-contiguous buffer is not contiguous in "
"dimension %d", dim);
goto fail;
} else if (unlikely(spec & (__Pyx_MEMVIEW_PTR))) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"C-contiguous buffer is not indirect in "
"dimension %d", dim);
goto fail;
} else if (unlikely(buf->suboffsets)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer exposes suboffsets but no strides");
goto fail;
}
}
return 1;
fail:
return 0;
}
static int
__pyx_check_suboffsets(Py_buffer *buf, int dim, CYTHON_UNUSED int ndim, int spec)
{
if (spec & __Pyx_MEMVIEW_DIRECT) {
if (unlikely(buf->suboffsets && buf->suboffsets[dim] >= 0)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer not compatible with direct access "
"in dimension %d.", dim);
goto fail;
}
}
if (spec & __Pyx_MEMVIEW_PTR) {
if (unlikely(!buf->suboffsets || (buf->suboffsets[dim] < 0))) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer is not indirectly accessible "
"in dimension %d.", dim);
goto fail;
}
}
return 1;
fail:
return 0;
}
static int
__pyx_verify_contig(Py_buffer *buf, int ndim, int c_or_f_flag)
{
int i;
if (c_or_f_flag & __Pyx_IS_F_CONTIG) {
Py_ssize_t stride = 1;
for (i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
if (unlikely(stride * buf->itemsize != buf->strides[i] && buf->shape[i] > 1)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer not fortran contiguous.");
goto fail;
}
stride = stride * buf->shape[i];
}
} else if (c_or_f_flag & __Pyx_IS_C_CONTIG) {
Py_ssize_t stride = 1;
for (i = ndim - 1; i >- 1; i--) {
if (unlikely(stride * buf->itemsize != buf->strides[i] && buf->shape[i] > 1)) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer not C contiguous.");
goto fail;
}
stride = stride * buf->shape[i];
}
}
return 1;
fail:
return 0;
}
static int __Pyx_ValidateAndInit_memviewslice(
int *axes_specs,
int c_or_f_flag,
int buf_flags,
int ndim,
__Pyx_TypeInfo *dtype,
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem stack[],
__Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice,
PyObject *original_obj)
{
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview, *new_memview;
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
Py_buffer *buf;
int i, spec = 0, retval = -1;
__Pyx_BufFmt_Context ctx;
int from_memoryview = __pyx_memoryview_check(original_obj);
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("ValidateAndInit_memviewslice", 0);
if (from_memoryview && __pyx_typeinfo_cmp(dtype, ((struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *)
original_obj)->typeinfo)) {
memview = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *) original_obj;
new_memview = NULL;
} else {
memview = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *) __pyx_memoryview_new(
original_obj, buf_flags, 0, dtype);
new_memview = memview;
if (unlikely(!memview))
goto fail;
}
buf = &memview->view;
if (unlikely(buf->ndim != ndim)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Buffer has wrong number of dimensions (expected %d, got %d)",
ndim, buf->ndim);
goto fail;
}
if (new_memview) {
__Pyx_BufFmt_Init(&ctx, stack, dtype);
if (unlikely(!__Pyx_BufFmt_CheckString(&ctx, buf->format))) goto fail;
}
if (unlikely((unsigned) buf->itemsize != dtype->size)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError,
"Item size of buffer (%" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "u byte%s) "
"does not match size of '%s' (%" CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "u byte%s)",
buf->itemsize,
(buf->itemsize > 1) ? "s" : "",
dtype->name,
dtype->size,
(dtype->size > 1) ? "s" : "");
goto fail;
}
if (buf->len > 0) {
for (i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
spec = axes_specs[i];
if (unlikely(!__pyx_check_strides(buf, i, ndim, spec)))
goto fail;
if (unlikely(!__pyx_check_suboffsets(buf, i, ndim, spec)))
goto fail;
}
if (unlikely(buf->strides && !__pyx_verify_contig(buf, ndim, c_or_f_flag)))
goto fail;
}
if (unlikely(__Pyx_init_memviewslice(memview, ndim, memviewslice,
new_memview != NULL) == -1)) {
goto fail;
}
retval = 0;
goto no_fail;
fail:
Py_XDECREF(new_memview);
retval = -1;
no_fail:
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return retval;
}
/* ObjectToMemviewSlice */
static CYTHON_INLINE __Pyx_memviewslice __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_dsds_double(PyObject *obj, int writable_flag) {
__Pyx_memviewslice result = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem stack[1];
int axes_specs[] = { (__Pyx_MEMVIEW_DIRECT | __Pyx_MEMVIEW_STRIDED), (__Pyx_MEMVIEW_DIRECT | __Pyx_MEMVIEW_STRIDED) };
int retcode;
if (obj == Py_None) {
result.memview = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *) Py_None;
return result;
}
retcode = __Pyx_ValidateAndInit_memviewslice(axes_specs, 0,
PyBUF_RECORDS_RO | writable_flag, 2,
&__Pyx_TypeInfo_double, stack,
&result, obj);
if (unlikely(retcode == -1))
goto __pyx_fail;
return result;
__pyx_fail:
result.memview = NULL;
result.data = NULL;
return result;
}
/* ObjectToMemviewSlice */
static CYTHON_INLINE __Pyx_memviewslice __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_ds_double(PyObject *obj, int writable_flag) {
__Pyx_memviewslice result = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem stack[1];
int axes_specs[] = { (__Pyx_MEMVIEW_DIRECT | __Pyx_MEMVIEW_STRIDED) };
int retcode;
if (obj == Py_None) {
result.memview = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *) Py_None;
return result;
}
retcode = __Pyx_ValidateAndInit_memviewslice(axes_specs, 0,
PyBUF_RECORDS_RO | writable_flag, 1,
&__Pyx_TypeInfo_double, stack,
&result, obj);
if (unlikely(retcode == -1))
goto __pyx_fail;
return result;
__pyx_fail:
result.memview = NULL;
result.data = NULL;
return result;
}
/* MemviewSliceCopyTemplate */
static __Pyx_memviewslice
__pyx_memoryview_copy_new_contig(const __Pyx_memviewslice *from_mvs,
const char *mode, int ndim,
size_t sizeof_dtype, int contig_flag,
int dtype_is_object)
{
__Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
int i;
__Pyx_memviewslice new_mvs = { 0, 0, { 0 }, { 0 }, { 0 } };
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *from_memview = from_mvs->memview;
Py_buffer *buf = &from_memview->view;
PyObject *shape_tuple = NULL;
PyObject *temp_int = NULL;
struct __pyx_array_obj *array_obj = NULL;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview_obj = NULL;
__Pyx_RefNannySetupContext("__pyx_memoryview_copy_new_contig", 0);
for (i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
if (unlikely(from_mvs->suboffsets[i] >= 0)) {
PyErr_Format(PyExc_ValueError, "Cannot copy memoryview slice with "
"indirect dimensions (axis %d)", i);
goto fail;
}
}
shape_tuple = PyTuple_New(ndim);
if (unlikely(!shape_tuple)) {
goto fail;
}
__Pyx_GOTREF(shape_tuple);
for(i = 0; i < ndim; i++) {
temp_int = PyInt_FromSsize_t(from_mvs->shape[i]);
if(unlikely(!temp_int)) {
goto fail;
} else {
PyTuple_SET_ITEM(shape_tuple, i, temp_int);
temp_int = NULL;
}
}
array_obj = __pyx_array_new(shape_tuple, sizeof_dtype, buf->format, (char *) mode, NULL);
if (unlikely(!array_obj)) {
goto fail;
}
__Pyx_GOTREF(array_obj);
memview_obj = (struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *) __pyx_memoryview_new(
(PyObject *) array_obj, contig_flag,
dtype_is_object,
from_mvs->memview->typeinfo);
if (unlikely(!memview_obj))
goto fail;
if (unlikely(__Pyx_init_memviewslice(memview_obj, ndim, &new_mvs, 1) < 0))
goto fail;
if (unlikely(__pyx_memoryview_copy_contents(*from_mvs, new_mvs, ndim, ndim,
dtype_is_object) < 0))
goto fail;
goto no_fail;
fail:
__Pyx_XDECREF(new_mvs.memview);
new_mvs.memview = NULL;
new_mvs.data = NULL;
no_fail:
__Pyx_XDECREF(shape_tuple);
__Pyx_XDECREF(temp_int);
__Pyx_XDECREF(array_obj);
__Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext();
return new_mvs;
}
/* CIntFromPyVerify */
#define __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(target_type, func_type, func_value)\
__PYX__VERIFY_RETURN_INT(target_type, func_type, func_value, 0)
#define __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(target_type, func_type, func_value)\
__PYX__VERIFY_RETURN_INT(target_type, func_type, func_value, 1)
#define __PYX__VERIFY_RETURN_INT(target_type, func_type, func_value, exc)\
{\
func_type value = func_value;\
if (sizeof(target_type) < sizeof(func_type)) {\
if (unlikely(value != (func_type) (target_type) value)) {\
func_type zero = 0;\
if (exc && unlikely(value == (func_type)-1 && PyErr_Occurred()))\
return (target_type) -1;\
if (is_unsigned && unlikely(value < zero))\
goto raise_neg_overflow;\
else\
goto raise_overflow;\
}\
}\
return (target_type) value;\
}
/* CIntFromPy */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyInt_As_int(PyObject *x) {
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wconversion"
#endif
const int neg_one = (int) -1, const_zero = (int) 0;
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
const int is_unsigned = neg_one > const_zero;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(PyInt_Check(x))) {
if (sizeof(int) < sizeof(long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, long, PyInt_AS_LONG(x))
} else {
long val = PyInt_AS_LONG(x);
if (is_unsigned && unlikely(val < 0)) {
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
return (int) val;
}
} else
#endif
if (likely(PyLong_Check(x))) {
if (is_unsigned) {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)x)->ob_digit;
switch (Py_SIZE(x)) {
case 0: return (int) 0;
case 1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, digit, digits[0])
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(int) > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, unsigned long, (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) >= 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) (((((int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(int) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, unsigned long, (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) >= 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) (((((((int)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(int) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, unsigned long, (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) >= 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) (((((((((int)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
}
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
if (unlikely(Py_SIZE(x) < 0)) {
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
#else
{
int result = PyObject_RichCompareBool(x, Py_False, Py_LT);
if (unlikely(result < 0))
return (int) -1;
if (unlikely(result == 1))
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
#endif
if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(unsigned long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(int, unsigned long, PyLong_AsUnsignedLong(x))
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(int, unsigned PY_LONG_LONG, PyLong_AsUnsignedLongLong(x))
#endif
}
} else {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)x)->ob_digit;
switch (Py_SIZE(x)) {
case 0: return (int) 0;
case -1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, sdigit, (sdigit) (-(sdigit)digits[0]))
case 1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, digit, +digits[0])
case -2:
if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, long, -(long) (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) (((int)-1)*(((((int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(int) > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, unsigned long, (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) ((((((int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case -3:
if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, long, -(long) (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) (((int)-1)*(((((((int)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(int) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, unsigned long, (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) ((((((((int)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case -4:
if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, long, -(long) (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) (((int)-1)*(((((((((int)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(int) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(int, unsigned long, (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(int) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (int) ((((((((((int)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (int)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
}
#endif
if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(int, long, PyLong_AsLong(x))
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(int, PY_LONG_LONG, PyLong_AsLongLong(x))
#endif
}
}
{
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(_PyLong_AsByteArray)
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_RuntimeError,
"_PyLong_AsByteArray() not available in PyPy, cannot convert large numbers");
#else
int val;
PyObject *v = __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(x);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(v) && !PyLong_Check(v)) {
PyObject *tmp = v;
v = PyNumber_Long(tmp);
Py_DECREF(tmp);
}
#endif
if (likely(v)) {
int one = 1; int is_little = (int)*(unsigned char *)&one;
unsigned char *bytes = (unsigned char *)&val;
int ret = _PyLong_AsByteArray((PyLongObject *)v,
bytes, sizeof(val),
is_little, !is_unsigned);
Py_DECREF(v);
if (likely(!ret))
return val;
}
#endif
return (int) -1;
}
} else {
int val;
PyObject *tmp = __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(x);
if (!tmp) return (int) -1;
val = __Pyx_PyInt_As_int(tmp);
Py_DECREF(tmp);
return val;
}
raise_overflow:
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"value too large to convert to int");
return (int) -1;
raise_neg_overflow:
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"can't convert negative value to int");
return (int) -1;
}
/* CIntFromPy */
static CYTHON_INLINE long __Pyx_PyInt_As_long(PyObject *x) {
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wconversion"
#endif
const long neg_one = (long) -1, const_zero = (long) 0;
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
const int is_unsigned = neg_one > const_zero;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(PyInt_Check(x))) {
if (sizeof(long) < sizeof(long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, long, PyInt_AS_LONG(x))
} else {
long val = PyInt_AS_LONG(x);
if (is_unsigned && unlikely(val < 0)) {
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
return (long) val;
}
} else
#endif
if (likely(PyLong_Check(x))) {
if (is_unsigned) {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)x)->ob_digit;
switch (Py_SIZE(x)) {
case 0: return (long) 0;
case 1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, digit, digits[0])
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(long) > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, unsigned long, (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) >= 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) (((((long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, unsigned long, (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) >= 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) (((((((long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, unsigned long, (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) >= 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) (((((((((long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
}
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
if (unlikely(Py_SIZE(x) < 0)) {
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
#else
{
int result = PyObject_RichCompareBool(x, Py_False, Py_LT);
if (unlikely(result < 0))
return (long) -1;
if (unlikely(result == 1))
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
#endif
if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(unsigned long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(long, unsigned long, PyLong_AsUnsignedLong(x))
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(long, unsigned PY_LONG_LONG, PyLong_AsUnsignedLongLong(x))
#endif
}
} else {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)x)->ob_digit;
switch (Py_SIZE(x)) {
case 0: return (long) 0;
case -1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, sdigit, (sdigit) (-(sdigit)digits[0]))
case 1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, digit, +digits[0])
case -2:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, long, -(long) (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) (((long)-1)*(((((long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(long) > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, unsigned long, (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) ((((((long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case -3:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, long, -(long) (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) (((long)-1)*(((((((long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, unsigned long, (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) ((((((((long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case -4:
if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, long, -(long) (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) (((long)-1)*(((((((((long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(long, unsigned long, (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(long) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (long) ((((((((((long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (long)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
}
#endif
if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(long, long, PyLong_AsLong(x))
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(long, PY_LONG_LONG, PyLong_AsLongLong(x))
#endif
}
}
{
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(_PyLong_AsByteArray)
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_RuntimeError,
"_PyLong_AsByteArray() not available in PyPy, cannot convert large numbers");
#else
long val;
PyObject *v = __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(x);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(v) && !PyLong_Check(v)) {
PyObject *tmp = v;
v = PyNumber_Long(tmp);
Py_DECREF(tmp);
}
#endif
if (likely(v)) {
int one = 1; int is_little = (int)*(unsigned char *)&one;
unsigned char *bytes = (unsigned char *)&val;
int ret = _PyLong_AsByteArray((PyLongObject *)v,
bytes, sizeof(val),
is_little, !is_unsigned);
Py_DECREF(v);
if (likely(!ret))
return val;
}
#endif
return (long) -1;
}
} else {
long val;
PyObject *tmp = __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(x);
if (!tmp) return (long) -1;
val = __Pyx_PyInt_As_long(tmp);
Py_DECREF(tmp);
return val;
}
raise_overflow:
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"value too large to convert to long");
return (long) -1;
raise_neg_overflow:
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"can't convert negative value to long");
return (long) -1;
}
/* CIntToPy */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(int value) {
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wconversion"
#endif
const int neg_one = (int) -1, const_zero = (int) 0;
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
const int is_unsigned = neg_one > const_zero;
if (is_unsigned) {
if (sizeof(int) < sizeof(long)) {
return PyInt_FromLong((long) value);
} else if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(unsigned long)) {
return PyLong_FromUnsignedLong((unsigned long) value);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)) {
return PyLong_FromUnsignedLongLong((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG) value);
#endif
}
} else {
if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(long)) {
return PyInt_FromLong((long) value);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(int) <= sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG)) {
return PyLong_FromLongLong((PY_LONG_LONG) value);
#endif
}
}
{
int one = 1; int little = (int)*(unsigned char *)&one;
unsigned char *bytes = (unsigned char *)&value;
return _PyLong_FromByteArray(bytes, sizeof(int),
little, !is_unsigned);
}
}
/* CIntToPy */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_From_long(long value) {
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wconversion"
#endif
const long neg_one = (long) -1, const_zero = (long) 0;
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
const int is_unsigned = neg_one > const_zero;
if (is_unsigned) {
if (sizeof(long) < sizeof(long)) {
return PyInt_FromLong((long) value);
} else if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(unsigned long)) {
return PyLong_FromUnsignedLong((unsigned long) value);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)) {
return PyLong_FromUnsignedLongLong((unsigned PY_LONG_LONG) value);
#endif
}
} else {
if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(long)) {
return PyInt_FromLong((long) value);
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(long) <= sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG)) {
return PyLong_FromLongLong((PY_LONG_LONG) value);
#endif
}
}
{
int one = 1; int little = (int)*(unsigned char *)&one;
unsigned char *bytes = (unsigned char *)&value;
return _PyLong_FromByteArray(bytes, sizeof(long),
little, !is_unsigned);
}
}
/* CIntFromPy */
static CYTHON_INLINE char __Pyx_PyInt_As_char(PyObject *x) {
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wconversion"
#endif
const char neg_one = (char) -1, const_zero = (char) 0;
#ifdef __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#pragma GCC diagnostic pop
#endif
const int is_unsigned = neg_one > const_zero;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(PyInt_Check(x))) {
if (sizeof(char) < sizeof(long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, long, PyInt_AS_LONG(x))
} else {
long val = PyInt_AS_LONG(x);
if (is_unsigned && unlikely(val < 0)) {
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
return (char) val;
}
} else
#endif
if (likely(PyLong_Check(x))) {
if (is_unsigned) {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)x)->ob_digit;
switch (Py_SIZE(x)) {
case 0: return (char) 0;
case 1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, digit, digits[0])
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(char) > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, unsigned long, (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) >= 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) (((((char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(char) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, unsigned long, (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) >= 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) (((((((char)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(char) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, unsigned long, (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) >= 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) (((((((((char)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0]));
}
}
break;
}
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
if (unlikely(Py_SIZE(x) < 0)) {
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
#else
{
int result = PyObject_RichCompareBool(x, Py_False, Py_LT);
if (unlikely(result < 0))
return (char) -1;
if (unlikely(result == 1))
goto raise_neg_overflow;
}
#endif
if (sizeof(char) <= sizeof(unsigned long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(char, unsigned long, PyLong_AsUnsignedLong(x))
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(char) <= sizeof(unsigned PY_LONG_LONG)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(char, unsigned PY_LONG_LONG, PyLong_AsUnsignedLongLong(x))
#endif
}
} else {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)x)->ob_digit;
switch (Py_SIZE(x)) {
case 0: return (char) 0;
case -1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, sdigit, (sdigit) (-(sdigit)digits[0]))
case 1: __PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, digit, +digits[0])
case -2:
if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, long, -(long) (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) (((char)-1)*(((((char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(char) > 1 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, unsigned long, (((((unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) ((((((char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case -3:
if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, long, -(long) (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) (((char)-1)*(((((((char)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(char) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, unsigned long, (((((((unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) ((((((((char)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case -4:
if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, long, -(long) (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) (((char)-1)*(((((((((char)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(char) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
if (8 * sizeof(unsigned long) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT(char, unsigned long, (((((((((unsigned long)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (unsigned long)digits[0])))
} else if (8 * sizeof(char) - 1 > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (char) ((((((((((char)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (char)digits[0])));
}
}
break;
}
#endif
if (sizeof(char) <= sizeof(long)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(char, long, PyLong_AsLong(x))
#ifdef HAVE_LONG_LONG
} else if (sizeof(char) <= sizeof(PY_LONG_LONG)) {
__PYX_VERIFY_RETURN_INT_EXC(char, PY_LONG_LONG, PyLong_AsLongLong(x))
#endif
}
}
{
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(_PyLong_AsByteArray)
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_RuntimeError,
"_PyLong_AsByteArray() not available in PyPy, cannot convert large numbers");
#else
char val;
PyObject *v = __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(x);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(v) && !PyLong_Check(v)) {
PyObject *tmp = v;
v = PyNumber_Long(tmp);
Py_DECREF(tmp);
}
#endif
if (likely(v)) {
int one = 1; int is_little = (int)*(unsigned char *)&one;
unsigned char *bytes = (unsigned char *)&val;
int ret = _PyLong_AsByteArray((PyLongObject *)v,
bytes, sizeof(val),
is_little, !is_unsigned);
Py_DECREF(v);
if (likely(!ret))
return val;
}
#endif
return (char) -1;
}
} else {
char val;
PyObject *tmp = __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(x);
if (!tmp) return (char) -1;
val = __Pyx_PyInt_As_char(tmp);
Py_DECREF(tmp);
return val;
}
raise_overflow:
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"value too large to convert to char");
return (char) -1;
raise_neg_overflow:
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_OverflowError,
"can't convert negative value to char");
return (char) -1;
}
/* CheckBinaryVersion */
static int __Pyx_check_binary_version(void) {
char ctversion[4], rtversion[4];
PyOS_snprintf(ctversion, 4, "%d.%d", PY_MAJOR_VERSION, PY_MINOR_VERSION);
PyOS_snprintf(rtversion, 4, "%s", Py_GetVersion());
if (ctversion[0] != rtversion[0] || ctversion[2] != rtversion[2]) {
char message[200];
PyOS_snprintf(message, sizeof(message),
"compiletime version %s of module '%.100s' "
"does not match runtime version %s",
ctversion, __Pyx_MODULE_NAME, rtversion);
return PyErr_WarnEx(NULL, message, 1);
}
return 0;
}
/* InitStrings */
static int __Pyx_InitStrings(__Pyx_StringTabEntry *t) {
while (t->p) {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (t->is_unicode) {
*t->p = PyUnicode_DecodeUTF8(t->s, t->n - 1, NULL);
} else if (t->intern) {
*t->p = PyString_InternFromString(t->s);
} else {
*t->p = PyString_FromStringAndSize(t->s, t->n - 1);
}
#else
if (t->is_unicode | t->is_str) {
if (t->intern) {
*t->p = PyUnicode_InternFromString(t->s);
} else if (t->encoding) {
*t->p = PyUnicode_Decode(t->s, t->n - 1, t->encoding, NULL);
} else {
*t->p = PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(t->s, t->n - 1);
}
} else {
*t->p = PyBytes_FromStringAndSize(t->s, t->n - 1);
}
#endif
if (!*t->p)
return -1;
if (PyObject_Hash(*t->p) == -1)
return -1;
++t;
}
return 0;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromString(const char* c_str) {
return __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(c_str, (Py_ssize_t)strlen(c_str));
}
static CYTHON_INLINE const char* __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(PyObject* o) {
Py_ssize_t ignore;
return __Pyx_PyObject_AsStringAndSize(o, &ignore);
}
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII || __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT
#if !CYTHON_PEP393_ENABLED
static const char* __Pyx_PyUnicode_AsStringAndSize(PyObject* o, Py_ssize_t *length) {
char* defenc_c;
PyObject* defenc = _PyUnicode_AsDefaultEncodedString(o, NULL);
if (!defenc) return NULL;
defenc_c = PyBytes_AS_STRING(defenc);
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII
{
char* end = defenc_c + PyBytes_GET_SIZE(defenc);
char* c;
for (c = defenc_c; c < end; c++) {
if ((unsigned char) (*c) >= 128) {
PyUnicode_AsASCIIString(o);
return NULL;
}
}
}
#endif
*length = PyBytes_GET_SIZE(defenc);
return defenc_c;
}
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE const char* __Pyx_PyUnicode_AsStringAndSize(PyObject* o, Py_ssize_t *length) {
if (unlikely(__Pyx_PyUnicode_READY(o) == -1)) return NULL;
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII
if (likely(PyUnicode_IS_ASCII(o))) {
*length = PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(o);
return PyUnicode_AsUTF8(o);
} else {
PyUnicode_AsASCIIString(o);
return NULL;
}
#else
return PyUnicode_AsUTF8AndSize(o, length);
#endif
}
#endif
#endif
static CYTHON_INLINE const char* __Pyx_PyObject_AsStringAndSize(PyObject* o, Py_ssize_t *length) {
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII || __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT
if (
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 && __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII
__Pyx_sys_getdefaultencoding_not_ascii &&
#endif
PyUnicode_Check(o)) {
return __Pyx_PyUnicode_AsStringAndSize(o, length);
} else
#endif
#if (!CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY) || (defined(PyByteArray_AS_STRING) && defined(PyByteArray_GET_SIZE))
if (PyByteArray_Check(o)) {
*length = PyByteArray_GET_SIZE(o);
return PyByteArray_AS_STRING(o);
} else
#endif
{
char* result;
int r = PyBytes_AsStringAndSize(o, &result, length);
if (unlikely(r < 0)) {
return NULL;
} else {
return result;
}
}
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(PyObject* x) {
int is_true = x == Py_True;
if (is_true | (x == Py_False) | (x == Py_None)) return is_true;
else return PyObject_IsTrue(x);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrueAndDecref(PyObject* x) {
int retval;
if (unlikely(!x)) return -1;
retval = __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(x);
Py_DECREF(x);
return retval;
}
static PyObject* __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLongWrongResultType(PyObject* result, const char* type_name) {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
if (PyLong_Check(result)) {
if (PyErr_WarnFormat(PyExc_DeprecationWarning, 1,
"__int__ returned non-int (type %.200s). "
"The ability to return an instance of a strict subclass of int "
"is deprecated, and may be removed in a future version of Python.",
Py_TYPE(result)->tp_name)) {
Py_DECREF(result);
return NULL;
}
return result;
}
#endif
PyErr_Format(PyExc_TypeError,
"__%.4s__ returned non-%.4s (type %.200s)",
type_name, type_name, Py_TYPE(result)->tp_name);
Py_DECREF(result);
return NULL;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(PyObject* x) {
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
PyNumberMethods *m;
#endif
const char *name = NULL;
PyObject *res = NULL;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(PyInt_Check(x) || PyLong_Check(x)))
#else
if (likely(PyLong_Check(x)))
#endif
return __Pyx_NewRef(x);
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
m = Py_TYPE(x)->tp_as_number;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (m && m->nb_int) {
name = "int";
res = m->nb_int(x);
}
else if (m && m->nb_long) {
name = "long";
res = m->nb_long(x);
}
#else
if (likely(m && m->nb_int)) {
name = "int";
res = m->nb_int(x);
}
#endif
#else
if (!PyBytes_CheckExact(x) && !PyUnicode_CheckExact(x)) {
res = PyNumber_Int(x);
}
#endif
if (likely(res)) {
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (unlikely(!PyInt_Check(res) && !PyLong_Check(res))) {
#else
if (unlikely(!PyLong_CheckExact(res))) {
#endif
return __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLongWrongResultType(res, name);
}
}
else if (!PyErr_Occurred()) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError,
"an integer is required");
}
return res;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE Py_ssize_t __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(PyObject* b) {
Py_ssize_t ival;
PyObject *x;
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
if (likely(PyInt_CheckExact(b))) {
if (sizeof(Py_ssize_t) >= sizeof(long))
return PyInt_AS_LONG(b);
else
return PyInt_AsSsize_t(b);
}
#endif
if (likely(PyLong_CheckExact(b))) {
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
const digit* digits = ((PyLongObject*)b)->ob_digit;
const Py_ssize_t size = Py_SIZE(b);
if (likely(__Pyx_sst_abs(size) <= 1)) {
ival = likely(size) ? digits[0] : 0;
if (size == -1) ival = -ival;
return ival;
} else {
switch (size) {
case 2:
if (8 * sizeof(Py_ssize_t) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (Py_ssize_t) (((((size_t)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[0]));
}
break;
case -2:
if (8 * sizeof(Py_ssize_t) > 2 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return -(Py_ssize_t) (((((size_t)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[0]));
}
break;
case 3:
if (8 * sizeof(Py_ssize_t) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (Py_ssize_t) (((((((size_t)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[0]));
}
break;
case -3:
if (8 * sizeof(Py_ssize_t) > 3 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return -(Py_ssize_t) (((((((size_t)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[0]));
}
break;
case 4:
if (8 * sizeof(Py_ssize_t) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return (Py_ssize_t) (((((((((size_t)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[0]));
}
break;
case -4:
if (8 * sizeof(Py_ssize_t) > 4 * PyLong_SHIFT) {
return -(Py_ssize_t) (((((((((size_t)digits[3]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[2]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[1]) << PyLong_SHIFT) | (size_t)digits[0]));
}
break;
}
}
#endif
return PyLong_AsSsize_t(b);
}
x = PyNumber_Index(b);
if (!x) return -1;
ival = PyInt_AsSsize_t(x);
Py_DECREF(x);
return ival;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject * __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(long b) {
return b ? __Pyx_NewRef(Py_True) : __Pyx_NewRef(Py_False);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject * __Pyx_PyInt_FromSize_t(size_t ival) {
return PyInt_FromSize_t(ival);
}
#endif /* Py_PYTHON_H */
�������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618748000.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/processing/circles_ext.pyx����������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000051512�00000000000�023113� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you must cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools
# File : occupancy_ext.pyx
# License : GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 23.11.2020
# cython: language_level=3
# cython: boundscheck=False
# cython: wraparound=False
# cython: initializedcheck=False
# cython: nonecheck=False
# cython: embedsignature=True
# cython: cdivision=True
#import numpy as np
from libc.math cimport floor, sqrt, acos, M_PI
from libc.float cimport DBL_MAX
cdef inline double fabs(double x) nogil:
return (x if x >= 0 else -x)
cdef inline double dist(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil:
# Distance between two 2D points
return sqrt((x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2)
cdef inline double dist2(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) nogil:
# Squared distance between two 2D points
return (x1 - x2) ** 2 + (y1 - y2) ** 2
cdef inline double term(double r, double _c, double _p) nogil:
# Term in calculation of `one_corner`
# Same for xc / xp and yc / yp
return sqrt(r ** 2 - (_c - _p) ** 2)
cdef inline double triangle(
double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3
) nogil:
return 0.5 * fabs(x1 * (y2 - y3) + x2 * (y3 - y1) + x3 * (y1 - y2))
cdef inline double dist_pl(
double x0,
double y0,
double x1,
double y1,
double x2,
double y2
) nogil:
# Distance from a point (x0, y0) to a line defined by two points
# (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)
denom = dist(x1, y1, x2, y2)
nom = fabs((y2 - y1) * x0 - (x2 - x1) * y0 + x2 * y1 - y2 * x1)
return nom / denom
cdef inline double circular_segment(double r, double h) nogil:
# Area of a circular segment from a circle of radius r and a line
# If the distance from the circle centre to the line is d, then
# h = r - d
if h < 0.0: # Happens for very small distances (d = r * 1e-13)
return 0.0
return r ** 2 * acos((r - h) / r) - (r - h) * sqrt(2 * r * h - h ** 2)
cdef inline double zero_corner(
Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
double px,
double py,
double xsize,
double ysize,
double x0,
double y0,
double r,
) nogil:
'''Compute the overlapping area between a circle and a rectangle when
exactly one of the rectangle's corners are inside the circle.
Parameters
----------
corners
Vector of 0 and 1 for the corner that is inside the circle. The
corners are in trigonometric order.
px, py
The pixel x and y coordinates.
xsize, ysize
The pixel width and height.
x, y
The circle origin x and y coordinates
r
The circle radius
Returns
-------
The overlapping area.
'''
# Distance from circle centre x0, y0 to line defined by the two
# intersections above and h = (r - d)
cdef double h
cdef double area = 0.
cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
# Corner case - if zero corners are inside, there might be no intersection
# This happens when the centre of the particle is in one of the corners
if ((x0 <= xmin and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom left
(x0 >= xmax and y0 <= ymin) or # Bottom right
(x0 >= xmax and y0 >= ymax) or # Top right
(x0 <= xmin and y0 >= ymax)): # Top left
return 0.
# Particle is fully encapsulated
if xmin < x0 < xmax and ymin < y0 < ymax:
return M_PI * r * r
# Below
elif xmin < x0 < xmax:
h = ysize / 2 + r - fabs(py - y0)
# Above
else:
h = xsize / 2 + r - fabs(px - x0)
# Area of the circular segment
area += circular_segment(r, h)
return area
cdef inline double one_corner(
Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
double px,
double py,
double xsize,
double ysize,
double x0,
double y0,
double r,
) nogil:
'''Compute the overlapping area between a circle and a rectangle when
exactly one of the rectangle's corners are inside the circle.
Parameters
----------
corners
Vector of 0 and 1 for the corner that is inside the circle. The
corners are in trigonometric order.
px, py
The pixel x and y coordinates.
xsize, ysize
The pixel width and height.
x, y
The circle origin x and y coordinates
r
The circle radius
Returns
-------
The overlapping area.
'''
# The bounded corner coordinates
cdef double xc = 0, yc = 0
# The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
cdef double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0
# Distance from circle centre x0, y0 to line defined by the two
# intersections above and h = (r - d)
cdef double d, h
cdef double area = 0.
# Pixel boundaries
cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
# Lower left corner
if corners[0] == 1:
xc = xmin
yc = ymin
x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0)
y1 = yc
x2 = xc
y2 = y0 + term(r, xc, x0)
# Lower right corner
elif corners[1] == 1:
xc = xmax
yc = ymin
x1 = xc
y1 = y0 + term(r, xc, x0)
x2 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0)
y2 = yc
# Upper right corner
elif corners[2] == 1:
xc = xmax
yc = ymax
x1 = x0 - term(r, yc, y0)
y1 = yc
x2 = xc
y2 = y0 - term(r, xc, x0)
# Upper left corner
elif corners[3] == 1:
xc = xmin
yc = ymax
x1 = x0 + term(r, yc, y0)
y1 = yc
x2 = xc
y2 = y0 - term(r, xc, x0)
d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
h = r - d
# Area of the circular segment
area += circular_segment(r, h)
# Area of the triangle
area += dist(xc, yc, x1, y1) * dist(xc, yc, x2, y2) / 2
return area
cdef inline double two_corner(
Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
double px,
double py,
double xsize,
double ysize,
double x0,
double y0,
double r,
) nogil:
'''Compute the overlapping area between a circle and a rectangle when
exactly one of the rectangle's corners are inside the circle.
Parameters
----------
corners
Vector of 0 and 1 for the corner that is inside the circle. The
corners are in trigonometric order.
px, py
The pixel x and y coordinates.
xsize, ysize
The pixel width and height.
x, y
The circle origin x and y coordinates
r
The circle radius
Returns
-------
The overlapping area.
'''
# The bounded corner coordinates
cdef double xc1 = 0, yc1 = 0, xc2 = 0, yc2 = 0
# The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
cdef double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0
# Distance from circle centre x0, y0 to line defined by the two
# intersections above and h = (r - d)
cdef double d, h
cdef double area = 0.
# Pixel boundaries
cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
# Bottom corners
if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1:
xc1 = xmin
yc1 = ymin
xc2 = xmax
yc2 = ymin
x1 = xc1
y1 = y0 + term(r, xc1, x0)
x2 = xc2
y2 = y0 + term(r, xc2, x0)
# Top corners
elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
xc1 = xmin
yc1 = ymax
xc2 = xmax
yc2 = ymax
x1 = xc1
y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0)
x2 = xc2
y2 = y0 - term(r, xc2, x0)
# Right corners
elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1:
xc1 = xmax
yc1 = ymin
xc2 = xmax
yc2 = ymax
x1 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0)
y1 = yc1
x2 = x0 - term(r, yc2, y0)
y2 = yc2
# Left corners
elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
xc1 = xmin
yc1 = ymin
xc2 = xmin
yc2 = ymax
x1 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0)
y1 = yc1
x2 = x0 + term(r, yc2, y0)
y2 = yc2
d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
h = r - d
# Area of the circular segment
area += circular_segment(r, h)
# Area of triangle1 and triangle2
area += triangle(x1, y1, xc2, yc2, xc1, yc1)
area += triangle(x1, y1, xc2, yc2, x2, y2)
return area
cdef inline double three_corner(
Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
double px,
double py,
double xsize,
double ysize,
double x0,
double y0,
double r,
) nogil:
'''Compute the overlapping area between a circle and a rectangle when
exactly one of the rectangle's corners are inside the circle.
Parameters
----------
corners
Vector of 0 and 1 for the corner that is inside the circle. The
corners are in trigonometric order.
px, py
The pixel x and y coordinates.
xsize, ysize
The pixel width and height.
x, y
The circle origin x and y coordinates
r
The circle radius
Returns
-------
The overlapping area.
'''
# The bounded corner coordinates
cdef double xc1 = 0, yc1 = 0, xc2 = 0, yc2 = 0
cdef double xc3 = 0, yc3 = 0, xc4 = 0, yc4 = 0
# The coords of the two intersections between the circle and the rectangle
cdef double x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0
# Distance from circle centre x0, y0 to line defined by the two
# intersections above and h = (r - d)
cdef double d, h
cdef double area = 0.
# Pixel boundaries
cdef double xmin = px - xsize / 2
cdef double xmax = px + xsize / 2
cdef double ymin = py - ysize / 2
cdef double ymax = py + ysize / 2
# Bottom right three corners
if corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1:
xc1 = xmin
yc1 = ymin
xc2 = xmax
yc2 = ymin
xc3 = xmax
yc3 = ymax
xc4 = xmin # Corner outside
yc4 = ymax # Corner outside
x1 = x0 - term(r, yc3, y0)
y1 = yc3
x2 = xc1
y2 = y0 + term(r, xc1, x0)
# Top right three corners
elif corners[1] == 1 and corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
xc1 = xmax
yc1 = ymin
xc2 = xmax
yc2 = ymax
xc3 = xmin
yc3 = ymax
xc4 = xmin # Corner outside
yc4 = ymin # Corner outside
x1 = xc3
y1 = y0 - term(r, xc3, x0)
x2 = x0 - term(r, yc1, y0)
y2 = yc1
# Top left three corners
elif corners[2] == 1 and corners[3] == 1 and corners[0] == 1:
xc1 = xmax
yc1 = ymax
xc2 = xmin
yc2 = ymax
xc3 = xmin
yc3 = ymin
xc4 = xmax # Corner outside
yc4 = ymin # Corner outside
x1 = xc1
y1 = y0 - term(r, xc1, x0)
x2 = x0 + term(r, yc3, y0)
y2 = yc3
# Bottom left three corners
elif corners[0] == 1 and corners[1] == 1 and corners[3] == 1:
xc1 = xmin
yc1 = ymax
xc2 = xmin
yc2 = ymin
xc3 = xmax
yc3 = ymin
xc4 = xmax # Corner outside
yc4 = ymax # Corner outside
x1 = xc3
y1 = y0 + term(r, xc3, x0)
x2 = x0 + term(r, yc1, y0)
y2 = yc1
d = dist_pl(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2)
h = r - d
# Area of the circular segment
area += circular_segment(r, h)
# Area of the rectangle
area += xsize * ysize
# Area of triangle
area -= dist(x1, y1, xc4, yc4) * dist(x2, y2, xc4, yc4) / 2
return area
cdef inline double four_corner(
Py_ssize_t[4] corners,
double px,
double py,
double xsize,
double ysize,
double x0,
double y0,
double r,
) nogil:
'''Compute the overlapping area between a circle and a rectangle when
exactly one of the rectangle's corners are inside the circle.
Parameters
----------
corners
Vector of 0 and 1 for the corner that is inside the circle. The
corners are in trigonometric order.
px, py
The pixel x and y coordinates.
xsize, ysize
The pixel width and height.
x, y
The circle origin x and y coordinates
r
The circle radius
Returns
-------
The overlapping area.
'''
return xsize * ysize
cpdef void circles2d_ext(
double[:, :] pixels,
double[:, :] positions,
double[:] radii,
double[:] xlim,
double[:] ylim,
) nogil:
'''Compute the 2D occupancy of circles of different radii.
::
Function signature:
void circles2d_ext(
double[:, :] pixels,
double[:, :] positions,
double[:] radii,
double[:] xlim,
double[:] ylim,
) nogil
This corresponds to the pixellisation of circular particles, such that
each pixel's value corresponds to the area covered by the particle.
It is important that all parameters sent to this function are initialised
properly. Please see the parameters below, or the function *will* segfault.
Alternatively, use the `pept.processing.occupancy2d` function which is
more robust and initialises all parameters for you.
Parameters
----------
pixels: (M, N) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 2, dtype = numpy.float64]
The 2D grid of pixels, initialised to zero. It can be created with
`numpy.zeros((nrows, ncols))`.
positions: (P, 2) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 2, dtype = numpy.float64]
The particles' 2D positions, where all rows are formatted as
`[x_coordinate, y_coordinate]`.
radii: (P,) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 1, dtype = numpy.float64]
The radii of each particle. It must have the same length as
`positions`.
xlim: (2,) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 1, dtype = numpy.float64]
The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the
x-dimension, formatted as [xmin, xmax].
ylim: (2,) numpy.ndarray[ndim = 1, dtype = numpy.float64]
The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the
y-dimension, formatted as [ymin, ymax].
'''
cdef Py_ssize_t nrows = positions.shape[0]
cdef Py_ssize_t nx = pixels.shape[0]
cdef Py_ssize_t ny = pixels.shape[1]
cdef double xsize = (xlim[1] - xlim[0]) / nx
cdef double ysize = (ylim[1] - ylim[0]) / ny
# print((
# f"nrows = {nrows}\n"
# f"nx = {nx}\n"
# f"ny = {ny}\n"
# f"xsize = {xsize}\n"
# f"ysize = {ysize}\n"
# ))
cdef double x, y, r # Particle x, y, radius
cdef double px, py # Pixel centre x, y
cdef Py_ssize_t min_nx, max_nx
cdef Py_ssize_t min_ny, max_ny
cdef Py_ssize_t num_corners # Number of intersected corners
cdef Py_ssize_t[4] corners # Intersected corners indices
cdef Py_ssize_t i, j, k, l
for i in range(nrows):
# Aliases
x = positions[i, 0]
y = positions[i, 1]
r = radii[i]
if r == 0:
if x == xlim[1]:
min_nx = nx - 1
else:
min_nx = floor((x - xlim[0]) / xsize)
if y == ylim[1]:
min_ny = ny - 1
else:
min_ny = floor((y - ylim[0]) / ysize)
if min_nx >= nx or min_nx < 0:
continue
if min_ny >= ny or min_ny < 0:
continue
pixels[min_nx, min_ny] += 1
continue
# Find minimum and maximum pixel indices over which the particle spans.
# This corresponds to the intersected cells
min_nx = floor((x - r - xlim[0]) / xsize)
max_nx = floor((x + r - xlim[0]) / xsize)
min_ny = floor((y - r - ylim[0]) / ysize)
max_ny = floor((y + r - ylim[0]) / ysize)
# print((
# "Before thresholding\n"
# f"x = {x}\n"
# f"y = {y}\n"
# f"r = {r}\n"
# f"min_nx = {min_nx}\n"
# f"max_nx = {max_nx}\n"
# f"min_ny = {min_ny}\n"
# f"max_ny = {max_ny}\n"
# ))
# Check pixel indices are within the system bounds
if min_nx >= nx:
continue
elif min_nx < 0:
min_nx = 0
if max_nx < 0:
continue
elif max_nx >= nx:
max_nx = nx - 1
if min_ny >= ny:
continue
elif min_ny < 0:
min_ny = 0
if max_ny < 0:
continue
elif max_ny >= ny:
max_ny = ny - 1
# print((
# "After thresholding\n"
# f"x = {x}\n"
# f"y = {y}\n"
# f"r = {r}\n"
# f"min_nx = {min_nx}\n"
# f"max_nx = {max_nx}\n"
# f"min_ny = {min_ny}\n"
# f"max_ny = {max_ny}\n"
# ))
# Iterate over all intersected pixels, computing the area covered by
# the particle
for j in range(min_nx, max_nx + 1):
for k in range(min_ny, max_ny + 1):
# Find the number of pixel corners inside the particle
num_corners = 0
for l in range(4):
corners[l] = 0
# Pixel centre coordinates
px = xlim[0] + (j + 0.5) * xsize
py = ylim[0] + (k + 0.5) * ysize
# print((
# f"For pixel indices [{j}, {k}]:\n"
# f"px = {px}\n"
# f"py = {py}\n"
# f"r2 = {r * r}\n"
# f"dist2 = {dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y)}\n"
# f"dist2 = {dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y)}\n"
# f"dist2 = {dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y)}\n"
# f"dist2 = {dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y)}\n"
# ))
# Lower left corner
if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
num_corners += 1
corners[0] = 1
# Lower right corner
if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py - 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
num_corners += 1
corners[1] = 1
# Upper right corner
if dist2(px + 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
num_corners += 1
corners[2] = 1
# Upper left corner
if dist2(px - 0.5 * xsize, py + 0.5 * ysize, x, y) < r * r:
num_corners += 1
corners[3] = 1
# print((
# f"num_corners = {num_corners}\n"
# f"corners = [{corners[0], corners[1], corners[2], corners[3]}]\n"
# ))
if num_corners == 0:
pixels[j, k] += zero_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
elif num_corners == 1:
pixels[j, k] += one_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
elif num_corners == 2:
pixels[j, k] += two_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
elif num_corners == 3:
pixels[j, k] += three_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
elif num_corners == 4:
pixels[j, k] += four_corner(corners, px, py, xsize, ysize, x, y, r)
��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1618748000.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/processing/occupancy.py�������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00000041771�00000000000�022411� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# pept is a Python library that unifies Positron Emission Particle
# Tracking (PEPT) research, including tracking, simulation, data analysis
# and visualisation tools.
#
# If you used this codebase or any software making use of it in a scientific
# publication, you should cite the following paper:
# Nicuşan AL, Windows-Yule CR. Positron emission particle tracking
# using machine learning. Review of Scientific Instruments.
# 2020 Jan 1;91(1):013329.
# https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5129251
#
# Copyright (C) 2019-2021 the pept developers
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program. If not, see .
# File : occupancy.py
# License: GNU v3.0
# Author : Andrei Leonard Nicusan
# Date : 23.11.2020
import time
import textwrap
import numpy as np
import pept
from .circles_ext import circles2d_ext
from .occupancy_ext import occupancy2d_ext
def circles2d(
positions,
number_of_pixels,
radii = 0.,
xlim = None,
ylim = None,
verbose = True,
):
'''Compute the 2D occupancy of circles of different radii.
This corresponds to the pixellisation of circular particles, such that
each pixel's value corresponds to the area covered by the particle.
You must specify the particles' `positions` (2D numpy array) and the
`number_of_pixels` in each dimension (`[nx, ny, nz]`). The `radii` can be
either:
1. Zero: the particles are considered to be points. Each pixel will have a
value +1 for every particle.
2. Single positive value: all particles have the same radius.
3. List of values of same length as `positions`: specify each particle's
radius.
The pixel area's bounds can be specified in `xlim` and `ylim`. If unset,
they will be computed automatically based on the minimum and maximum
values found in `positions`.
Parameters
----------
positions: (P, 2) numpy.ndarray
The particles' 2D positions, where each row is formatted as
`[x_coordinate, y_coordinate]`.
number_of_pixels: (2,) list-like
The number of pixels in the x-dimension and y-dimension. Each dimension
must have at least 2 pixels.
radii: float or (P,) list-like
The radius of each particle. If zero, every particle is considered as
a discrete point. If a single `float`, all particles are considered to
have the same radius. If it is a numpy array, it specifies each
particle's radius, and must have the same length as `positions`.
xlim: (2,) list-like, optional
The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the
x-dimension, formatted as [xmin, xmax]. If unset, they will be computed
automatically based on the minimum and maximum values found in
`positions`.
ylim: (2,) list-like, optional
The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the
y-dimension, formatted as [ymin, ymax]. If unset, they will be computed
automatically based on the minimum and maximum values found in
`positions`.
verbose: bool, default True
Time the pixellisation step and print it to the terminal.
Returns
-------
pept.Pixels (numpy.ndarray subclass)
The created pixels, each cell containing the area covered by particles.
The `pept.Pixels` class inherits all properties and methods from
`numpy.ndarray`, so you can use it exactly like you would a numpy
array. It just contains extra attributes (e.g. `xlim`, `ylim`) and
some PEPT-oriented methods (e.g. `pixels_trace`).
Raises
------
ValueError
If `positions` is not a 2D array-like with exactly 2 columns, or
`number_of_pixels` is not a 1D list-like with exactly 2 values or it
contains a value smaller than 2. If `radii` is a list-like that does
not have the same length as `positions`.
Examples
--------
Create ten random particle positions between 0-100 and radii between
0.5-2.5:
>>> positions = np.random.random((10, 2)) * 100
>>> radii = 0.5 + np.random.random(len(positions)) * 2
Now pixellise those particles as circles over a grid of (20, 10) pixels:
>>> import pept.processing as pp
>>> num_pixels = (20, 10)
>>> pixels = pp.circles2d(positions, num_pixels, radii)
Alternatively, specify the system's bounds explicitly:
>>> pixels = pp.circles2d(
>>> positions, (20, 10), radii, xlim = [10, 90], ylim = [-5, 105]
>>> )
You can plot those pixels in two ways - using `PlotlyGrapher` (this plots a
3D "heatmap", as a coloured surface):
>>> from pept.visualisation import PlotlyGrapher
>>> grapher = PlotlyGrapher()
>>> grapher.add_pixels(pixels)
>>> grapher.show()
Or using raw `Plotly` (this plots a "true" heatmap) - this is recommended:
>>> import plotly.graph_objs as go
>>> fig = go.Figure()
>>> fig.add_trace(pixels.heatmap_trace())
>>> fig.show()
'''
if verbose:
start = time.time()
# Type-checking inputs
positions = np.asarray(positions, order = 'C', dtype = np.float64)
# Check that points has at least 4 columns.
if positions.ndim != 2 or positions.shape[1] != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `positions` should have exactly 2 columns, "
"corresponding to the [x, y] coordinates of the particle "
f"positions. Received array with shape {positions.shape}."
)))
number_of_pixels = np.asarray(
number_of_pixels,
order = "C",
dtype = int
)
if number_of_pixels.ndim != 1 or len(number_of_pixels) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must be a list-like "
"with exactly two values, corresponding to the "
"number of pixels in the x- and y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {number_of_pixels.shape}."
)))
if (number_of_pixels < 2).any():
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must set at least two "
"pixels in each dimension (i.e. all elements in "
"`number_of_elements` must be larger or equal to two). "
f"Received `{number_of_pixels}`."
)))
# `radii` is either a float, or a numpy array
try:
radii = float(radii)
radii = np.ones(len(positions)) * radii
except Exception:
radii = np.asarray(radii, order = 'C', dtype = np.float64)
if radii.ndim != 1 or len(radii) != len(positions):
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `radii` must be a float (i.e. single radius "
"for all particles) or a 1D numpy array of radii for each "
"particle in the system - so `radii` must have the same "
"length as `positions`. Received array with length "
f"{len(radii)} != {len(positions)}."
)))
# Maximum particle radius
max_radius = radii.max()
if xlim is None:
xmin = (positions[:, 0].min() - max_radius)
xmax = (positions[:, 0].max() + max_radius)
xlim = np.array([
xmin - 0.01 * abs(xmin),
xmax + 0.01 * abs(xmax),
])
else:
xlim = np.asarray(xlim, dtype = np.float64)
if xlim.ndim != 1 or len(xlim) != 2 or xlim[0] >= xlim[1]:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `xlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the x-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {xlim.shape}."
)))
if ylim is None:
ymin = (positions[:, 1].min() - max_radius)
ymax = (positions[:, 1].max() + max_radius)
ylim = np.array([
ymin - 0.01 * abs(ymin),
ymax + 0.01 * abs(ymax),
])
else:
ylim = np.asarray(ylim, dtype = np.float64)
if ylim.ndim != 1 or len(ylim) != 2 or ylim[0] >= ylim[1]:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `ylim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
pixels = np.zeros(tuple(number_of_pixels), order = "C", dtype = np.float64)
# This modifies `pixels` in-place
circles2d_ext(
pixels,
positions,
radii,
xlim,
ylim,
)
occupancy_grid = pept.Pixels(pixels, xlim = xlim, ylim = ylim)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print(f"Computed occupancy grid in {end - start} s")
return occupancy_grid
def occupancy2d(
points,
number_of_pixels,
radius,
xlim = None,
ylim = None,
omit_last = False,
verbose = True,
):
'''Compute the 2D occupancy / residence time distribution of a single
circular particle moving along a trajectory.
This corresponds to the pixellisation of moving circular particles, such
that for every two consecutive particle locations, a 2D cylinder (i.e.
convex hull of two circles at the two particle positions), the fraction of
its area that intersets a pixel is multiplied with the time between the
two particle locations and saved in the input `pixels`.
You must specify the `points` (2D numpy array) recorded along a particle's
trajectory, formatted as [time, x, y] of each location, along with the
`number_of_pixels` in each dimension (`[nx, ny]`) and particle `radius`.
The pixel area's bounds can be specified in `xlim` and `ylim`. If unset,
they will be computed automatically based on the minimum and maximum
values found in `points`.
Parameters
----------
points: (P, 3) numpy.ndarray
The particles' 2D locations and corresponding timestamp, where each row
is formatted as `[time, x_coordinate, y_coordinate]`. Must have at
least two points.
number_of_pixels: (2,) list-like
The number of pixels in the x-dimension and y-dimension. Each dimension
must have at least 2 pixels.
radius: float
The radius of the particle. It can be given in any system of units, as
long as it is consistent with what is used for the particle locations.
xlim: (2,) list-like, optional
The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the
x-dimension, formatted as [xmin, xmax]. If unset, they will be computed
automatically based on the minimum and maximum values found in
`positions`.
ylim: (2,) list-like, optional
The limits of the system over which the pixels span in the
y-dimension, formatted as [ymin, ymax]. If unset, they will be computed
automatically based on the minimum and maximum values found in
`positions`.
omit_last: bool, default False
If true, omit the last circle in the particle positions. Useful if
rasterizing the same trajectory piece-wise; if you split the trajectory
and call this function multiple times, set `omit_last = 0` to avoid
considering the last particle location twice.
verbose: bool, default True
Time the pixellisation step and print it to the terminal.
Returns
-------
pept.Pixels (numpy.ndarray subclass)
The created pixels, each cell containing the area covered by particles.
The `pept.Pixels` class inherits all properties and methods from
`numpy.ndarray`, so you can use it exactly like you would a numpy
array. It just contains extra attributes (e.g. `xlim`, `ylim`) and
some PEPT-oriented methods (e.g. `pixels_trace`).
Raises
------
ValueError
If `positions` is not a 2D array-like with exactly 3 columns, or
`number_of_pixels` is not a 1D list-like with exactly 2 values or it
contains a value smaller than 2. If `xlim` or `ylim` have `max` < `min`
or there are particle positions falling outside the system defined by
`xlim` and `ylim`, including the area.
Examples
--------
Create ten random particle positions between 0-100 and radius 0.2:
>>> positions = np.random.random((10, 2)) * 100
>>> radius = 0.2
Now pixellise this trajectory over a grid of (20, 10) pixels:
>>> import pept.processing as pp
>>> num_pixels = (20, 10)
>>> pixels = pp.occupancy2d(positions, num_pixels, radius)
Alternatively, specify the system's bounds explicitly:
>>> pixels = pp.occupancy2d(
>>> positions, (20, 10), radius, xlim = [10, 90], ylim = [-5, 105]
>>> )
You can plot those pixels in two ways - using `PlotlyGrapher` (this plots a
3D "heatmap", as a coloured surface):
>>> from pept.visualisation import PlotlyGrapher
>>> grapher = PlotlyGrapher()
>>> grapher.add_pixels(pixels)
>>> grapher.show()
Or using raw `Plotly` (this plots a "true" heatmap) - this is recommended:
>>> import plotly.graph_objs as go
>>> fig = go.Figure()
>>> fig.add_trace(pixels.heatmap_trace())
>>> fig.show()
'''
if verbose:
start = time.time()
# Type-checking inputs
points = np.array(points, order = 'C', dtype = np.float32)
# Check that points has exactly 3 columns for [time, x, y]
if points.ndim != 2 or points.shape[1] != 3:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `points` should have exactly 3 columns, "
"formatted as the [time, x, y] coordinates of the particle "
f"positions. Received array with shape {points.shape}."
)))
times = np.array(points[:, 0], order = "C", dtype = np.float32)
positions = np.array(points[:, 1:], order = "C", dtype = np.float32)
number_of_pixels = np.asarray(
number_of_pixels,
order = "C",
dtype = np.int32,
)
if number_of_pixels.ndim != 1 or len(number_of_pixels) != 2:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must be a list-like "
"with exactly two values, corresponding to the "
"number of pixels in the x- and y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {number_of_pixels.shape}."
)))
if (number_of_pixels < 2).any():
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `number_of_pixels` must set at least two "
"pixels in each dimension (i.e. all elements in "
"`number_of_elements` must be larger or equal to two). "
f"Received `{number_of_pixels}`."
)))
radius = np.float32(radius)
if xlim is None:
xlim = np.array([
positions[:, 0].min() - radius,
positions[:, 0].max() + radius,
], dtype = np.float32)
else:
xlim = np.asarray(xlim, dtype = np.float32)
if xlim.ndim != 1 or len(xlim) != 2 or xlim[0] >= xlim[1]:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `xlim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the x-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {xlim.shape}."
)))
if ylim is None:
ylim = np.array([
positions[:, 1].min() - radius,
positions[:, 1].max() + radius,
], dtype = np.float32)
else:
ylim = np.asarray(ylim, dtype = np.float32)
if ylim.ndim != 1 or len(ylim) != 2 or ylim[0] >= ylim[1]:
raise ValueError(textwrap.fill((
"The input `ylim` parameter must be a list with exactly "
"two values, corresponding to the minimum and maximum "
"coordinates of the pixel space in the y-dimension. "
f"Received parameter with shape {ylim.shape}."
)))
omit_last = bool(omit_last)
# `occupancy2d_ext` expects a single-precision pixels array
grid = np.zeros(tuple(number_of_pixels), order = "C", dtype = np.float32)
# This modifies `pixels` in-place
occupancy2d_ext(
grid,
xlim,
ylim,
positions,
times,
radius,
omit_last,
)
pixels = pept.Pixels(grid, xlim = xlim, ylim = ylim)
if verbose:
end = time.time()
print(f"Computed occupancy grid in {end - start} s")
return pixels
�������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000026�00000000000�010213� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������22 mtime=1619626438.0
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������pept-0.3.2/pept/processing/occupancy_ext.c����������������������������������������������������������0000644�0001750�0001750�00002745324�00000000000�023072� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00andreinicusan�������������������andreinicusan����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������/* Generated by Cython 0.29.23 */
/* BEGIN: Cython Metadata
{
"distutils": {
"depends": [
"pept/processing/rtd2d.c",
"pept/processing/rtd2d.h"
],
"extra_compile_args": [
"-Ofast",
"-flto",
"-Werror=vla",
"/O2",
"/fp:fast",
"/GL"
],
"extra_link_args": [
"-flto",
"/LTCG"
],
"include_dirs": [
"pept/processing",
"/tmp/pip-build-env-_m6gckns/overlay/lib/python3.9/site-packages/numpy/core/include"
],
"name": "pept.processing.occupancy_ext",
"sources": [
"pept/processing/occupancy_ext.pyx"
]
},
"module_name": "pept.processing.occupancy_ext"
}
END: Cython Metadata */
#ifndef PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN
#define PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN
#endif /* PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN */
#include "Python.h"
#ifndef Py_PYTHON_H
#error Python headers needed to compile C extensions, please install development version of Python.
#elif PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02060000 || (0x03000000 <= PY_VERSION_HEX && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03030000)
#error Cython requires Python 2.6+ or Python 3.3+.
#else
#define CYTHON_ABI "0_29_23"
#define CYTHON_HEX_VERSION 0x001D17F0
#define CYTHON_FUTURE_DIVISION 1
#include
#ifndef offsetof
#define offsetof(type, member) ( (size_t) & ((type*)0) -> member )
#endif
#if !defined(WIN32) && !defined(MS_WINDOWS)
#ifndef __stdcall
#define __stdcall
#endif
#ifndef __cdecl
#define __cdecl
#endif
#ifndef __fastcall
#define __fastcall
#endif
#endif
#ifndef DL_IMPORT
#define DL_IMPORT(t) t
#endif
#ifndef DL_EXPORT
#define DL_EXPORT(t) t
#endif
#define __PYX_COMMA ,
#ifndef HAVE_LONG_LONG
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x02070000
#define HAVE_LONG_LONG
#endif
#endif
#ifndef PY_LONG_LONG
#define PY_LONG_LONG LONG_LONG
#endif
#ifndef Py_HUGE_VAL
#define Py_HUGE_VAL HUGE_VAL
#endif
#ifdef PYPY_VERSION
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY 1
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 0
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03050000
#undef CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS)
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 0
#undef CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
#define CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS 1
#undef CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS 0
#undef CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS
#define CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS 0
#undef CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE 0
#undef CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL 0
#undef CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
#define CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
#define CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
#define CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK 0
#elif defined(PYSTON_VERSION)
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON 1
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON 0
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS 0
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 0
#ifndef CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
#define CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS 0
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS
#define CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS 1
#endif
#undef CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE 0
#undef CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL 0
#undef CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
#define CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
#define CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS 0
#undef CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
#define CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK 0
#else
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON 0
#define CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON 1
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS 1
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070000
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP)
#define CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP 1
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
#undef CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS)
#define CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS 1
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070000
#undef CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS)
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS 1
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030300F0
#undef CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 0
#elif !defined(CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER)
#define CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_WRITER 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS
#define CYTHON_AVOID_BORROWED_REFS 0
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS
#define CYTHON_UNPACK_METHODS 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL 1
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT
#define CYTHON_PEP489_MULTI_PHASE_INIT (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03050000)
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE
#define CYTHON_USE_TP_FINALIZE (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030400a1)
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030600B1)
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
#define CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK (PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030700A3)
#endif
#endif
#if !defined(CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL)
#define CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL (CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL && PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030600B1)
#endif
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLONG_INTERNALS
#include "longintrepr.h"
#undef SHIFT
#undef BASE
#undef MASK
#ifdef SIZEOF_VOID_P
enum { __pyx_check_sizeof_voidp = 1 / (int)(SIZEOF_VOID_P == sizeof(void*)) };
#endif
#endif
#ifndef __has_attribute
#define __has_attribute(x) 0
#endif
#ifndef __has_cpp_attribute
#define __has_cpp_attribute(x) 0
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_RESTRICT
#if defined(__GNUC__)
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT __restrict__
#elif defined(_MSC_VER) && _MSC_VER >= 1400
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT __restrict
#elif defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT restrict
#else
#define CYTHON_RESTRICT
#endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_UNUSED
# if defined(__GNUC__)
# if !(defined(__cplusplus)) || (__GNUC__ > 3 || (__GNUC__ == 3 && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= 4))
# define CYTHON_UNUSED __attribute__ ((__unused__))
# else
# define CYTHON_UNUSED
# endif
# elif defined(__ICC) || (defined(__INTEL_COMPILER) && !defined(_MSC_VER))
# define CYTHON_UNUSED __attribute__ ((__unused__))
# else
# define CYTHON_UNUSED
# endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_MAYBE_UNUSED_VAR
# if defined(__cplusplus)
template void CYTHON_MAYBE_UNUSED_VAR( const T& ) { }
# else
# define CYTHON_MAYBE_UNUSED_VAR(x) (void)(x)
# endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED
# if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
# define CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED
# else
# define CYTHON_NCP_UNUSED CYTHON_UNUSED
# endif
#endif
#define __Pyx_void_to_None(void_result) ((void)(void_result), Py_INCREF(Py_None), Py_None)
#ifdef _MSC_VER
#ifndef _MSC_STDINT_H_
#if _MSC_VER < 1300
typedef unsigned char uint8_t;
typedef unsigned int uint32_t;
#else
typedef unsigned __int8 uint8_t;
typedef unsigned __int32 uint32_t;
#endif
#endif
#else
#include
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#if defined(__cplusplus) && __cplusplus >= 201103L
#if __has_cpp_attribute(fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH [[fallthrough]]
#elif __has_cpp_attribute(clang::fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH [[clang::fallthrough]]
#elif __has_cpp_attribute(gnu::fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH [[gnu::fallthrough]]
#endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#if __has_attribute(fallthrough)
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH __attribute__((fallthrough))
#else
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#endif
#endif
#if defined(__clang__ ) && defined(__apple_build_version__)
#if __apple_build_version__ < 7000000
#undef CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#define CYTHON_FALLTHROUGH
#endif
#endif
#endif
#ifndef CYTHON_INLINE
#if defined(__clang__)
#define CYTHON_INLINE __inline__ __attribute__ ((__unused__))
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
#define CYTHON_INLINE __inline__
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
#define CYTHON_INLINE __inline
#elif defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L
#define CYTHON_INLINE inline
#else
#define CYTHON_INLINE
#endif
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070600 && !defined(Py_OptimizeFlag)
#define Py_OptimizeFlag 0
#endif
#define __PYX_BUILD_PY_SSIZE_T "n"
#define CYTHON_FORMAT_SSIZE_T "z"
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
#define __Pyx_BUILTIN_MODULE_NAME "__builtin__"
#define __Pyx_PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)\
PyCode_New(a+k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)
#define __Pyx_DefaultClassType PyClass_Type
#else
#define __Pyx_BUILTIN_MODULE_NAME "builtins"
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030800A4 && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030800B2
#define __Pyx_PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)\
PyCode_New(a, 0, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)\
PyCode_New(a, k, l, s, f, code, c, n, v, fv, cell, fn, name, fline, lnos)
#endif
#define __Pyx_DefaultClassType PyType_Type
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES
#define Py_TPFLAGS_CHECKTYPES 0
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_INDEX
#define Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_INDEX 0
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER
#define Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_NEWBUFFER 0
#endif
#ifndef Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE
#define Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_FINALIZE 0
#endif
#ifndef METH_STACKLESS
#define METH_STACKLESS 0
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX <= 0x030700A3 || !defined(METH_FASTCALL)
#ifndef METH_FASTCALL
#define METH_FASTCALL 0x80
#endif
typedef PyObject *(*__Pyx_PyCFunctionFast) (PyObject *self, PyObject *const *args, Py_ssize_t nargs);
typedef PyObject *(*__Pyx_PyCFunctionFastWithKeywords) (PyObject *self, PyObject *const *args,
Py_ssize_t nargs, PyObject *kwnames);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCFunctionFast _PyCFunctionFast
#define __Pyx_PyCFunctionFastWithKeywords _PyCFunctionFastWithKeywords
#endif
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
#define __Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(func)\
((PyCFunction_Check(func) && (METH_FASTCALL == (PyCFunction_GET_FLAGS(func) & ~(METH_CLASS | METH_STATIC | METH_COEXIST | METH_KEYWORDS | METH_STACKLESS)))))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyFastCFunction_Check(func) 0
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyObject_Malloc)
#define PyObject_Malloc(s) PyMem_Malloc(s)
#define PyObject_Free(p) PyMem_Free(p)
#define PyObject_Realloc(p) PyMem_Realloc(p)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030400A1
#define PyMem_RawMalloc(n) PyMem_Malloc(n)
#define PyMem_RawRealloc(p, n) PyMem_Realloc(p, n)
#define PyMem_RawFree(p) PyMem_Free(p)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYSTON
#define __Pyx_PyCode_HasFreeVars(co) PyCode_HasFreeVars(co)
#define __Pyx_PyFrame_SetLineNumber(frame, lineno) PyFrame_SetLineNumber(frame, lineno)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCode_HasFreeVars(co) (PyCode_GetNumFree(co) > 0)
#define __Pyx_PyFrame_SetLineNumber(frame, lineno) (frame)->f_lineno = (lineno)
#endif
#if !CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE || PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x02070000
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current PyThreadState_GET()
#elif PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03060000
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current _PyThreadState_UncheckedGet()
#elif PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x03000000
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current PyThreadState_GET()
#else
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current _PyThreadState_Current
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030700A2 && !defined(PyThread_tss_create) && !defined(Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT)
#include "pythread.h"
#define Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT 0
typedef int Py_tss_t;
static CYTHON_INLINE int PyThread_tss_create(Py_tss_t *key) {
*key = PyThread_create_key();
return 0;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE Py_tss_t * PyThread_tss_alloc(void) {
Py_tss_t *key = (Py_tss_t *)PyObject_Malloc(sizeof(Py_tss_t));
*key = Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT;
return key;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void PyThread_tss_free(Py_tss_t *key) {
PyObject_Free(key);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int PyThread_tss_is_created(Py_tss_t *key) {
return *key != Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void PyThread_tss_delete(Py_tss_t *key) {
PyThread_delete_key(*key);
*key = Py_tss_NEEDS_INIT;
}
static CYTHON_INLINE int PyThread_tss_set(Py_tss_t *key, void *value) {
return PyThread_set_key_value(*key, value);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE void * PyThread_tss_get(Py_tss_t *key) {
return PyThread_get_key_value(*key);
}
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON || defined(_PyDict_NewPresized)
#define __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(n) ((n <= 8) ? PyDict_New() : _PyDict_NewPresized(n))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyDict_NewPresized(n) PyDict_New()
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 || CYTHON_FUTURE_DIVISION
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Divide(x,y) PyNumber_TrueDivide(x,y)
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_InPlaceDivide(x,y) PyNumber_InPlaceTrueDivide(x,y)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Divide(x,y) PyNumber_Divide(x,y)
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_InPlaceDivide(x,y) PyNumber_InPlaceDivide(x,y)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON && PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030500A1 && CYTHON_USE_UNICODE_INTERNALS
#define __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(dict, name) _PyDict_GetItem_KnownHash(dict, name, ((PyASCIIObject *) name)->hash)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyDict_GetItemStr(dict, name) PyDict_GetItem(dict, name)
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX > 0x03030000 && defined(PyUnicode_KIND)
#define CYTHON_PEP393_ENABLED 1
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READY(op) (likely(PyUnicode_IS_READY(op)) ?\
0 : _PyUnicode_Ready((PyObject *)(op)))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u) PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ_CHAR(u, i) PyUnicode_READ_CHAR(u, i)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_MAX_CHAR_VALUE(u) PyUnicode_MAX_CHAR_VALUE(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_KIND(u) PyUnicode_KIND(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_DATA(u) PyUnicode_DATA(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ(k, d, i) PyUnicode_READ(k, d, i)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_WRITE(k, d, i, ch) PyUnicode_WRITE(k, d, i, ch)
#if defined(PyUnicode_IS_READY) && defined(PyUnicode_GET_SIZE)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_IS_TRUE(u) (0 != (likely(PyUnicode_IS_READY(u)) ? PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u) : PyUnicode_GET_SIZE(u)))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_IS_TRUE(u) (0 != PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u))
#endif
#else
#define CYTHON_PEP393_ENABLED 0
#define PyUnicode_1BYTE_KIND 1
#define PyUnicode_2BYTE_KIND 2
#define PyUnicode_4BYTE_KIND 4
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READY(op) (0)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_GET_LENGTH(u) PyUnicode_GET_SIZE(u)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ_CHAR(u, i) ((Py_UCS4)(PyUnicode_AS_UNICODE(u)[i]))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_MAX_CHAR_VALUE(u) ((sizeof(Py_UNICODE) == 2) ? 65535 : 1114111)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_KIND(u) (sizeof(Py_UNICODE))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_DATA(u) ((void*)PyUnicode_AS_UNICODE(u))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_READ(k, d, i) ((void)(k), (Py_UCS4)(((Py_UNICODE*)d)[i]))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_WRITE(k, d, i, ch) (((void)(k)), ((Py_UNICODE*)d)[i] = ch)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_IS_TRUE(u) (0 != PyUnicode_GET_SIZE(u))
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_Concat(a, b) PyNumber_Add(a, b)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_ConcatSafe(a, b) PyNumber_Add(a, b)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_Concat(a, b) PyUnicode_Concat(a, b)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_ConcatSafe(a, b) ((unlikely((a) == Py_None) || unlikely((b) == Py_None)) ?\
PyNumber_Add(a, b) : __Pyx_PyUnicode_Concat(a, b))
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyUnicode_Contains)
#define PyUnicode_Contains(u, s) PySequence_Contains(u, s)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyByteArray_Check)
#define PyByteArray_Check(obj) PyObject_TypeCheck(obj, &PyByteArray_Type)
#endif
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY && !defined(PyObject_Format)
#define PyObject_Format(obj, fmt) PyObject_CallMethod(obj, "__format__", "O", fmt)
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyString_FormatSafe(a, b) ((unlikely((a) == Py_None || (PyString_Check(b) && !PyString_CheckExact(b)))) ? PyNumber_Remainder(a, b) : __Pyx_PyString_Format(a, b))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FormatSafe(a, b) ((unlikely((a) == Py_None || (PyUnicode_Check(b) && !PyUnicode_CheckExact(b)))) ? PyNumber_Remainder(a, b) : PyUnicode_Format(a, b))
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyString_Format(a, b) PyUnicode_Format(a, b)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyString_Format(a, b) PyString_Format(a, b)
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 && !defined(PyObject_ASCII)
#define PyObject_ASCII(o) PyObject_Repr(o)
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define PyBaseString_Type PyUnicode_Type
#define PyStringObject PyUnicodeObject
#define PyString_Type PyUnicode_Type
#define PyString_Check PyUnicode_Check
#define PyString_CheckExact PyUnicode_CheckExact
#ifndef PyObject_Unicode
#define PyObject_Unicode PyObject_Str
#endif
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_Check(obj) PyUnicode_Check(obj)
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_CheckExact(obj) PyUnicode_CheckExact(obj)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_Check(obj) (PyString_Check(obj) || PyUnicode_Check(obj))
#define __Pyx_PyBaseString_CheckExact(obj) (PyString_CheckExact(obj) || PyUnicode_CheckExact(obj))
#endif
#ifndef PySet_CheckExact
#define PySet_CheckExact(obj) (Py_TYPE(obj) == &PySet_Type)
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030900A4
#define __Pyx_SET_REFCNT(obj, refcnt) Py_SET_REFCNT(obj, refcnt)
#define __Pyx_SET_SIZE(obj, size) Py_SET_SIZE(obj, size)
#else
#define __Pyx_SET_REFCNT(obj, refcnt) Py_REFCNT(obj) = (refcnt)
#define __Pyx_SET_SIZE(obj, size) Py_SIZE(obj) = (size)
#endif
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define __Pyx_PySequence_SIZE(seq) Py_SIZE(seq)
#else
#define __Pyx_PySequence_SIZE(seq) PySequence_Size(seq)
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define PyIntObject PyLongObject
#define PyInt_Type PyLong_Type
#define PyInt_Check(op) PyLong_Check(op)
#define PyInt_CheckExact(op) PyLong_CheckExact(op)
#define PyInt_FromString PyLong_FromString
#define PyInt_FromUnicode PyLong_FromUnicode
#define PyInt_FromLong PyLong_FromLong
#define PyInt_FromSize_t PyLong_FromSize_t
#define PyInt_FromSsize_t PyLong_FromSsize_t
#define PyInt_AsLong PyLong_AsLong
#define PyInt_AS_LONG PyLong_AS_LONG
#define PyInt_AsSsize_t PyLong_AsSsize_t
#define PyInt_AsUnsignedLongMask PyLong_AsUnsignedLongMask
#define PyInt_AsUnsignedLongLongMask PyLong_AsUnsignedLongLongMask
#define PyNumber_Int PyNumber_Long
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define PyBoolObject PyLongObject
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 && CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
#ifndef PyUnicode_InternFromString
#define PyUnicode_InternFromString(s) PyUnicode_FromString(s)
#endif
#endif
#if PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030200A4
typedef long Py_hash_t;
#define __Pyx_PyInt_FromHash_t PyInt_FromLong
#define __Pyx_PyInt_AsHash_t PyInt_AsLong
#else
#define __Pyx_PyInt_FromHash_t PyInt_FromSsize_t
#define __Pyx_PyInt_AsHash_t PyInt_AsSsize_t
#endif
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyMethod_New(func, self, klass) ((self) ? ((void)(klass), PyMethod_New(func, self)) : __Pyx_NewRef(func))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyMethod_New(func, self, klass) PyMethod_New(func, self, klass)
#endif
#if CYTHON_USE_ASYNC_SLOTS
#if PY_VERSION_HEX >= 0x030500B1
#define __Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct PyAsyncMethods
#define __Pyx_PyType_AsAsync(obj) (Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_as_async)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyType_AsAsync(obj) ((__Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct*) (Py_TYPE(obj)->tp_reserved))
#endif
#else
#define __Pyx_PyType_AsAsync(obj) NULL
#endif
#ifndef __Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct
typedef struct {
unaryfunc am_await;
unaryfunc am_aiter;
unaryfunc am_anext;
} __Pyx_PyAsyncMethodsStruct;
#endif
#if defined(WIN32) || defined(MS_WINDOWS)
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#endif
#include
#ifdef NAN
#define __PYX_NAN() ((float) NAN)
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE float __PYX_NAN() {
float value;
memset(&value, 0xFF, sizeof(value));
return value;
}
#endif
#if defined(__CYGWIN__) && defined(_LDBL_EQ_DBL)
#define __Pyx_truncl trunc
#else
#define __Pyx_truncl truncl
#endif
#define __PYX_MARK_ERR_POS(f_index, lineno) \
{ __pyx_filename = __pyx_f[f_index]; (void)__pyx_filename; __pyx_lineno = lineno; (void)__pyx_lineno; __pyx_clineno = __LINE__; (void)__pyx_clineno; }
#define __PYX_ERR(f_index, lineno, Ln_error) \
{ __PYX_MARK_ERR_POS(f_index, lineno) goto Ln_error; }
#ifndef __PYX_EXTERN_C
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define __PYX_EXTERN_C extern "C"
#else
#define __PYX_EXTERN_C extern
#endif
#endif
#define __PYX_HAVE__pept__processing__occupancy_ext
#define __PYX_HAVE_API__pept__processing__occupancy_ext
/* Early includes */
#include
#include "rtd2d.c"
#include "rtd2d.h"
#include "pythread.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include "pystate.h"
#ifdef _OPENMP
#include
#endif /* _OPENMP */
#if defined(PYREX_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS) && !defined(CYTHON_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS)
#define CYTHON_WITHOUT_ASSERTIONS
#endif
typedef struct {PyObject **p; const char *s; const Py_ssize_t n; const char* encoding;
const char is_unicode; const char is_str; const char intern; } __Pyx_StringTabEntry;
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII 0
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_UTF8 0
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT (PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3 && __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_UTF8)
#define __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING ""
#define __Pyx_PyObject_FromString __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyObject_FromStringAndSize __Pyx_PyBytes_FromStringAndSize
#define __Pyx_uchar_cast(c) ((unsigned char)c)
#define __Pyx_long_cast(x) ((long)x)
#define __Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(v, type, is_signed) (\
(sizeof(type) < sizeof(Py_ssize_t)) ||\
(sizeof(type) > sizeof(Py_ssize_t) &&\
likely(v < (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ||\
v == (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX) &&\
(!is_signed || likely(v > (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MIN ||\
v == (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MIN))) ||\
(sizeof(type) == sizeof(Py_ssize_t) &&\
(is_signed || likely(v < (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX ||\
v == (type)PY_SSIZE_T_MAX))) )
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_is_valid_index(Py_ssize_t i, Py_ssize_t limit) {
return (size_t) i < (size_t) limit;
}
#if defined (__cplusplus) && __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) std::abs(value)
#elif SIZEOF_INT >= SIZEOF_SIZE_T
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) abs(value)
#elif SIZEOF_LONG >= SIZEOF_SIZE_T
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) labs(value)
#elif defined (_MSC_VER)
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) ((Py_ssize_t)_abs64(value))
#elif defined (__STDC_VERSION__) && __STDC_VERSION__ >= 199901L
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) llabs(value)
#elif defined (__GNUC__)
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) __builtin_llabs(value)
#else
#define __Pyx_sst_abs(value) ((value<0) ? -value : value)
#endif
static CYTHON_INLINE const char* __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE const char* __Pyx_PyObject_AsStringAndSize(PyObject*, Py_ssize_t* length);
#define __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromString(s) PyByteArray_FromStringAndSize((const char*)s, strlen((const char*)s))
#define __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromStringAndSize(s, l) PyByteArray_FromStringAndSize((const char*)s, l)
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString PyBytes_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_FromStringAndSize PyBytes_FromStringAndSize
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromString(const char*);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromString __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromStringAndSize __Pyx_PyBytes_FromStringAndSize
#else
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromString __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromString
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromStringAndSize __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsWritableString(s) ((char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsWritableSString(s) ((signed char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsWritableUString(s) ((unsigned char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsString(s) ((const char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsSString(s) ((const signed char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_AsUString(s) ((const unsigned char*) PyBytes_AS_STRING(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsWritableString(s) ((char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsWritableSString(s) ((signed char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsWritableUString(s) ((unsigned char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsSString(s) ((const signed char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_AsUString(s) ((const unsigned char*) __Pyx_PyObject_AsString(s))
#define __Pyx_PyObject_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyObject_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyBytes_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyBytes_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyByteArray_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyStr_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyStr_FromString((const char*)s)
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromCString(s) __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromString((const char*)s)
static CYTHON_INLINE size_t __Pyx_Py_UNICODE_strlen(const Py_UNICODE *u) {
const Py_UNICODE *u_end = u;
while (*u_end++) ;
return (size_t)(u_end - u - 1);
}
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromUnicode(u) PyUnicode_FromUnicode(u, __Pyx_Py_UNICODE_strlen(u))
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromUnicodeAndLength PyUnicode_FromUnicode
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_AsUnicode PyUnicode_AsUnicode
#define __Pyx_NewRef(obj) (Py_INCREF(obj), obj)
#define __Pyx_Owned_Py_None(b) __Pyx_NewRef(Py_None)
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject * __Pyx_PyBool_FromLong(long b);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrue(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyObject_IsTrueAndDecref(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyNumber_IntOrLong(PyObject* x);
#define __Pyx_PySequence_Tuple(obj)\
(likely(PyTuple_CheckExact(obj)) ? __Pyx_NewRef(obj) : PySequence_Tuple(obj))
static CYTHON_INLINE Py_ssize_t __Pyx_PyIndex_AsSsize_t(PyObject*);
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject * __Pyx_PyInt_FromSize_t(size_t);
#if CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
#define __pyx_PyFloat_AsDouble(x) (PyFloat_CheckExact(x) ? PyFloat_AS_DOUBLE(x) : PyFloat_AsDouble(x))
#else
#define __pyx_PyFloat_AsDouble(x) PyFloat_AsDouble(x)
#endif
#define __pyx_PyFloat_AsFloat(x) ((float) __pyx_PyFloat_AsDouble(x))
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Int(x) (PyLong_CheckExact(x) ? __Pyx_NewRef(x) : PyNumber_Long(x))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Int(x) (PyInt_CheckExact(x) ? __Pyx_NewRef(x) : PyNumber_Int(x))
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyNumber_Float(x) (PyFloat_CheckExact(x) ? __Pyx_NewRef(x) : PyNumber_Float(x))
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3 && __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_ASCII
static int __Pyx_sys_getdefaultencoding_not_ascii;
static int __Pyx_init_sys_getdefaultencoding_params(void) {
PyObject* sys;
PyObject* default_encoding = NULL;
PyObject* ascii_chars_u = NULL;
PyObject* ascii_chars_b = NULL;
const char* default_encoding_c;
sys = PyImport_ImportModule("sys");
if (!sys) goto bad;
default_encoding = PyObject_CallMethod(sys, (char*) "getdefaultencoding", NULL);
Py_DECREF(sys);
if (!default_encoding) goto bad;
default_encoding_c = PyBytes_AsString(default_encoding);
if (!default_encoding_c) goto bad;
if (strcmp(default_encoding_c, "ascii") == 0) {
__Pyx_sys_getdefaultencoding_not_ascii = 0;
} else {
char ascii_chars[128];
int c;
for (c = 0; c < 128; c++) {
ascii_chars[c] = c;
}
__Pyx_sys_getdefaultencoding_not_ascii = 1;
ascii_chars_u = PyUnicode_DecodeASCII(ascii_chars, 128, NULL);
if (!ascii_chars_u) goto bad;
ascii_chars_b = PyUnicode_AsEncodedString(ascii_chars_u, default_encoding_c, NULL);
if (!ascii_chars_b || !PyBytes_Check(ascii_chars_b) || memcmp(ascii_chars, PyBytes_AS_STRING(ascii_chars_b), 128) != 0) {
PyErr_Format(
PyExc_ValueError,
"This module compiled with c_string_encoding=ascii, but default encoding '%.200s' is not a superset of ascii.",
default_encoding_c);
goto bad;
}
Py_DECREF(ascii_chars_u);
Py_DECREF(ascii_chars_b);
}
Py_DECREF(default_encoding);
return 0;
bad:
Py_XDECREF(default_encoding);
Py_XDECREF(ascii_chars_u);
Py_XDECREF(ascii_chars_b);
return -1;
}
#endif
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT && PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(c_str, size) PyUnicode_DecodeUTF8(c_str, size, NULL)
#else
#define __Pyx_PyUnicode_FromStringAndSize(c_str, size) PyUnicode_Decode(c_str, size, __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING, NULL)
#if __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING_IS_DEFAULT
static char* __PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING;
static int __Pyx_init_sys_getdefaultencoding_params(void) {
PyObject* sys;
PyObject* default_encoding = NULL;
char* default_encoding_c;
sys = PyImport_ImportModule("sys");
if (!sys) goto bad;
default_encoding = PyObject_CallMethod(sys, (char*) (const char*) "getdefaultencoding", NULL);
Py_DECREF(sys);
if (!default_encoding) goto bad;
default_encoding_c = PyBytes_AsString(default_encoding);
if (!default_encoding_c) goto bad;
__PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING = (char*) malloc(strlen(default_encoding_c) + 1);
if (!__PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING) goto bad;
strcpy(__PYX_DEFAULT_STRING_ENCODING, default_encoding_c);
Py_DECREF(default_encoding);
return 0;
bad:
Py_XDECREF(default_encoding);
return -1;
}
#endif
#endif
/* Test for GCC > 2.95 */
#if defined(__GNUC__) && (__GNUC__ > 2 || (__GNUC__ == 2 && (__GNUC_MINOR__ > 95)))
#define likely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 1)
#define unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 0)
#else /* !__GNUC__ or GCC < 2.95 */
#define likely(x) (x)
#define unlikely(x) (x)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_pretend_to_initialize(void* ptr) { (void)ptr; }
static PyObject *__pyx_m = NULL;
static PyObject *__pyx_d;
static PyObject *__pyx_b;
static PyObject *__pyx_cython_runtime = NULL;
static PyObject *__pyx_empty_tuple;
static PyObject *__pyx_empty_bytes;
static PyObject *__pyx_empty_unicode;
static int __pyx_lineno;
static int __pyx_clineno = 0;
static const char * __pyx_cfilenm= __FILE__;
static const char *__pyx_filename;
static const char *__pyx_f[] = {
"pept/processing/occupancy_ext.pyx",
"stringsource",
};
/* MemviewSliceStruct.proto */
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj;
typedef struct {
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview;
char *data;
Py_ssize_t shape[8];
Py_ssize_t strides[8];
Py_ssize_t suboffsets[8];
} __Pyx_memviewslice;
#define __Pyx_MemoryView_Len(m) (m.shape[0])
/* Atomics.proto */
#include
#ifndef CYTHON_ATOMICS
#define CYTHON_ATOMICS 1
#endif
#define __pyx_atomic_int_type int
#if CYTHON_ATOMICS && __GNUC__ >= 4 && (__GNUC_MINOR__ > 1 ||\
(__GNUC_MINOR__ == 1 && __GNUC_PATCHLEVEL >= 2)) &&\
!defined(__i386__)
#define __pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(value, lock) __sync_fetch_and_add(value, 1)
#define __pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(value, lock) __sync_fetch_and_sub(value, 1)
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#warning "Using GNU atomics"
#endif
#elif CYTHON_ATOMICS && defined(_MSC_VER) && 0
#include
#undef __pyx_atomic_int_type
#define __pyx_atomic_int_type LONG
#define __pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(value, lock) InterlockedIncrement(value)
#define __pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(value, lock) InterlockedDecrement(value)
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#pragma message ("Using MSVC atomics")
#endif
#elif CYTHON_ATOMICS && (defined(__ICC) || defined(__INTEL_COMPILER)) && 0
#define __pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(value, lock) _InterlockedIncrement(value)
#define __pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(value, lock) _InterlockedDecrement(value)
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#warning "Using Intel atomics"
#endif
#else
#undef CYTHON_ATOMICS
#define CYTHON_ATOMICS 0
#ifdef __PYX_DEBUG_ATOMICS
#warning "Not using atomics"
#endif
#endif
typedef volatile __pyx_atomic_int_type __pyx_atomic_int;
#if CYTHON_ATOMICS
#define __pyx_add_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_atomic_incr_aligned(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#define __pyx_sub_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_atomic_decr_aligned(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#else
#define __pyx_add_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_add_acquisition_count_locked(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#define __pyx_sub_acquisition_count(memview)\
__pyx_sub_acquisition_count_locked(__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview), memview->lock)
#endif
/* ForceInitThreads.proto */
#ifndef __PYX_FORCE_INIT_THREADS
#define __PYX_FORCE_INIT_THREADS 0
#endif
/* NoFastGil.proto */
#define __Pyx_PyGILState_Ensure PyGILState_Ensure
#define __Pyx_PyGILState_Release PyGILState_Release
#define __Pyx_FastGIL_Remember()
#define __Pyx_FastGIL_Forget()
#define __Pyx_FastGilFuncInit()
/* BufferFormatStructs.proto */
#define IS_UNSIGNED(type) (((type) -1) > 0)
struct __Pyx_StructField_;
#define __PYX_BUF_FLAGS_PACKED_STRUCT (1 << 0)
typedef struct {
const char* name;
struct __Pyx_StructField_* fields;
size_t size;
size_t arraysize[8];
int ndim;
char typegroup;
char is_unsigned;
int flags;
} __Pyx_TypeInfo;
typedef struct __Pyx_StructField_ {
__Pyx_TypeInfo* type;
const char* name;
size_t offset;
} __Pyx_StructField;
typedef struct {
__Pyx_StructField* field;
size_t parent_offset;
} __Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem;
typedef struct {
__Pyx_StructField root;
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem* head;
size_t fmt_offset;
size_t new_count, enc_count;
size_t struct_alignment;
int is_complex;
char enc_type;
char new_packmode;
char enc_packmode;
char is_valid_array;
} __Pyx_BufFmt_Context;
/*--- Type declarations ---*/
struct __pyx_array_obj;
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj;
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj;
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj;
struct __pyx_opt_args_4pept_10processing_13occupancy_ext_occupancy2d_ext;
/* "pept/processing/occupancy_ext.pyx":73
*
*
* cpdef void occupancy2d_ext( # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* float[:, :] pixels,
* const float[:] xlim,
*/
struct __pyx_opt_args_4pept_10processing_13occupancy_ext_occupancy2d_ext {
int __pyx_n;
int omit_last;
};
/* "View.MemoryView":105
*
* @cname("__pyx_array")
* cdef class array: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef:
*/
struct __pyx_array_obj {
PyObject_HEAD
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array *__pyx_vtab;
char *data;
Py_ssize_t len;
char *format;
int ndim;
Py_ssize_t *_shape;
Py_ssize_t *_strides;
Py_ssize_t itemsize;
PyObject *mode;
PyObject *_format;
void (*callback_free_data)(void *);
int free_data;
int dtype_is_object;
};
/* "View.MemoryView":279
*
* @cname('__pyx_MemviewEnum')
* cdef class Enum(object): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* cdef object name
* def __init__(self, name):
*/
struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj {
PyObject_HEAD
PyObject *name;
};
/* "View.MemoryView":330
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview')
* cdef class memoryview(object): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef object obj
*/
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj {
PyObject_HEAD
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *__pyx_vtab;
PyObject *obj;
PyObject *_size;
PyObject *_array_interface;
PyThread_type_lock lock;
__pyx_atomic_int acquisition_count[2];
__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count_aligned_p;
Py_buffer view;
int flags;
int dtype_is_object;
__Pyx_TypeInfo *typeinfo;
};
/* "View.MemoryView":965
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryviewslice')
* cdef class _memoryviewslice(memoryview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Internal class for passing memoryview slices to Python"
*
*/
struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj {
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj __pyx_base;
__Pyx_memviewslice from_slice;
PyObject *from_object;
PyObject *(*to_object_func)(char *);
int (*to_dtype_func)(char *, PyObject *);
};
/* "View.MemoryView":105
*
* @cname("__pyx_array")
* cdef class array: # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef:
*/
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array {
PyObject *(*get_memview)(struct __pyx_array_obj *);
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct_array *__pyx_vtabptr_array;
/* "View.MemoryView":330
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryview')
* cdef class memoryview(object): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
*
* cdef object obj
*/
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview {
char *(*get_item_pointer)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*is_slice)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*setitem_slice_assignment)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*setitem_slice_assign_scalar)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*setitem_indexed)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *, PyObject *);
PyObject *(*convert_item_to_object)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *);
PyObject *(*assign_item_from_object)(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, char *, PyObject *);
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview *__pyx_vtabptr_memoryview;
/* "View.MemoryView":965
*
* @cname('__pyx_memoryviewslice')
* cdef class _memoryviewslice(memoryview): # <<<<<<<<<<<<<<
* "Internal class for passing memoryview slices to Python"
*
*/
struct __pyx_vtabstruct__memoryviewslice {
struct __pyx_vtabstruct_memoryview __pyx_base;
};
static struct __pyx_vtabstruct__memoryviewslice *__pyx_vtabptr__memoryviewslice;
/* --- Runtime support code (head) --- */
/* Refnanny.proto */
#ifndef CYTHON_REFNANNY
#define CYTHON_REFNANNY 0
#endif
#if CYTHON_REFNANNY
typedef struct {
void (*INCREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void (*DECREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void (*GOTREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void (*GIVEREF)(void*, PyObject*, int);
void* (*SetupContext)(const char*, int, const char*);
void (*FinishContext)(void**);
} __Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct;
static __Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct *__Pyx_RefNanny = NULL;
static __Pyx_RefNannyAPIStruct *__Pyx_RefNannyImportAPI(const char *modname);
#define __Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations void *__pyx_refnanny = NULL;
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
#define __Pyx_RefNannySetupContext(name, acquire_gil)\
if (acquire_gil) {\
PyGILState_STATE __pyx_gilstate_save = PyGILState_Ensure();\
__pyx_refnanny = __Pyx_RefNanny->SetupContext((name), __LINE__, __FILE__);\
PyGILState_Release(__pyx_gilstate_save);\
} else {\
__pyx_refnanny = __Pyx_RefNanny->SetupContext((name), __LINE__, __FILE__);\
}
#else
#define __Pyx_RefNannySetupContext(name, acquire_gil)\
__pyx_refnanny = __Pyx_RefNanny->SetupContext((name), __LINE__, __FILE__)
#endif
#define __Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext()\
__Pyx_RefNanny->FinishContext(&__pyx_refnanny)
#define __Pyx_INCREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->INCREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_DECREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->DECREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_GOTREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->GOTREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_GIVEREF(r) __Pyx_RefNanny->GIVEREF(__pyx_refnanny, (PyObject *)(r), __LINE__)
#define __Pyx_XINCREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_INCREF(r); }} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XDECREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_DECREF(r); }} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XGOTREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_GOTREF(r); }} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XGIVEREF(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {__Pyx_GIVEREF(r);}} while(0)
#else
#define __Pyx_RefNannyDeclarations
#define __Pyx_RefNannySetupContext(name, acquire_gil)
#define __Pyx_RefNannyFinishContext()
#define __Pyx_INCREF(r) Py_INCREF(r)
#define __Pyx_DECREF(r) Py_DECREF(r)
#define __Pyx_GOTREF(r)
#define __Pyx_GIVEREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XINCREF(r) Py_XINCREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XDECREF(r) Py_XDECREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XGOTREF(r)
#define __Pyx_XGIVEREF(r)
#endif
#define __Pyx_XDECREF_SET(r, v) do {\
PyObject *tmp = (PyObject *) r;\
r = v; __Pyx_XDECREF(tmp);\
} while (0)
#define __Pyx_DECREF_SET(r, v) do {\
PyObject *tmp = (PyObject *) r;\
r = v; __Pyx_DECREF(tmp);\
} while (0)
#define __Pyx_CLEAR(r) do { PyObject* tmp = ((PyObject*)(r)); r = NULL; __Pyx_DECREF(tmp);} while(0)
#define __Pyx_XCLEAR(r) do { if((r) != NULL) {PyObject* tmp = ((PyObject*)(r)); r = NULL; __Pyx_DECREF(tmp);}} while(0)
/* RaiseArgTupleInvalid.proto */
static void __Pyx_RaiseArgtupleInvalid(const char* func_name, int exact,
Py_ssize_t num_min, Py_ssize_t num_max, Py_ssize_t num_found);
/* RaiseDoubleKeywords.proto */
static void __Pyx_RaiseDoubleKeywordsError(const char* func_name, PyObject* kw_name);
/* ParseKeywords.proto */
static int __Pyx_ParseOptionalKeywords(PyObject *kwds, PyObject **argnames[],\
PyObject *kwds2, PyObject *values[], Py_ssize_t num_pos_args,\
const char* function_name);
/* MemviewSliceInit.proto */
#define __Pyx_BUF_MAX_NDIMS %(BUF_MAX_NDIMS)d
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_DIRECT 1
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_PTR 2
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_FULL 4
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_CONTIG 8
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_STRIDED 16
#define __Pyx_MEMVIEW_FOLLOW 32
#define __Pyx_IS_C_CONTIG 1
#define __Pyx_IS_F_CONTIG 2
static int __Pyx_init_memviewslice(
struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *memview,
int ndim,
__Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice,
int memview_is_new_reference);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __pyx_add_acquisition_count_locked(
__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count, PyThread_type_lock lock);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __pyx_sub_acquisition_count_locked(
__pyx_atomic_int *acquisition_count, PyThread_type_lock lock);
#define __pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview) (memview->acquisition_count_aligned_p)
#define __pyx_get_slice_count(memview) (*__pyx_get_slice_count_pointer(memview))
#define __PYX_INC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil) __Pyx_INC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil, __LINE__)
#define __PYX_XDEC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil) __Pyx_XDEC_MEMVIEW(slice, have_gil, __LINE__)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_INC_MEMVIEW(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int);
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_XDEC_MEMVIEW(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int);
/* ArgTypeTest.proto */
#define __Pyx_ArgTypeTest(obj, type, none_allowed, name, exact)\
((likely((Py_TYPE(obj) == type) | (none_allowed && (obj == Py_None)))) ? 1 :\
__Pyx__ArgTypeTest(obj, type, name, exact))
static int __Pyx__ArgTypeTest(PyObject *obj, PyTypeObject *type, const char *name, int exact);
/* PyObjectGetAttrStr.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStr(o,n) PyObject_GetAttr(o,n)
#endif
/* GetBuiltinName.proto */
static PyObject *__Pyx_GetBuiltinName(PyObject *name);
/* PyObjectCall.proto */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_Call(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg, PyObject *kw);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_Call(func, arg, kw) PyObject_Call(func, arg, kw)
#endif
/* PyThreadStateGet.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_declare PyThreadState *__pyx_tstate;
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_assign __pyx_tstate = __Pyx_PyThreadState_Current;
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Occurred() __pyx_tstate->curexc_type
#else
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_declare
#define __Pyx_PyThreadState_assign
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Occurred() PyErr_Occurred()
#endif
/* PyErrFetchRestore.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Clear() __Pyx_ErrRestore(NULL, NULL, NULL)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestoreWithState(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(PyThreadState_GET(), type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetchWithState(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(PyThreadState_GET(), type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestore(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetch(type, value, tb) __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb);
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
#define __Pyx_PyErr_SetNone(exc) (Py_INCREF(exc), __Pyx_ErrRestore((exc), NULL, NULL))
#else
#define __Pyx_PyErr_SetNone(exc) PyErr_SetNone(exc)
#endif
#else
#define __Pyx_PyErr_Clear() PyErr_Clear()
#define __Pyx_PyErr_SetNone(exc) PyErr_SetNone(exc)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestoreWithState(type, value, tb) PyErr_Restore(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetchWithState(type, value, tb) PyErr_Fetch(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestoreInState(tstate, type, value, tb) PyErr_Restore(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetchInState(tstate, type, value, tb) PyErr_Fetch(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrRestore(type, value, tb) PyErr_Restore(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ErrFetch(type, value, tb) PyErr_Fetch(type, value, tb)
#endif
/* RaiseException.proto */
static void __Pyx_Raise(PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb, PyObject *cause);
/* PyCFunctionFastCall.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCCALL
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(PyObject *func, PyObject **args, Py_ssize_t nargs);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyCFunction_FastCall(func, args, nargs) (assert(0), NULL)
#endif
/* PyFunctionFastCall.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_PYCALL
#define __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCall(func, args, nargs)\
__Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallDict((func), (args), (nargs), NULL)
#if 1 || PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x030600B1
static PyObject *__Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallDict(PyObject *func, PyObject **args, Py_ssize_t nargs, PyObject *kwargs);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyFunction_FastCallDict(func, args, nargs, kwargs) _PyFunction_FastCallDict(func, args, nargs, kwargs)
#endif
#define __Pyx_BUILD_ASSERT_EXPR(cond)\
(sizeof(char [1 - 2*!(cond)]) - 1)
#ifndef Py_MEMBER_SIZE
#define Py_MEMBER_SIZE(type, member) sizeof(((type *)0)->member)
#endif
static size_t __pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset = 0;
#include "frameobject.h"
#define __Pxy_PyFrame_Initialize_Offsets()\
((void)__Pyx_BUILD_ASSERT_EXPR(sizeof(PyFrameObject) == offsetof(PyFrameObject, f_localsplus) + Py_MEMBER_SIZE(PyFrameObject, f_localsplus)),\
(void)(__pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset = ((size_t)PyFrame_Type.tp_basicsize) - Py_MEMBER_SIZE(PyFrameObject, f_localsplus)))
#define __Pyx_PyFrame_GetLocalsplus(frame)\
(assert(__pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset), (PyObject **)(((char *)(frame)) + __pyx_pyframe_localsplus_offset))
#endif
/* PyObjectCall2Args.proto */
static CYTHON_UNUSED PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_Call2Args(PyObject* function, PyObject* arg1, PyObject* arg2);
/* PyObjectCallMethO.proto */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_CallMethO(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg);
#endif
/* PyObjectCallOneArg.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_CallOneArg(PyObject *func, PyObject *arg);
/* IncludeStringH.proto */
#include
/* BytesEquals.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyBytes_Equals(PyObject* s1, PyObject* s2, int equals);
/* UnicodeEquals.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyUnicode_Equals(PyObject* s1, PyObject* s2, int equals);
/* StrEquals.proto */
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
#define __Pyx_PyString_Equals __Pyx_PyUnicode_Equals
#else
#define __Pyx_PyString_Equals __Pyx_PyBytes_Equals
#endif
/* UnaryNegOverflows.proto */
#define UNARY_NEG_WOULD_OVERFLOW(x)\
(((x) < 0) & ((unsigned long)(x) == 0-(unsigned long)(x)))
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_array_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_array_get_memview(struct __pyx_array_obj *); /*proto*/
/* GetAttr.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetAttr(PyObject *, PyObject *);
/* GetItemInt.proto */
#define __Pyx_GetItemInt(o, i, type, is_signed, to_py_func, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck)\
(__Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(i, type, is_signed) ?\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_Fast(o, (Py_ssize_t)i, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck) :\
(is_list ? (PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "list index out of range"), (PyObject*)NULL) :\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(o, to_py_func(i))))
#define __Pyx_GetItemInt_List(o, i, type, is_signed, to_py_func, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck)\
(__Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(i, type, is_signed) ?\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_List_Fast(o, (Py_ssize_t)i, wraparound, boundscheck) :\
(PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "list index out of range"), (PyObject*)NULL))
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_List_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
int wraparound, int boundscheck);
#define __Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple(o, i, type, is_signed, to_py_func, is_list, wraparound, boundscheck)\
(__Pyx_fits_Py_ssize_t(i, type, is_signed) ?\
__Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple_Fast(o, (Py_ssize_t)i, wraparound, boundscheck) :\
(PyErr_SetString(PyExc_IndexError, "tuple index out of range"), (PyObject*)NULL))
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Tuple_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
int wraparound, int boundscheck);
static PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Generic(PyObject *o, PyObject* j);
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetItemInt_Fast(PyObject *o, Py_ssize_t i,
int is_list, int wraparound, int boundscheck);
/* ObjectGetItem.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(PyObject *obj, PyObject* key);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GetItem(obj, key) PyObject_GetItem(obj, key)
#endif
/* decode_c_string_utf16.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors) {
int byteorder = 0;
return PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(s, size, errors, &byteorder);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16LE(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors) {
int byteorder = -1;
return PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(s, size, errors, &byteorder);
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16BE(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors) {
int byteorder = 1;
return PyUnicode_DecodeUTF16(s, size, errors, &byteorder);
}
/* decode_c_string.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_decode_c_string(
const char* cstring, Py_ssize_t start, Py_ssize_t stop,
const char* encoding, const char* errors,
PyObject* (*decode_func)(const char *s, Py_ssize_t size, const char *errors));
/* PyErrExceptionMatches.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatches(err) __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatchesInState(__pyx_tstate, err)
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatchesInState(PyThreadState* tstate, PyObject* err);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyErr_ExceptionMatches(err) PyErr_ExceptionMatches(err)
#endif
/* GetAttr3.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx_GetAttr3(PyObject *, PyObject *, PyObject *);
/* PyDictVersioning.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS && CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS
#define __PYX_DICT_VERSION_INIT ((PY_UINT64_T) -1)
#define __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict) (((PyDictObject*)(dict))->ma_version_tag)
#define __PYX_UPDATE_DICT_CACHE(dict, value, cache_var, version_var)\
(version_var) = __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict);\
(cache_var) = (value);
#define __PYX_PY_DICT_LOOKUP_IF_MODIFIED(VAR, DICT, LOOKUP) {\
static PY_UINT64_T __pyx_dict_version = 0;\
static PyObject *__pyx_dict_cached_value = NULL;\
if (likely(__PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(DICT) == __pyx_dict_version)) {\
(VAR) = __pyx_dict_cached_value;\
} else {\
(VAR) = __pyx_dict_cached_value = (LOOKUP);\
__pyx_dict_version = __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(DICT);\
}\
}
static CYTHON_INLINE PY_UINT64_T __Pyx_get_tp_dict_version(PyObject *obj);
static CYTHON_INLINE PY_UINT64_T __Pyx_get_object_dict_version(PyObject *obj);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_object_dict_version_matches(PyObject* obj, PY_UINT64_T tp_dict_version, PY_UINT64_T obj_dict_version);
#else
#define __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(dict) (0)
#define __PYX_UPDATE_DICT_CACHE(dict, value, cache_var, version_var)
#define __PYX_PY_DICT_LOOKUP_IF_MODIFIED(VAR, DICT, LOOKUP) (VAR) = (LOOKUP);
#endif
/* GetModuleGlobalName.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_DICT_VERSIONS
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(var, name) {\
static PY_UINT64_T __pyx_dict_version = 0;\
static PyObject *__pyx_dict_cached_value = NULL;\
(var) = (likely(__pyx_dict_version == __PYX_GET_DICT_VERSION(__pyx_d))) ?\
(likely(__pyx_dict_cached_value) ? __Pyx_NewRef(__pyx_dict_cached_value) : __Pyx_GetBuiltinName(name)) :\
__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name, &__pyx_dict_version, &__pyx_dict_cached_value);\
}
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalNameUncached(var, name) {\
PY_UINT64_T __pyx_dict_version;\
PyObject *__pyx_dict_cached_value;\
(var) = __Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name, &__pyx_dict_version, &__pyx_dict_cached_value);\
}
static PyObject *__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(PyObject *name, PY_UINT64_T *dict_version, PyObject **dict_cached_value);
#else
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalName(var, name) (var) = __Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name)
#define __Pyx_GetModuleGlobalNameUncached(var, name) (var) = __Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(name)
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__Pyx__GetModuleGlobalName(PyObject *name);
#endif
/* RaiseTooManyValuesToUnpack.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseTooManyValuesError(Py_ssize_t expected);
/* RaiseNeedMoreValuesToUnpack.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseNeedMoreValuesError(Py_ssize_t index);
/* RaiseNoneIterError.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseNoneNotIterableError(void);
/* ExtTypeTest.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_TypeTest(PyObject *obj, PyTypeObject *type);
/* GetTopmostException.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_EXC_INFO_STACK
static _PyErr_StackItem * __Pyx_PyErr_GetTopmostException(PyThreadState *tstate);
#endif
/* SaveResetException.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_ExceptionSave(type, value, tb) __Pyx__ExceptionSave(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionSave(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#define __Pyx_ExceptionReset(type, value, tb) __Pyx__ExceptionReset(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionReset(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject *type, PyObject *value, PyObject *tb);
#else
#define __Pyx_ExceptionSave(type, value, tb) PyErr_GetExcInfo(type, value, tb)
#define __Pyx_ExceptionReset(type, value, tb) PyErr_SetExcInfo(type, value, tb)
#endif
/* GetException.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_GetException(type, value, tb) __Pyx__GetException(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static int __Pyx__GetException(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#else
static int __Pyx_GetException(PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#endif
/* SwapException.proto */
#if CYTHON_FAST_THREAD_STATE
#define __Pyx_ExceptionSwap(type, value, tb) __Pyx__ExceptionSwap(__pyx_tstate, type, value, tb)
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx__ExceptionSwap(PyThreadState *tstate, PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#else
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_ExceptionSwap(PyObject **type, PyObject **value, PyObject **tb);
#endif
/* Import.proto */
static PyObject *__Pyx_Import(PyObject *name, PyObject *from_list, int level);
/* FastTypeChecks.proto */
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
#define __Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, type) __Pyx_IsSubtype(Py_TYPE(obj), (PyTypeObject *)type)
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_IsSubtype(PyTypeObject *a, PyTypeObject *b);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(PyObject *err, PyObject *type);
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches2(PyObject *err, PyObject *type1, PyObject *type2);
#else
#define __Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, type) PyObject_TypeCheck(obj, (PyTypeObject *)type)
#define __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type) PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type)
#define __Pyx_PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches2(err, type1, type2) (PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type1) || PyErr_GivenExceptionMatches(err, type2))
#endif
#define __Pyx_PyException_Check(obj) __Pyx_TypeCheck(obj, PyExc_Exception)
static CYTHON_UNUSED int __pyx_memoryview_getbuffer(PyObject *__pyx_v_self, Py_buffer *__pyx_v_info, int __pyx_v_flags); /*proto*/
/* ListCompAppend.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS && CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_ListComp_Append(PyObject* list, PyObject* x) {
PyListObject* L = (PyListObject*) list;
Py_ssize_t len = Py_SIZE(list);
if (likely(L->allocated > len)) {
Py_INCREF(x);
PyList_SET_ITEM(list, len, x);
__Pyx_SET_SIZE(list, len + 1);
return 0;
}
return PyList_Append(list, x);
}
#else
#define __Pyx_ListComp_Append(L,x) PyList_Append(L,x)
#endif
/* PyIntBinop.proto */
#if !CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_PYPY
static PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_AddObjC(PyObject *op1, PyObject *op2, long intval, int inplace, int zerodivision_check);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyInt_AddObjC(op1, op2, intval, inplace, zerodivision_check)\
(inplace ? PyNumber_InPlaceAdd(op1, op2) : PyNumber_Add(op1, op2))
#endif
/* ListExtend.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyList_Extend(PyObject* L, PyObject* v) {
#if CYTHON_COMPILING_IN_CPYTHON
PyObject* none = _PyList_Extend((PyListObject*)L, v);
if (unlikely(!none))
return -1;
Py_DECREF(none);
return 0;
#else
return PyList_SetSlice(L, PY_SSIZE_T_MAX, PY_SSIZE_T_MAX, v);
#endif
}
/* ListAppend.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_PYLIST_INTERNALS && CYTHON_ASSUME_SAFE_MACROS
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyList_Append(PyObject* list, PyObject* x) {
PyListObject* L = (PyListObject*) list;
Py_ssize_t len = Py_SIZE(list);
if (likely(L->allocated > len) & likely(len > (L->allocated >> 1))) {
Py_INCREF(x);
PyList_SET_ITEM(list, len, x);
__Pyx_SET_SIZE(list, len + 1);
return 0;
}
return PyList_Append(list, x);
}
#else
#define __Pyx_PyList_Append(L,x) PyList_Append(L,x)
#endif
/* None.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE void __Pyx_RaiseUnboundLocalError(const char *varname);
/* ImportFrom.proto */
static PyObject* __Pyx_ImportFrom(PyObject* module, PyObject* name);
/* HasAttr.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_HasAttr(PyObject *, PyObject *);
/* PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03070000
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttrNoDict PyObject_GenericGetAttr
#endif
/* PyObject_GenericGetAttr.proto */
#if CYTHON_USE_TYPE_SLOTS && CYTHON_USE_PYTYPE_LOOKUP && PY_VERSION_HEX < 0x03070000
static PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
#else
#define __Pyx_PyObject_GenericGetAttr PyObject_GenericGetAttr
#endif
/* SetVTable.proto */
static int __Pyx_SetVtable(PyObject *dict, void *vtable);
/* PyObjectGetAttrStrNoError.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyObject_GetAttrStrNoError(PyObject* obj, PyObject* attr_name);
/* SetupReduce.proto */
static int __Pyx_setup_reduce(PyObject* type_obj);
/* CLineInTraceback.proto */
#ifdef CYTHON_CLINE_IN_TRACEBACK
#define __Pyx_CLineForTraceback(tstate, c_line) (((CYTHON_CLINE_IN_TRACEBACK)) ? c_line : 0)
#else
static int __Pyx_CLineForTraceback(PyThreadState *tstate, int c_line);
#endif
/* CodeObjectCache.proto */
typedef struct {
PyCodeObject* code_object;
int code_line;
} __Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry;
struct __Pyx_CodeObjectCache {
int count;
int max_count;
__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry* entries;
};
static struct __Pyx_CodeObjectCache __pyx_code_cache = {0,0,NULL};
static int __pyx_bisect_code_objects(__Pyx_CodeObjectCacheEntry* entries, int count, int code_line);
static PyCodeObject *__pyx_find_code_object(int code_line);
static void __pyx_insert_code_object(int code_line, PyCodeObject* code_object);
/* AddTraceback.proto */
static void __Pyx_AddTraceback(const char *funcname, int c_line,
int py_line, const char *filename);
#if PY_MAJOR_VERSION < 3
static int __Pyx_GetBuffer(PyObject *obj, Py_buffer *view, int flags);
static void __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer(Py_buffer *view);
#else
#define __Pyx_GetBuffer PyObject_GetBuffer
#define __Pyx_ReleaseBuffer PyBuffer_Release
#endif
/* BufferStructDeclare.proto */
typedef struct {
Py_ssize_t shape, strides, suboffsets;
} __Pyx_Buf_DimInfo;
typedef struct {
size_t refcount;
Py_buffer pybuffer;
} __Pyx_Buffer;
typedef struct {
__Pyx_Buffer *rcbuffer;
char *data;
__Pyx_Buf_DimInfo diminfo[8];
} __Pyx_LocalBuf_ND;
/* MemviewSliceIsContig.proto */
static int __pyx_memviewslice_is_contig(const __Pyx_memviewslice mvs, char order, int ndim);
/* OverlappingSlices.proto */
static int __pyx_slices_overlap(__Pyx_memviewslice *slice1,
__Pyx_memviewslice *slice2,
int ndim, size_t itemsize);
/* Capsule.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject *__pyx_capsule_create(void *p, const char *sig);
/* IsLittleEndian.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_Is_Little_Endian(void);
/* BufferFormatCheck.proto */
static const char* __Pyx_BufFmt_CheckString(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx, const char* ts);
static void __Pyx_BufFmt_Init(__Pyx_BufFmt_Context* ctx,
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem* stack,
__Pyx_TypeInfo* type);
/* TypeInfoCompare.proto */
static int __pyx_typeinfo_cmp(__Pyx_TypeInfo *a, __Pyx_TypeInfo *b);
/* MemviewSliceValidateAndInit.proto */
static int __Pyx_ValidateAndInit_memviewslice(
int *axes_specs,
int c_or_f_flag,
int buf_flags,
int ndim,
__Pyx_TypeInfo *dtype,
__Pyx_BufFmt_StackElem stack[],
__Pyx_memviewslice *memviewslice,
PyObject *original_obj);
/* ObjectToMemviewSlice.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE __Pyx_memviewslice __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_dsds_float(PyObject *, int writable_flag);
/* ObjectToMemviewSlice.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE __Pyx_memviewslice __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_ds_float__const__(PyObject *, int writable_flag);
/* ObjectToMemviewSlice.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE __Pyx_memviewslice __Pyx_PyObject_to_MemoryviewSlice_dsds_float__const__(PyObject *, int writable_flag);
/* MemviewSliceCopyTemplate.proto */
static __Pyx_memviewslice
__pyx_memoryview_copy_new_contig(const __Pyx_memviewslice *from_mvs,
const char *mode, int ndim,
size_t sizeof_dtype, int contig_flag,
int dtype_is_object);
/* GCCDiagnostics.proto */
#if defined(__GNUC__) && (__GNUC__ > 4 || (__GNUC__ == 4 && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= 6))
#define __Pyx_HAS_GCC_DIAGNOSTIC
#endif
/* CIntFromPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE int __Pyx_PyInt_As_int(PyObject *);
/* CIntFromPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE long __Pyx_PyInt_As_long(PyObject *);
/* CIntToPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_From_int(int value);
/* CIntToPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE PyObject* __Pyx_PyInt_From_long(long value);
/* CIntFromPy.proto */
static CYTHON_INLINE char __Pyx_PyInt_As_char(PyObject *);
/* CheckBinaryVersion.proto */
static int __Pyx_check_binary_version(void);
/* InitStrings.proto */
static int __Pyx_InitStrings(__Pyx_StringTabEntry *t);
static PyObject *__pyx_array_get_memview(struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_v_self); /* proto*/
static char *__pyx_memoryview_get_item_pointer(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_is_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_obj); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assignment(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_dst, PyObject *__pyx_v_src); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_slice_assign_scalar(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_dst, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_setitem_indexed(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, PyObject *__pyx_v_index, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_convert_item_to_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_assign_item_from_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_convert_item_to_object(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp); /* proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_assign_item_from_object(struct __pyx_memoryviewslice_obj *__pyx_v_self, char *__pyx_v_itemp, PyObject *__pyx_v_value); /* proto*/
/* Module declarations from 'libc.stdint' */
/* Module declarations from 'pept.processing.occupancy_ext' */
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_array_type = 0;
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_MemviewEnum_type = 0;
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_memoryview_type = 0;
static PyTypeObject *__pyx_memoryviewslice_type = 0;
static PyObject *generic = 0;
static PyObject *strided = 0;
static PyObject *indirect = 0;
static PyObject *contiguous = 0;
static PyObject *indirect_contiguous = 0;
static int __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks_used;
static PyThread_type_lock __pyx_memoryview_thread_locks[8];
static void __pyx_f_4pept_10processing_13occupancy_ext_occupancy2d_ext(__Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, float const , int __pyx_skip_dispatch, struct __pyx_opt_args_4pept_10processing_13occupancy_ext_occupancy2d_ext *__pyx_optional_args); /*proto*/
static struct __pyx_array_obj *__pyx_array_new(PyObject *, Py_ssize_t, char *, char *, char *); /*proto*/
static void *__pyx_align_pointer(void *, size_t); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_new(PyObject *, int, int, __Pyx_TypeInfo *); /*proto*/
static CYTHON_INLINE int __pyx_memoryview_check(PyObject *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *_unellipsify(PyObject *, int); /*proto*/
static PyObject *assert_direct_dimensions(Py_ssize_t *, int); /*proto*/
static struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *__pyx_memview_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, PyObject *); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_slice_memviewslice(__Pyx_memviewslice *, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, int, int, int *, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t, int, int, int, int); /*proto*/
static char *__pyx_pybuffer_index(Py_buffer *, char *, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memslice_transpose(__Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_fromslice(__Pyx_memviewslice, int, PyObject *(*)(char *), int (*)(char *, PyObject *), int); /*proto*/
static __Pyx_memviewslice *__pyx_memoryview_get_slice_from_memoryview(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, __Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_slice_copy(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, __Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_object(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_memoryview_copy_object_from_slice(struct __pyx_memoryview_obj *, __Pyx_memviewslice *); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t abs_py_ssize_t(Py_ssize_t); /*proto*/
static char __pyx_get_best_slice_order(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int); /*proto*/
static void _copy_strided_to_strided(char *, Py_ssize_t *, char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, size_t); /*proto*/
static void copy_strided_to_strided(__Pyx_memviewslice *, __Pyx_memviewslice *, int, size_t); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_memoryview_slice_get_size(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int); /*proto*/
static Py_ssize_t __pyx_fill_contig_strides_array(Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t, int, char); /*proto*/
static void *__pyx_memoryview_copy_data_to_temp(__Pyx_memviewslice *, __Pyx_memviewslice *, char, int); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err_extents(int, Py_ssize_t, Py_ssize_t); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err_dim(PyObject *, char *, int); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_err(PyObject *, char *); /*proto*/
static int __pyx_memoryview_copy_contents(__Pyx_memviewslice, __Pyx_memviewslice, int, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_broadcast_leading(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_copying(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice_with_gil(char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_refcount_objects_in_slice(char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview_slice_assign_scalar(__Pyx_memviewslice *, int, size_t, void *, int); /*proto*/
static void __pyx_memoryview__slice_assign_scalar(char *, Py_ssize_t *, Py_ssize_t *, int, size_t, void *); /*proto*/
static PyObject *__pyx_unpickle_Enum__set_state(struct __pyx_MemviewEnum_obj *, PyObject *); /*proto*/
static __Pyx_TypeInfo __Pyx_TypeInfo_float = { "float", NULL, sizeof(float), { 0 }, 0, 'R', 0, 0 };
static __Pyx_TypeInfo __Pyx_TypeInfo_float__const__ = { "const float", NULL, sizeof(float const ), { 0 }, 0, 'R', 0, 0 };
#define __Pyx_MODULE_NAME "pept.processing.occupancy_ext"
extern int __pyx_module_is_main_pept__processing__occupancy_ext;
int __pyx_module_is_main_pept__processing__occupancy_ext = 0;
/* Implementation of 'pept.processing.occupancy_ext' */
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_ValueError;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_MemoryError;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_enumerate;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_range;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_TypeError;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_Ellipsis;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_id;
static PyObject *__pyx_builtin_IndexError;
static const char __pyx_k_O[] = "O";
static const char __pyx_k_c[] = "c";
static const char __pyx_k_id[] = "id";
static const char __pyx_k_new[] = "__new__";
static const char __pyx_k_obj[] = "obj";
static const char __pyx_k_base[] = "base";
static const char __pyx_k_dict[] = "__dict__";
static const char __pyx_k_main[] = "__main__";
static const char __pyx_k_mode[] = "mode";
static const char __pyx_k_name[] = "name";
static const char __pyx_k_ndim[] = "ndim";
static const char __pyx_k_pack[] = "pack";
static const char __pyx_k_size[] = "size";
static const char __pyx_k_step[] = "step";
static const char __pyx_k_stop[] = "stop";
static const char __pyx_k_test[] = "__test__";
static const char __pyx_k_xlim[] = "xlim";
static const char __pyx_k_ylim[] = "ylim";
static const char __pyx_k_ASCII[] = "ASCII";
static const char __pyx_k_class[] = "__class__";
static const char __pyx_k_error[] = "error";
static const char __pyx_k_flags[] = "flags";
static const char __pyx_k_range[] = "range";
static const char __pyx_k_shape[] = "shape";
static const char __pyx_k_start[] = "start";
static const char __pyx_k_times[] = "times";
static const char __pyx_k_encode[] = "encode";
static const char __pyx_k_format[] = "format";
static const char __pyx_k_import[] = "__import__";
static const char __pyx_k_name_2[] = "__name__";
static const char __pyx_k_pickle[] = "pickle";
static const char __pyx_k_pixels[] = "pixels";
static const char __pyx_k_radius[] = "radius";
static const char __pyx_k_reduce[] = "__reduce__";
static const char __pyx_k_struct[] = "struct";
static const char __pyx_k_unpack[] = "unpack";
static const char __pyx_k_update[] = "update";
static const char __pyx_k_fortran[] = "fortran";
static const char __pyx_k_memview[] = "memview";
static const char __pyx_k_Ellipsis[] = "Ellipsis";
static const char __pyx_k_getstate[] = "__getstate__";
static const char __pyx_k_itemsize[] = "itemsize";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_type[] = "__pyx_type";
static const char __pyx_k_setstate[] = "__setstate__";
static const char __pyx_k_TypeError[] = "TypeError";
static const char __pyx_k_enumerate[] = "enumerate";
static const char __pyx_k_omit_last[] = "omit_last";
static const char __pyx_k_positions[] = "positions";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_state[] = "__pyx_state";
static const char __pyx_k_reduce_ex[] = "__reduce_ex__";
static const char __pyx_k_IndexError[] = "IndexError";
static const char __pyx_k_ValueError[] = "ValueError";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_result[] = "__pyx_result";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_vtable[] = "__pyx_vtable__";
static const char __pyx_k_MemoryError[] = "MemoryError";
static const char __pyx_k_PickleError[] = "PickleError";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_checksum[] = "__pyx_checksum";
static const char __pyx_k_stringsource[] = "stringsource";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_getbuffer[] = "__pyx_getbuffer";
static const char __pyx_k_reduce_cython[] = "__reduce_cython__";
static const char __pyx_k_View_MemoryView[] = "View.MemoryView";
static const char __pyx_k_allocate_buffer[] = "allocate_buffer";
static const char __pyx_k_dtype_is_object[] = "dtype_is_object";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_PickleError[] = "__pyx_PickleError";
static const char __pyx_k_setstate_cython[] = "__setstate_cython__";
static const char __pyx_k_pyx_unpickle_Enum[] = "__pyx_unpickle_Enum";
static const char __pyx_k_cline_in_traceback[] = "cline_in_traceback";
static const char __pyx_k_strided_and_direct[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_strided_and_indirect[] = "";
static const char __pyx_k_contiguous_and_direct[] = "